- About time synchronisation
- How time synchronisation works
- About timesyncd
- About timedatectl
- Further reading
- Commands to Sync Time with NTP Server in Linux
- What is NTP
- How to Enable NTP Synchronization on Linux
- How to Enable NTP for Linux Distributions without “systemd”
- Настройка даты и времени в Linux
- Узнать текущее системное время
- Узнать текущее время BIOS
- Исправить текущее время
- Синхронизация с ntp
- Заставить систему синхронизовать время с ntp
About time synchronisation
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for synchronising time over a network. Basically, a client requests the current time from a server, and uses it to set its own clock.
Behind this simple description, there is a lot of complexity. There are three tiers of NTP servers; tier one NTP servers are connected to atomic clocks, while tier two and tier three three servers spread the load of actually handling requests across the Internet.
The client software is also a lot more complex than you might expect. It must factor in communication delays and adjust the time in a way that does not upset all the other processes that run on the server. Luckily, all that complexity is hidden from you!
By default, Ubuntu uses timedatectl / timesyncd to synchronise time, and they are available by default. See our guide If you would like to know how to configure timedatectl and timesyncd .
Users can also optionally use chrony to serve NTP.
How time synchronisation works
Since Ubuntu 16.04, timedatectl / timesyncd (which are part of systemd ) replace most of ntpdate / ntp .
About timesyncd
timesyncd replaces not only ntpdate , but also the client portion of chrony (formerly ntpd ). So, on top of the one-shot action that ntpdate provided on boot and network activation, timesyncd now regularly checks and keeps your local time in sync. It also stores time updates locally, so that after reboots the time monotonically advances (if applicable).
About timedatectl
If chrony is installed, timedatectl steps back to let chrony handle timekeeping. This ensures that no two time-syncing services can conflict with each other.
ntpdate is now considered deprecated in favor of timedatectl (or chrony ) and is no longer installed by default. timesyncd will generally keep your time in sync, and chrony will help with more complex cases. But if you had one of a few known special ntpdate use cases, consider the following:
- If you require a one-shot sync, use: chronyd -q
- If you require a one-shot time check (without setting the time), use: chronyd -Q
While use of ntpd is no longer recommended, this also still applies to ntpd being installed to retain any previous behaviour/config that you had through an upgrade. However, it also implies that on an upgrade from a former release, ntp / ntpdate might still be installed and therefore renders the new systemd -based services disabled.
Further reading
- ntp.org: home of the Network Time Protocol project
- pool.ntp.org: project of virtual cluster of timeservers
- Freedesktop.org info on timedatectl
- Freedesktop.org info on systemd-timesyncd service
- Chrony FAQ
- Feeding chrony from GPSD
- Also see the Ubuntu Time wiki page for more information.
Commands to Sync Time with NTP Server in Linux
For many people, computer clocks in your devices, network machines, and servers are generally accurate. But that’s not true! These clocks are manually maintained and backed by batteries which over time drift the clock, especially in the older machines.
So why is accurate time so important? Having exact time on your machine is quite significant because of several reasons. Many aspects of your computer activity are linked with time. Perfectly synched time is crucial for tracking security-related issues; troubleshooting can become quite difficult if the timestamps in log files are incorrect. Even for financial services, keeping accurate time is critical.
Many companies solve time-related issues by connecting their networks with NTP. So what is NTP? Let’s dig into it first:
What is NTP
The full form of NTP is “Network Time Protocol”, which has been one of the most authentic ways to synchronize the clock over a network. If your system uses NTP, you don’t need to check and set your time manually. It automatically updates the clock every time the device reboots. It is an extremely accurate way to update the clock of your device. Since the internet is everywhere, NTP is being used by every modern computer.
How to Enable NTP Synchronization on Linux
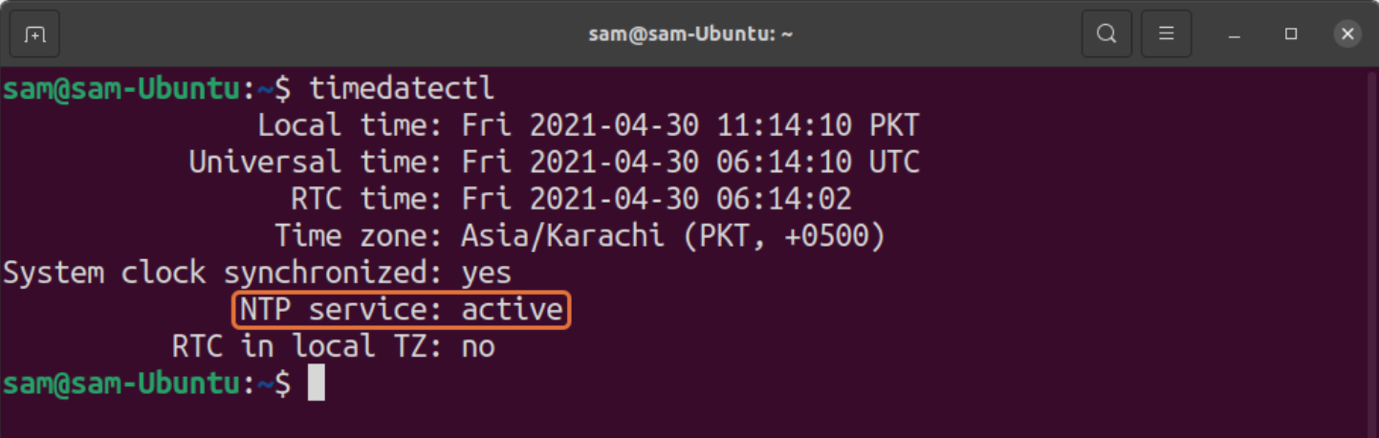
Most of the Linux distributions are using “systemd”, which comes with NTP for clock synchronization. To verify this, use the command given below:
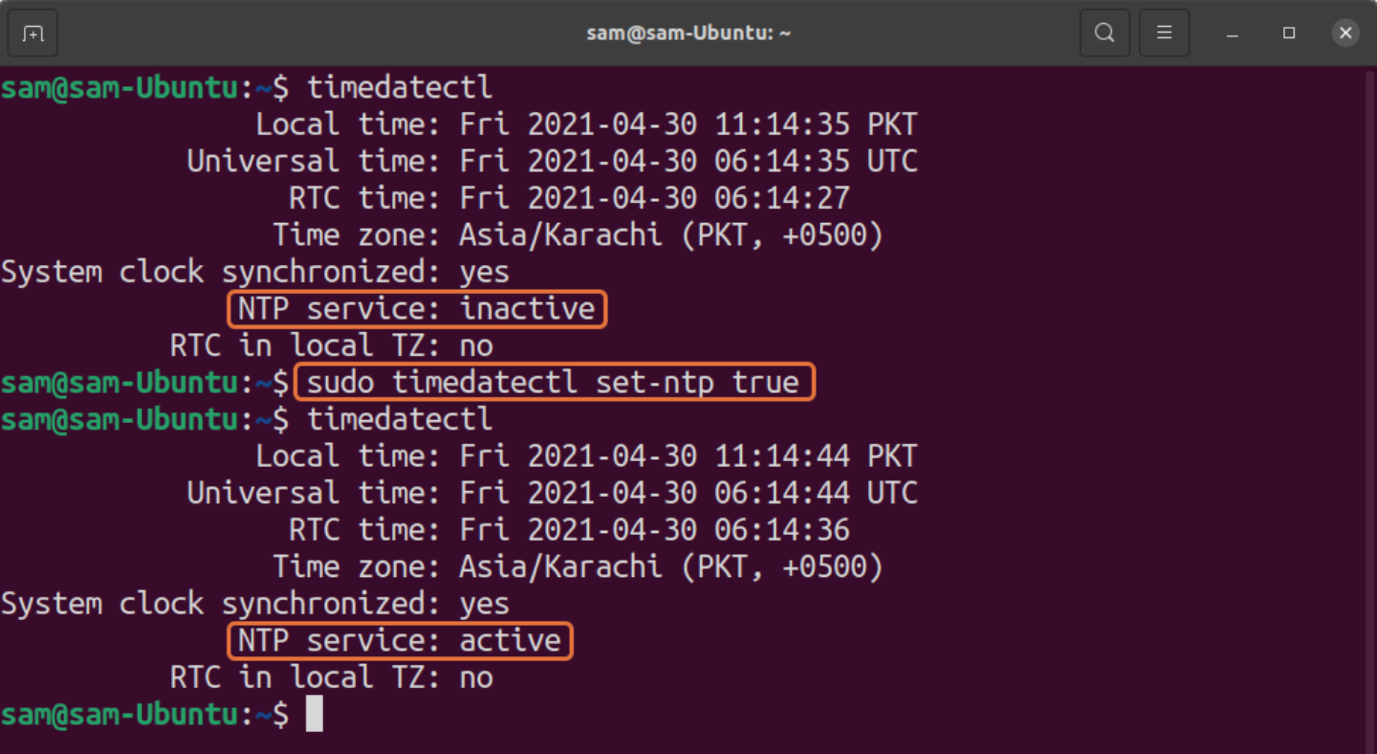
It indicates that NTP is active. If, for some reasons, it is not active, then use the below-mentioned command to enable it:
How to Enable NTP for Linux Distributions without “systemd”
But what if your distribution does not come with “systemd”? Well, in that case, you can install NTP.
Настройка даты и времени в Linux
При работе в сети синхронизация времени и даты это важный фактор увеличивающий стабильность и безопасность работы всех систем.
В этой статье вы узнаете как настраивать дату и время вручную. И, что более важно — как синхронизировать их с ntp сервером.
Узнать текущее системное время
Узнать текущее системное время можно командой date
Узнать текущее время BIOS
Узнать текущее системное время BIOS можно командой hwclock
date и hwclock могут показывать совершенно разное время
Исправить текущее время
Сначала нужно задать время командой date
Также можно вводить «date MMDDhhmmCCYY» без секунд, тогда секунды выставляются на ноль.
После выполнения date нужно внести новое установленное время в BIOS:
Теперь осталось только проверить сохранились ли изменения
Синхронизация с ntp
Проверьте установлен ли ntp командой
Если ntp не установлен выполните
Проверьте запускается ли ntpd автоматически командой
systemctl list-unit-files | grep ntpd.s
Если ntpd неактивен (disabled) выполните
systemctl start ntpd
systemctl enable ntpd
Проверить добавлен ли сервис ntp в зону public в firewall можно командой
sudo firewall-cmd —get-services | grep ntp
Если ещё не добавлен, то чтобы разрешить UDP траффик от ntp выполните
firewall-cmd —permanent —add-service=ntp
firewall-cmd —reload
Отредактируйте файл ntp.conf с настройками сервера
Найдите свою временную зону на сайте www.ntppool.org
Я нашёл зону Helsinki и добавляю строки
server 0.fi.pool.ntp.org server 1.fi.pool.ntp.org server 2.fi.pool.ntp.org server 3.fi.pool.ntp.org
Теперь нужно перезапустить ntpd
Проверить откуда берётся время можно командой
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter ============================================================================== time.cloudflare 10.79.8.177 3 u 14 64 7 3.987 -0.366 0.016 37.228.129.2 193.66.253.94 2 u 16 64 7 5.301 -1.639 1.908 ivanova.ganneff 237.17.204.95 2 u 13 64 7 5.296 3.850 0.266 ntp23.kashra-se 192.168.100.15 2 u 12 64 5 32.935 -2.213 0.192
Выставить время BIOS по только что полученному времени можно командой
Заставить систему синхронизовать время с ntp
Вместо 0.fi.pool.ntp.org поставьте нужный вам сервер