- Linux Shutdown Command – 8 Examples with All Options
- Linux Shutdown Command
- Syntax
- Useful Shutdown Commands
- How to Use Linux Shutdown Command
- 1. Shutdown After 1 Minute
- 2. Shutdown Now
- 3. Shutdown at a Specified Time
- 4. Shutdown Message
- 5. Cancel a Scheduled shutdown
- 6. Shutdown command to reboot
- 7. Shutdown command to Schedule a Reboot
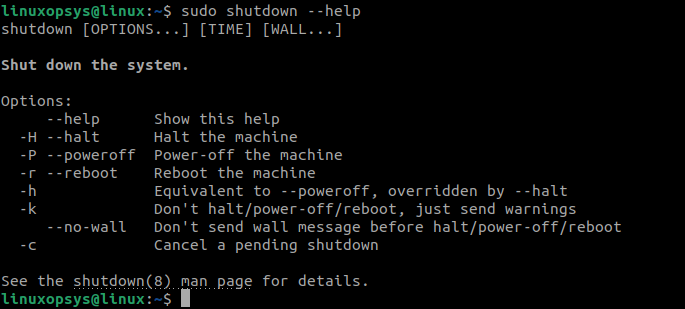
- Shutdown Help
- Linux Shutdown Command Options
- Conclusion
- How To Use The shutdown Command in Linux?
- Why does the shutdown command in Linux exist?
- Understanding the shutdown command
- Using the shutdown command in Linux
- Scheduling the shutdown
- Initiating the shutdown with a message
- Restarting the system
- Powering off the system
- Wrapping up
Linux Shutdown Command – 8 Examples with All Options
In some cases, you must shut down or reboot your computer to apply updates, install a new application, migrations, or perform other operations. Linux provides the shutdown command to securely stop all the running processes on your server and to notify all the logged-in users about the shutdown operation.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to use the Linux shutdown command-line utility with practical examples.
Linux Shutdown Command
The shutdown command is used to securely shut down the system. Use this command in Linux for system shutdown either immediately or at a specific time. Shutdown can also be used to reboot your computer system.
When you run the Linux shutdown command-line tool, then all running applications are closed, active system processes are saved, and all currently logged-in users are notified about the shutdown operation. This command also prevents new users from logging in after the shutdown process starts.
Syntax
The basic syntax of this command is as follows:
shutdown [option] [time] [message]- option denotes the operation that you want to perform, such as power-off (default option), halt, or reboot.
- time denotes when to execute the command. You can use this parameter to schedule a shutdown or reboot.
- message denotes a comment or message that you want to broadcast to all the logged-in users.
Useful Shutdown Commands
Shutdown provides several options and variations that you can use to perform different options. The following table lists some of the most useful shutdown commands:
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
| shutdown | Shuts down the computer in one minute. |
| shutdown -h | Halts and turns off the system. |
| shutdown -r | Reboots the system in one minute. |
| shutdown -h | Halts and turns off the system at a specified time. |
| shutdown now | Shuts down your computer immediately. |
| shutdown -r | Reboots the system at a specified time. |
| shutdown -r now | Reboots the system immediately. |
| shutdown -P | Brings down the system and then powers it off. |
| shutdown -c | Cancels a scheduled shutdown. |
How to Use Linux Shutdown Command
The following examples show you some of the most common usages of Linux shutdown command:
1. Shutdown After 1 Minute
This is the default behavior of the shutdown command. Use shutdown without any options to shut down the system after one minute:
2. Shutdown Now
To do an immediate shutdown, use the Linux shutdown command with now option.
Instead of using the time to now, you can use +0 time option to down the system immediately.
On a systemd based Linux Distributions the shutdown now equivalent command is systemctl poweroff. In those systems, shutdown command is a symbolic link systemctl.
3. Shutdown at a Specified Time
Use the time argument with the shutdown command to turn off your computer at a specified time. The time argument can be used in two formats- specified time of the day in HH:MM format or +m where you can specify the number of minutes from the current time when the shutdown process will start.
To shut down the system at 10 AM, specify the time after the shutdown command:
To shut down your computer after five minutes from the current time, specify the five minutes in +5 format:
4. Shutdown Message
System administrators can notify users with a warning message about the system shut down.
To shutdown the system in 30 minutes with a broadcast message, use the following command:
sudo shutdown +30 "System is going under maintenance in 30 minutes"5. Cancel a Scheduled shutdown
There may be a situation where you must cancel a scheduled shutdown. For example, suppose there is a planned release and you need to hold off the shutdown. In that case, you can cancel it using the -c option with the shutdown command and can also specify a custom wall message:
sudo shutdown -c "Ops needs the scheduled shutdown"This command does not show any output on the screen.
Unfortunately in systemd system the systemctl command doesn’t have a schedule or cancel the shutdown. Another option is to add cron to /run/systemd/shutdown/scheduled script.
6. Shutdown command to reboot
By default, the shutdown -r command reboots your system after one minute. To shutdown immediately and automatically reboot your system use the following command:
7. Shutdown command to Schedule a Reboot
To schedule a reboot, use the time parameter with the following command as you do with the system shutdown:
sudo shutdown -r +10 “Rebooting for maintenance”Shutdown Help
The shutdown command provides a help page that you can refer to know more about the shutdown command options:
Linux Shutdown Command Options
The following table some of the useful options that you can use with the shutdown command:
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| -r | Brings down your system and requests for a system reboot. |
| -h | Sends a request to either halt or power off the system after bringing the system down. |
| -H | Sends a request to halt the system after bringing the system down. |
| -P | Sends a request to power off the system after bringing the system down. |
| -c | Cancels any scheduled shutdown. You can not specify a time with this option, but you can broadcast a custom message for the system users. |
| -k | Sends a warning message to the users and disables all system logins. It does not bring the system down. |
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how to use the shutdown command to power down or reboot your Linux system. Shutdown provides various options that you can use to either shut down your system immediately or schedule a shutdown. This command can also be used to reboot your system. You can try these command options and examples in a test environment, but you should use them carefully in a production environment.
If this resource helped you, let us know your care by a Thanks Tweet. Tweet a thanks
How To Use The shutdown Command in Linux?
How can you shutdown Linux from the command line? Let’s learn to use the shutdown command in Linux for the same purpose!
A Linux system admin is in charge of keeping a system and running and maintaining updates on the machine. But for core kernel updates, your system needs to be shut down safely and restarted.
You also need to let all the currently logged in users know that the system is about to be shut down. This gives them the chance to save important files before the system goes offline.
This further prevents them from losing data, which might happen in case the system goes down suddenly. To take care of these requirements, we make use of the shutdown command in Linux.
Why does the shutdown command in Linux exist?
The shutdown command in Linux command is a safe way to terminate running processes on a system and shut it down. It can be used to shut a system down either immediately or at a scheduled time.
When a shut down is initiated, all the users who are currently logged on to the system are notified about it. Further, the system prevents any new user from logging on.
All the running process receive a SIGTERM kill signal (read more about termination signals here) so that they can be terminated gracefully.
Next, the shutdown command in Linux signals to the init command to modify the runlevel for the system.
The runlevel 0 sends the system into the halt stage, runlevel 1 makes the system work in a single user mode while runlevel 6 reboots the system.
Understanding the shutdown command
The best way to understand any command is through understanding it’s syntax. Here is how the syntax for the shutdown command in Linux looks like.
shutdown [option] [time] [message]
Here, the time can refer to a specified time (based on a 24-hour clock) or a period from the time of initiating the command. The ‘message’ specifies the message which the users will receive when they are notified about the shutdown being initiated.
The shutdown command allows several options to dictate how you initiate a shutdown signal. Here is a list of some of the commonly used options offered by the shutdown command in Linux.
| Option | Effect |
| -r | Reboots the system |
| -k | Sends shutdown warning to all logged-in users without actually shutting down |
| -h | This option is used to tell the command to halt the system. In the case of ‘halt’, all the running processes are terminated and the system is shut down. |
| -P | Emulates the power button shut down by sending a system power-off signal. |
| -c | Cancel scheduled shutdowns |
While this list covered the basic options used in the shutdown command, you should explore the other options to understand its full potential.
Using the shutdown command in Linux
Now we have developed an understanding of the shutdown command in Linux along with its parameters. It’s time to use this knowledge for practical application of the shutdown command.
For this tutorial, we will go over some examples to learn how to use the shutdown command. Note that the shutdown command in Linux can only be initiated by the root user.
Scheduling the shutdown
The most basic use of the shutdown command in Linux is to schedule a shutdown. For this example, we will schedule our system to perform the shutdown at 5 PM. Type the following in your command line.
Note that we need to enter the time in a 24-hour format. entering 5:00 here will schedule the shutdown for 5 AM instead of 5 PM.
Initiating the shutdown with a message
When you initiate a shutdown, the users who are logged on the system might need to be informed about the reason for the shutdown. For this task, we make use of a message. This can be done as shown below.
shutdown +20 "The system will be down in 20 minutes for hardware upgrades"
As you can notice, the users will receive a custom message specifying the reason for the shutdown. Further, we used +20 instead of a specified time in this command. This tells the compiler to shut down the system 20 minutes after the command is entered into the terminal.
Restarting the system
Sometimes the system just requires a quick reboot. This can be done using the ‘-r- option of the shutdown command on your system. The -r command, as we discussed in the table earlier, would execute a proper shutdown.
Then it will immediately signal the system to reboot itself. This command can be written as the following.
shutdown -r now shutdown -r 17:00
Notice that we replaced the time with the keyword ‘now’. This keyword will cause the shutdown command to be executed immediately, without waiting for any other input.
Also, you can see how I’ve specified the time right after the command to schedule that specific action, which in this case is restart.
Powering off the system
When you wish to turn off your system and disconnect it from the power supply, we use the ‘-P’ option of the shutdown command. This can be done as follows.
This will shut down the system and send an ACPI signal to the PSU to cut off the power supply for our system.
Wrapping up
The shutdown command is an important tool for Linux system admins as it allows the root user to halt, reboot and power off their system or schedule the process.
It also has basic defenses against sudden shutdowns as all processes are terminated gracefully before the system is turned off.
We hope this tutorial was able to help you understand the shutdown command in Linux. If you have any feedback, queries or suggestions, feel free to reach out to us in the comments below. For further details, read through the shutdown command manpage.