- lsusb Command in Linux (Display USB device Details)
- Syntax
- Options
- Examples
- Using the lsusb Command with Other Utilities
- Conclusion
- How to Use the LSUSB Command
- Install usbutils Package
- Using the lsusb Command
- Options Used with the lsusb Command
- Example 1: Display a Specific USB Device
- Example 2: Display Detailed Information about All USB Devices
- Example 3: Display Information about a Specific USB Device
- Example 4: Display All USB Devices in a Tree Structure
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Aqsa Yasin
lsusb Command in Linux (Display USB device Details)
The `lsusb` command is a utility in Linux that allows users to list the USB (Universal Serial Bus) devices connected to the system. This utility is the part of “usbutils” package, which provides utilities to display information about USB buses in the system and the devices connected to them.
A USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a widely used standard for connecting devices to computers. It allows users to connect a many of devices such as keyboards, mice, printers, and external storage devices to their computers with ease. The `lsusb` command can be used to display information about these devices, including their vendor and product ID, device name, device driver, and others.
In this article, we will discuss the syntax and options of the lsusb command, and provide examples of how to use it to list and display information about USB devices in Linux.
Syntax
The basic syntax of the lsusb command is:
Options
Some common options used with the lsusb command are:
- -v : Display detailed information about the USB devices.
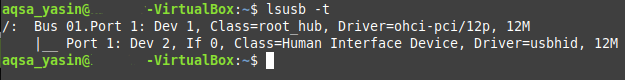
- -t : Display a tree-like view of the USB devices.
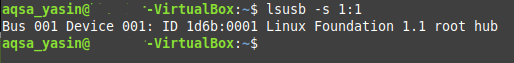
- -s : Display information about a specific USB device, specified by its bus and device number.
- -d : Display information about a specific USB device, specified by its vendor and product ID.
- -D : Selects which device will be examined.
Examples
OutputBus 002 Device 004: ID 046d:0a37 Logitech, Inc. USB Headset H540 Bus 002 Device 002: ID 8087:0024 Intel Corp. Integrated Rate Matching Hub Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub Bus 001 Device 004: ID 413c:301a Dell Computer Corp. Bus 001 Device 003: ID c0f4:05e0 Bus 001 Device 002: ID 8087:0024 Intel Corp. Integrated Rate Matching Hub Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
Output/: Bus 02.Port 1: Dev 1, Driver=ehci-pci/2p, 480M |__ Port 1: Dev 2, If 0, Driver=hub/6p, 480M |__ Port 1: Dev 4, If 0, Driver=snd-usb-audio, 12M |__ Port 1: Dev 4, If 1, Driver=snd-usb-audio, 12M |__ Port 1: Dev 4, If 2, Driver=snd-usb-audio, 12M |__ Port 1: Dev 4, If 3, Interface Device, Driver=usbhid, 12M /: Bus 01.Port 1: Dev 1, Driver=ehci-pci/2p, 480M |__ Port 1: Dev 2, If 0, Driver=hub/4p, 480M |__ Port 1: Dev 3, If 0, Interface Device, Driver=usbhid, 1.5M |__ Port 1: Dev 3, If 1, Interface Device, Driver=usbhid, 1.5M |__ Port 2: Dev 4, If 0, Interface Device, Driver=usbhid, 1.5M
OutputBus 002 Device 004: ID 046d:0a37 Logitech, Inc. USB Headset H540 Couldn't open device, some information will be missing Device Descriptor: bLength 18 bDescriptorType 1 bcdUSB 2.00 bDeviceClass 0 bDeviceSubClass 0 bDeviceProtocol 0 bMaxPacketSize0 64 idVendor 0x046d Logitech, Inc. idProduct 0x0a37 USB Headset H540 bcdDevice 1.22 iManufacturer 1 iProduct 2 iSerial 3 bNumConfigurations 1 Configuration Descriptor: bLength 9 bDescriptorType 2 wTotalLength 0x011c
OutputBus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub Couldn't open device, some information will be missing Device Descriptor: bLength 18 bDescriptorType 1 bcdUSB 2.00 bDeviceClass 9 Hub bDeviceSubClass 0 bDeviceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub bMaxPacketSize0 64 idVendor 0x1d6b Linux Foundation idProduct 0x0002 2.0 root hub bcdDevice 5.15 iManufacturer 3 iProduct 2 iSerial 1
Using the lsusb Command with Other Utilities
The lsusb command can be used in combination with other utilities to perform a variety of tasks.
To find the vendor and product ID of a USB device, use the lsusb command with the -v option and grep for the idVendor and idProduct fields:
lsusb -v | grep -E 'idVendor|idProduct' OutputidVendor 0x046d Logitech, Inc. idProduct 0x0a37 USB Headset H540 idVendor 0x8087 Intel Corp. idProduct 0x0024 Integrated Rate Matching Hub idVendor 0x8087 Intel Corp. idProduct 0x0024 Integrated Rate Matching Hub idVendor 0x1d6b Linux Foundation idProduct 0x0002 2.0 root hub
To find the device name of a USB device, use the lsusb command with the -v option and grep for the iProduct field:
OutputiProduct 2 Logitech USB Headset H540 iProduct 2 EHCI Host Controller iProduct 2 Dell MS116 USB Optical Mouse iProduct 2 usb keyboard
To find the device driver of a USB device, use the lsusb command with the -t option and grep for the device name:
Output|__ Port 2: Dev 4, If 0, Interface Device, Driver=usbhid, 1.5M
To find the device node of a USB device, use the lsusb command with the -t option and look for the device name in the /dev directory:
Outputby-id event0 event10 event2 event4 event6 event8 mice by-path event1 event11 event3 event5 event7 event9 mouse0
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned about the `lsusb` command line utility and how to use it to list and display information about USB devices connected to a Linux system. We also saw how to use the lsusb command with other utilities to perform various tasks related to USB devices.
How to Use the LSUSB Command
The lsusb command, commonly known as the “List USB” command, is one of the most commonly used commands in Linux. As the name implies, this command is used to list all the USB devices that are attached to your Linux system. When combined with different parameters or options, this command can also be used to serve other purposes. This article shows you how to use the lsusb command in Linux.
Note: Linux Mint 20 is used throughout this article to demonstrate the usage of this command. However, you can work with any Linux distribution of your choice.
Install usbutils Package
Before getting started with the lsusb command, install the usbutils package onto your Linux Mint 20 system. To install the package, follow the steps shown below:
Launch the terminal by clicking on the terminal icon, highlighted in the following image:
After you click on this icon, the terminal window will immediately pop up, as shown below:
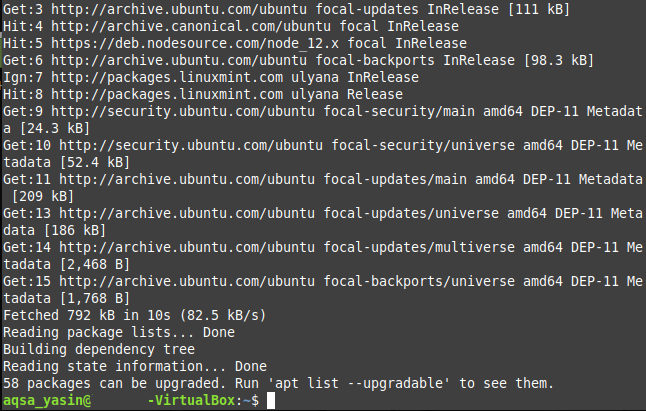
Before installing the usbutils package, it is highly recommended to update your Linux Mint 20 system to avoid hindrances during the installation. This can be done by executing the update command in the following manner:
This command can be seen in the image shown below:
Once your system has been updated, you will see the following output, as mentioned in the image on your terminal:
After successfully updating your system, you can now run the following command without any worries:
This command will install the usbutils package on your Linux Mint 20 system.
The successful installation of the said package will render the following output on your terminal:
Using the lsusb Command
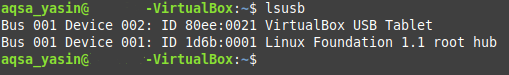
The lsusb command provides information about the USB devices attached to your Linux system. This command may either be used individually or combined with various choices. For this section, we are only interested in running the lsusb command independently, i.e., without any additional parameters or options. Simply run the following command in your Linux Mint 20 terminal to do so:
Upon successful execution of this command, you will see all the information related to any USB buses and devices connected to your system, as in the following image:
Options Used with the lsusb Command
As mentioned previously, the lsusb command can also be used in conjunction with different options. These options include the following:
- -s: Displays information about any particular USB device, according to the device’s bus number and device number.
- -v: Shows more detailed information about the USB devices connected to your system.
- -D: Provides detailed information read from a specific USB device file.
- -t: Displays all the connected USB devices in the form of a tree or hierarchy.
In the examples given below, you will learn more about the usage of these options.
Example 1: Display a Specific USB Device
To display a specific USB device, you need to know two things about the device: its bus number and its device number. These two items can be determined simply by running the lsusb command alone, as discussed above. Once you know the bus and device numbers of the USB device, run the following command on your terminal:
Replace the BusNum and DeviceNum with the device’s bus number and device number, respectively. For the sake of demonstrating this method, we have used bus number 1 and port number 1, which you can verify in the image below:
After running this command, you will see the USB device, along with the specified bus number and device number on your terminal, as shown in the following image:
Example 2: Display Detailed Information about All USB Devices
To display every detail about all the USB devices that are connected to your system, run the following command in your terminal:
You can also see this command in the image below, for more clarity:
After this command is executed successfully, you will be able to see more details about all the USB devices connected to your system, as seen in the image below:
Example 3: Display Information about a Specific USB Device
As you may have noticed, in the method above, the output with the –v option was quite long. In some situations, you might want to have detailed information only about a single device, instead of having it for all the USB devices attached to your system. If this is the goal, then a detailed output about a single USB device can be achieved by executing the following command in your terminal:
Again, to run this command, you will need to know the bus number and device number of the specific USB device that you would like more information about from the device’s particular file. In this example, we have replaced the ‘BusNum’ with 001 and the ‘DeviceNum’ with 002, as shown in the image below:
After running this command, you will be able to see all the details about the specified USB device, read directly from the device’s file, as shown in the following image:
Example 4: Display All USB Devices in a Tree Structure
At times, you may also want to list down all the connected USB devices in the form of a hierarchy or a tree structure, for easier readability. This can be done by executing the following command in your terminal:
This command can also be seen in the image below:
Running this command will display all the USB devices that are connected to your system in the form of a tree structure, as shown in the following image:
Conclusion
This article gives you a detailed overview of the usage of the lsusb command in Linux Mint 20. Now, whenever you require more information about the USB devices attached to your system, you can conveniently make use of this command.
About the author
Aqsa Yasin
I am a self-motivated information technology professional with a passion for writing. I am a technical writer and love to write for all Linux flavors and Windows.