- Linux SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol:
- Installation:
- Configure:
- Start:
- Test:
- Installation:
- How To Install and Use SNMP On Linux Tutorial with Examples?
- What Is SNMP?
- Install SNMP Packages
- Fedora, CentOS, RedHat
- Ubuntu, Debian, Mint, Kali
- Start SNMP Service
- Check SNMP Service
- SNMP Configuration File
- Change Public Community String
- Restart SNMP Service and Reload Configuration
- Get and Display SNMP Attributes/Values with snmpwalk
- How To Install and Use SNMP On Linux Tutorial with Examples? Infographic
Linux SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol:
SNMP or Simple Network Management Protocol, is a technology standard for alert messages (trap), monitoring (get), and configuring (set) network devices. SNMP comes in three varieties: v1, v2 and v3, of which v3 is the only version to be considered secure.
The variables associated with a network device configuration is defined in the Management Information Base, or MIB. The MIB is a collection of information for managing the network element and is comprised of managed objects identified by the Object Identifier (OID). Each OID is unique and identifies a special characteristic of the managed network device. SNMP is built upon a client (SNMP manager) — server (SNMP agent/network device) architecture pattern with a message schema defined by the MIB and sent over UDP port 161 (SNMP agent) and port 162 (SNMP manager). Each of the data values defined by the MIB are associated with an OID identified by a hierarchy of numbers separated by periods.
Installation:
- CentOS/RedHat: sudo yum install net-snmp-utils net-snmp net-snmp-devel
(RPMs also included with CentOS/RHEL 6 and 7 install DVDs) - Ubuntu: sudo apt-get install snmp snmpd snmp-mibs-downloader
Configure:
- System file /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf
This file default restricts access to localhost only. - User file ~/.snmp/snmp.conf
Start:
- CentOS/RedHat:
- sudo systemctl enable snmpd.service
- sudo systemctl start snmpd.service
- sudo systemctl status snmpd.service
snmpd.service - Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Daemon. Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/snmpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-07-02 17:03:02 PDT; 3s ago Main PID: 345 (snmpd) Memory: 6.8M CGroup: /system.slice/snmpd.service └─345 /usr/sbin/snmpd -LS0-6d -f Jul 02 17:03:01 myhostname systemd[1]: Starting Simple Network Management Protocol (. Jul 02 17:03:02 myhostname snmpd[345]: NET-SNMP version 5.7.2 Jul 02 17:03:02 myhostname systemd[1]: Started Simple Network Management Protocol (S. Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
- sudo systemctl enable snmpd.service
- sudo systemctl start snmpd.service
- sudo systemctl status snmpd.service
Test:
- snmpwalk -v 1 localhost -c public .1.3.6.1
- snmpwalk -v 1 localhost -c public system
- Open firewall to everything (if using iptables): sudo iptables -F
or - if using firewald: sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --new-service=snmp
this command will add service to directory /etc/firewalld/services/
snmp 161/tcp # Simple Net Mgmt Proto snmp 161/udp # Simple Net Mgmt Proto snmptrap 162/tcp # SNMPTRAP snmptrap 162/udp snmp-trap # Traps for SNMP cmip-man 163/tcp # ISO mgmt over IP (CMOT)
- RHEL 7: snmpget -v 1 -c public localhost sysDescr.0
SNMPv2-MIB::sysDescr.0 = STRING: Linux myhostname 3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Thu Jul 6 19:56:57 EDT 2017 x86_64
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0 = STRING: "Linux myhostname 4.15.0-70-generic #79-Ubuntu SMP Tue Nov 12 10:36:11 UTC 2019 x86_64"
+--iso(1) | +--org(3) | +--dod(6) | +--internet(1) | +--directory(1) | +--mgmt(2) | | | +--mib-2(1) | | | +--system(1) | | | | | +-- -R-- String sysDescr(1) | | | Textual Convention: DisplayString | | | Size: 0..255 | | +-- -R-- ObjID sysObjectID(2) | | +-- -R-- TimeTicks sysUpTime(3) | | | | | | | +--sysUpTimeInstance(0) | | | | | +-- -RW- String sysContact(4) | | | Textual Convention: DisplayString | | | Size: 0..255 . .
:HOST-RESOURCES-MIB:HOST-RESOURCES-TYPES:UCD-DISKIO-MIB:TCP-MIB:UDP-MIB:MTA-MIB:NETWORK-SERVICES-MIB:SCTP-MIB:RMON-MIB:EtherLike-MIB:LM-SENSORS-MIB:SNMPv2-MIB:IF-MIB:IP-MIB:NOTIFICATION-LOG-MIB:DISMAN-EVENT-MIB:DISMAN-SCHEDULE-MIB:UCD-SNMP-MIB:UCD-DEMO-MIB:SNMP-TARGET-MIB:NET-SNMP-AGENT-MIB:SNMP-MPD-MIB:SNMP-USER-BASED-SM-MIB:SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB:SNMP-VIEW-BASED-ACM-MIB:SNMP-COMMUNITY-MIB:IPV6-ICMP-MIB:IPV6-MIB:IPV6-TCP-MIB:IPV6-UDP-MIB:IP-FORWARD-MIB:NET-SNMP-PASS-MIB:NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB:UCD-DLMOD-MIB:SNMP-NOTIFICATION-MIB:SNMPv2-TM:NET-SNMP-VACM-MIB /home/userx/.snmp/mibs:/usr/share/snmp/mibs
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0 = Timeticks: (1310658) 3:38:26.58
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.3 = STRING: "0.10"
Command Description snmpcmd options and behavior common to most of the Net-SNMP command-line tools snmpwalk retrieve a subtree of management values using SNMP GETNEXT requests snmpget communicates with a network entity using SNMP GET requests snmpset communicates with a network entity using SNMP SET requests snmptrap sends an SNMP notification to a manager (also snmpinform) snmpgetnext communicates with a network entity using SNMP GETNEXT requests to get the next variable that is lexicographically «next» in the remote entity’s MIB snmptable retrieve an SNMP table and display it in tabular form snmpdelta Monitor delta differences in SNMP Counter values snmptest flexible SNMP application that can monitor and manage information on a network entity snmpdf display disk space usage on a network entity via SNMP snmpusm creates and maintains SNMPv3 users on a network entity snmpstatus retrieves a fixed set of management information from a network entity snmpnetstat display networking status and configuration information from a network entity via SNMP snmpbulkget SNMP application that uses the SNMP GETBULK request to query a network entity efficiently for information snmpbulkwalk retrieve a subtree of management values using SNMP GETBULK requests snmp.conf configuration files for the Net-SNMP applications SNMP Variables Format of specifying variable names to SNMP tools The Object Identifiers (OID)s are used to identify a specific characteristic of a managed device.
- Scalar: managed object with a single instance (a single key to a key-value pair)
- Tabular: multiple data instances such as the rows of a table (e.g. CPU with multiple cores each with its’ own specific charateristics)
SNMP uses ASN.1 (Abstract Syntax Notation One) to define the data types used to build an SNMP message and uses Basic Encoding Rules (BER) to define the data types.
- Primitive Type: type/length(bytes)/data
- integer
- octet (byte, char)
- string
- null
- boolean
- OID
- sequence
- SNMP PDU (Protocol Data Unit) — complex data types specific to SNMP
Installation:
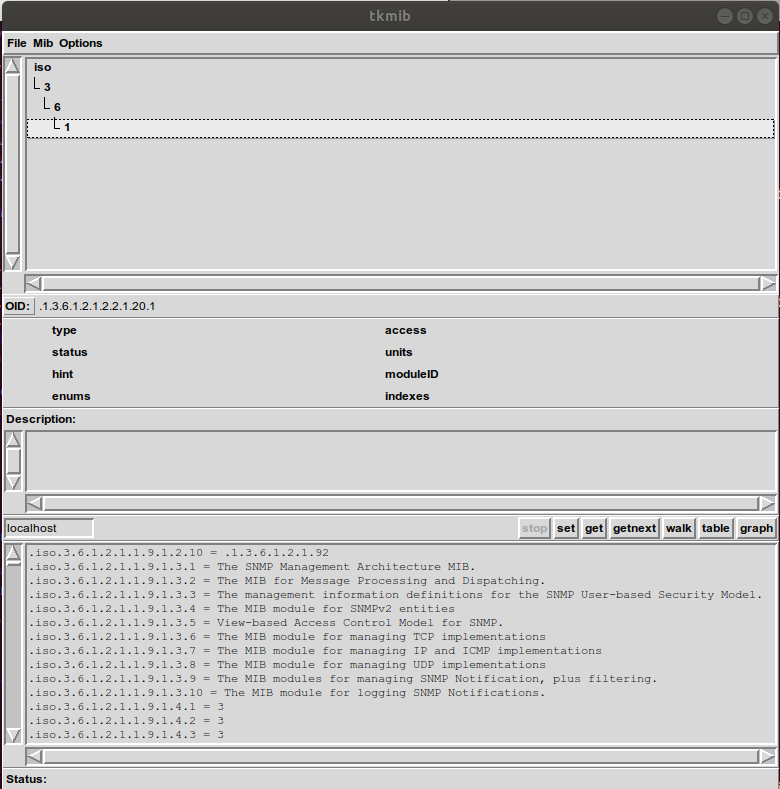
Select the «walk» button to traverse the OIDs.
Acronym Description ASN.1 Abstract Syntax Notation One BER Basic Encoding Rules MIB Management Information Base (data schema for an SNMP device and its variables) OID Object Identifiers (period separated number notation used to define the SNMP device variables) PDU Protocol Data Unit (SNMP packet construction definition) SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol How To Install and Use SNMP On Linux Tutorial with Examples?
Today we will look SNMP in Linux operating systems. Simple network management protocol named SNMP is designed for getting info and setting configuration in its entities. These entities may be a switch, router, pc, cabinet, printer, etc. Snmp was very popular in the 2000s. Today it is popular too but used for information gathering.
What Is SNMP?
SNMP is a standard which is mainly created to manage and monitor the network and network-connected devices. But during time the monitoring functionalities became popular and management functionalities are not used. SNMP has an index database named Management Information Base (MIB) used for data classification. Vendors generally publish their MIBs. For example, the Cisco MIB can be found http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml . The system that gathers SNMP info generally named Network management station. The systems that provide info or apply settings about yourself named Managed device. An agent is a tool that runs on a Managed Device and responsible for SNMP. SNMP works with UDP, ip, TCP, UNIX, udp6, tcp6
Install SNMP Packages
Fedora, CentOS, RedHat
In rpm-based distributions like Fedora, CentOS, Red Hat we will install the packages named net-snmp-utils and net-snmp like below.
$ sudo yum install net-snmp-utils net-snmp
Ubuntu, Debian, Mint, Kali
Firstly we install SNMP daemon, library, and tool with this command in fedora. Also, we can install it Debian based distributions like Ubuntu from official repositories.
Start SNMP Service
After installing check the status of SNMP service named snmpd. As shown it is not started so we start it and check again the status
$ sudo systemctl start snmpd
Check SNMP Service
We can check the SNMP daemon or service status with the following command.
$ sudo systemctl status snmpd
SNMP Configuration File
SNMP daemon configuration file is stored under /etc/snmp with the name snmpd.conf .
$ sudo nano /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf
Change Public Community String
We will change the public community string with ismailbaydan in this line.
com2sec notConfigUser default ismailbaydan
Restart SNMP Service and Reload Configuration
After changing the SNMP configuration we have to reload the SNMP service to take effect new configuration. We will restart the snmpd daemon with the following command.
$ sudo systemctl restart snmpd
Get and Display SNMP Attributes/Values with snmpwalk
Here we run snmpwalk for system OUID with new password and SNMP community version 2. So we get all value in the system OUID and in its sub-branches.
$ snmpwalk -v2c -c ismailbaydan localhost system
How To Install and Use SNMP On Linux Tutorial with Examples? Infographic