- How to change the Home directory of the currently logged In user
- 5 Answers 5
- How to Change Default User Home Directory in Linux
- Benefits of Having a Linux Home Directory
- Changing Default User Home Directory in Linux
- How to Change Home Directory Linux
- Understanding the Linux Home Directory
- How to Change the Home Directory Linux
- Change Default Home Directory When Adding New User
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Denis Kariuki
- Change Home Directory in Linux
- Change the home directory using usermod
- Change the home directory by editing /etc/passwd
How to change the Home directory of the currently logged In user
I am currently logged in into a CentOS server and I would like to change my home directory from /home/myuserName/ to /var/www/html/ I tried the below command :
> sudo usermod -d /var/www/html myuserName usermod: user myUserName is currently logged in That helps, But i would like to change my home directory permanently, not for just the current session.
5 Answers 5
short answer : you can’t.
long answer:
HOME dir is set in /etc/passwd , 6th field. It is read upon login; your shell is started with this home dir.
The proper way to change home dir for joe is :
Once session is run, you must do two things:
- edit $HOME to change home dir for session (to be repeated on all active session).
- use sudo vipw to edit home dir for next session
Also, be aware you might have an issue with permissions/ownership on /var/www/html .
editing /etc/passwd for an account that is logged in, and then start a new session with that same account, and it obeys the new home dir. For the already logged in account, that session still has the old home location in the Environment.
You need to edit the /etc/passwd file to change home directory of users that are currently logged in.
Edit the /etc/passwd with sudo vipw and change home directory of the user.
vipw highly recommended other than vim or other editors since vipw will set lock to prevent any data corruption.
The usermod command won’t work if you’re logged in with the user you are trying to make changes on.
From the manual page on usermod it says:
CAVEATS usermod will not allow you to change the name of a user who is logged in. You must make certain that the named user is not executing any processes when this command is being executed if the user’s numerical user ID is being changed. You must change the owner of any crontab files manually. You must change the owner of any at jobs manually. You must make any changes involving NIS on the NIS server.
Try logging in with a different user and running the command again.
If that isn’t possible then you can manually edit the /etc/passwd file (which is actually what the usermod command is doing). If you do that make sure you back the file up in case you inadvertently do something silly.
How to Change Default User Home Directory in Linux
Before we can jump into changing the default user home directory on a Linux operating system environment, we should brief through some theoretical and practical information related to the Linux home directory.
By definition, Linux is a multi-user operating system, which creates the need for a universal directory called the Home directory where different OS users can store and create personalized/user-centered files and directories.
These files and directories are only accessible to the homeowner (currently logged-in user). Therefore, each time a new user is created on a Linux environment, the user is associated with a unique home directory accessible only to that user.
On the other hand, the existence of these universal directories also permits a universal user (other than the homeowner) to have access to them. This user is known as root and can access all homeowner directories within a Linux system.
The syntax associated with a user’s Home directory is as follows:
For instance, if a Linux system has a user called dnyce, then the absolute path to this user’s Home directory will be:
We can even list the permission settings associated with the user in the following manner:
This article will walk us through changing the default user home directory on a Linux operating system environment.
Benefits of Having a Linux Home Directory
We can summarize the benefits of having a Linux Home directory in the following manner.
- User Access Restriction – It is only the homeowner and root user that can access this directory making it impossible for other users to tamper with existing customization settings and stored configuration files. Therefore, privacy and security are guaranteed.
- Controlled Environment – Since multiple homeowners can exist within a single Linux system, their restriction on their Home directories is very advantageous. For instance, if a homeowner’s Home directory contains malicious code in stored executable files, the execution of this code will only affect that user environment and not the entire system.
- Controlled Flexibility – The user’s Home directory is automatically created during the Linux installation. During this installation process, a user can decide to assign this directory an exclusive partition. This step makes it easier to execute backup and restoration tasks.
Changing Default User Home Directory in Linux
We will need to create a sample Linux user account for this tutorial to be more practical. Since creating a new user in Linux is associated with a Home directory, let us create one.
# useradd -m homeowner # passwd homeowner
The -m flag makes sure that a default user Home directory is created and set a password to the user.
We can now switch to the newly created user account and confirm the default user home directory.
Switch back to the root user account.
and create a new directory replacement for the default user Home directory.
We will assign user homeowner directory ownership for the newowner.
# chown -R homeowner:homeowner /home/newowner
Now, to change the user’s default Home directory from /home/homeowner to the new directory /home/newowner, we will make use of the usermod -d command in the following manner.
# usermod -d /home/newowner homeowner
The -d flag sets the directory.
We can switch back to the homeowner account and confirm the changes.
Alternatively, we could set the preferred user Home directory during user creation in the following manner.
# useradd -m -d /home/newowner homeowner
The -d flag sets the directory.
While changing the default user Home directory, we might also need to migrate/move already existing user content to the new location. The usermod command to implement is:
# usermod -m -d /home/newowner homeowner
The -m flag moves the old directory content to the new one.
We can now easily change the default Home directory in Linux. I hope this article guide was helpful. Feel free to leave a comment or feedback.
How to Change Home Directory Linux
When you create a new user in your Linux system, a home directory is created for them. The home directory contains the individual files for the particular user and can be accessed using the tilde (~). The home directory is the directory that opens when you log in to a Linux system.
Suppose you are looking for how to change your home directory in Linux. This guide details all the steps to follow. Let us dig in!
Understanding the Linux Home Directory
The home directory is the working space for a user in a Linux system, except the root. Each user has a home directory when you have multiple users in your system. The absolute path for the home directory is /home/[username]/. This absolute path is the default location for the home directory for all users except the root.
Above, we have verified that we are in the user’s home directory named kyletech.
There are different ways of accessing the home directory in Linux. Graphically, when you open files, clicking the Home option opens the Linux home directory for the logged-in user.
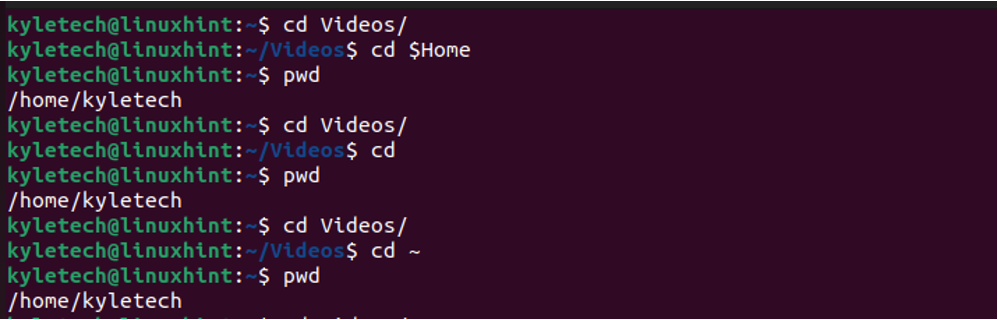
If you are in a different location and want to access the home directory on your command line, use any below commands. Verify your current location using the pwd command.
Suppose you have multiple users in your system. You can access the /home directory to view the available home groups using the command below.
In the below output, we notice that accessing the home groups gives us the list of users in the system. For this case, we have two users and you can access the contents of their home directory provided you are root.
Note that the home directory is a subdirectory of your root directory, whereas the root directory is the topmost level in your system drive. The home directory is denoted using the tilde (~), while the root is denoted using the slash (/).
How to Change the Home Directory Linux
So far, we have discussed the Linux home directory and how to access it. Suppose you are uncomfortable with the current home directory or want to switch it to another location. You can achieve that provided you are root.
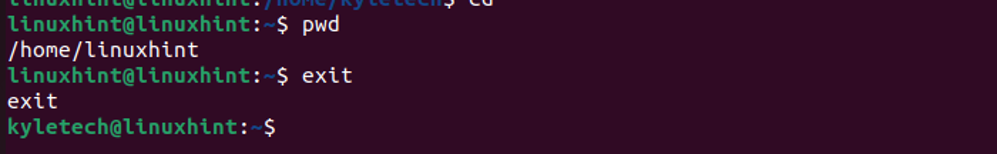
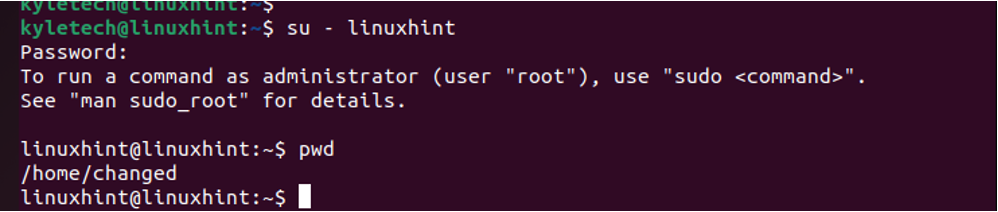
For this example, we will use a user named linuxhint. Let us verify the user’s home directory before we change it.
The current home directory is /home/linuxhint. Let us change it to a new directory named changed.
First, switch back to the root account.
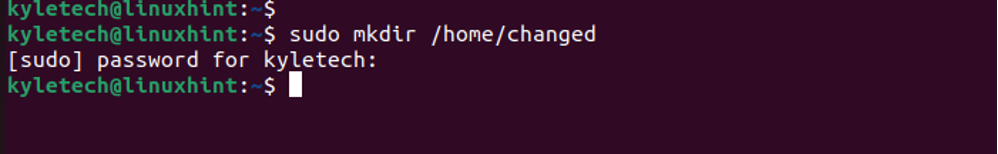
Create the new directory that you want to use as the home directory. In our case, we will use changed/
Note that you must be root to create a directory in /home or use the sudo keyword.
For the target user, assign them ownership of the newly created folder using the chown command.
With the ownership changed, we can now use the usermod command to change the home directory for user Linuxhint from /home/linuxhint to /home/changed/ with the -d option.
Although the command above will change the home directory for the target user, it doesn’t move the existing contents. So, a better approach is to change the home directory and move the existing files in the current home directory to the new home directory using the -m flag. For that, use the command below.
Once you execute the command, switch to the user and check their new home directory. You will notice it changed to the one we created.
That is how to switch the home directory in Linux.
Change Default Home Directory When Adding New User
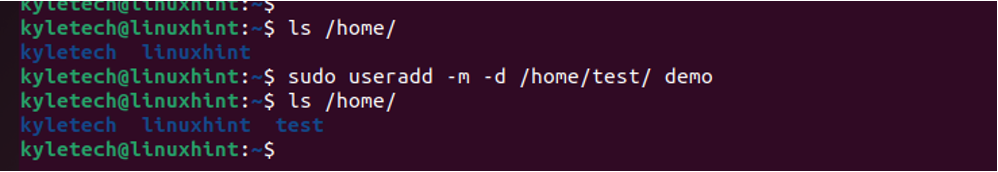
When creating a new user, Linux automatically creates their home directory in the /home/[username]/. However, you can specify the home directory using the -d flag. Use the syntax below.
Here is an example of creating a user named demo whose home directory is /home/test.
Conclusion
Linux creates a home directory when you create a new user. By default, the home directory is the user’s username in the /home. However, you can change this home directory using the usermod command. This post details everything about the Linux home directory and how to change it.
About the author
Denis Kariuki
Denis is a Computer Scientist with a passion for Networking and Cyber Security. I love the terminal, and using Linux is a hobby. I am passionate about sharing tips and ideas about Linux and computing.
Change Home Directory in Linux
Change the home directory of a Linux user with a simple usermod command. While creating a user if you didn’t specify any –home parameter Linux assumes the home directory of the user to be /home/username even if you did specify you can later change it to something else according to your needs. Apart from changing the home directory using the usermod command you’ll have to assign proper ownership and permissions to the new folder. You can also change the home directory by editing the /etc/passwd file. I’ll outline both the steps here.
Change the home directory using usermod
This method is for command line warriors. Before you use the usermod command the new home directory should be created, ownership should be assigned to the new user and the folder should be chmoded correctly so that no one else can access it. Run the following commands to do it.
mkdir /home/new_home_directory
chown username:username /home/new_home_directory
chmod 700 /home/new_home_directory
usermod —home /home/new_home_directory username
Change the home directory by editing /etc/passwd
Alternatively you can also edit the /etc/passwd to change the home directory. But you should be careful not to edit anything else. Before editing this file it is always better to create the new home directory and assign proper permissions and ownership to it. Execute the following commands.
mkdir /home/new_home_directory
chown username:username /home/new_home_directory
chmod 700 /home/new_home_directory
Open the /etc/passwd file using a text editor and locate the line containing the required username it should look something like this
username:x:500:500::/home/username:/bin/bash
change it to
username:x:500:500::/home/new_home_directory:/bin/bash
Save the file.
Finally copy all the old content to the new home directory
cp -f /home/username/* /home/new_home_dir/