- Sort by Column in Bash
- How to sort by column in bash
- Sort columns by numbers in bash
- Sort by columns in reverse in bash
- Sort command can do a lot more.
- How to Sort By Column In Linux
- Sort By Column
- Option -k
- Option -n
- Option -r
- Option -t
- Option -o
- Additional Options
- How to Sort in Linux Bash by Column
- Basic Usage
- Sort Command Options
- How to Sort In Linux Bash By Numerical Values
- How to Sort In Linux Bash By Reverse Order
- How to Sort In Linux Bash by Column
- How to Save Sort Output to a File
- Conclusion
- About the author
- John Otieno
Sort by Column in Bash
Learn various examples of sorting data by columns in bash scripts and Linux command line.
Once in a while, we all encounter a situation where we have a huge text file and want to sort the data accordingly.
Especially in times when you are given data in tabular form.
Sure, if you have access to GUI, there are multiple tools that do sorting effortlessly for you but what about sorting data by columns in bash directly?
And in this guide, I will walk you through how you can sort data by column in bash.
How to sort by column in bash
Throughout this guide, I will be using the sort command to sort data by column.
To sort columns, you will have to use a -k flag followed by the number of a column you want to sort.
So the syntax to sort columns using the sort command will look like this:
sort -k [Column_number] FilenameBut before going to the sorting examples, let me share how the sort command will sort the data by default:
- Sorts data in alphabetical order
- Numbers will always come before the alphabet
- Lowercase letters are prioritized before the capital ones
In conclusion, It looks like this: Numbers>Lowercase>Uppercase .
And for the sake of this tutorial, I will be using a file named Students.txt which contains the basic data of 7 students as follows:
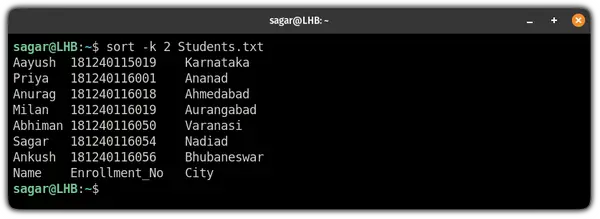
Name Enrollment_No City Sagar 181240116054 Nadiad Milan 181240116019 Aurangabad Anurag 181240116018 Ahmedabad Priya 181240116001 Ananad Abhiman 181240116050 Varanasi Aayush 181240115019 Karnataka Ankush 181240116056 BhubaneswarLet’s say I want to sort the 2nd column in the Student.txt file so I will be using the following:
And as you can see, the 2nd column is sorted in ascending order (the default behavior).
But what if you want to change how the data is sorted?
Sort columns by numbers in bash
You might be wondering if the numbers are sorted by default then why would I’m even writing this?
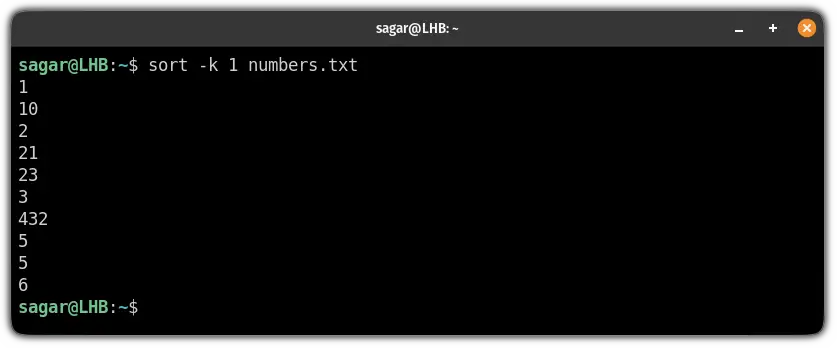
Well, the problem is the sort command by default will sort numbers from the leading characters only.
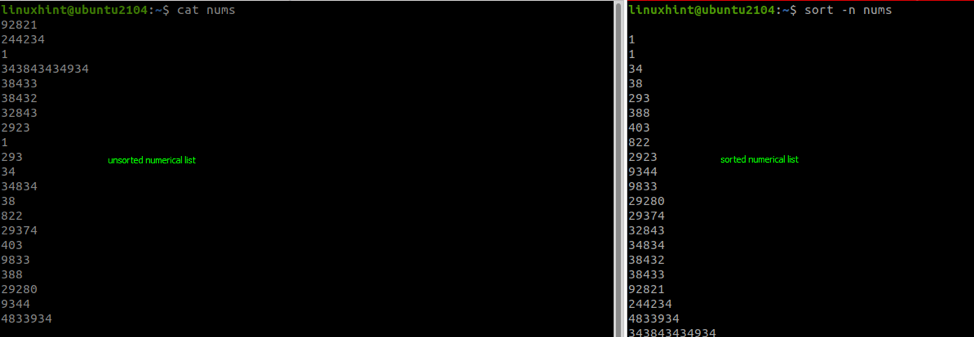
Let me share an example here. Here, I created a sample file with random numbers in one column and used the sort command without any additional options:
And as you can see, the result is messed up!
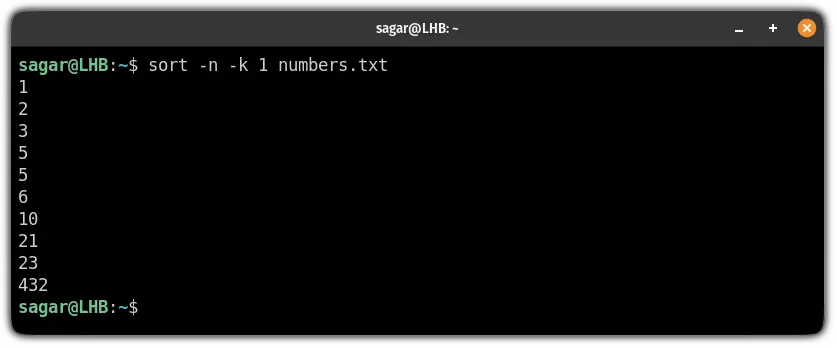
To solve this issue, you will need to use the -n flag with the existing command:
sort -n -k [Column_number] FilenameSort by columns in reverse in bash
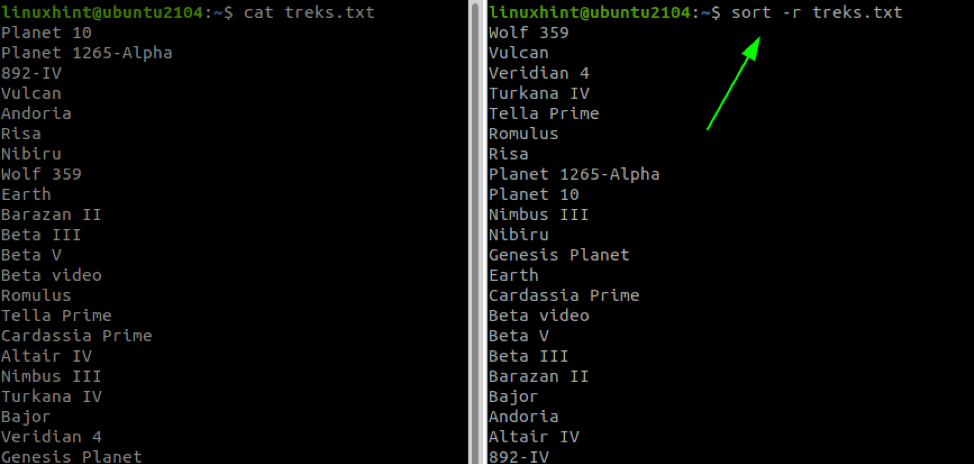
You may encounter times when you want to sort columns in descending order.
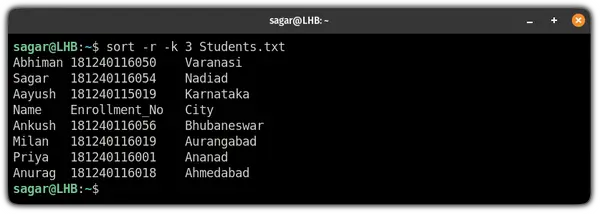
For that purpose, you will have to utilize the -r flag:
sort -r -k [Column_number] FilenameHere, I sorted the 3rd column in reverse:
Sort command can do a lot more.
Sort command when used with multiple flags can do wonders for you, especially when you have multiple files to deal with.
For this purpose, we have a dedicated guide on you can use the sort command with multiple examples:
I hope this guide has solved the queries you had before.
And if you still have doubts, feel free to ask in the comments.
How to Sort By Column In Linux
When dealing with a file that has a large number of entries, sorting the contents in a certain order can make things so much easier. In Linux, the sort command, which employs the merge sort algorithm, is used for this purpose.
The sort command compares all lines from the given files and sorts them in the specified order based on the sort keys. The -k option, in particular, is used to sort on a certain column.
In conjunction with the -k option, you’ll also need to know about other options like -n or -r to efficiently sort by column. We’ve detailed these and other related topics in the sections below.
Sort By Column
The base syntax for the sort command is sort . To apply this, let’s start with an example. Let’s say we have a contacts.txt file with the following entries:
Emma Smith US 51 Edward Dyer UK 19 Natalie Russell Canada 22 Mathew Roberts Germany 21 Ruth Abraham Australia 44 Joseph Smith France 25Just using the sort contacts command would sort the entries in alphabetical order based on the first column. To sort by another specific column, or in another order, you’ll have to use various options, which we’ve listed below.
Option -k
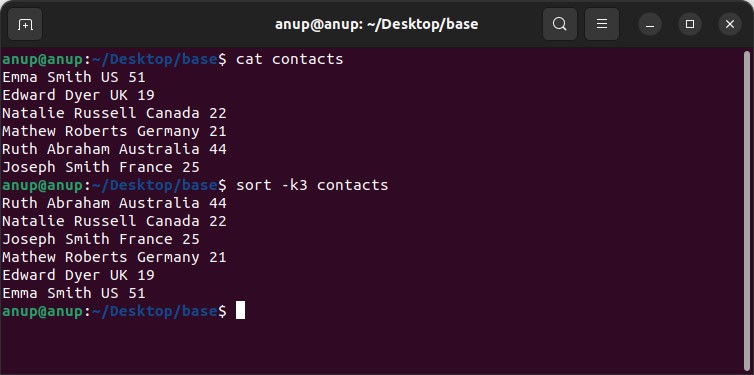
As stated, the —key , or -k option is used to sort on a specific column or field. For instance, in our example, if you wanted to sort by nationality, you’d use the following command to sort on the third column:
sort -k3 contacts
This command will take all fields from 3 to the end of the line into account. Alternatively, if you used sort -k3,4 contacts , this would specify to use the fields from #3 to #4, i.e., the third to fourth fields.
If you were trying to sort by surnames in the second column, there are two scenarios to consider. As there are identical entries (Smith), sort will use the next entry for the tiebreaker. I.e., in the case of the two smiths, France would be sorted above US.
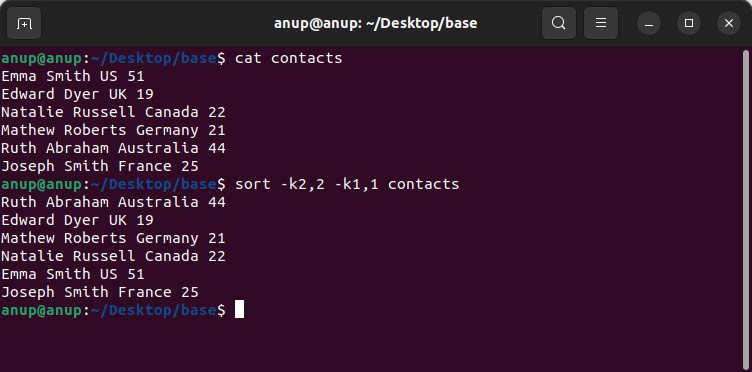
But what if you needed to sort by surname, name, and only then nationality? In such cases, you can manipulate the sort order by specifying keys multiple times as such:
sort -k2,2 -k1,1 contacts
Option -n
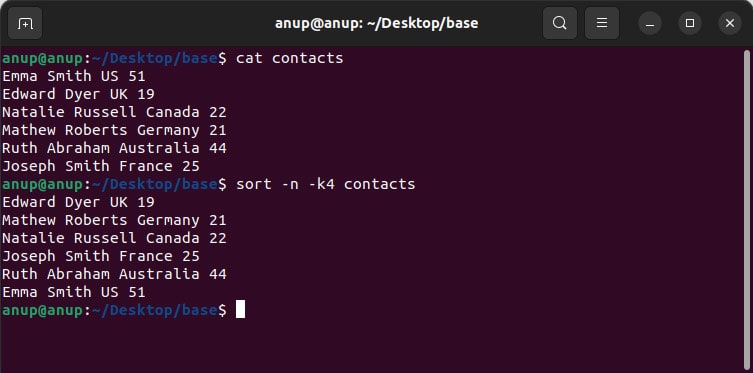
If you use the commands shown above to sort by age on the fourth column, the results would seem inaccurate. As sort takes a lexicographic approach, fiftyone would rank above nineteen.
To sort a column by numbers, you have to instead specify the -n option as such:
sort -n -k4 contacts
Option -r
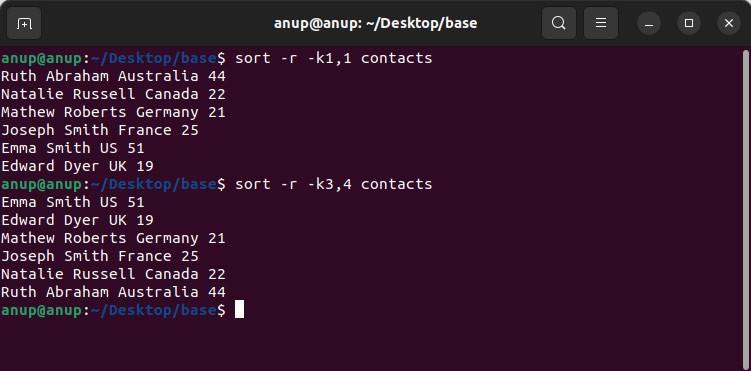
If you were trying to sort entries in reverse order, you would use the -r option. This is true for both alphabetical and numeric values, as shown below:
sort -r -k1,1 contacts
sort -r -k3,4 contacts
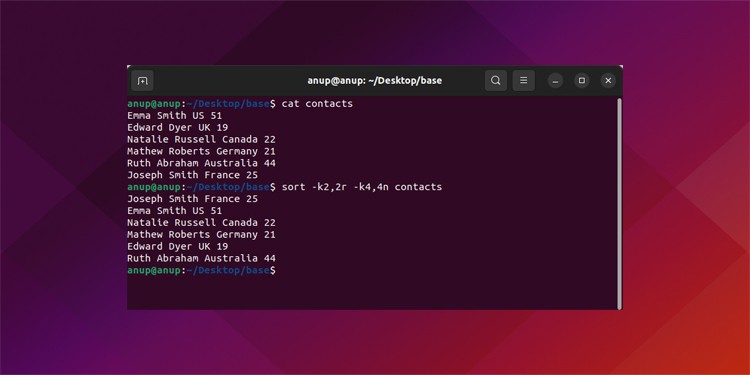
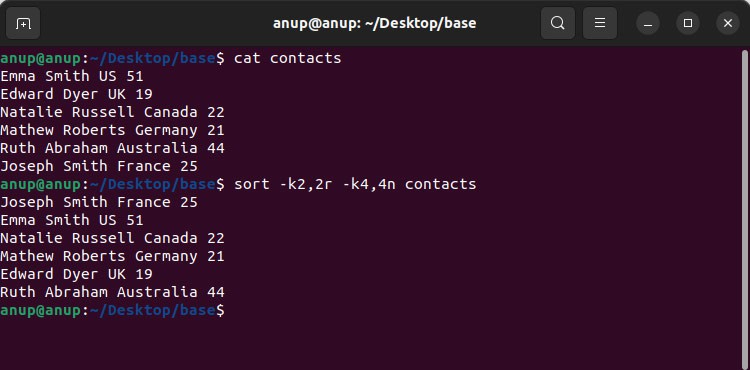
By combining the basic options we’ve listed so far, you could perform complex sorting operations like reverse sorting on the second column and numerically sorting on the fourth column at once:
sort -k2,2r -k4,4n contacts
Option -t
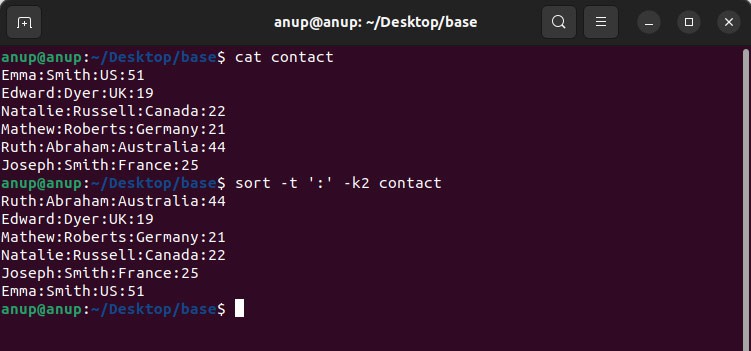
A blank space is the default field separator, i.e., delimiter with sort. But CSV files use commas (,) to separate values. Depending on what delimiter is used, you can specify it using the -t option. For instance, if : is the delimiter, you would specify it as such:
sort -t ‘:’ -k2 contact
Option -o
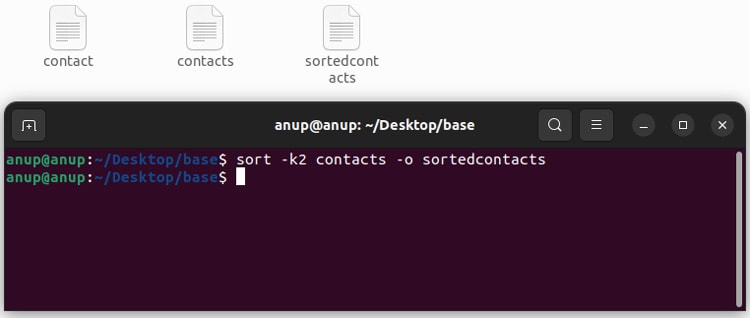
You can use the -o option to save the sorted output into a specified file as such:
sort -k2 contacts -o sortedcontacts
Additional Options
The options detailed above are the most commonly used ones. But sort has countless other flags that could be useful in niche scenarios like -b to ignore blank spaces at the start of the file, -M to sort the contents as per the calendar month, or -c to check if data is already sorted. As there are too many to list here, we recommend referring to the sort man page for the full list of such options.
Anup Thapa primarily covers Windows systems, networking, and computer hardware at TechNewsToday. Anup has been writing professionally for almost 5 years, and tinkering with PCs for much longer. His love for all things tech started when he got his first PC over 15 years ago. It was a Pentium IV system running Windows XP on a single 256 MB stick. He spent his formative years glued to this PC, troubleshooting any hardware or software problems he encountered by himself. Professionally, Anup has had brief forays into a variety of fields from coding and hardware installation to writing. In doing so, he’s worked with people of different backgrounds and skill levels, from average joes to industry leaders and experts. This has given him not just a versatile skill set, but also a unique perspective for writing that enables him to concisely communicate complex information and solve his reader’s problems efficiently. You can reach out to him at anup@technewstoday.com.
How to Sort in Linux Bash by Column
The sort command available in Linux allows users to perform sorting operations on a file or an input. The sort command is handy when we want to get an ordered output of a file ascending, descending, or custom-defined sort order. By default, the sort command does not alter the original file unless the output is redirected back to the file.
This article covers how to use the sort command to perform sorting operations on specific columns in a file.
Basic Usage
The sort command is simple to use and very useful in daily Linux operations. The general syntax of the command is as:
The options you pass to the command modifies how the file is sorted and the specific conditions to sort the target file. You can omit the options to use the default sorting parameters.
By default, the sort command:
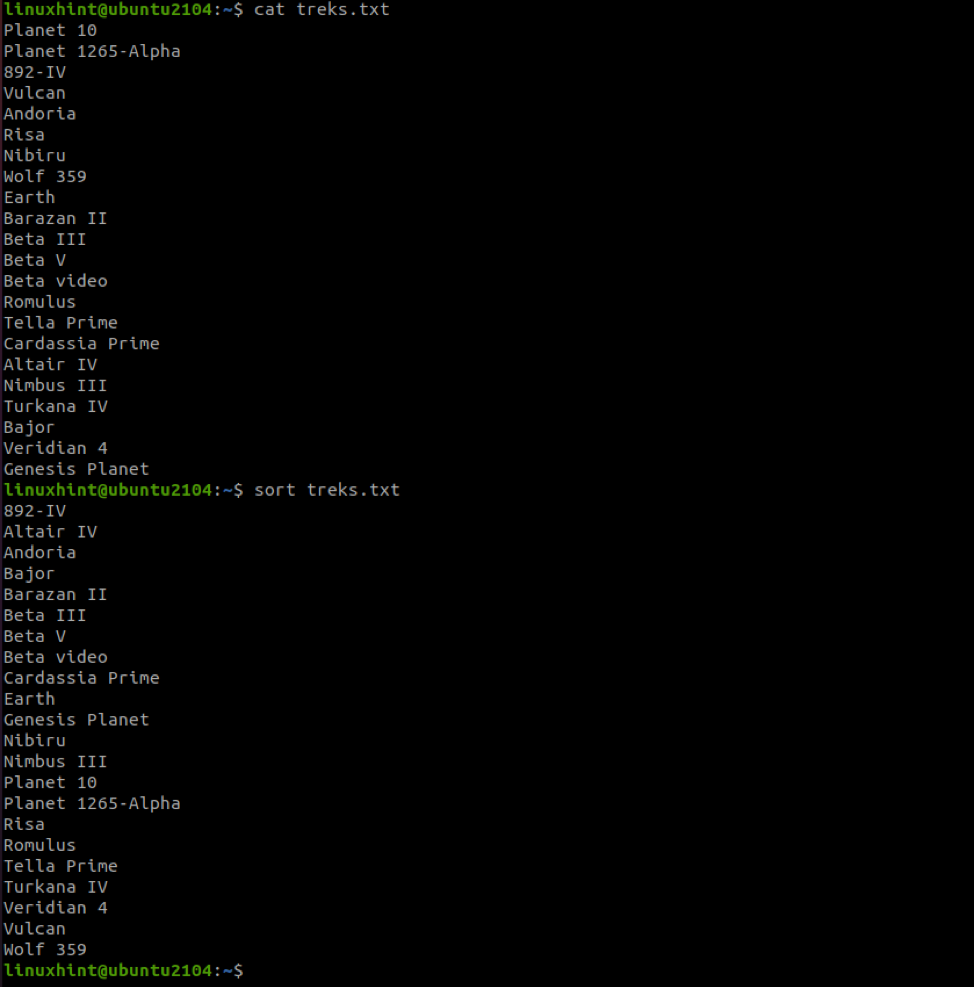
- Sorts the alphabets in ascending order.
- Letters come after numerical values
- Assigns higher precedence to lowercase letters than to uppercase letters.
For example, to sort a file without options:
Once we run the sort command against the file, we get the information sorted in alphabetical order (ascending).
NOTE: Numerical values take precedence as from the example above.
Sort Command Options
You can use the following options in conjunction with the raw command to modify how the values are sorted.
- -n – sorts in numerical values.
- -h – compares human-readable numbers such as 1k, 1G
- -R – sort in random order but group the identical keys.
- -r – sort the values in reverse (descending order).
- -o – save ouput to a file
- -c – check if the input file is sorted; do not sort if true.
- -u – show unique values only.
- -k – sort the data via a specific key (useful when sorting columnar data).
Those are some popular options you can tweak to get the best-sorted result. For more options, check the manual.
How to Sort In Linux Bash By Numerical Values
How to Sort In Linux Bash By Reverse Order
To sort input in reverse order, we use the -r flag. For example:
The command above will sort in ascending alphabetical order (numerical values first) and reverse order.
How to Sort In Linux Bash by Column
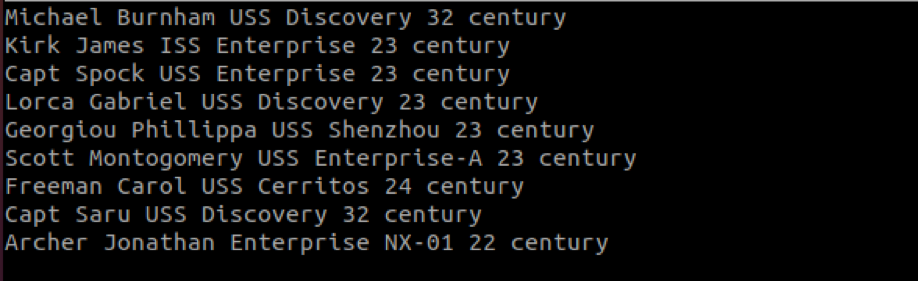
Sort allows us to sort a file by columns by using the -k option. Let us start by creating a file with more than one column. In sort, we separate a column by a single space.
In the example file below, we have six columns.
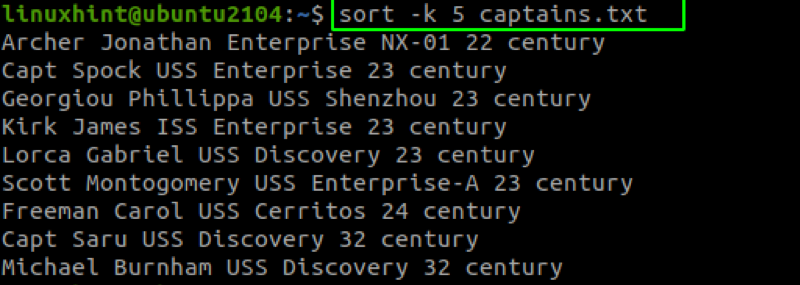
To sort the captains’ file above by their century, we can specify the -k followed by the column number as:
Once we specify the column to sort the data, the sort command will try to sort the values in ascending order. In the example above, the command sorts the values from the earliest century to the latest.
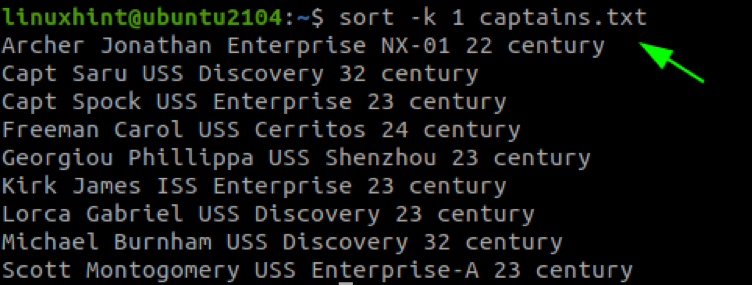
To sort by the first name, set the sort column as 1:
How to Save Sort Output to a File
To save the sorted output to a file, we can use the -o option as:
The command above will sort the captains.txt file by the 5 th column and save the result to the captains_century.txt file.
Conclusion
That is the end of this tutorial on the sort command in Linux. We covered the basics of using the sort command to get the most out of your sorted data. Feel free to explore how you can use the sort command.
About the author
John Otieno
My name is John and am a fellow geek like you. I am passionate about all things computers from Hardware, Operating systems to Programming. My dream is to share my knowledge with the world and help out fellow geeks. Follow my content by subscribing to LinuxHint mailing list