- How to Find Files With SUID and SGID Permissions in Linux
- What is SUID and SGID?
- How to Find Files with SUID Set in Linux
- How to Find Files with SGID Set in Linux
- Linux permissions: SUID, SGID, and sticky bit
- Career advice
- Symbolic method
- Numeric method
- Special permission explained
- user + s (pecial)
- group + s (pecial)
- Great Linux resources
- other + t (sticky)
- Setting special permissions
- Summary
How to Find Files With SUID and SGID Permissions in Linux
In this tutorial, we will explain auxiliary file permissions, commonly referred to as “special permissions” in Linux, and also we will show you how to find files which have SUID (Setuid) and SGID (Setgid) set.
What is SUID and SGID?
SUID is a special file permission for executable files which enables other users to run the file with effective permissions of the file owner. Instead of the normal x which represents execute permissions, you will see an s (to indicate SUID) special permission for the user.
SGID is a special file permission that also applies to executable files and enables other users to inherit the effective GID of file group owner. Likewise, rather than the usual x which represents execute permissions, you will see an s (to indicate SGID) special permission for group user.
Let’s look at how to find files which have SUID and SGID set using the find command.
$ find directory -perm /permissions
Important: Certain directories (such as /etc, /bin, /sbin etc.) or files require root privileges in order to be accessed or listed, if you are managing your system as a normal user, use the sudo command to gain root privileges.
How to Find Files with SUID Set in Linux
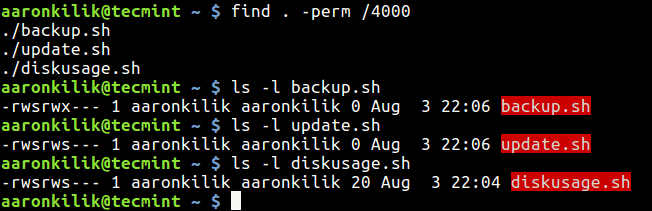
This below example command will find all files with SUID set in the current directory using -perm (print files only with permissions set to 4000) option.
You can use the ls command with -l option (for long listing) to view the permissions on the listed files as shown in the image above.
How to Find Files with SGID Set in Linux
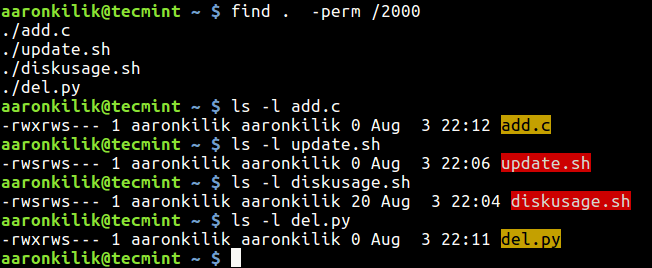
To find files which have SGID set, type the following command.
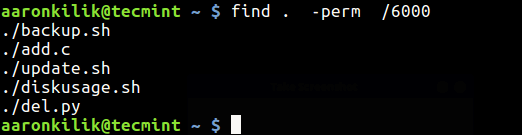
To find files which have both SUID and SGID set, run the command below.
You may also like to read these useful guides about file permissions in Linux:
That’s it for now! In this guide, we showed you how to find files which have SUID (Setuid) and SGID (Setgid) set in Linux. If you have any questions, use the feedback form below to share any queries or additional thoughts about this topic.
Linux permissions: SUID, SGID, and sticky bit
Getting permissions in Linux can sometimes be a ‘sticky’ situation. Learn how to set the appropriate permissions, even in special circumstances.
Linux permissions are a concept that every user becomes intimately familiar with early on in their development. We need to execute scripts, modify files, and run processes in order to administer systems effectively, but what happens when we see Permission denied? Do you know why we see this message? If you know the cause of the problem, do you know how to implement the solution?
Career advice
I will give a quick explanation of the various ways to calculate permissions, and then we will focus on the special permissions within Linux. If you want an in-depth look at the chmod command, check out this article from Sudoer Shashank Hegde, Linux permissions: An introduction to chmod.
The TL;DR is that there are two main ways of assigning permissions.
Symbolic method
The symbolic method uses the following syntax:
[tcarrigan@server ~]$ chmod WhoWhatWhich file | directory- Who — represents identities: u,g,o,a (user, group, other, all)
- What — represents actions: +, -, = (add, remove, set exact)
- Which — represents access levels: r, w, x (read, write, execute)
An example of this is if I want to add the read and write permissions to a file named test.txt for user and group, I use the following command:
[tcarrigan@server ~]$ chmod ug+rw test.txtFull disclosure, this is not my preferred method of assigning permissions, and if you would like more information around this method, I recommend your nearest search engine.
Numeric method
The numeric method is, in my experience, the best way to learn and practice permissions. It is based on the following syntax:
[tcarrigan@server ~]$ chmod ### file | directoryHere, from left to right, the character # represents an access level. There are three access levels—user, group, and others. To determine what each digit is, we use the following:
- Start at 0
- If the read permission should be set, add 4
- If the write permission should be set, add 2
- If the execute permission should be set, add 1
This is calculated on a per access level basis. Let’s interpret this permissions example:
The permissions are represented as 650. How did I arrive at those numbers?
To put this into the command syntax, it looks like this:
[tcarrigan@server ~]$ chmod 650 test.txtNow that you understand the basics of permission calculation in Linux, let’s look at the special permissions included in the OS.
Special permission explained
Special permissions make up a fourth access level in addition to user, group, and other. Special permissions allow for additional privileges over the standard permission sets (as the name suggests). There is a special permission option for each access level discussed previously. Let’s take a look at each one individually, beginning with Set UID:
user + s (pecial)
Commonly noted as SUID, the special permission for the user access level has a single function: A file with SUID always executes as the user who owns the file, regardless of the user passing the command. If the file owner doesn’t have execute permissions, then use an uppercase S here.
Now, to see this in a practical light, let’s look at the /usr/bin/passwd command. This command, by default, has the SUID permission set:
[tcarrigan@server ~]$ ls -l /usr/bin/passwd -rwsr-xr-x. 1 root root 33544 Dec 13 2019 /usr/bin/passwdNote the s where x would usually indicate execute permissions for the user.
group + s (pecial)
Commonly noted as SGID, this special permission has a couple of functions:
- If set on a file, it allows the file to be executed as the group that owns the file (similar to SUID)
- If set on a directory, any files created in the directory will have their group ownership set to that of the directory owner
[tcarrigan@server article_submissions]$ ls -l total 0 drwxrws---. 2 tcarrigan tcarrigan 69 Apr 7 11:31 my_articlesGreat Linux resources
This permission set is noted by a lowercase s where the x would normally indicate execute privileges for the group. It is also especially useful for directories that are often used in collaborative efforts between members of a group. Any member of the group can access any new file. This applies to the execution of files, as well. SGID is very powerful when utilized properly.
As noted previously for SUID, if the owning group does not have execute permissions, then an uppercase S is used.
other + t (sticky)
The last special permission has been dubbed the «sticky bit.» This permission does not affect individual files. However, at the directory level, it restricts file deletion. Only the owner (and root) of a file can remove the file within that directory. A common example of this is the /tmp directory:
[tcarrigan@server article_submissions]$ ls -ld /tmp/ drwxrwxrwt. 15 root root 4096 Sep 22 15:28 /tmp/The permission set is noted by the lowercase t, where the x would normally indicate the execute privilege.
Setting special permissions
To set special permissions on a file or directory, you can utilize either of the two methods outlined for standard permissions above: Symbolic or numerical.
Let’s assume that we want to set SGID on the directory community_content .
To do this using the symbolic method, we do the following:
[tcarrigan@server article_submissions]$ chmod g+s community_content/Using the numerical method, we need to pass a fourth, preceding digit in our chmod command. The digit used is calculated similarly to the standard permission digits:
[tcarrigan@server ~]$ chmod X### file | directoryWhere X is the special permissions digit.
Here is the command to set SGID on community_content using the numerical method:
[tcarrigan@server article_submissions]$ chmod 2770 community_content/ [tcarrigan@server article_submissions]$ ls -ld community_content/ drwxrws---. 2 tcarrigan tcarrigan 113 Apr 7 11:32 community_content/Summary
In closing, permissions are fundamentally important to being an effective Linux administrator. There are two defined ways to set permissions using the chmod command: Symbolic and numerical. We examined the syntax and calculations required for both methods. We also considered the special permissions and their role in the system. Now that you understand permissions and the underlying concepts, you can solve the ever-annoying Permission denied error when it tries to impede your work.