- How to see top processes sorted by actual memory usage?
- 12 Answers 12
- 5 commands to check memory usage on Linux
- 1. free command
- 2. /proc/meminfo
- 3. vmstat
- 4. top command
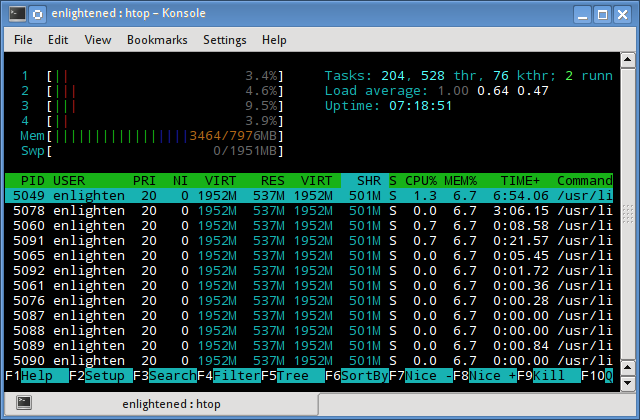
- 5. htop
- RAM Information
- Summary
- 67 Comments
- Информация об оперативной памяти в Linux. Свободная, занятая и тип памяти
- Свободная и занятая оперативная память
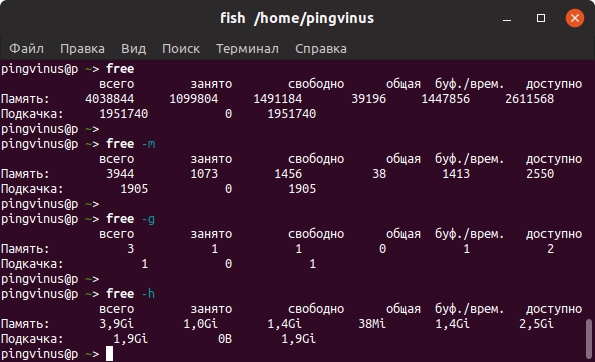
- Команда free
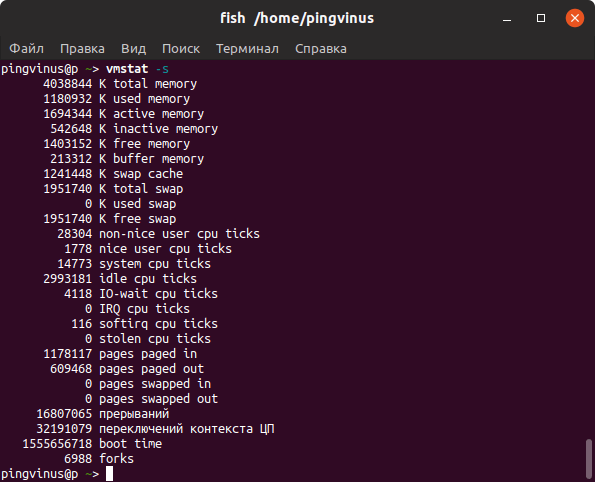
- Команда vmstat
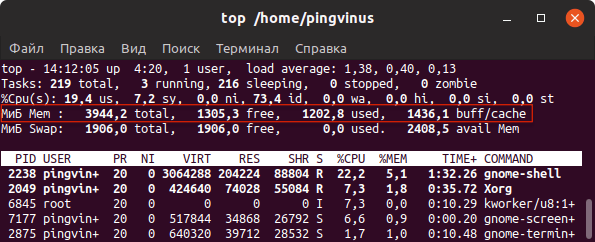
- Команда top
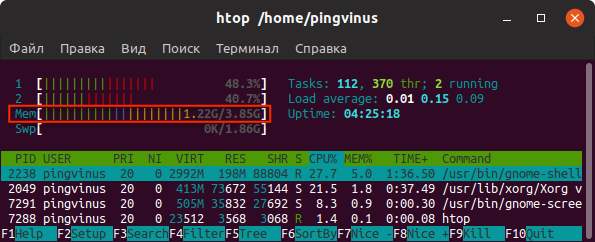
- Команда htop
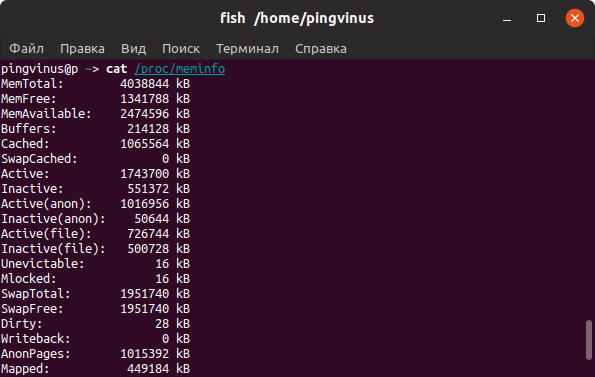
- Файл /proc/meminfo
- Тип памяти и частота
- Заключение
How to see top processes sorted by actual memory usage?
If I understand correctly, the system has only 362 MB of available memory. My question is: How can I find out which process is consuming most of the memory? Just as background info, the system is running 64bit OpenSuse 12 .
12 Answers 12
use quick tip using top command in linux/unix
and then hit Shift + m (i.e. write a capital M ).
SORTING of task window For compatibility, this top supports most of the former top sort keys. Since this is primarily a service to former top users, these commands do not appear on any help screen. command sorted-field supported A start time (non-display) No M %MEM Yes N PID Yes P %CPU Yes T TIME+ Yes Or alternatively: hit Shift + f , then choose the display to order by memory usage by hitting key n then press Enter . You will see active process ordered by memory usage
hi codecowboy, perhaps you can look at commandlinefu.com/commands/view/3/… for more detailed memory used in my server i am using third party app like newrelic.com
First, repeat this mantra for a little while: «unused memory is wasted memory». The Linux kernel keeps around huge amounts of file metadata and files that were requested, until something that looks more important pushes that data out. It’s why you can run:
find /home -type f -name '*.mp3' find /home -type f -name '*.aac' and have the second find instance run at ridiculous speed.
Linux only leaves a little bit of memory ‘free’ to handle spikes in memory usage without too much effort.
Second, you want to find the processes that are eating all your memory; in top use the M command to sort by memory use. Feel free to ignore the VIRT column, that just tells you how much virtual memory has been allocated, not how much memory the process is using. RES reports how much memory is resident, or currently in ram (as opposed to swapped to disk or never actually allocated in the first place, despite being requested).
But, since RES will count e.g. /lib/libc.so.6 memory once for nearly every process, it isn’t exactly an awesome measure of how much memory a process is using. The SHR column reports how much memory is shared with other processes, but there is no guarantee that another process is actually sharing — it could be sharable, just no one else wants to share.
The smem tool is designed to help users better gage just how much memory should really be blamed on each individual process. It does some clever work to figure out what is really unique, what is shared, and proportionally tallies the shared memory to the processes sharing it. smem may help you understand where your memory is going better than top will, but top is an excellent first tool.
5 commands to check memory usage on Linux
On linux, there are commands for almost everything, because the gui might not be always available. When working on servers only shell access is available and everything has to be done from these commands. So today we shall be checking the commands that can be used to check memory usage on a linux system. Memory include RAM and swap.
It is often important to check memory usage and memory used per process on servers so that resources do not fall short and users are able to access the server. For example a website. If you are running a webserver, then the server must have enough memory to serve the visitors to the site. If not, the site would become very slow or even go down when there is a traffic spike, simply because memory would fall short. Its just like what happens on your desktop PC.
1. free command
The free command is the most simple and easy to use command to check memory usage on linux. Here is a quick example
$ free -m total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 7976 6459 1517 0 865 2248 -/+ buffers/cache: 3344 4631 Swap: 1951 0 1951
The m option displays all data in MBs. The total os 7976 MB is the total amount of RAM installed on the system, that is 8GB. The used column shows the amount of RAM that has been used by linux, in this case around 6.4 GB. The output is pretty self explanatory. The catch over here is the cached and buffers column. The second line tells that 4.6 GB is free. This is the free memory in first line added with the buffers and cached amount of memory.
Linux has the habit of caching lots of things for faster performance, so that memory can be freed and used if needed.
The last line is the swap memory, which in this case is lying entirely free.
2. /proc/meminfo
The next way to check memory usage is to read the /proc/meminfo file. Know that the /proc file system does not contain real files. They are rather virtual files that contain dynamic information about the kernel and the system.
$ cat /proc/meminfo MemTotal: 8167848 kB MemFree: 1409696 kB Buffers: 961452 kB Cached: 2347236 kB SwapCached: 0 kB Active: 3124752 kB Inactive: 2781308 kB Active(anon): 2603376 kB Inactive(anon): 309056 kB Active(file): 521376 kB Inactive(file): 2472252 kB Unevictable: 5864 kB Mlocked: 5880 kB SwapTotal: 1998844 kB SwapFree: 1998844 kB Dirty: 7180 kB Writeback: 0 kB AnonPages: 2603272 kB Mapped: 788380 kB Shmem: 311596 kB Slab: 200468 kB SReclaimable: 151760 kB SUnreclaim: 48708 kB KernelStack: 6488 kB PageTables: 78592 kB NFS_Unstable: 0 kB Bounce: 0 kB WritebackTmp: 0 kB CommitLimit: 6082768 kB Committed_AS: 9397536 kB VmallocTotal: 34359738367 kB VmallocUsed: 420204 kB VmallocChunk: 34359311104 kB HardwareCorrupted: 0 kB AnonHugePages: 0 kB HugePages_Total: 0 HugePages_Free: 0 HugePages_Rsvd: 0 HugePages_Surp: 0 Hugepagesize: 2048 kB DirectMap4k: 62464 kB DirectMap2M: 8316928 kB
Check the values of MemTotal, MemFree, Buffers, Cached, SwapTotal, SwapFree.
They indicate same values of memory usage as the free command.
3. vmstat
The vmstat command with the s option, lays out the memory usage statistics much like the proc command. Here is an example
$ vmstat -s 8167848 K total memory 7449376 K used memory 3423872 K active memory 3140312 K inactive memory 718472 K free memory 1154464 K buffer memory 2422876 K swap cache 1998844 K total swap 0 K used swap 1998844 K free swap 392650 non-nice user cpu ticks 8073 nice user cpu ticks 83959 system cpu ticks 10448341 idle cpu ticks 91904 IO-wait cpu ticks 0 IRQ cpu ticks 2189 softirq cpu ticks 0 stolen cpu ticks 2042603 pages paged in 2614057 pages paged out 0 pages swapped in 0 pages swapped out 42301605 interrupts 94581566 CPU context switches 1382755972 boot time 8567 forks $
The top few lines indicate total memory, free memory etc and so on.
4. top command
The top command is generally used to check memory and cpu usage per process. However it also reports total memory usage and can be used to monitor the total RAM usage. The header on output has the required information. Here is a sample output
top - 15:20:30 up 6:57, 5 users, load average: 0.64, 0.44, 0.33 Tasks: 265 total, 1 running, 263 sleeping, 0 stopped, 1 zombie %Cpu(s): 7.8 us, 2.4 sy, 0.0 ni, 88.9 id, 0.9 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st KiB Mem: 8167848 total, 6642360 used, 1525488 free, 1026876 buffers KiB Swap: 1998844 total, 0 used, 1998844 free, 2138148 cached PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND 2986 enlighte 20 0 584m 42m 26m S 14.3 0.5 0:44.27 yakuake 1305 root 20 0 448m 68m 39m S 5.0 0.9 3:33.98 Xorg 7701 enlighte 20 0 424m 17m 10m S 4.0 0.2 0:00.12 kio_thumbnail
Check the KiB Mem and KiB Swap lines on the header. They indicate total, used and free amounts of the memory. The buffer and cache information is present here too, like the free command.
5. htop
Similar to the top command, the htop command also shows memory usage along with various other details.
The header on top shows cpu usage along with RAM and swap usage with the corresponding figures.
RAM Information
To find out hardware information about the installed RAM, use the demidecode command. It reports lots of information about the installed RAM memory.
$ sudo dmidecode -t 17 # dmidecode 2.11 SMBIOS 2.4 present. Handle 0x0015, DMI type 17, 27 bytes Memory Device Array Handle: 0x0014 Error Information Handle: Not Provided Total Width: 64 bits Data Width: 64 bits Size: 2048 MB Form Factor: DIMM Set: None Locator: J1MY Bank Locator: CHAN A DIMM 0 Type: DDR2 Type Detail: Synchronous Speed: 667 MHz Manufacturer: 0xFF00000000000000 Serial Number: 0xFFFFFFFF Asset Tag: Unknown Part Number: 0x524D32474235383443412D36344643FFFFFF
Provided information includes the size (2048MB), type (DDR2) , speed(667 Mhz) etc.
Summary
All the above mentioned commands work from the terminal and do not have a gui. When working on a desktop with a gui, it is much easier to use a GUI tool with graphical output. The most common tools are gnome-system-monitor on gnome and
ksysguard on KDE. Both provide resource usage information about cpu, ram, swap and network bandwidth in a graphical and easy to understand visual output.
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
67 Comments
Информация об оперативной памяти в Linux. Свободная, занятая и тип памяти
Мы воспользуемся утилитами командной строки доступными для большинства Linux дистрибутивов.
Свободная и занятая оперативная память
Для получения информации о количестве свободной и занятой оперативной памяти в Linux можно использовать различные утилиты и команды. Рассмотрим несколько распространенных способов.
Команда free
Команда free очень простая, она выводит информацию о общем количестве оперативной памяти, о количестве занятой и свободной памяти, а также об использовании файла подкачки.
free всего занято свободно общая буф./врем. доступно Память: 4038844 1099804 1491184 39196 1447856 2611568 Подкачка: 1951740 0 1951740По умолчанию объем памяти выводится в килобайтах. Используя опции, можно выводить объем памяти в других форматах. Некоторые опции:
Команда vmstat
Команда vmstat выводит различную статистику по использованию памяти. Используя ключ -s можно вывести подробную статистику в табличном виде.
vmstat -s 4038844 K total memory 1180932 K used memory 1694344 K active memory 542648 K inactive memory 1403152 K free memory 213312 K buffer memory 1241448 K swap cache . Команда top
top — это утилита командной строки, которая используется для мониторинга процессов и используемых ресурсов компьютера.
В заголовке выводится информация об использованной оперативной памяти.
Команда htop
Утилита htop, также как и top, используется для мониторинга ресурсов и процессов.
Для установки утилиты htop в Ubuntu Linux (Linux Mint и других Ubuntu/Debian-дистрибутивах) выполните команду:
Файл /proc/meminfo
Описанные выше команды, в качестве источника информации используют системные файлы из файлов, хранящихся в виртуальной файловой системе /proc . В файле /proc/meminfo содержится информация об использовании памяти. Выведем содержимое файла /proc/meminfo :
cat /proc/meminfo MemTotal: 4038844 kB MemFree: 1341788 kB MemAvailable: 2474596 kB Buffers: 214128 kB Cached: 1065564 kB SwapCached: 0 kB Active: 1743700 kB . Тип памяти и частота
Рассмотрим, как получить информацию об установленных в компьютер модулях оперативной памяти. Воспользуемся командной dmidecode
Используем следующую команду:
sudo dmidecode --type 17 sudo dmidecode --type 17 # dmidecode 3.1 Getting SMBIOS data from sysfs. SMBIOS 2.4 present. Handle 0x0026, DMI type 17, 27 bytes Memory Device Array Handle: 0x0025 Error Information Handle: Not Provided Total Width: 64 bits Data Width: 64 bits Size: 2048 MB Form Factor: DIMM Set: None Locator: A0 Bank Locator: Bank0/1 Type: DDR2 Speed: 800 MT/s . В выводе команды будет информация о слотах оперативной памяти. Для каждого слота отображается установленный модуль оперативной памяти, его тип (поле Type ), размер (поле Size ), скорость/частота (поле Speed ) и другая информация.
В зависимости от системы и оборудования не всегда удается получить все данные, поэтому некоторые поля могут быть пустыми или иметь надписи Not provided/Unknown.
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели различные способы для просмотра информации о доступной и занятой оперативной памяти, а также показали, как вывести информацию об установленных модулях оперативной памяти.
Для отслеживания использования ресурсов компьютера существует множество графических программ. Найти их можно в нашем каталоге программ для Linux в разделе Система/Мониторинг.