- CentOS Linux 7.2 и HP Array Config Utility (ACU) для управления устаревшими контроллерами HP Smart Array
- DESCRIPTION
- Options
- Supported hardware
- Configuration details
- FILES
- Device nodes
- HPSA-specific host attribute files in /sys
- HPSA-specific disk attribute files in /sys
- Supported ioctl() operations
- SEE ALSO
- HPE — hpssacli для работы с RAID Smart Array в Linux
- Список полезных команд
CentOS Linux 7.2 и HP Array Config Utility (ACU) для управления устаревшими контроллерами HP Smart Array
Ранее я рассматривал пример развёртывания набора утилит HP System Management Tools на сервере HP ProLiant DL360 G5 с CentOS Linux 7.2. В составе этого набора упоминалась и утилита HPE Smart Storage Administrator (SSA), позволяющая управлять контроллерами семейства HP Smart Array. Однако если с помощью SSA мы захотим управлять устаревшими контроллерами Smart Array, то можно столкнуться с фактом того, что SSA не увидит эти контроллеры. Например в моём случае, установленный в сервер SCSI U320 контроллер HP Smart Array 6400 попросту не отображается в интерфейсе SSA.
В такой ситуации поможет установка старой утилиты HP Array Configuration Utility (ACU). Последний раз эта утилита была обновлена в 2013 году и на текущий момент она имеет версию 9.40.12.0. Вообще, чтобы найти ссылки на актуальные версии SSA, ACU и других утилит управления и диагностики контроллеров HP Smart Array для разных операционных систем, можно воспользоваться статьей: HPE Smart Array Controllers — Array Configuration, Diagnostic, Storage Administrator and SmartSSD Wear Gauge Utility .
В нашем случае, для возможности управления контроллером SA6400 на CentOS Linux 7.2, можно загрузить и установить 2 инструмента:
Скачиваем и устанавливаем соответствующие пакеты (ссылку указаны на текущую версию):
# wget https://downloads.hpe.com/pub/softlib2/software1/pubsw-linux/p2141321215/v80068/cpqacuxe-9.40-12.0.x86_64.rpm -P ~/HP/ # wget https://downloads.hpe.com/pub/softlib2/software1/pubsw-linux/p1257348637/v80070/hpacucli-9.40-12.0.x86_64.rpm -P ~/HP/ # yum install ~/HP/cpqacuxe-9.40-12.0.x86_64.rpm # yum install ~/HP/hpacucli-9.40-12.0.x86_64.rpm После установки нам станет доступна консольная утилита управления hpacucli, запустив которую, мы сможем удостовериться в том, что теперь нам доступно управление нашим устаревшим контроллером SA6400 и доступна информация о состоянии дисковых полок MSA20 подключённых к этому контроллеру.
Что же касается веб-утилиты HP Array Configuration Utility, то стоит отметить тот факт, что после установки по умолчанию веб-приложение ACU не запущено, так как по сути своей оно не носит характер инструмента постоянного использования, да и в целях дополнительной безопасности это более правильный вариант. Поэтому, в случае необходимости доступа к ACU через веб-интерфейс HP System Management Homepage (SMH), запускать его нужно отдельно с последующим перезапуском службы SMH — hpsmhd:
# /opt/compaq/cpqacuxe/init.d/cpqacuxed start # service hpsmhd restart
После этого в веб-интерфейсе SMH в разделе Storage появится соответствующая ссылка :
При переходе по этой ссылке будет открыто отдельное окно веб-браузера, где ACU предоставит нам функции управления Smart Array.
Соответственно, после того мы поработали с ACU через веб-интерфейс, можно выключить функции удалённого доступа к ACU командами:
# /opt/compaq/cpqacuxe/init.d/cpqacuxed stop # service hpsmhd restart После этого ссылка на ACU из веб-интерфейса SMH исчезнет.
Если же у вас, исходя из каких-то соображений, есть желание сделать так, чтобы веб-приложение ACU всегда было доступно, то есть загружалось вместе с SMH при старте системы, то можно воспользоваться советом, который написан в тестовом файле /opt/compaq/cpqacuxe/init.d/README.cpqacuxed.txt :
To have ACU start at boot time, the file /opt/compaq/cpqacuxe/init.d/cpqacuxed needs to be copied to directory for system start-up scripts - typically it is the /etc/init.d directory. Enter this command: # cp /opt/compaq/cpqacuxe/init.d/cpqacuxed /etc/init.d By default, ALL runlevels are disabled (turned off). The chkconfig command should be used to turn it on for the specific runlevels you want cpqacuxed to be turned on. For example: # chkconfig --levels 345 cpqacuxed on Также не забываем про то, что для удалённого доступа к функциям ACU через к веб-интерфейс HP System Management Homepage на сервере нужно настроить разрешающее правило брандмауэра для входящего трафика (по умолчанию используется HTTPS на порту TCP 2381). Пример того, как это сделать в CentOS также рассматривался ранее .
DESCRIPTION
hpsa is a SCSI driver for HP Smart Array RAID controllers.
Options
hpsa_allow_any=1: This option allows the driver to attempt to operate on any HP Smart Array hardware RAID controller, even if it is not explicitly known to the driver. This allows newer hardware to work with older drivers. Typically this is used to allow installation of operating systems from media that predates the RAID controller, though it may also be used to enable hpsa to drive older controllers that would normally be handled by the cciss(4) driver. These older boards have not been tested and are not supported with hpsa, and cciss(4) should still be used for these.
Supported hardware
The hpsa driver supports the following Smart Array boards:
Smart Array P700M
Smart Array P212
Smart Array P410
Smart Array P410i
Smart Array P411
Smart Array P812
Smart Array P712m
Smart Array P711m
StorageWorks P1210m
Since Linux 4.14, the following Smart Array boards are also supported:
Smart Array 5300
Smart Array 5312
Smart Array 532
Smart Array 5i
Smart Array 6400
Smart Array 6400 EM
Smart Array 641
Smart Array 642
Smart Array 6i
Smart Array E200
Smart Array E200i
Smart Array E200i
Smart Array E200i
Smart Array E200i
Smart Array E500
Smart Array P400
Smart Array P400i
Smart Array P600
Smart Array P700m
Smart Array P800
Configuration details
To configure HP Smart Array controllers, use the HP Array Configuration Utility (either hpacuxe(8) or hpacucli(8)) or the Offline ROM-based Configuration Utility (ORCA) run from the Smart Array’s option ROM at boot time.
FILES
Device nodes
Logical drives are accessed via the SCSI disk driver (sd(4)), tape drives via the SCSI tape driver (st(4)), and the RAID controller via the SCSI generic driver (sg(4)), with device nodes named /dev/sd*, /dev/st*, and /dev/sg*, respectively.
HPSA-specific host attribute files in /sys
/sys/class/scsi_host/host*/rescan This is a write-only attribute. Writing to this attribute will cause the driver to scan for new, changed, or removed devices (e.g., hot-plugged tape drives, or newly configured or deleted logical drives, etc.) and notify the SCSI midlayer of any changes detected. Normally a rescan is triggered automatically by HP’s Array Configuration Utility (either the GUI or the command-line variety); thus, for logical drive changes, the user should not normally have to use this attribute. This attribute may be useful when hot plugging devices like tape drives, or entire storage boxes containing preconfigured logical drives. /sys/class/scsi_host/host*/firmware_revision This attribute contains the firmware version of the Smart Array. For example:
# cd /sys/class/scsi_host/host4 # cat firmware_revision 7.14
HPSA-specific disk attribute files in /sys
/sys/class/scsi_disk/c:b:t:l/device/unique_id This attribute contains a 32 hex-digit unique ID for each logical drive. For example:
# cd /sys/class/scsi_disk/4:0:0:0/device # cat unique_id 600508B1001044395355323037570F77
/sys/class/scsi_disk/c:b:t:l/device/raid_level This attribute contains the RAID level of each logical drive. For example:
# cd /sys/class/scsi_disk/4:0:0:0/device # cat raid_level RAID 0
/sys/class/scsi_disk/c:b:t:l/device/lunid This attribute contains the 16 hex-digit (8 byte) LUN ID by which a logical drive or physical device can be addressed. c:b:t:l are the controller, bus, target, and lun of the device.
# cd /sys/class/scsi_disk/4:0:0:0/device # cat lunid 0x0000004000000000
Supported ioctl() operations
For compatibility with applications written for the cciss(4) driver, many, but not all of the ioctls supported by the cciss(4) driver are also supported by the hpsa driver. The data structures used by these ioctls are described in the Linux kernel source file include/linux/cciss_ioctl.h.
CCISS_DEREGDISK, CCISS_REGNEWDISK, CCISS_REGNEWD These three ioctls all do exactly the same thing, which is to cause the driver to rescan for new devices. This does exactly the same thing as writing to the hpsa-specific host «rescan» attribute. CCISS_GETPCIINFO Returns PCI domain, bus, device, and function and «board ID» (PCI subsystem ID). CCISS_GETDRIVVER Returns driver version in three bytes encoded as:
(major_version (subminor_version)
CCISS_PASSTHRU, CCISS_BIG_PASSTHRU Allows «BMIC» and «CISS» commands to be passed through to the Smart Array. These are used extensively by the HP Array Configuration Utility, SNMP storage agents, and so on. See cciss_vol_status at http://cciss.sf.net for some examples.
SEE ALSO
http://cciss.sf.net, and Documentation/scsi/hpsa.txt and Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci-devices-cciss in the Linux kernel source tree
Package name: core/man-pages Version: 6.04-1 Upstream: https://www.kernel.org/doc/man-pages/ Licenses: GPL, custom Manuals: /listing/core/man-pages/ Table of contents
Powered by archmanweb, using mandoc for the conversion of manual pages.
The website is available under the terms of the GPL-3.0 license, except for the contents of the manual pages, which have their own license specified in the corresponding Arch Linux package.
HPE — hpssacli для работы с RAID Smart Array в Linux
На сервере HPE ProLiant сдох диск в RAID массиве. Массив аппаратный на базе контроллера Smart Array. Вместо неисправного диска был использован SPARE диск. iLO отображает статус Degraded (Rebuilding). Массив перестраивается, но процент перестроения не указан. Можно загрузить Smart Storage Administrator и посмотреть процент выполнения там. Но сервер выключать нельзя.
На помощь приходит утилита hpssacli для работы с RAID массивами Smart Array в Linux. Мне уже приходилось раньше работать с данной утилитой из ОС ESXi (там она называется ssacli):
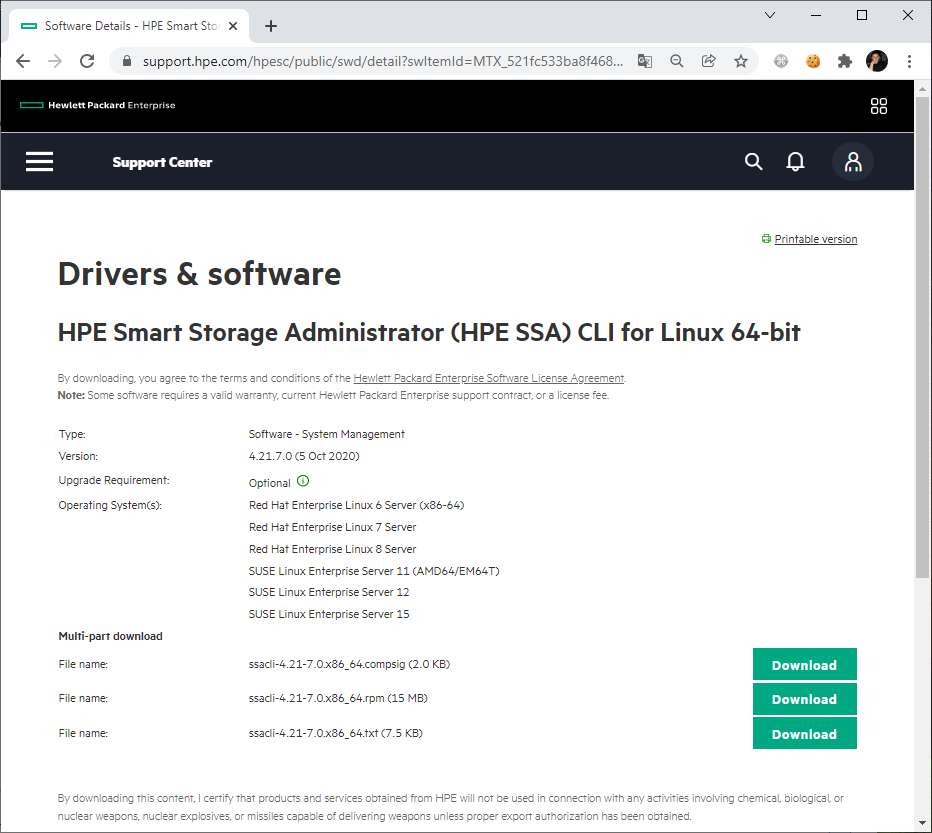
Но теперь у меня другая операционная система. Утилиту нужно устанавливать вручную:
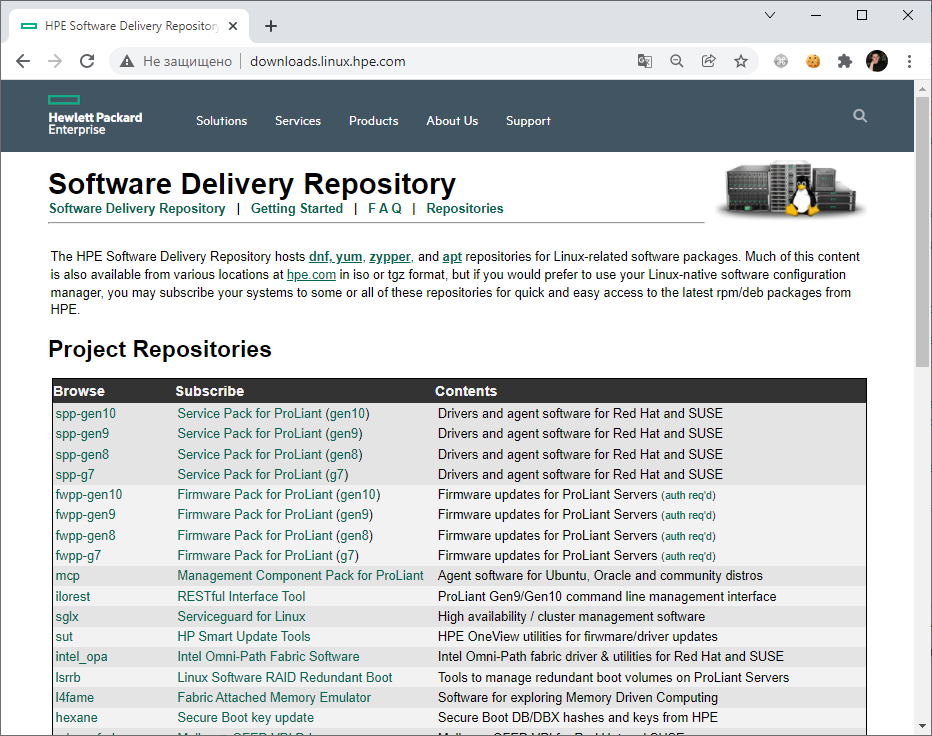
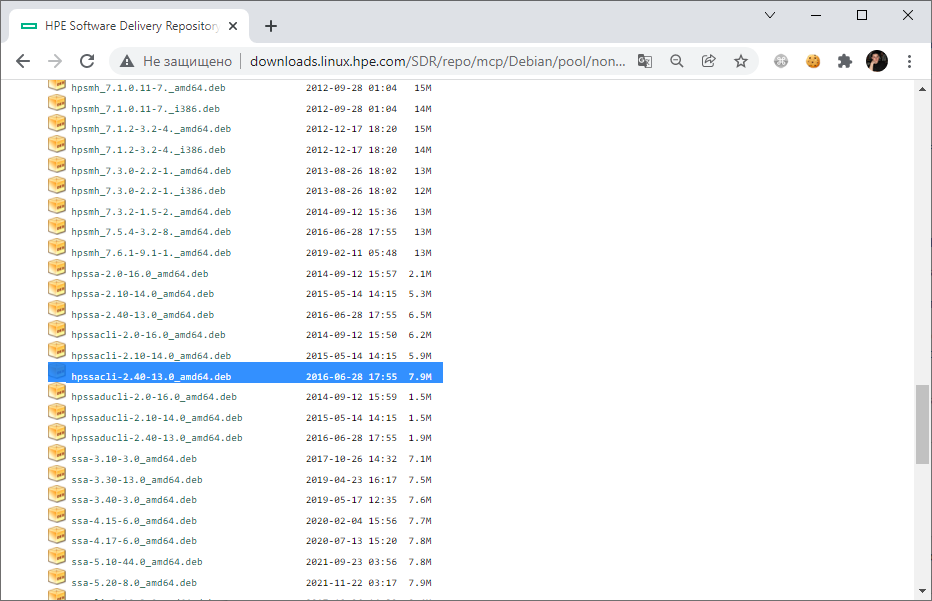
Доступен пакет RPM, казалось бы, ставим и пользуемся. Однако, у меня Debian, как быть? Пакеты для других типов Linux можно найти здесь:
Интересует раздел mpc — Management Component Pack for Proliant.
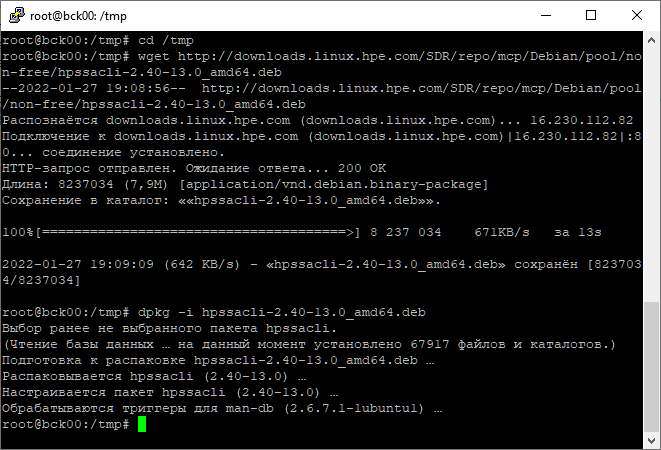
Вот и hpssacli. Копирую ссылку, качаю и устанавливаю:
cd /tmp wget http://downloads.linux.hpe.com/SDR/repo/mcp/Debian/pool/non-free/hpssacli-2.40-13.0_amd64.deb dpkg -i hpssacli-2.40-13.0_amd64.debПакет hpssacli установлен.
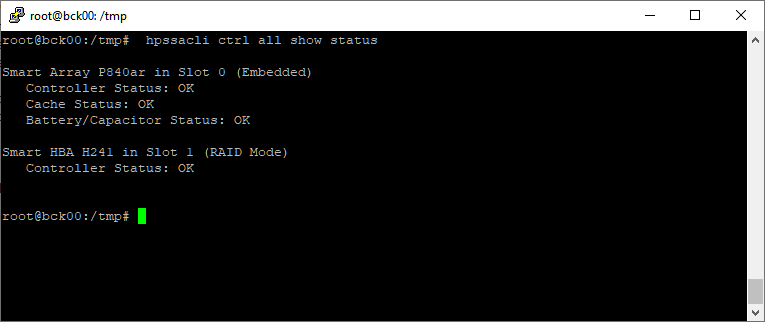
Посмотрим статус контроллеров:
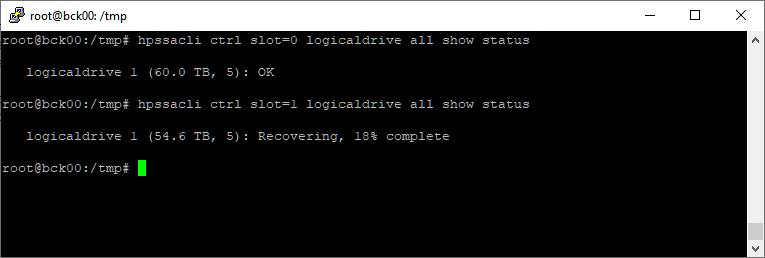
hpssacli ctrl all show statusУзнаем процент перестроения массива:
hpssacli ctrl slot=0 logicaldrive all show status hpssacli ctrl slot=1 logicaldrive all show statusМассив на первом контроллере в порядке, а на втором перестроился на 18%.
Список полезных команд
#Show configuration hpssacli ctrl all show config #Controller status hpssacli ctrl all show status #Show detailed controller information for all controllers hpssacli ctrl all show detail #Show detailed controller information for controller in slot 0 hpssacli ctrl slot=0 show detail #Rescan for New Devices hpssacli rescan #Physical disk status hpssacli ctrl slot=0 pd all show status #Show detailed physical disk information hpssacli ctrl slot=0 pd all show detail #Logical disk status hpssacli ctrl slot=0 ld all show status #View Detailed Logical Drive Status hpssacli ctrl slot=0 ld 2 show #Create New RAID 0 Logical Drive hpssacli ctrl slot=0 create type=ld drives=1I:1:2 raid=0 #Create New RAID 1 Logical Drive hpssacli ctrl slot=0 create type=ld drives=1I:1:1,1I:1:2 raid=1 #Create New RAID 5 Logical Drive hpssacli ctrl slot=0 create type=ld drives=1I:1:1,1I:1:2,2I:1:6,2I:1:7,2I:1:8 raid=5 #Delete Logical Drive hpssacli ctrl slot=0 ld 2 delete #Add New Physical Drive to Logical Volume hpssacli ctrl slot=0 ld 2 add drives=2I:1:6,2I:1:7 #Add Spare Disks hpssacli ctrl slot=0 array all add spares=2I:1:6,2I:1:7 #Enable Drive Write Cache hpssacli ctrl slot=0 modify dwc=enable #Disable Drive Write Cache hpssacli ctrl slot=0 modify dwc=disable #Erase Physical Drive hpssacli ctrl slot=0 pd 2I:1:6 modify erase #Turn on Blink Physical Disk LED hpssacli ctrl slot=0 ld 2 modify led=on #Turn off Blink Physical Disk LED hpssacli ctrl slot=0 ld 2 modify led=off #Modify smart array cache read and write ratio (cacheratio=readratio/writeratio) hpssacli ctrl slot=0 modify cacheratio=100/0 #Enable smart array write cache when no battery is present (No-Battery Write Cache option) hpssacli ctrl slot=0 modify nbwc=enable #Disable smart array cache for certain Logical Volume hpssacli ctrl slot=0 logicaldrive 1 modify arrayaccelerator=disable #Enable smart array cache for certain Logical Volume hpssacli ctrl slot=0 logicaldrive 1 modify arrayaccelerator=enable #Status of all Logical Volumes hpssacli ctrl slot=0 logicaldrive all show status #Enable SSD Smart Path hpssacli ctrl slot=0 array a modify ssdsmartpath=enable #Disable SSD Smart Path hpssacli ctrl slot=0 array a modify ssdsmartpath=disable