- How do I shut down or reboot from a terminal?
- For Ubuntu 15.04 and later
- For Ubuntu 14.10 or earlier
- On 16.04 no need of sudo
- How to Shut Down Your Linux System
- How to Shut Down Your Linux System
- Command 1: Shutdown Linux System Through “shutdown” Command
- Command 2: Shutdown Linux System Through “halt” Command
- Command 3: Shutdown Linux System Through “poweroff” Command
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Awais Khan
- How to use Linux Shutdown Command with Examples
- shutdown Command Syntax
- How to Use the shutdown Command
- Shutdown With All Parameters
- How to Shut Down the System at a Specific Time
- How to Shut Down the System Immediately
- How to Broadcast a Custom Message
- How to Cancel a Scheduled Shutdown
How do I shut down or reboot from a terminal?
Appendix: If your keyboard is «locked up», so you can’t enter a command like «reboot» which would run from «su» anyway, use the keyboard: hold down Alt + PrintScreen/SysRq , buttons and type «REISUB». It doesn’t have to be capital letters. It will restart your computer gently. http://blog.kember.net/articles/reisub-the-gentle-linux-restart/
@NicolasRaoul nopes, for me i see this without sudo . Failed to set wall message, ignoring: Interactive authentication required. Failed to reboot system via logind: Interactive authentication required. Failed to open /dev/initctl: Permission denied Failed to talk to init daemon.
Open your terminal with CTRL + ALT + T and do these following commands
& one more command for restart:
Another way as one of the user mentioned.
You can get more info on the shutdown command by using one of the following:
Can anyone explain why sudo halt might not perform shutdown in some cases, whereas sudo halt -p does?
Hate passwords ( sudo ) and love one-liners?
For Ubuntu 15.04 and later
This is due to Ubuntu’s shift in using systemd instead of Upstart
systemctl poweroff systemctl reboot systemctl suspend systemctl hibernate systemctl hybrid-sleep Since hibernate is normally disabled by default in Ubuntu systems, you can enable this by checking this answer.
For Ubuntu 14.10 or earlier
/usr/bin/dbus-send --system --print-reply --dest="org.freedesktop.ConsoleKit" /org/freedesktop/ConsoleKit/Manager org.freedesktop.ConsoleKit.Manager.Stop /usr/bin/dbus-send --system --print-reply --dest="org.freedesktop.ConsoleKit" /org/freedesktop/ConsoleKit/Manager org.freedesktop.ConsoleKit.Manager.Restart Other commands you may like:
/usr/bin/dbus-send --system --print-reply --dest="org.freedesktop.UPower" /org/freedesktop/UPower org.freedesktop.UPower.Suspend Hibernate: (if enabled on your system)
/usr/bin/dbus-send --system --print-reply --dest="org.freedesktop.UPower" /org/freedesktop/UPower org.freedesktop.UPower.Hibernate On 16.04 no need of sudo
sudo shutdown -h (time) (message) This will shutdown your computer and halt it. That is what the -h is for. Then, in the time area you can choose the shutdown delay (in minutes) and if you want you can send a broadcast message in the message area (like goodbye, or I’m shutting the thing down :P).
To restart the computer, type
sudo shutdown -r (time) (message) Now, instead of shutting it down and halting it, you will restart your computer once it’s shutdown. 🙂
How to Shut Down Your Linux System
Shutting down a Linux system safely is beneficial since it helps protect your data, which may damage in case of improper shutdown. When you securely perform the shutdown, the system will be notified that it will go down soon and stop all the processes and services running on the system before the shutdown. You may also get approval to stop those services and in case of any important service running, you can skip the shutdown.
This article will show you different ways to shut down the Linux system safely.
How to Shut Down Your Linux System
There are different Linux commands you can use to shut down the Linux system, which are as follows:
Command 1: Shutdown Linux System Through “shutdown” Command
The “shutdown” command is one of the most widely used commands in Linux systems that can safely shutdown the system.
The fundamental syntax to use this command is given below:
If you apply the above command directly, it will schedule the shutdown time and within 1 minute, it will automatically shut down the Linux system.
You can cancel the shutdown anytime using the following command:
If you want to immediately shut down your Linux system without waiting, you can use the following command:
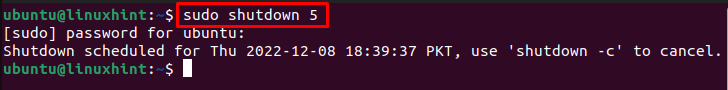
You can also set the timer for the shutdown as well using the following syntax:
If you want to shut down the Linux system after 5 minutes, you can run the following command:
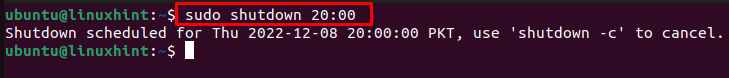
In case if you want to schedule a time for a specific hour, you can schedule the time accordingly. Like in my case, I want to shut down the system at 8 pm. For this reason, the command will look like the following:
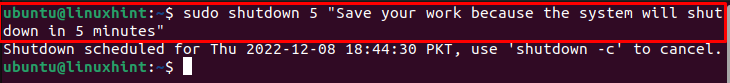
If your Linux system is accessed by multiple users simultaneously, it’s better to broadcast a message to notify them about the shutdown time. You can do this on a Linux system using the following command:
Command 2: Shutdown Linux System Through “halt” Command
You can also use the “halt” command to shut down the system. If you directly apply the “halt” command, it will instruct the hardware to stop the CPU function.
However, if you want to shut down the system immediately, you can apply the following command:
Command 3: Shutdown Linux System Through “poweroff” Command
The “poweroff” command can also be used to shut down the system as it sends the signal to power down the system processor. The “poweroff” command immediately shuts down the system as soon as you execute the command in the terminal:
Conclusion
Linux users can easily shut down the system from the terminal using the “shutdown” command, which can be used in different ways already discussed in the above guidelines. The users can also apply the “halt” command to stop the CPU functionality and shut down the system. Further, the “poweroff” command can also be used to shut down the Linux system immediately.
About the author
Awais Khan
I’m an Engineer and an academic researcher by profession. My interest for Raspberry Pi, embedded systems and blogging has brought me here to share my knowledge with others.
How to use Linux Shutdown Command with Examples
All Linux users and system administrators need to know how to shut down the entire system safely. There are several options to do so, including scheduling a shutdown at a specific time, shutting down immediately, broadcasting a unique message, and so on.
In this tutorial, learn how to use the Linux shutdown command with examples.
shutdown Command Syntax
Before going into specific ways to shut down your Linux system, you should understand the basic syntax of the shutdown command:
shutdown [options] [time] [message]- [options] define whether you want to halt, power-off, or reboot the machine.
- [time] specifies when you want the shutdown to perform.
- [message] adds a message that announces the shutdown.
Note: If you need to reboot instead of shut down the system, refer to How To Restart Or Reboot Linux Server From The Command Line.
How to Use the shutdown Command
To use the shutdown command on Linux systems, a root user or a user with sudo privileges is required.
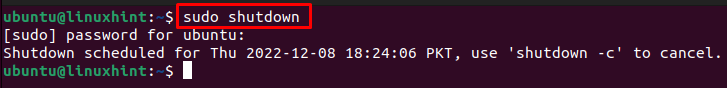
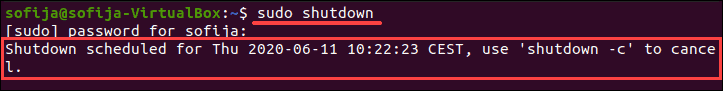
If you use the command without additional arguments, running sudo shutdown in a terminal window executes the shutdown in 60 seconds.
In the image below, see the output received after running the shutdown command.
Shutdown With All Parameters
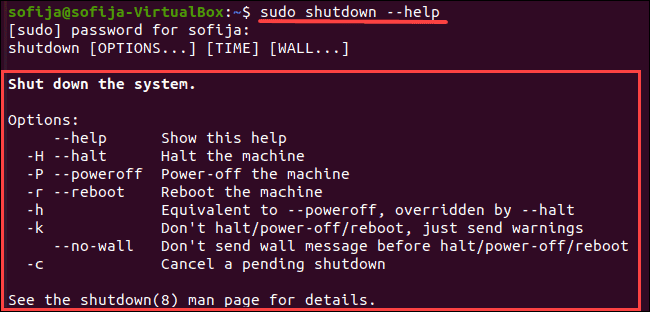
To view all parameters when shutting down the Linux system, use the following command:
The output displays a list of shutdown parameters, as well as a description for each.
How to Shut Down the System at a Specific Time
To schedule a shutdown, add the [time] argument and specify when you want it to take place. There are two ways to shut down the system at a specific time – using the absolute or relative time format.
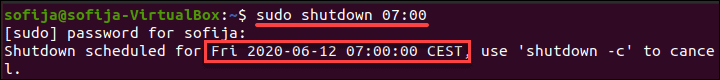
The absolute time follows the format hh:mm and allows you to schedule a shutdown at a specified time. The command follows the syntax:
For example, to require a shutdown at 7 AM in the morning, the command is:
Alternatively, use the relative format ( +m ) and schedule a shutdown in a defined number of minutes from the time you run the command. In that case, the command syntax is:
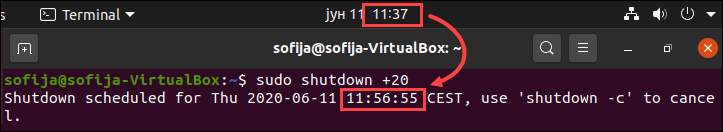
To shut down the system in 20 minutes, run:
How to Shut Down the System Immediately
As previously mentioned, running the shutdown command without any arguments prompts the system to shut down a minute after running the command. However, if you require an immediate shutdown, use:
Another option would be to schedule a shutdown using the relative time format with the value 0, as in the command below:
How to Broadcast a Custom Message
Once you schedule a system shutdown, all users within the system receive a message notifying them of the shutdown. To add a custom message to the shutdown notification to inform the users what is about to take place.
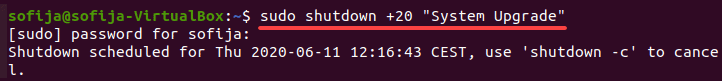
You can add a [message] only if the command also includes the [time] attribute:
sudo shutdown [time] "[message]"For instance, to shut down the system in 20 minutes and broadcast the message System Upgrade, run:
sudo shutdown +20 "System Upgrade"Note: Another way to broadcast messages to users in Linux is via the wall command.
How to Cancel a Scheduled Shutdown
To cancel a scheduled shutdown, use the command:
You can also add a message to notify users that the shutdown is canceled. To do so, add the [message] option (within quotations) to the command above. For example:
sudo shutdown -c "Canceling System Upgrade"This article includes all the basic shutdown commands every Linux user should know. Utilizing this command is a safe way to shut down your system. Also, it is a useful method of informing all users about scheduled shutdowns.
Sofija Simic is an experienced Technical Writer. Alongside her educational background in teaching and writing, she has had a lifelong passion for information technology. She is committed to unscrambling confusing IT concepts and streamlining intricate software installations.
In most modern Linux operating systems, managing a service is quite simple when it comes to basic commands.
A list of all the important Linux commands in one place. Find the command you need, whenever you need it or.
Vim allows you to delete entire lines, words or characters using various Vim commands. Learn the most.
Use the command line interface to display directory size and for display disk space. This guide will help you.