- Установка PHP в Ubuntu
- Установка PHP в Ubuntu
- 1. Версия по умолчанию — 7.4
- 2. Устаревшая версия — 5.6
- 3. Новая версия — 8.0
- Установка расширений PHP
- Выбор версии PHP по умолчанию
- Выводы
- Installation on Unix systems
- How to install and configure PHP
- Prerequisites
- Install PHP
- Install optional packages
- Configure PHP
- Test your setup
- Further reading
Установка PHP в Ubuntu
PHP — это очень популярный скриптовый язык программирования с открытым исходным кодом, который часто используется для разработки веб-сайтов и веб-приложений. PHP означает рекурсивный акроним от PHP Hypertext Processor. Скрипты выполняются на стороне сервера и могут находиться как в отдельных файлах, так и быть встроенными в HTML.
На данный момент официально поддерживается три версии PHP — это 5.6, 7.4 и 8. Предыдущие версии больше не получают обновлений безопасности. В этой статье мы рассмотрим как выполняется установка PHP Ubuntu. Будем устанавливать только поддерживаемые версии. Кроме того, рассмотрим как установить расширения для Apache, а также изменить версию по умолчанию.
Установка PHP в Ubuntu
1. Версия по умолчанию — 7.4
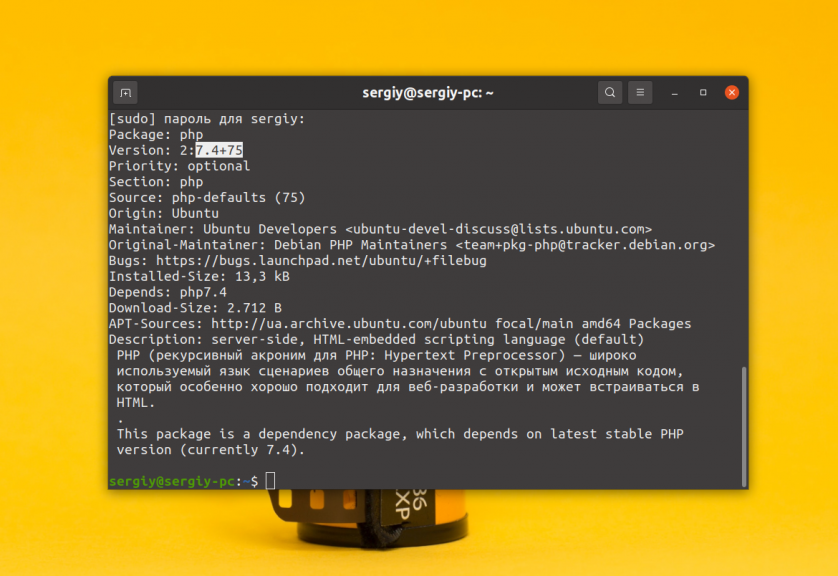
PHP версии 7.4 поставляется в официальных репозиториях Ubuntu, поэтому если вы хотите эту версию, то можете очень просто установить ее с помощью команды apt. Сначала смотрим информацию:
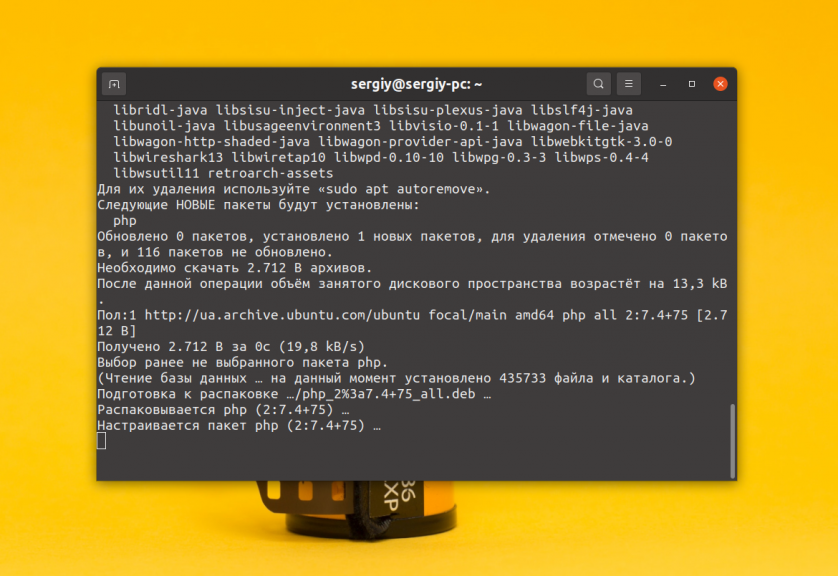
Теперь для установки версии из репозиториев наберите:
Для того чтобы интерпретатор php работал с Apache необходимо установить ещё этот пакет:
sudo apt install libapache2-mod-php
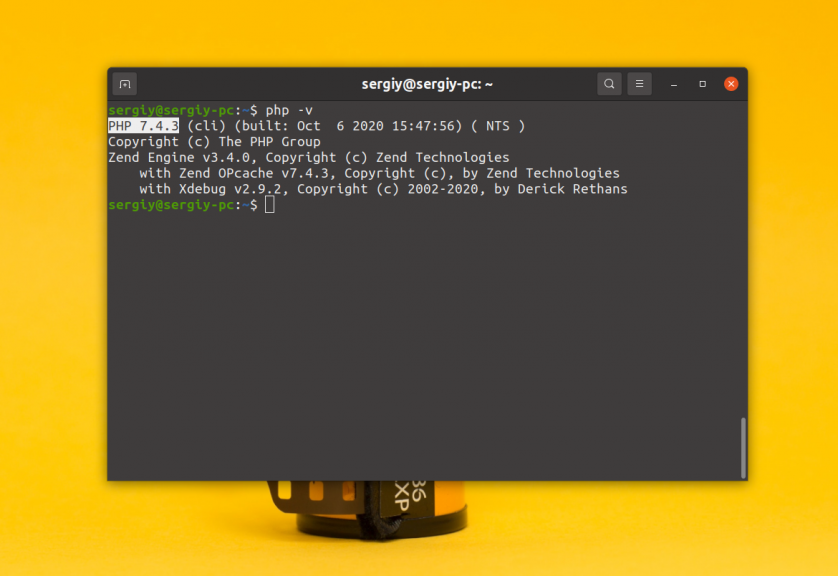
После этого можно посмотреть версию php в терминале:
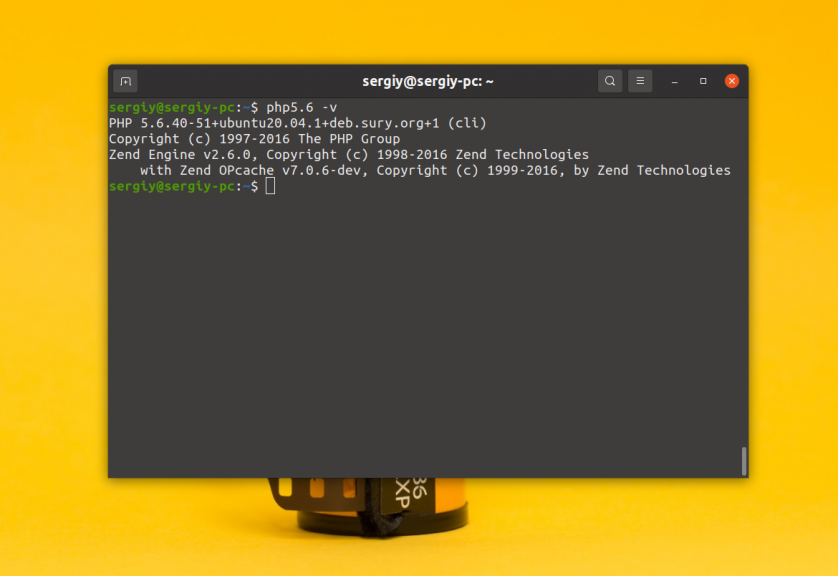
2. Устаревшая версия — 5.6
Если вам нужна другая версия PHP, например, 5.6, то вам придется добавить в систему репозиторий PPA. Сначала необходимо установить зависимости:
sudo apt install python-software-properties
Затем для добавления PPA репозитория выполните:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php
Теперь вы можете установить php ubuntu нужной вам версии. В данном случае 5.6. Для Apache выполните такие команды:
sudo apt install php5.6 libapache2-mod-php5.6
Затем можно смотреть версию:
Обратите внимание, что установленная версия PHP не конфликтует с версией из официальных репозиториев. Обе версии могут существовать в системе и между ними можно переключаться.
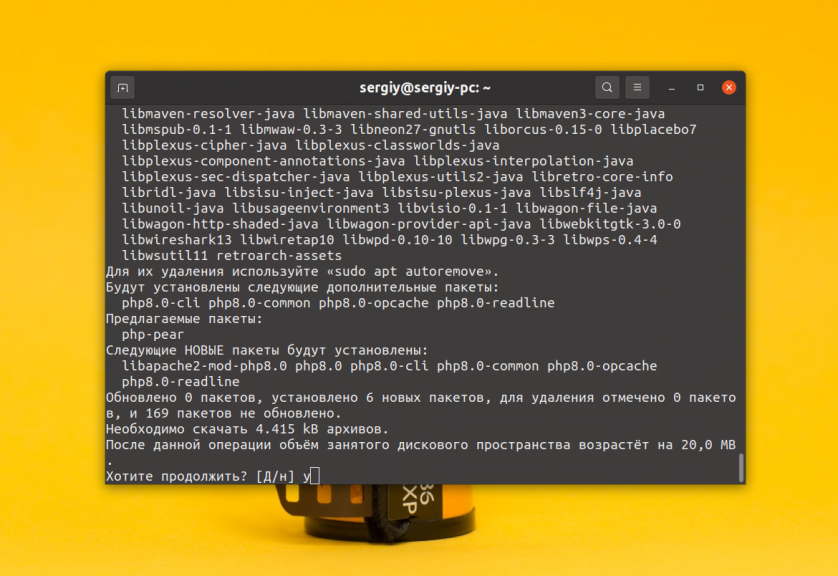
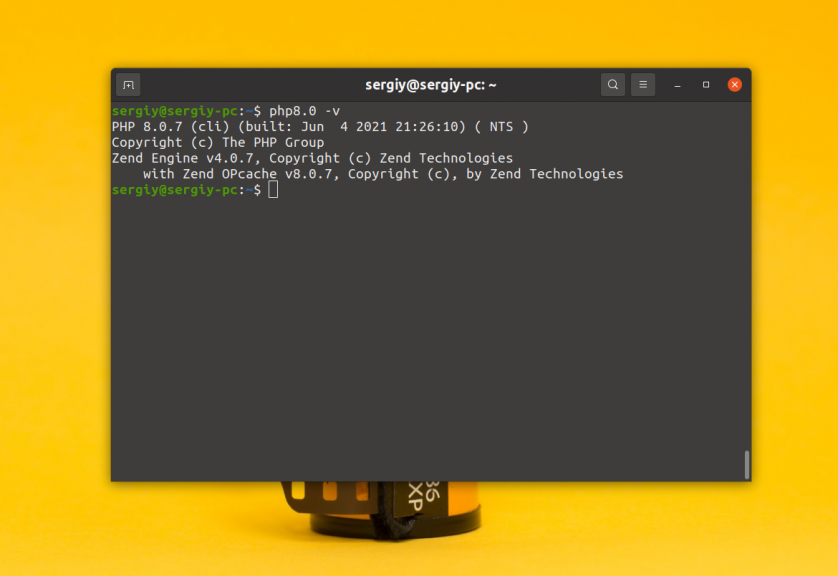
3. Новая версия — 8.0
На момент написания статьи, версия PHP 8.0 вышла относительно недавно и в официальных репозиториях LTS релиза Ubuntu её нет. В этой версии было много улучшений и исправлений и если вы хотите её попробовать, то можете установить из того же самого PPA:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php
Затем, как и в предыдущем пункте необходимо указать версию php, которая вам нужна в команде установки:
sudo apt install php8.0 libapache2-mod-php8.0
После завершения установки интерпретатор появится в системе:
Установка расширений PHP
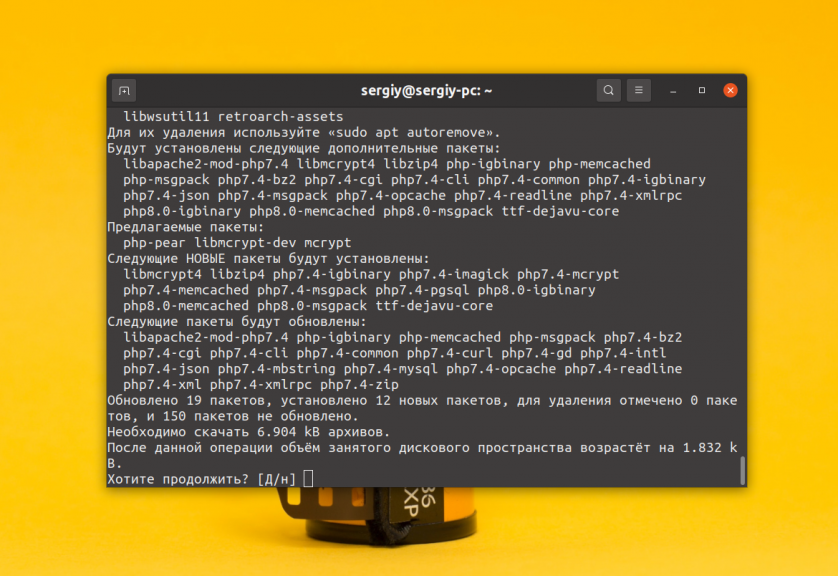
Не зависимо от того какую версию PHP вы установили, обычно для полноценной работы программ необходимо ещё установить расширения. Вот основные расширения, которые требуются чаще всего:
- php-curl — поддержка библиотеки CURL для отправки сетевых запросов;
- php-memcached — кэширование с помощью Memcache;
- php-mysql — поддержка баз данных MySQL и MariaDB;
- php-pgsql — поддержка PostgreSQL;
- php-gd — обработка графики с помощью библиотеки GD;
- php-imagick — обработка графики с помощью библиотеки ImageMagick;
- php-intl — локализация и интернационализация;
- php-mcrypt — шифрование;
- php-xml — работа с XML файлами и DOM;
- php-zip — работа с ZIP архивами;
- php-mbstring — работа со строками содержащими UTF-8 символы, в том числе и кириллицу.
Для того чтобы установить все эти расширения для версии PHP по умолчанию выполните такую команду:
sudo apt install php-curl php-memcached php-mysql php-pgsql php-gd php-imagick php-intl php-mcrypt php-xml php-zip php-mbstring
Если надо установить расширения PHP для определённой версии, то следует указать эту версию в названии пакета:
sudo apt install php7.4-curl php7.4-memcached php7.4-mysql php7.4-pgsql php7.4-gd php7.4-imagick php7.4-intl php7.4-mcrypt php7.4-xml php7.4-zip php7.4-mbstring
Аналогично можно установить расширения для PHP 5.6 или 8.0.
Выбор версии PHP по умолчанию
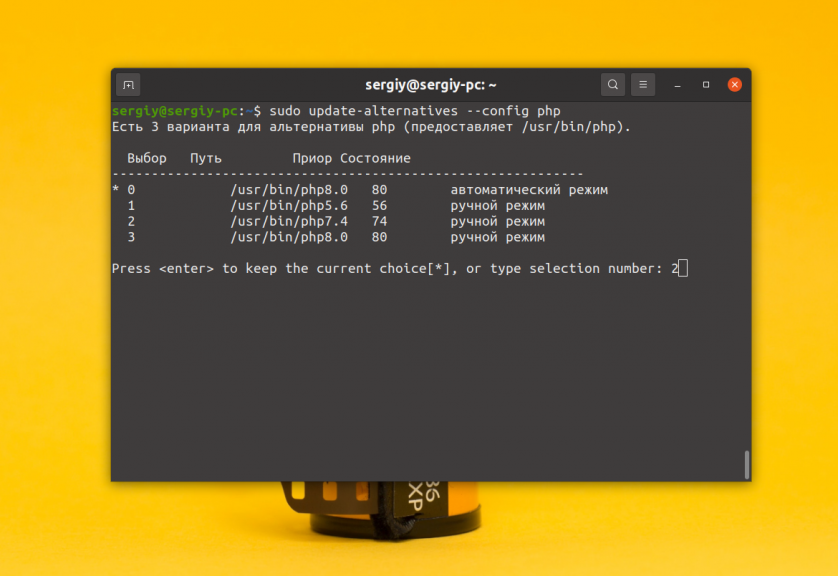
Вы можете выбрать какую версию php нужно использовать по умолчанию с помощью утилиты update-alternatives. Сначала смотрим доступные версии:
sudo update-alternatives —config php
После этого следует ввести номер версии, которую вы хотите использовать по умолчанию:
Или можно сразу установить php ubuntu по умолчанию:
sudo update-alternatives —set php /usr/bin/php5.6
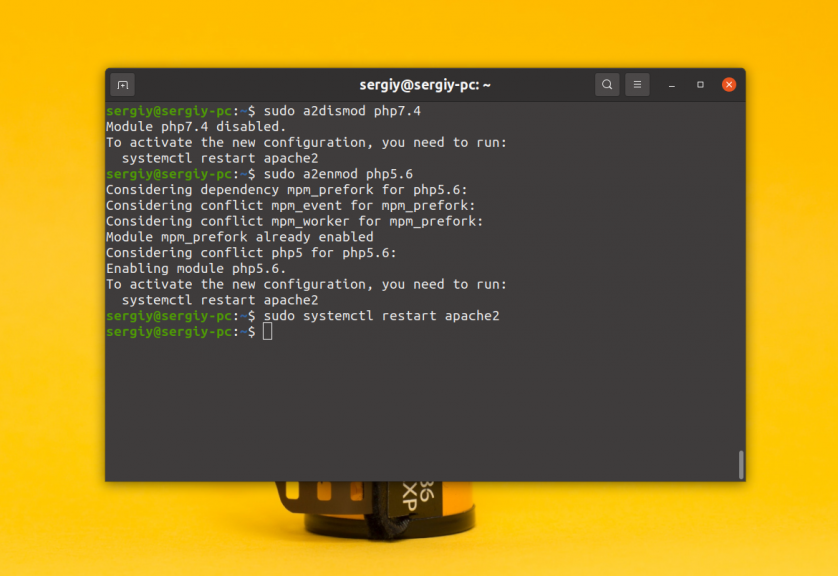
Чтобы используемая версия обновилась в Apache нужно подключить правильный модуль и перезагрузить веб-сервер. Например, для того чтобы отключить 7.4 и включить 5.6 выполните:
sudo a2dismod php7.4
sudo a2enmod php5.6
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Установка php 8 Ubuntu выполняется так же. Теперь вы знаете как переключить версию php Ubuntu. Установка и настройка PHP вместе с Nginx отдельная обширная тема и она описана в статье про настройку PHP-FPM.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели как выполняется установка PHP 8 ubuntu 20.04 и других версиях системы. Теперь вы знаете как установить не только PHP 8, но и другие поддерживаемые версии. Как видите, это очень просто, вы можете получить нужную версию PHP буквально в несколько кликов. Надеюсь, эта информация была вам полезной.

Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Installation on Unix systems
This section will guide you through the general configuration and installation of PHP on Unix systems. Be sure to investigate any sections specific to your platform or web server before you begin the process.
As our manual outlines in the General Installation Considerations section, we are mainly dealing with web centric setups of PHP in this section, although we will cover setting up PHP for command line usage as well.
There are several ways to install PHP for the Unix platform, either with a compile and configure process, or through various pre-packaged methods. This documentation is mainly focused around the process of compiling and configuring PHP. Many Unix like systems have some sort of package installation system. This can assist in setting up a standard configuration, but if you need to have a different set of features (such as a secure server, or a different database driver), you may need to build PHP and/or your web server. If you are unfamiliar with building and compiling your own software, it is worth checking to see whether somebody has already built a packaged version of PHP with the features you need.
- Basic Unix skills (being able to operate «make» and a C compiler)
- An ANSI C compiler
- A web server
- Any module specific components (such as GD , PDF libs, etc.)
- autoconf: 2.59+ (for PHP >= 7.0.0), 2.64+ (for PHP >= 7.2.0)
- automake: 1.4+
- libtool: 1.4.x+ (except 1.4.2)
- re2c: 0.13.4+
- bison:
- PHP 7.0 — 7.3: 2.4 or later (including Bison 3.x)
- PHP 7.4: > 3.0
The initial PHP setup and configuration process is controlled by the use of the command line options of the configure script. You could get a list of all available options along with short explanations running ./configure —help. Our manual documents the different options separately. You will find the core options in the appendix, while the different extension specific options are described on the reference pages.
When PHP is configured, you are ready to build the module and/or executables. The command make should take care of this. If it fails and you can’t figure out why, see the Problems section.
Note:
Some Unix systems (such as OpenBSD and SELinux) may disallow mapping pages both writable and executable for security reasons, what is called PaX MPROTECT or W^X violation protection. This kind of memory mapping is, however, necessary for PCRE’s JIT support, so either PHP has to be built without PCRE’s JIT support, or the binary has to be whitelisted by any means provided by the system.
Note: Cross-compiling for ARM with the Android toolchain is currently not supported.
How to install and configure PHP
PHP is a general-purpose scripting language well-suited for Web development since PHP scripts can be embedded into HTML. This guide explains how to install and configure PHP in an Ubuntu System with Apache2 and MySQL.
Prerequisites
Before installing PHP you should install Apache (or a preferred web server) and a database service such as MySQL.
- To install the Apache package, please refer to our Apache guide.
- To install and configure a MySQL database service, refer to our MySQL guide.
Install PHP
PHP is available on Ubuntu Linux, but unlike Python (which comes pre-installed), must be manually installed.
To install PHP – and the Apache PHP module – you can enter the following command into a terminal prompt:
sudo apt install php libapache2-mod-phpInstall optional packages
The following packages are optional, and can be installed if you need them for your setup.
- PHP-CLI
You can run PHP scripts via the Command Line Interface (CLI). To do this, you must first install the php-cli package. You can install it by running the following command:sudo apt install php-mysqlsudo apt install php-pgsqlConfigure PHP
If you have installed the libapache2-mod-php or php-cgi packages, you can run PHP scripts from your web browser. If you have installed the php-cli package, you can run PHP scripts at a terminal prompt.
By default, when libapache2-mod-php is installed, the Apache2 web server is configured to run PHP scripts using this module. First, verify if the files /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/php8.*.conf and /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/php8.*.load exist. If they do not exist, you can enable the module using the a2enmod command.
Once you have installed the PHP-related packages and enabled the Apache PHP module, you should restart the Apache2 web server to run PHP scripts, by running the following command:
sudo systemctl restart apache2.serviceTest your setup
To verify your installation, you can run the following PHP phpinfo script:
You can save the content in a file – phpinfo.php for example – and place it under the DocumentRoot directory of the Apache2 web server. Pointing your browser to http://hostname/phpinfo.php will display the values of various PHP configuration parameters.
Further reading
- For more in depth information see the php.net documentation.
- There are a plethora of books on PHP 7 and PHP 8. A good book from O’Reilly is Learning PHP, which includes an exploration of PHP 7’s enhancements to the language.
- Also, see the Apache MySQL PHP Ubuntu Wiki page for more information.