- How to Set the Default Gateway on Ubuntu
- Checking the Default Gateway
- How to Set a New Default Gateway
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Denis Kariuki
- How to set the Default gateway
- You must log in to answer this question.
- Linked
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- How to Add or Change the Default Gateway in Linux
- Using the Terminal
- Editing Your Configuration File
- Community Q&A
- Tips
- You Might Also Like
- How to add or change the default gateway in Debian
- How traffic maneuvers via a default gateway
- Types of Default Gateways
How to Set the Default Gateway on Ubuntu
All the devices on your network rely on the default gateway for communication. Data packets pass through the router to and from your network before being routed to the particular device that owns the packet.
Each operating system comes with a default gateway. However, you can temporarily or permanently change the default gateway to add another route for your network devices. You can use the IP command on Ubuntu to modify your default gateway.
Checking the Default Gateway
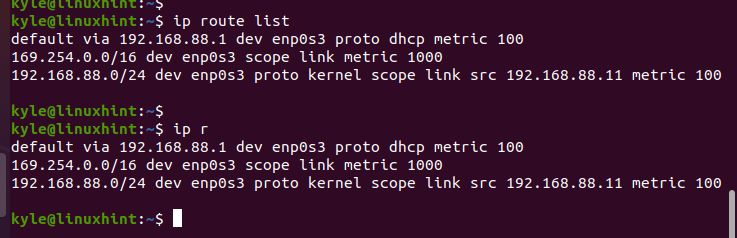
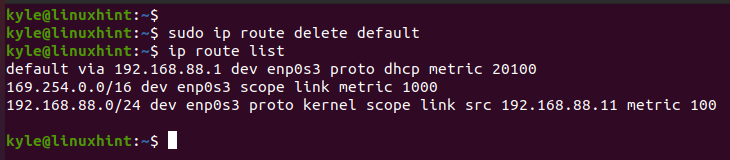
Changing the default gateway is common when you have different sub-networks or when you must point a specific machine to a particular gateway. Before changing the default gateway, let’s list the available routes.
Use the list option with the IP command or its shorthand r to stand for the route.
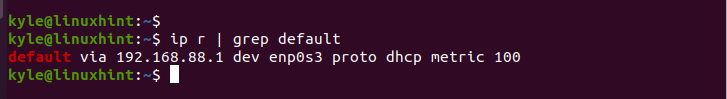
The default gateway has the default keyword in it. If you configured multiple routes on your network, you can use the grep command to filter the router and get the default gateway.
Use the following command:
The current default gateway is 192.168.88.1 on enp0s3 interface. Let’s proceed to set a new default gateway.
How to Set a New Default Gateway
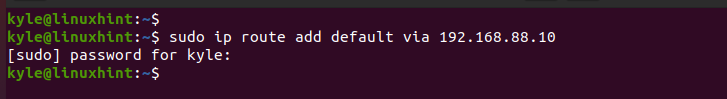
The ip command uses the route option to set the new default gateway. You must specify the type of route that you want to add. In our case, it’s “default”.
For instance, let’s set the default gateway as 192.168.88.10.
Suppose we want to set the default gateway for a particular network interface. In that case, specify the network interface after the gateway. In our case, the interface is enp0s3.
Note that we must add sudo to use the administrator privileges since we are editing the routing table for Ubuntu which is an administrative task.
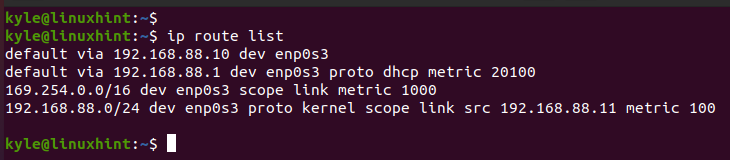
We can use the list or route options to verify the newly added default gateway.
Note how the currently added default gateway is the one that we specified earlier. In the previous output, we now have two default gateways. The keynote is that the changes we made are temporary until you add them to the network manager configuration files.
In the previous case, we can delete the added gateway such that we remain with only one.
Use the delete keyword to remove the added gateway.
If we check the available default gateway after running the delete command, we confirm that we only have one default gateway remaining which is 192.168.88.1.
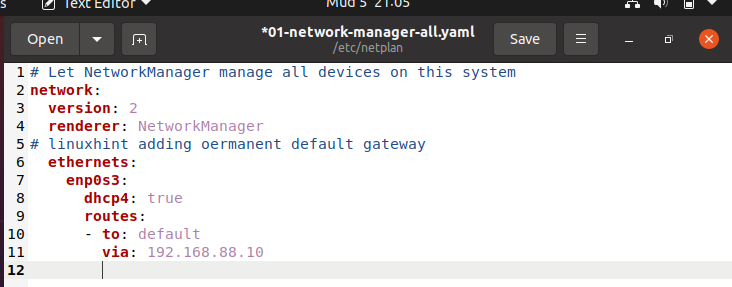
Suppose we want to make the permanent network changes to implement the new gateway. We must edit the configuration file. Open the network manager file using a file editor of your choice. In this case, let’s use gedit with the following command:
Add the new gateway using the following presented format. Make sure that the spacing is set to two whitespaces with the correct indention. Once edited, save the file and exit the editor.
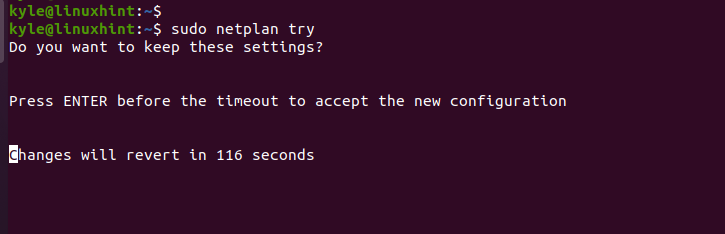
Before applying the changes using the netplan command, run a dry test.
If you are sure with the new network configuration, press the enter key. Otherwise, the changes will revert to the previous settings after the specified seconds.
Conclusion
Ubuntu comes with a default gateway, but that doesn’t mean that you can’t set a new gateway. This guide covered everything about adding a new gateway using the ip command and how to save the changes permanently to the configuration file.
About the author
Denis Kariuki
Denis is a Computer Scientist with a passion for Networking and Cyber Security. I love the terminal, and using Linux is a hobby. I am passionate about sharing tips and ideas about Linux and computing.
How to set the Default gateway
You can use route like in route add default gw 192.168.0.254 for example.
And if route is not present, but ip is, you can use it like this: ip route add default via 192.168.0.254 dev eth0 , assuming that 192.168.0.254 is the ip of your gateway
ifconfig is deprecated on Linux and furthermore, it’s the wrong tool for the job. To set the default gateway on Linux use the ip command as follows:
ip route add default via dev # e.g. ip route add default via 192.168.0.101 dev eth0 For remove gateway in Linux Command : route delete default gw 192.168.1.1 eth1
For add gateway in Linux Command : route add default gw 192.168.1.250 eth1
example: route add default gw 192.168.1.2 eth0
OR use hostname such as dsl-router:
route add default gw dsl-router eth0 Or use the ip command (newer syntax) to route all traffic via 192.168.1.254 gateway connected via eth0 network interface for example:
ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth0 ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 via 192.168.1.254 You must log in to answer this question.
Highly active question. Earn 10 reputation (not counting the association bonus) in order to answer this question. The reputation requirement helps protect this question from spam and non-answer activity.
Linked
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.14.43533
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This site is not affiliated with Linus Torvalds or The Open Group in any way.
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
How to Add or Change the Default Gateway in Linux
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 14 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 1,010,863 times.
If you need to find or change the IP address of your default gateway or router on Linux, you’re in luck—it’s super easy to do. This wikiHow article will show you how to use the route command to find the default gateway IP address on Linux, and how to set a new default gateway in your /etc/network/interfaces configuration file.
Using the Terminal
Open the Terminal. You can open the Terminal from the side bar, or by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T . [1] X Research source
View your current default gateway. You can check what your default gateway is set to by typing route and pressing ↵ Enter . The address next to «default» shows your default gateway, and the interface it is assigned to is displayed on the right side of the table.
- Type sudo route delete default gw IP Address Adapter . For example, to delete the default gateway 10.0.2.2 on the eth0 adapter, type sudo route delete default gw 10.0.2.2 eth0 .
Type . sudo route add default gw IP Address Adapter . For example, to change the default gateway of the eth0 adapter to 192.168.1.254, you would type sudo route add default gw 192.168.1.254 eth0 . [3] X Research source You’ll be prompted for your user password in order to complete the command.
Editing Your Configuration File
Open the configuration file in an editor. Type sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces to open the file in the nano editor. Editing your configuration file will keep your changes every time the system restarts. [4] X Research source
Navigate to the correct section. Find the section for the adapter you want to change the default gateway for. For a wired connection, this is usually eth0 .
Add . gateway IP Address to the section. For example, type gateway 192.168.1.254 to make the default gateway 192.168.1.254. [5] X Research source
Restart your network. Restart your network by typing sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart . [6] X Research source
Community Q&A
Thanks! We’re glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even $1 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHow

Tips
You Might Also Like
A Complete Guide to Managing an iPod in Linux
Can Linux Run .exe Files? How to Run Windows Software on Linux
How to Open Linux Firewall Ports: Ubuntu, Debian, & More
How to Run an INSTALL.sh Script on Linux in 4 Easy Steps
Use Ping in Linux: Tutorial, Examples, & Interpreting Results
How to Delete Read-Only Files in Linux
How to Install Linux on Your Computer
How to add or change the default gateway in Debian
A default gateway is a node in a PC network. The node, in this case, uses an internet protocol suite that serves as the forwarding host(router) to other networks. This occurs when no other route specification matches the destination IP address of a packet.
A gateway makes it possible for devices in one network to converse with devices in another network. For instance, if a PC requests a web page, the request goes via the default gateway exiting the LAN (local area network) to reach the internet.
You can contemplate a default gateway as an immediate device between the internet and the local network. We say this because the default gateway facilitates internal data transfer to and from the internet.
Let us now look at how traffic moves via a default gateway
How traffic maneuvers via a default gateway
Ideally, all the clients on a network point to a default gateway that routes their traffic. This traffic is passed by the default gateway from the local subnet to devices on other subnets. The default/primary gateway connects a local network to the internet, albeit internal gateways for communication purposes within a local network are utilized in corporate networks.
For instance, the default gateway in a home network setting understands particular routes that must be taken to move internet requests from a PC out of the network to the next equipment that comprehends what needs to be done. From there now, the same process recurs until data reaches its destination. Note that the word default, in this case, is the primary device that is looked for when info needs to be sent via the network.
To each network that the traffic arrives at, that network’s default gateway relays info to the internet and back to the PC that requested it.
Additionally, the default gateway is also utilized to understand the request when traffic is cosigned for other interior devices and not an external device. Therefore, instead of sending the data out of the network, it pinpoints it to the correct local device connected to the same local network.
This whole process is appreciated based on the IP address that the originating device requests.
Types of Default Gateways
There are typically two default gateway types.