Sharing folder in vmware with linux
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
You can enable folder sharing for a specific virtual machine. To set up a folder for sharing between virtual machines, you must configure each virtual machine to use the same directory on the host system or network share.
Prerequisites
- Verify that the virtual machines use a guest operating system that supports shared folders. See Guest Operating Systems That Support Shared Folders.
- Verify that the latest version of VMware Tools is installed in the guest operating system.
- Verify that permission settings on the host system allow access to files in the shared folders. For example, if you are running Workstation Pro as a user named User, the virtual machine can read and write files in the shared folder only if User has permission to read and write them.
Procedure
- Select the virtual machine and select VM > Settings .
- On the Options tab, select Shared Folders .
- Select a folder sharing option.
Option Description Always enabled Keep folder sharing enabled, even when the virtual machine is shut down, suspended, or powered off. Enabled until next power off or suspend Enable folder sharing temporarily, until you power off, suspend, or shut down the virtual machine. If you restart the virtual machine, shared folders remain enabled. This setting is available only when the virtual machine is powered on. - (Optional) To map a drive to the Shared Folders directory, select Map as a network drive in Windows guests .
This directory contains all of the shared folders that you enable. Workstation Pro selects the drive letter.
On Windows hosts, the Add Shared Folder wizard starts. On Linux hosts, the Shared Folder Properties dialog box opens.
If you specify a directory on a network share, such as D:\share , Workstation Pro always attempts to use that path. If the directory is later connected to the host on a different drive letter, Workstation Pro cannot locate the shared folder.
Characters that the guest operating system considers illegal in a share name appear differently when viewed inside the guest. For example, if you use an asterisk in a share name, you see %002A instead of * in the share name on the guest. Illegal characters are converted to their ASCII hexadecimal value.
The shared folder appears in the Folders list. The check box next to folder name indicates that the folder is being shared. You can deselect this check box to turn off sharing for the folder.
What to do next
View the shared folder. On Linux guests, shared folders appear under /mnt/hgfs . On Solaris guests, shared folders appear under /hgfs . To view shared folders on a Windows guest, see View Shared Folders in a Windows Guest.
Sharing folder in vmware with linux
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
After you enable a shared folder, you can mount one or more directories or subdirectories in the shared folder to any location in the file system in addition to the default location of /mnt/hgfs .
Depending on the kernel version of the Linux guest operating system, VMware Tools uses different components to provide shared-folder functionality. In Linux kernels prior to version 4.0, the VMware Tools services script loads a driver that performs the mount. Linux kernels 4.0 and later use a FUSE file system component.
You can use different mount commands to mount all shares, one share, or a subdirectory within a share to any location in the file system. The commands also vary depending on the Linux-kernel version of the guest.
| Linux Kernel Prior to 4.0 | Linux Kernel 4.0 and Later | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/ /home/user1/shares | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /home/user1/shares -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts all shares to /home/user1/shares |
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/foo /tmp/foo | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/foo /tmp/foo -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts the share named foo to /tmp/foo |
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/foo/bar /var/lib/bar | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/foo/bar /var/lib/bar -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts the subdirectory bar within the share foo to /var/lib/bar |
For Linux kernel prior to version 4.0, you can use VMware-specific options in addition to the standard mount syntax. Enter the command /sbin/mount.vmhgfs -h to list the options.
For Linux kernel version 4.0 or later, enter the command /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse -h to list the available options.
Note: The mount can fail if shared folders are not enabled or if the share does not exist. You are not prompted to run the VMware Tools vmware-config-tools.pl configuration program again.
Sharing folder in vmware with linux
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
After you enable a shared folder, you can mount one or more directories or subdirectories in the shared folder to any location in the file system in addition to the default location of /mnt/hgfs .
Depending on the kernel version of the Linux guest operating system, VMware Tools uses different components to provide shared-folder functionality. In Linux kernels prior to version 4.0, the VMware Tools services script loads a driver that performs the mount. Linux kernels 4.0 and later use a FUSE file system component.
You can use different mount commands to mount all shares, one share, or a subdirectory within a share to any location in the file system. The commands also vary depending on the Linux-kernel version of the guest.
| Linux Kernel Prior to 4.0 | Linux Kernel 4.0 and Later | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/ /home/user1/shares | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /home/user1/shares -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts all shares to /home/user1/shares |
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/foo /tmp/foo | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/foo /tmp/foo -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts the share named foo to /tmp/foo |
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/foo/bar /var/lib/bar | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/foo/bar /var/lib/bar -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts the subdirectory bar within the share foo to /var/lib/bar |
For Linux kernel prior to version 4.0, you can use VMware-specific options in addition to the standard mount syntax. Enter the command /sbin/mount.vmhgfs -h to list the options.
For Linux kernel version 4.0 or later, enter the command /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse -h to list the available options.
Note: The mount can fail if shared folders are disabled or if the share does not exist. You are not prompted to run the VMware Tools vmware-config-tools.pl configuration program again.
Sharing folder in vmware with linux
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
After you enable a shared folder, you can mount one or more directories or subdirectories in the shared folder to any location in the file system in addition to the default location of /mnt/hgfs .
Depending on the kernel version of the Linux guest operating system, VMware Tools uses different components to provide shared-folder functionality. In Linux kernels prior to version 4.0, the VMware Tools services script loads a driver that performs the mount. Linux kernels 4.0 and later use a FUSE file system component.
You can use different mount commands to mount all shares, one share, or a subdirectory within a share to any location in the file system. The commands also vary depending on the Linux-kernel version of the guest.
| Linux Kernel Prior to 4.0 | Linux Kernel 4.0 and Later | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/ /home/user1/shares | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /home/user1/shares -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts all shares to /home/user1/shares |
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/foo /tmp/foo | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/foo /tmp/foo -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts the share named foo to /tmp/foo |
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/foo/bar /var/lib/bar | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/foo/bar /var/lib/bar -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts the subdirectory bar within the share foo to /var/lib/bar |
For Linux kernel prior to version 4.0, you can use VMware-specific options in addition to the standard mount syntax. Enter the command /sbin/mount.vmhgfs -h to list the options.
For Linux kernel version 4.0 or later, enter the command /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse -h to list the available options.
Note: The mount can fail if shared folders are disabled or if the share does not exist. You are not prompted to run the VMware Tools vmware-config-tools.pl configuration program again.
Общая папка VMware в Linux
Общая папка для виртуальной машины и основной системы очень часто необходима для обмена файлами между хостовой и гостевой операционной системой. В одной из прошлых статей мы говорили о том как настроить общую папку VirtualBox. Но VMware — это тоже очень популярная виртуальная машина.
Поэтому в сегодняшней статье мы рассмотрим как сделать общую папку VMware Player в вашей системе. Я буду подразумевать, что обе операционные системы, хост и гость — это какой-либо дистрибутив Linux. В данном случае это Ubuntu.
Настройка общей папки VMware в Linux
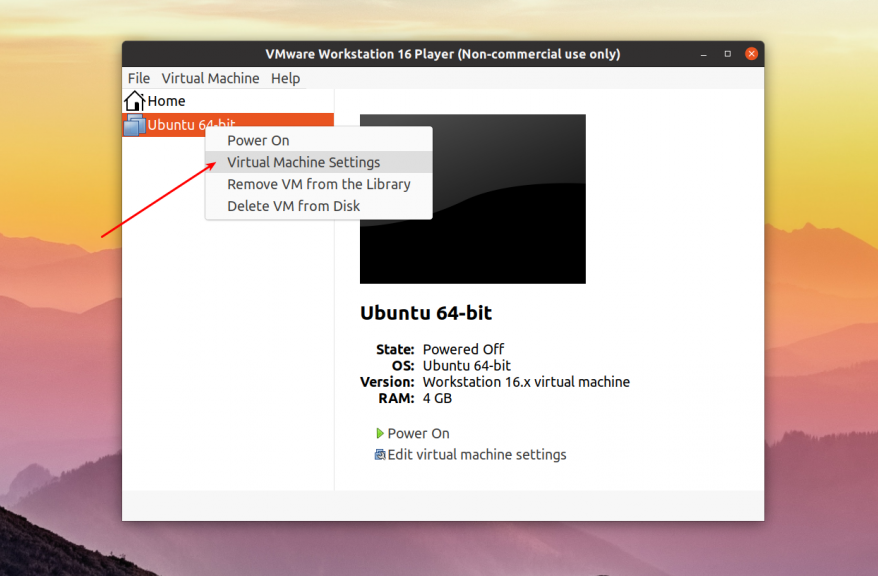
Начать надо с настройки самой виртуальной машины. Запустите VMware и откройте контекстное меню для нужной машины. В нём выберите Virtual Machine Settings:
В открывшемся окне перейдите на вкладку Options:
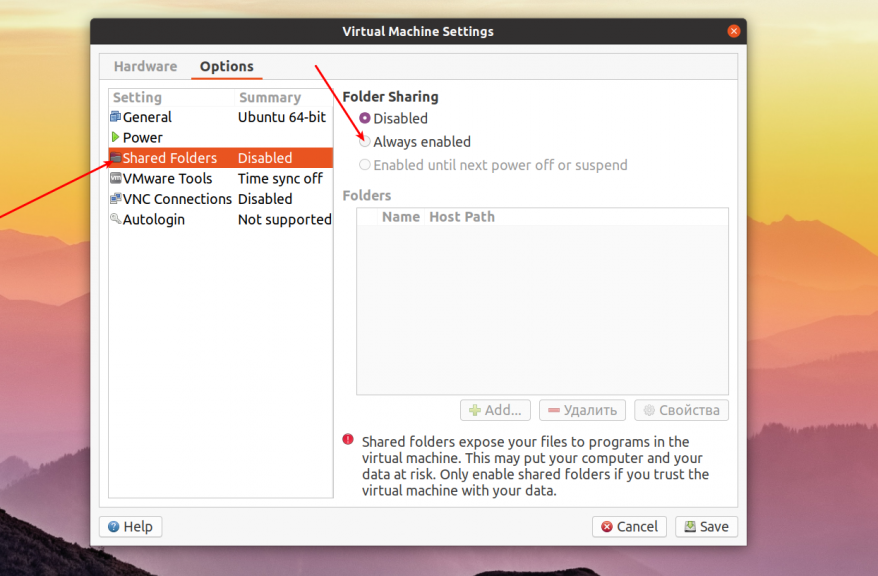
На этой вкладке откройте пункт Shared Folders, а значение переключателя Folder Sharing установите в положение Always enabled:
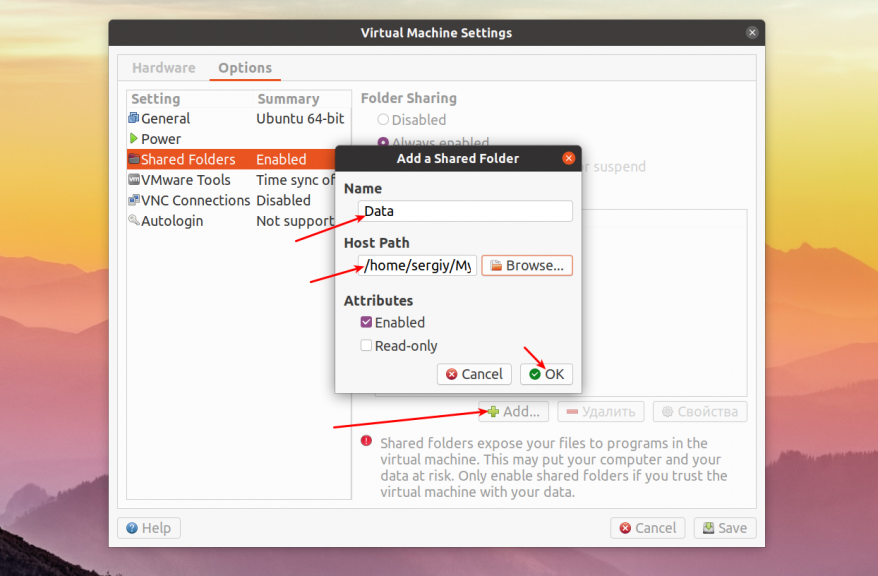
Затем надо добавить общую папку. Для этого кликните по кнопке Add. , в открывшемся окне введите название общей папки, а затем введите или выберите путь к нужной папке в основной системе. Затем нажмите кнопку OK и Save внизу окна чтобы всё сохранить.
После этого можно запускать виртуальную машину. В самой виртуальной машине общая папка должна монтироваться в /mnt/hgfs. Если такой папки нет проверьте установлены ли пакеты open-vm-tools и open-vm-tools-desktop:
sudo apt install open-vm-tools open-vm-tools-desktop
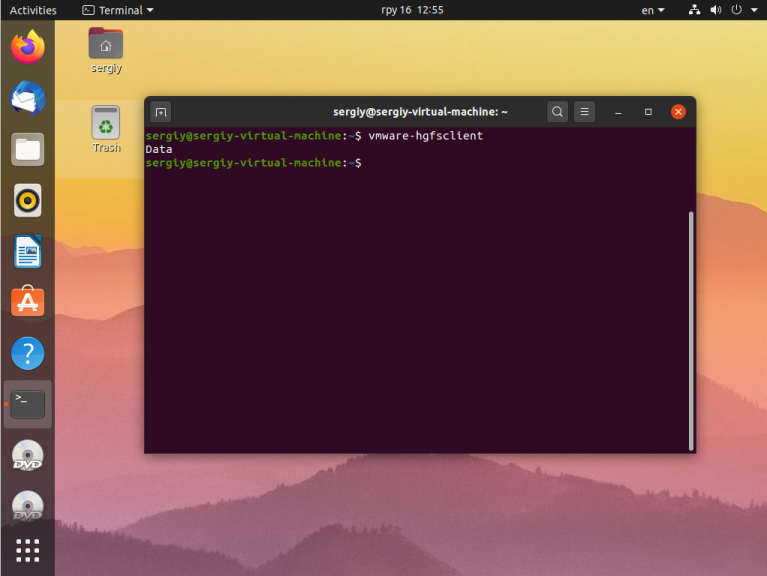
Затем с помощью такой команды, вы можете проверить видна ли ваша общая папка в гостевой системе:
Затем можно смонтировать попытаться смонтировать все общие папки в /mnt. Для этого сначала создайте папку /mnt/hgfs, если она не существует:
Затем осталось выполнить монтирование с помощью утилиты vmhgfs-fuse:
sudo vmhgfs-fuse .host: /mnt/hgfs -o allow_other -o uid=1000
Кроме, непосредственно, пути к точке монтирования надо передать опцию allow_other чтобы все пользователи могли получить доступ к папке, а владельцем папки сделать пользователя с идентификатором 1000, обычно это идентификатор первого зарегистрированного в системе пользователя, если у вас другой идентификатор замените на свой. Это позволит этому пользователю записывать файлы в эту папку.
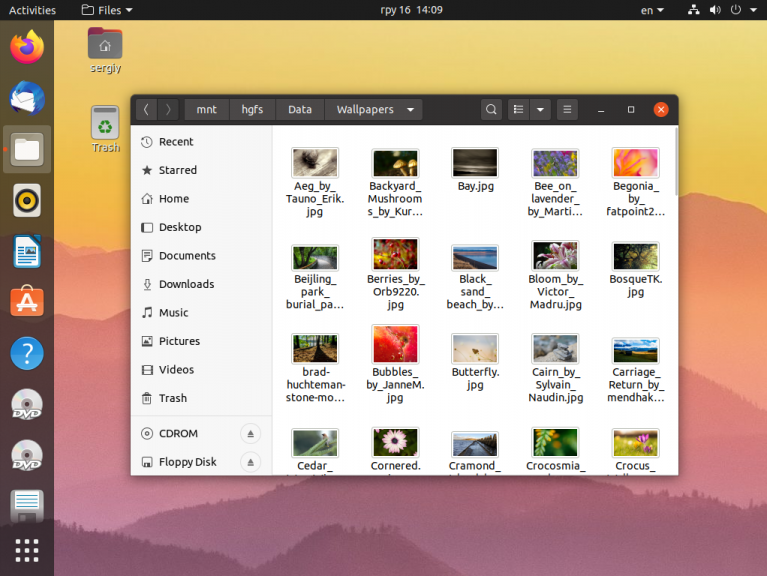
Теперь можно посмотреть её содержимое:
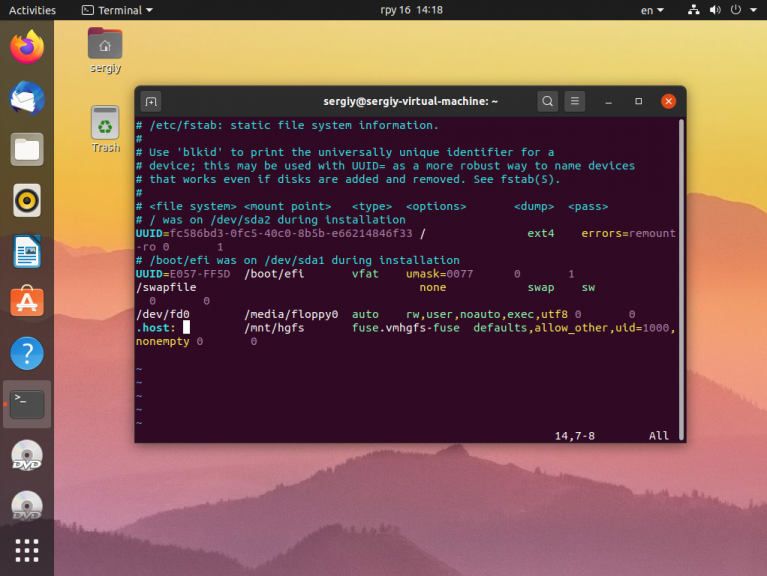
Теперь, чтобы эта папка монтировалась всегда при запуске системы надо добавить такую строчку в /etc/fstab:
.host: /mnt/hgfs fuse.vmhgfs-fuse defaults,allow_other,uid=1000,nonempty 0 0
Или если вы хотите монтировать только определённую общую папку, например, Data, то надо указать её имя после адреса .host:
.host:/Data /mnt/hgfs fuse.vmhgfs-fuse defaults,allow_other,uid=1000,nonempty 0 0
Вот и всё. Теперь вы знаете как настраивается общая папка VMware в Linux, а также как смонтировать её, если автоматическое монтирование не работает. Как видите, всё довольно просто.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.