- The “uptime” Command in Linux [5 Practical Examples]
- A. Description
- B. Syntax
- C. Options
- Practical Examples of the “uptime” Command in Linux
- Example 1: Displaying the Gross Status of the System Uptime
- Example 2: Check the Start Time of the System Using the “uptime” Command in Linux
- Example 3: Check Linux Server Uptime in a Convenient Format
- Example 4: Get Help About the “uptime” Command in Linux
- Example 5: Get the Version of the “uptime” Command in Linux
- Conclusion
- Linux Uptime Command With Usage Examples
- Using Uptime
- Check Linux Server Uptime
- Check Linux Server Starting Time
- Uptime Version & Help
- How to Check System Uptime in Linux
- What is Uptime?
- Check System Uptime in Linux
- Check Last Reboot in Linux
- Linux Uptime Command
- How Does the Uptime Command Work?
- Example 1: Uptime in Human-Readable Format
- Example 2: Check the Start Time of the System
- Example 3: Check the Version of the Installed Uptime Command
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Syed Minhal Abbas
The “uptime” Command in Linux [5 Practical Examples]
The uptime command in Linux is an essential tool for anyone who needs to monitor the performance of a Linux system. Whether you are a system administrator, a developer, or simply a user, understanding the basic usage of this command and its advanced features can help you optimize your system and make decisions while troubleshooting. In this article, I will explore the basic usage of the uptime command, as well as some of its options and features, with some practical examples.
A. Description
The uptime command in Linux is a simple but powerful tool for monitoring the performance of your system. It provides helpful information about the amount of time the system has been running, the number of users currently logged in, and the system load averages for a specified period of time. This information is important for the system administrators.
B. Syntax
Note: In the syntax above, the OPTION enclosed by the square brackets means it is not mandatory and three dots after the square brackets mean multiple OPTIONS can be used simultaneously after the uptime command.
C. Options
The uptime command has multiple options available. Here, I have listed a few of them. However, you can learn more about the uptime command, its options and their uses by checking the man page.
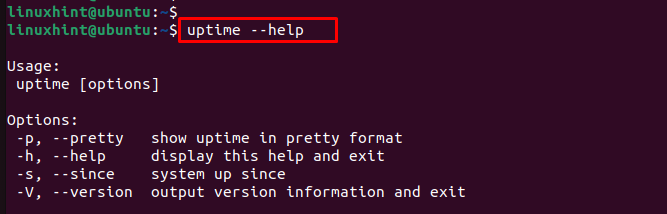
- -p, –pretty: Shows uptime information in a human-readable format.
- -h, –help: Displays this help page
- -s, –since: Prints the date and time since the system has been up, in yyyy-mm-dd HH:MM:SS format.
- -V, –version: Displays version information.
Note: Commands and their options are case-sensitive in Linux. So, be careful while using them.
Practical Examples of the “uptime” Command in Linux
In Linux, the uptime command is a helpful tool to get information about the system and monitor its performance. In the section below, I will show you some of the most useful applications for the uptime command in Linux.
Example 1: Displaying the Gross Status of the System Uptime
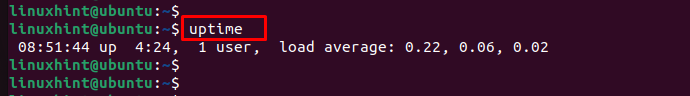
The uptime command in Linux allows you to see the gross status, i.e., the starting time of the system, the amount of time that the system has been running, the number of users currently logged in, and system load averages for a specified period of time. In this example, I will show you the uptime status of my system. You can do the same by following the steps below.
Steps to Follow:
➊ First, open the Ubuntu Terminal.
➋ Then, execute the following command.
➌ Finally, press the ENTER key.
In the following image, you can see that I have displayed the uptime status of my system.
Note: The uptime command gives an output in the order given below.
- Starting time of the system.
- Amount of time that system has been running.
- The number of users currently logged in.
- System load averages for a specified period of time.
Similar Readings
- The “reboot” Command in Linux [3 Practical Examples]
- The “sync” Command in Linux [8 Practical Examples]
- The “chage” Command in Linux [7 Practical Examples]
- The “env ” Command in Linux [9 Practical Examples]
Example 2: Check the Start Time of the System Using the “uptime” Command in Linux
You can check the starting time of the system by using the uptime command followed by the option -s. In this example, I will show you the starting time of my system. You can do the same by following the steps below.
Steps to Follow:
➊ At first, open the Ubuntu Terminal.
➋ Then, execute the following command.
➌ Then, press the ENTER key.
In the following image, you can see that I have displayed the starting time of my system.
Example 3: Check Linux Server Uptime in a Convenient Format
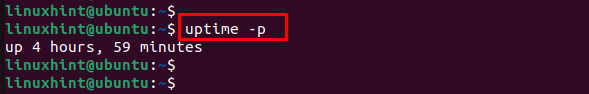
The uptime command, along with option -p allows you to see the amount of time the system has been running. Instead of displaying the uptime as the number of seconds since the system started, it displays the uptime in days, hours, minutes, and seconds. Here, I will show you the amount of time that my system has been running using the option -p with the uptime command. You can follow the steps below to get the same for your system.
Steps to Follow:
➊ First, open the Ubuntu Terminal.
➋ Next, run the command to see the amount of time the system has been running.
➌ Finally, tap the ENTER button.
As you can see in the image below, I have displayed the amount of time that my system has been running in a more convenient format.
Example 4: Get Help About the “uptime” Command in Linux
In Linux, the help page for the uptime command contains a brief description of the command. You can see the help page by following the steps mentioned below.
Steps to Follow:
➊ At first, open the Ubuntu Terminal.
➋ Then, type the following command into the command prompt:
➌ Now, press the ENTER button.
In the image below, you can see the help page for the uptime command in Linux.
Example 5: Get the Version of the “uptime” Command in Linux
You can see the current version of the uptime command on your Linux machine with the -V or –version option. Here, I will show you the version of the uptime command for my machine on the terminal. You can do the same by following the steps below:
Steps to Follow:
➊ Open the Ubuntu Terminal.
➋ Next, run the following command.
➌ Press the ENTER key.
In the following image, you can see that I have displayed the version of the uptime command in Linux.
Conclusion
The uptime command in Linux is a simple and powerful tool for monitoring performance on the system. By utilizing its various options, you can understand your system’s resource utilization and make decisions about system optimization. I have designed this article aiming to provide a comprehensive guide to the uptime command, with practical examples to help you get started and become an advanced user.
Similar Readings
- The “time” Command in Linux [4 Practical Examples]
- The “tty” Command in Linux [4 Practical Examples]
- The “vmstat” Command in Linux [6 Practical Examples]
- The “service” Command in Linux [6 Practical Examples]
- The “sestatus” Command in Linux [4 Practical Examples]
- The “shutdown” Command in Linux [7 Practical Examples]
Linux Uptime Command With Usage Examples
The Linux Operating System is filled with several commands which any aspiring Linux expert or power user e.g. system admin must have a good grasp of. One of such commands is uptime and today, I’ll briefly discuss its purpose and syntax.
Uptime is a command that returns information about how long your system has been running together with the current time, number of users with running sessions, and the system load averages for the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes. It can also filter the information displayed at once depending on your specified options.
uptime uses a simple syntax:
Using Uptime
You can run the uptime command without any options like so:
It will display an output similar to:
09:10:18 up 106 days, 32 min, 2 users, load average: 0.22, 0.41, 0.32
In order of appearance, the command displays the current time as the 1st entry, up means that the system is running and it is displayed next to the total time for which the system has been running, the user count (number of logged on users), and lastly, the system load averages.
What are system load averages? It is the average number of processes that are in a runnable or uninterruptable state. A process is in a runnable state when it is using the CPU or waiting to use the CPU; while a process is in an uninterruptable state when it is waiting for I/O access like waiting for a disk.
To know more about uptime, check out our article: Understand Linux Load Averages and Monitor Performance of Linux
Now let’s see some useful uptime command usage with examples.
Check Linux Server Uptime
You can filter uptime’s result to show only the running time of the system with the command:
# uptime -p up 58 minutes
Check Linux Server Starting Time
Using option -s will display the date/time since when the system has been running.
# uptime -s 2019-05-31 11:49:17
Uptime Version & Help
As it is with most command line apps, you can display uptime’s version information and quick help page with the following command.
# uptime -h Usage: uptime [options] Options: -p, --pretty show uptime in pretty format -h, --help display this help and exit -s, --since system up since -V, --version output version information and exit For more details see uptime(1).
Having gotten to this point in the article, you can now use uptime for your daily runs and you’ll determine its level of usefulness to you. If you have any doubts, here’s its man page.
How to Check System Uptime in Linux
Linux/Unix systems keep the details of the system uptime. You may also need to know when the server is running. This tutorial we will use Linux uptime command.
What is Uptime?
The uptime is the amount of time a system is continuously running since the last start/restart.
Check System Uptime in Linux
You can use the uptime command to find the system uptime. Uptime command is available under procps package. This command also provides the current system time, number of logged in users and current CPU load.
uptime 07:33:31 up 174 days, 5:12, 2 users, load average: 0.17, 0.14, 0.17
as per the above output, the system is running from 174 days, 5 hours and 12 minutes.
Check Last Reboot in Linux
Additionally, you can also use the last command to find the system reboot history. This will help you to find when the system was last rebooted.
last reboot reboot system boot 2.6.18-92.el5 Sat Feb 11 12:00 (12+22:51) reboot system boot 2.6.18-92.el5 Sun Feb 5 12:57 (5+21:17) reboot system boot 2.6.18-92.el5 Sat Jan 28 15:58 (13+18:16) reboot system boot 2.6.18-92.el5 Thu Jan 26 17:15 (15+17:00) reboot system boot 2.6.18-92.el5 Mon Jan 9 13:40 (32+20:35) reboot system boot 2.6.18-92.el5 Sun Jan 8 15:50 (33+18:24) reboot system boot 2.6.18-92.el5 Sat Dec 24 12:58 (48+21:17)
The above output shows that the system was last rebooted on Feb 11 at 12:00 PM and others as well.
Linux Uptime Command
Any Linux distro comes with the “uptime” command. It’s an important command for system administrators to know. It helps troubleshoot the issues related to power and scheduling. Of course, there are other alternative tools available for this purpose but uptime is relatively simple and easy to use.
The content of this guide is as follows:
Let’s start the uptime command.
How Does the Uptime Command Work?
If you use the system’s uptime command via command prompt, you get many benefits out of it. For example, suppose you are facing a problem in connecting to the server. Then, you can easily run the uptime command on the server to check if there has been a recent reboot on the server. This helps in troubleshooting the situation and provides you with better visibility to apply the required solution.
The output specifies the current time. “Up” specifies that the system is up and running along with the total time that the system is up to the user count and the system load averages.
Running the uptime command of a Linux system via the command line, you get a specified output in the following order:
- The current time of the system.
- The total uptime of the system.
- The active users that are currently running the system.
- The average of the system loads that is available for the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes.
Uptime command comes with various options. To check the options, we can run the “help” command.
Example 1: Uptime in Human-Readable Format
With the use of the “-p” option, you can get a pretty clear output which displays the uptime in the number of days, hours, minutes, and seconds format:
Example 2: Check the Start Time of the System
Another option is to check the exact time when the system is first started rather than the time spent since it started. Run the following command on the command-line interface with the “-s” option:
Example 3: Check the Version of the Installed Uptime Command
If you want to check the version of the installed uptime package in the system, run the following command with the “-V” option:
The output shows the current version of the “uptime” command.
Conclusion
Linux is a well-known environment and is highly recommended for various projects due to its stability and various configurations. The “uptime” command checks the system information. We explained the “uptime” command with its various options.
About the author
Syed Minhal Abbas
I hold a master’s degree in computer science and work as an academic researcher. I am eager to read about new technologies and share them with the rest of the world.