- How do I change the computer name?
- 14 Answers 14
- Как изменить Hostname (имя компьютера)
- Просмотр текущего Hostname
- Как изменить Hostname
- Способ 1. Используем команду hostnamectl
- Способ 2. Редактируем файлы /etc/hostname и /etc/hosts
- Проверка результата
- Как временно изменить Hostname
- How to change hostname on Linux
- Change hostname from command line
- Change hostname from command line (init systems)
- Change hostname from command line (hostname command)
- Change hostname from GNOME GUI
- Conclusion
- Related Linux Tutorials:
- NEWSLETTER
- WRITE FOR US
- TAGS
- FEATURED TUTORIALS
- LATEST TUTORIALS
How do I change the computer name?
Try editing /etc/ hosts. gksudo gedit /etc/hosts and replace server-name.belkin by whatever name you desire.
@warren the current consensus is to close by «quality»: meta.stackexchange.com/questions/147643/… Since «quality» is not measurable, I just go by upvotes. 😉 Likely it comes down to which question hit the best newbie Google keywords on the title.
14 Answers 14
You need to edit the computer name in two files:
These will both need administrative access, so run
Replace any instances of the existing computer name with your new one. When complete run
sudo service hostname start The name will also be changed if you restart your computer.
sudo service hostname restart doesn’t work on default install of ubuntu server 14.04 on AWS. I had to do full server restart
On 14.04, I simply ran sudo hostname , and that did the trick. I didn’t notice any immediate change, but when I opened a new terminal, I saw my hostname had indeed changed.
hostnamectl set-hostname on 13.10+ desktop
This is the best way if you have systemd (13.10 onwards) and if cloud-init is not active (see below):
hostnamectl set-hostname 'new-hostname' 18.04 onwards: cloud-init
18.04 Introduced cloud-init which can control setting of the hostname so hostnamectl changes it won’t stick after a reboot if cloud-init is installed. TODO: how to check if it is installed, is it installed by default on the desktop image or just server?
If you want hostnamectl changes to stay after a reboot, then you’ll need to edit the cloud-init config files, disable cloud-init’s hostname set/update module:
sudo sed -i 's/preserve_hostname: false/preserve_hostname: true/' /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg or disable cloud-init entirely:
sudo touch /etc/cloud/cloud-init.disabled I had to add my new-hostname into /etc/hosts else using sudo would cause some error «sudo: unable to resolve host xxxxx»
Working also with Ubuntu 20 LTS as desktop, and only using sudo hostnamectl set-hostname myNewName . After new terminal and after boot (!), the` myNewName`, no problem.
- Edit /etc/hostname , make the name change, save the file.
- You should also make the same changes in /etc/hosts file
- Run sudo service hostname start
As long as you have no application settings depending on the ‘old’ hostname, you should be ok 😉
WARNING: If you do this without changing /etc/hosts accordingly you will be unable to use sudo because your hostname will fail to lookup
You’re right regarding editing the /etc/hosts, i forgot about it (just added it to my answer), though sudo seems to be working fine for me without changing it (i’ve restarted the machine and it still works)
It’s ok, you can do that as hostname is now a service managed from upstart . It’ll do exactly the same thing,restart the service.
Warning: won’t work with Ubuntu 18+ which is running cloud-init by default, which controls hostname on boot.
It is safe to do, you just need to be sure you edit both the system hostname configuration file (/etc/hostname) and the hostname name resolution file (/etc/hosts). From a terminal execute the following:
sudo -s editor /etc/hostname editor /etc/hosts shutdown -ry now Warning: won’t work with Ubuntu 18+ which is running cloud-init by default, which controls hostname on boot.
In addition to editing /etc/hosts and /etc/hostname, various services might have issues with the change as well. Mysql and postfix are installed by default in ubuntu. A broken postfix won’t affect most ubuntu users, since it’s a background email server that isn’t used by much.
sudo editor /etc/postfix/main.cf sudo service postfix restart The default config for mysql doesn’t use hostname, so it will work fine as-is. If you have customized it, edit the files in /etc/mysql/ and restart the service.
You may also want to edit /etc/motd (message of the day), which is shown on virtual terminals and remote logins. That one won’t harm anything though.
Other services that you may have installed that would need fixing are apache, bind9, etc. In each case, find and edit the hostname in their config and restart the service.
Как изменить Hostname (имя компьютера)
Hostname (имя компьютера, имя хоста) задается во время установки системы Linux. Hostname определяет название компьютера и используется преимущественно для идентификации компьютера в сети. Нельзя назначать два одинаковых Hostname для компьютеров в одной сети.
Просмотр текущего Hostname
Чтобы показать текущий Hostname можно использовать команду hostname без параметров:
Также Hostname можно отобразить командой hostnamectl :
Как изменить Hostname
Рассмотрим, как изменить Hostname двумя разными способами.
Способ 1. Используем команду hostnamectl
Во многих systemd-based дистрибутивах (например, в Ubuntu Linux) есть утилита hostnamectl .
Воспользуемся командой hostnamectl , чтобы установить новое значение Hostname равным pingvinus . Используется аргумент set-hostname:
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname pingvinusСпособ 2. Редактируем файлы /etc/hostname и /etc/hosts
Еще один способ изменения Hostname — это ручное редактирование файла /etc/hostname и файла /etc/hosts .
Сначала выполните команду (вместо pingvinus укажите свое значение):
Отредактируем файл /etc/hostname для редактирования в редакторе nano, выполняем команду:
Измените текущее значение в файле на новое. Сохраните изменения и закройте файл. Это можно сделать, нажав Ctrl+C , затем Y и Enter .
Hostname прописывается также в файле /etc/hosts , поэтому нужно изменить его значение в этом файле. Откроем файл:
Найдите строку вида « 127.0.0.1 ваш_hostname » и впишите новое имя хоста. Сохраните изменения и закройте файл.
Проверка результата
Чтобы проверить, изменилось ли значение Hostname, откройте новое окно терминала и введите команду:
Как временно изменить Hostname
Чтобы изменить Hostname в текущей работающей системе Linux, но до первой перезагрузки, можно использовать просто команду hostname , указав ей новое значение имени хоста:
How to change hostname on Linux
The hostname of a Linux system is important because it’s used to identify the device on a network. The hostname is also shown in other prominent places, such as in the terminal prompt. This gives you a constant reminder of which system you’re working with. It’s a real life saver when you’re managing multiple systems through SSH and those command line terminals start to blend together in your mind.
Of course, IP addresses are used when devices need to communicate with each other, but those can change frequently. Hostnames give us a way to know which device we’re interacting with either on the network or physically, without remembering a bunch of numbers that are subject to change. Thus, it’s important that your system bears a hostname which helps you to identify it quickly. For example, “backup-server” is much more informative than “server2.”
In this guide, we’ll show you how to change the hostname on Linux. This can be done via command line or from GUI, and we’ll be showing the methods for both. If you can’t easily identify a system’s purpose from the hostname, it’s time to change it.
In this tutorial you will learn:
| Category | Requirements, Conventions or Software Version Used |
|---|---|
| System | Any Linux distro |
| Software | N/A |
| Other | Privileged access to your Linux system as root or via the sudo command. |
| Conventions | # – requires given linux commands to be executed with root privileges either directly as a root user or by use of sudo command $ – requires given linux commands to be executed as a regular non-privileged user |
Change hostname from command line
The following method will work on systems that use systemd (most of the popular Linux distros today). If your system uses init, we cover a separate method in the next section.
$ hostname linux-server $ hostnamectl Static hostname: linux-server Icon name: computer-vm Chassis: vm Machine ID: e94c741849c848f8baca2ec406f88c41 Boot ID: 55f7533a0cb6448ba677ef30b2104481 Virtualization: oracle Operating System: Ubuntu 20.04.1 LTS Kernel: Linux 5.4.0-42-generic Architecture: x86-64
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname linuxconfig
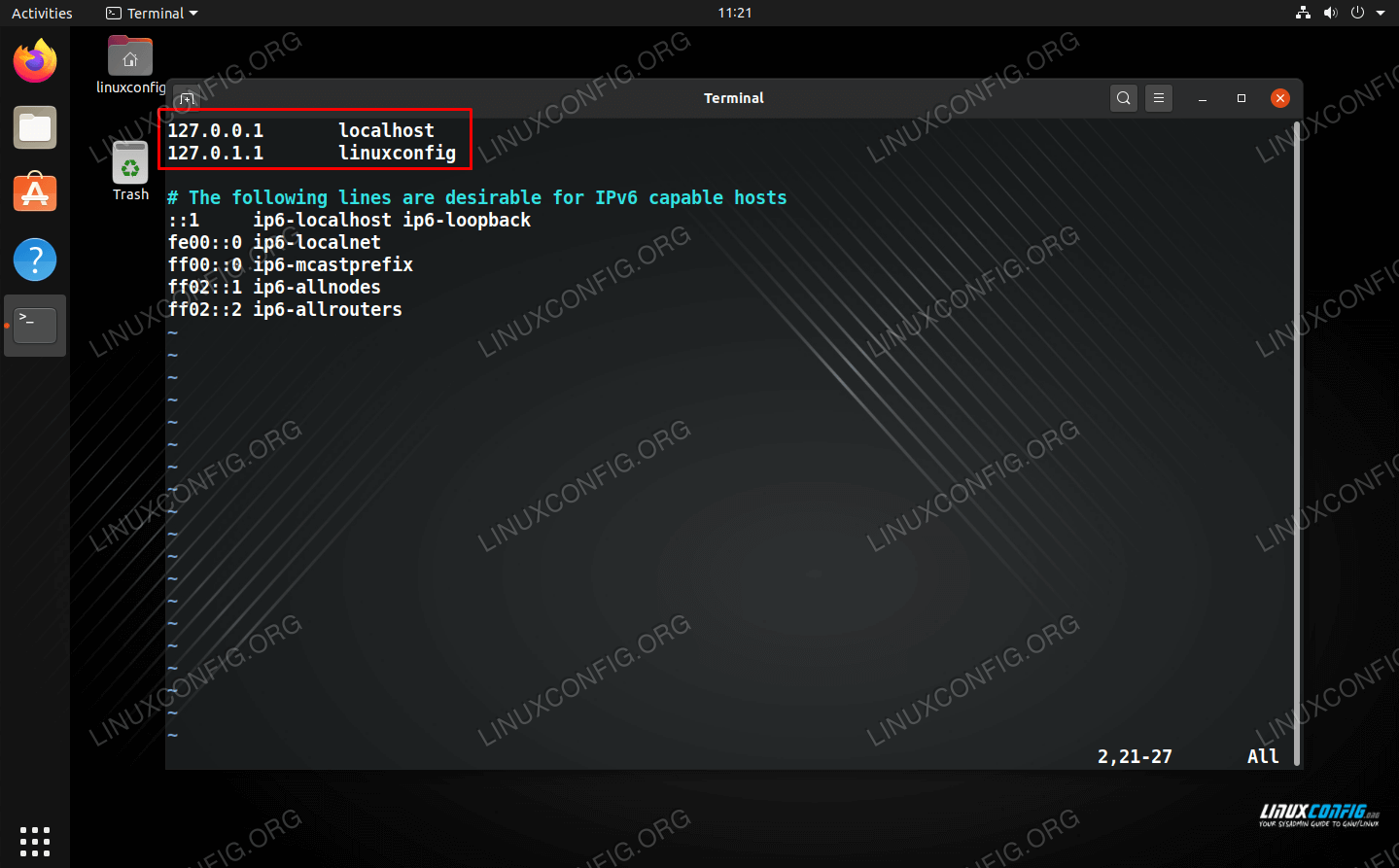
127.0.0.1 localhost 127.0.1.1 linux-server
127.0.0.1 localhost 127.0.1.1 linuxconfig
That’s all there is to it. But there are more command line methods to change the hostname than just this one. We cover more below.
Change hostname from command line (init systems)
An alternative method to the above instructions is to edit the following two files.
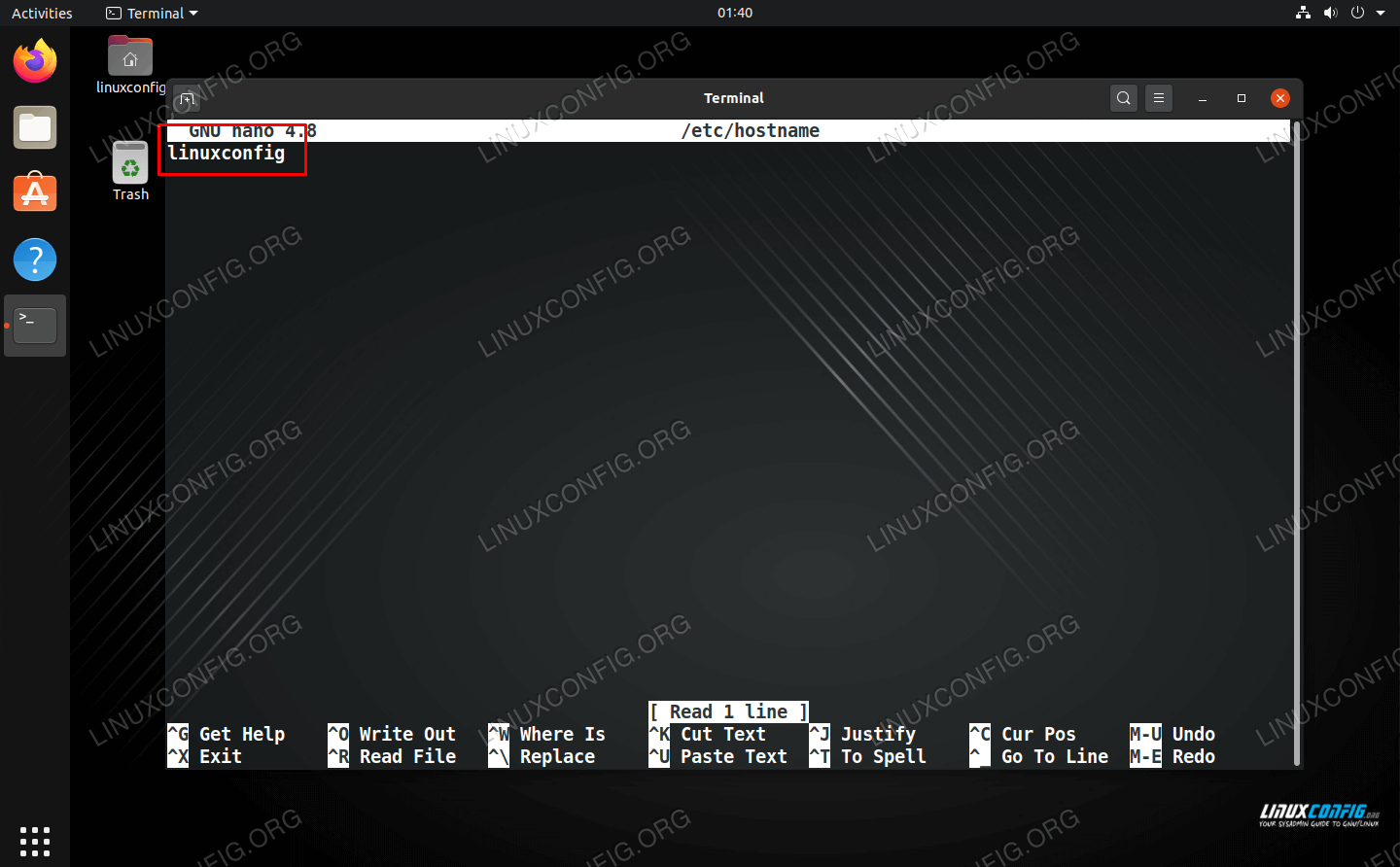
- Open /etc/hostname with nano or your preferred text editor and change the name inside of it.
Change hostname from command line (hostname command)
The last method for changing the hostname from command line is with the hostname command. In most environments, this only temporarily changes the name and it will revert once the system is rebooted. For example, to change the hostname to linuxconfig :
Check the changes by just typing hostname :
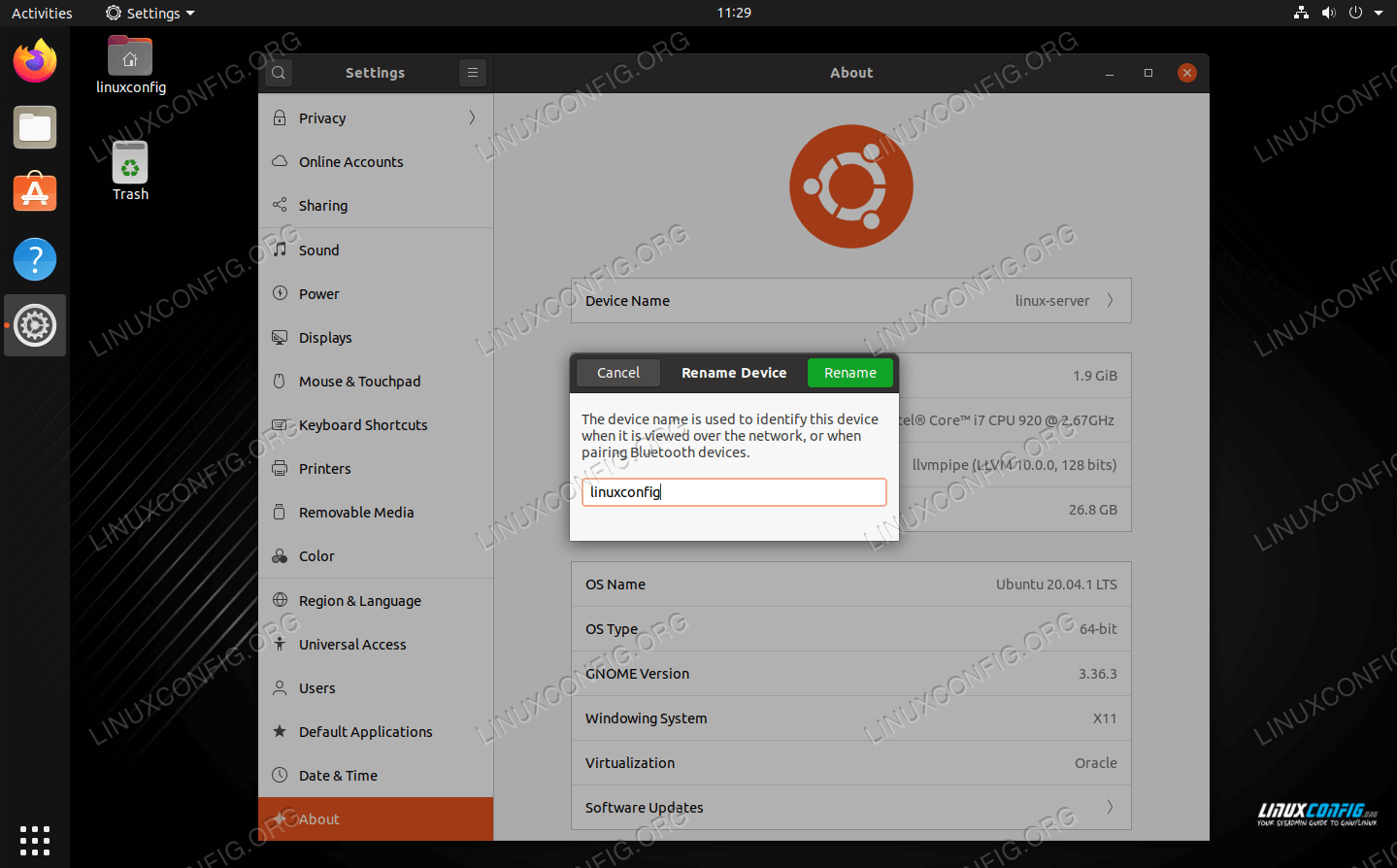
Change hostname from GNOME GUI
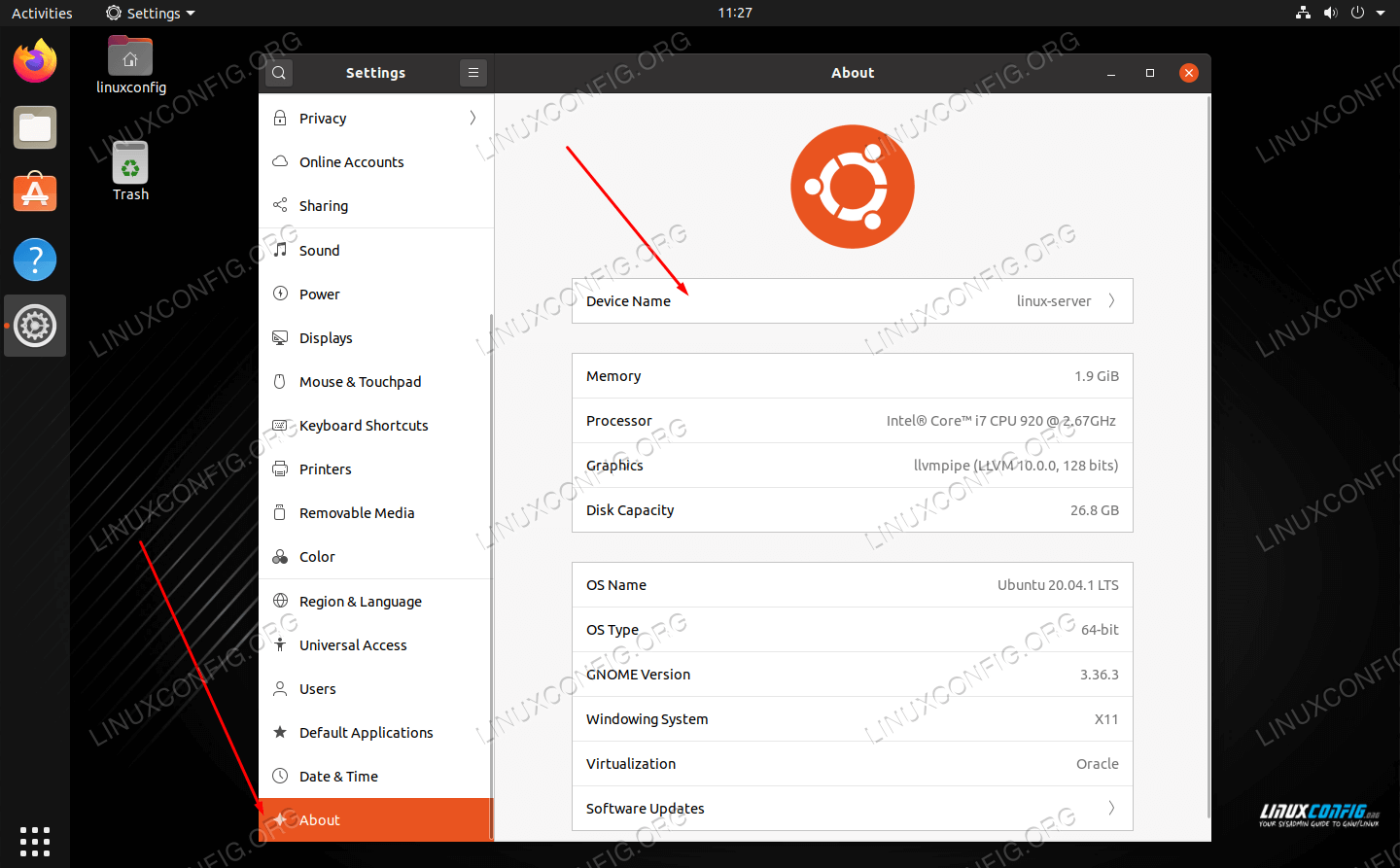
If you’re running the GNOME desktop environment and don’t wish to use the command line method, follow along with the steps below.
Conclusion
In this guide, we saw various methods for changing the hostname of a Linux system via command line and GUI. We also learned about the importance of picking an applicable hostname to assist in the easy identification of a system. Administrators can use these methods to ensure that they have a network of appropriately named devices.
Related Linux Tutorials:
Comments and Discussions
NEWSLETTER
Subscribe to Linux Career Newsletter to receive latest news, jobs, career advice and featured configuration tutorials.
WRITE FOR US
LinuxConfig is looking for a technical writer(s) geared towards GNU/Linux and FLOSS technologies. Your articles will feature various GNU/Linux configuration tutorials and FLOSS technologies used in combination with GNU/Linux operating system.
When writing your articles you will be expected to be able to keep up with a technological advancement regarding the above mentioned technical area of expertise. You will work independently and be able to produce at minimum 2 technical articles a month.
TAGS
FEATURED TUTORIALS
- VIM tutorial for beginners
- How to install the NVIDIA drivers on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa Linux
- Bash Scripting Tutorial for Beginners
- How to check CentOS version
- How to find my IP address on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa Linux
- Ubuntu 20.04 Remote Desktop Access from Windows 10
- Howto mount USB drive in Linux
- How to install missing ifconfig command on Debian Linux
- AMD Radeon Ubuntu 20.04 Driver Installation
- Ubuntu Static IP configuration
- How to use bash array in a shell script
- Linux IP forwarding – How to Disable/Enable
- How to install Tweak Tool on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa Linux
- How to enable/disable firewall on Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic Beaver Linux
- Netplan static IP on Ubuntu configuration
- How to change from default to alternative Python version on Debian Linux
- Set Kali root password and enable root login
- How to Install Adobe Acrobat Reader on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa Linux
- How to install the NVIDIA drivers on Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic Beaver Linux
- How to check NVIDIA driver version on your Linux system
- Nvidia RTX 3080 Ethereum Hashrate and Mining Overclock settings on HiveOS Linux
LATEST TUTORIALS
- Easy Steps to Update Your Raspberry Pi
- Connecting Your Raspberry Pi to Wi-Fi: A How-To
- How to install RealVNC viewer on Linux
- How to check Raspberry Pi RAM size and usage
- How to check Raspberry Pi model
- Understanding UEFI and BIOS in Relation to Linux Nvidia Driver Installation
- How to orchestrate Borg backups with Borgmatic
- How to monitor filesystem events on files and directories on Linux
- Debian USB Firmware Loader Script
- How to install and self host an Ntfy server on Linux
- How to backup your git repositories with gickup
- How to bind an SSH public key to a specific command
- Creating a Bootable USB for Windows 10 and 11 on Linux
- How to list all displays on Linux
- List of QR code generators on Linux
- How to extract text from image
- Linux EOF explained
- How to use xclip on Linux
- List of window managers on Linux
- What is zombie process on Linux