- Как быстро создать пустой и непустой текстовый файл в Linux через терминал?
- Создание пустых файлов
- Создание файлов с текстом
- Другие способы создания файлов
- Создание пустого файла с помощью touch
- Создание файла «с текстом» с помощью cat
- Пример
- Создание файла с помощью редактора.
- Создание файла с данными через dd
- Выделение места под файл средствами файловой системы
- How to Make a File in Linux from the Command Line – Create a File in the Terminal
- Pre-requisites:
- Method #1: How to Create Files Using the touch Command
- Method #2: How to Create Files Using the cat Command
- Method #3: How to Create Files Using the echo Command
- Conclusion
- How to Create a File in Linux Using Terminal/Command Line
- Creating New Linux Files from Command Line
- Create a File with Touch Command
- Create a New File With the Redirect Operator
- Create File with cat Command
- Create File with echo Command
- Create File with printf Command
- Using Text Editors to Create a Linux File
- Vi Text Editor
- Vim Text Editor
- Nano Text Editor
Как быстро создать пустой и непустой текстовый файл в Linux через терминал?
Ответ общий, вы можете исправить его, если считаете нужным.
Существует N-ое количество способов создания текстовых файлов, мы приведём два основных, которые, на наш взляд, самые быстрые с точки зрения клавиатурного ввода, и несколько других.
Под фразой «при вводе» подразумевается, что нужно ввести команду в терминал и нажать клавишу Enter .
Создание пустых файлов
При вводе этой команды в текущей директории будет создан пустой файл с именем a .
Можно вводить без пробела:
Более читаемый вариант, помогает не ошибиться и не записать случайно результат предыдущей команды в файл:
Можно создать сразу сколь угодно файлов:
Хотя так удобней (о touch будет далее):
Создание файлов с текстом
При вводе этой команды в текущей директории будет создан файл с именем h , содержащий текст blablabla и один перевод строки.
Можно вводить без пробела вокруг оператора > :
Выводимый контекст можно заключить в кавычки, а можно и не заключать, даже если он содержит пробелы:
echo bla bla bla > j echo 'bla bla bla' > k echo "bla bla bla" > l Все три вышеперечисленные команды дают одинаковый результат (кроме имён файлов, естественно).
Также можно провернуть такую штуку:
При вводе этой команды в текущей директории будут созданы два пустых файла: m и n ; и файл o , содержащий текст 123 и один перевод строки.
Иными словами, результат всех команд, которые что-нибудь выводят, можно запихнуть в файл .
Ман по man ‘у . При вводе этой команды в текущей директории будет создан файл с именем p , содержащий мануал по команде man .
Другие способы создания файлов
Создание пустого файла с помощью touch
При вводе этой команды в текущей директории будет создан пустой файл с именем q .
Если быть точным, то touch это команда, основное назначение которой изменить время последнего изменения или последнего доступа файла, если же файл не существует, то она создает его. Цитата.
Создание файла «с текстом» с помощью cat
При вводе этой команды в текущей директории будет создан пустой файл с именем r и терминал перейдёт в режим конкатенации вводимых строк к концу содержимого этого файла. То есть мы можем сразу же начать заполнять файл текстом. Сохранение набранного текста будет происходит построчно по нажатию клавиши Enter . Иными словами, по нажатию клавиши Enter будет выполняться конкатенация.
Можно вводить без пробела:
Пример
- Вводим cat>s — в текущей директории создан пустой файл с именем s .
- Набираем 123 — этого текста ещё не будет в файле.
- Нажимаем Enter — текст 123 записался в файл и курсор, как в терминале, так и в файле, перешёл на новую строку.
На строку выше вернуться нельзя.
Выйти из режима конкатенации можно с помощью Ctrl+D (EOF — End Of File) в начале строки. Если вы уже начали набирать строку, Ctrl+D не закончит ввод файла, но запишет набранную часть строки без символа конца строки. Так вы можете записывать строки частями. Для выхода с незавершённой строкой можно нажать Ctrl+D дважды, тогда последняя строка в файле не будет иметь символа конца строки (EOL — End Of Line).
Создание файла с помощью редактора.
Очевидно, что мы можем исользовать редактор типа nano , vi , vim , etc для создания файла.
- Вводим nano t — открывается редактор nano в терминальном режиме.
- Вводим 123 и нажимаем Ctrl + O (не ноль, а буква), а затем Enter — в текущей директории создался файл с именем t , содержащий текст 123 и один перевод строки.
- Чтобы выйти и редактора нажимаем Ctrl + X (внизу редактора подсказки).
Создание файла с данными через dd
Полезно иногда создавать файл определенного размера с нулями
dd if=/dev/zero of=./file bs=10M count=100 dd if=/dev/urandom of=./file bs=10M count=100 Создается файл из 100 блоков по 10 мегабайт — 1 ГБ.
Выделение места под файл средствами файловой системы
Такие команды работают быстерее dd потому как сами данные не записываются, а просто выделяется область диска
fallocate резервирует место под файл на диске, а truncate обрезает файл или добавляет до нужного размера, резервируя место на диске.
При создании файлов таким образом в них могут содержаться куски удаленных рание файлов на некоторых системах.
How to Make a File in Linux from the Command Line – Create a File in the Terminal
Zaira Hira
Managing files from the command line is one of the most common tasks for a Linux user.
Files are created, edited, deleted, and used by many of the background OS processes. Files are also used by regular users to accomplish daily tasks such as taking notes, writing code, or simply duplicating content.
In this article, we will see three methods through which we can create files using the terminal. The three commands that we’ll discuss are touch , cat and echo .
Pre-requisites:
You should have access to the Linux terminal to try out the commands mentioned in this tutorial. You can access the terminal in either of the following ways:
- Install a Linux distro of your choice on your system.
- Use WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux), if you want to use Windows and Linux side by side. Here is a guide to do that.
- Use Replit which is a browser-based IDE. You can create a Bash project and access the terminal right away.
Method #1: How to Create Files Using the touch Command
The touch command creates empty files. You can use it to create multiple files as well.
Syntax of the touch command:
Examples of the touch command:
Let’s create a single empty file using the syntax provided above.
Next, we’ll create multiple files by providing the file names separated with spaces after the touch command.
touch mod.log messages.log security.logThe above command will create three separate empty files named mod.log , messages.log , and security.log .
Method #2: How to Create Files Using the cat Command
The cat command is most commonly used to view the contents of a file. But you can also use it to create files.
Syntax of the cat command:
This will ask you to enter the text that you can save and exit by pressing ctrl+c .
When I enter the above command, my terminal output looks like this:
zaira@Zaira:~$ cat > sample.txt This is a sample file created using the "cat" command ^CNote the ^C sign, which corresponds to Ctrl+c and signals to the terminal to save and exit.
Here are the contents of the created file:
zaira@Zaira:~$ more sample.txt This is a sample file created using the "cat" commandMethod #3: How to Create Files Using the echo Command
The echo command is used to add and append text to files. It also creates the file if it doesn’t already exist.
Syntax of the echo command:
echo "some text" > sample.txtecho "some text" >> sample.txtThe difference between > and >> is that > overwrites the file if it exists whereas >> appends to the existing file.
If you would like to follow along with the video tutorial of this article, here is the link:

Conclusion
In this article, we discussed three different methods to create files in the Linux command line. I hope you found this tutorial helpful.
What’s your favorite thing you learned from this tutorial? Let me know on Twitter!
You can read my other posts here.
How to Create a File in Linux Using Terminal/Command Line
Creating a new file in Linux is straightforward, but there are also some surprising and clever techniques.
In this tutorial learn how to to create a file from a Linux terminal.
- Access to a command line/terminal window (Ctrl–Alt–F2 or Ctrl–Alt–T)
- A user account with sudo privileges (optional for some files/directories)
Creating New Linux Files from Command Line
Linux is designed to create any file you specify, even if it doesn’t already exist. One smart feature is that you can create a file directly, without needing to open an application first.
Here are a few commands for creating a file directly from the command line.
Create a File with Touch Command
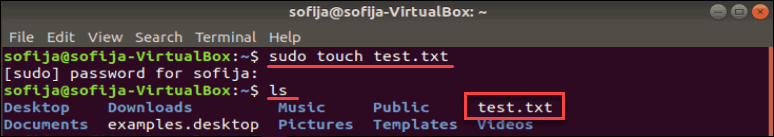
The easiest way to create a new file in Linux is by using the touch command.
In a terminal window, enter the following:
This creates a new empty file named test.txt. You can see it by entering:
The ls command lists the contents of the current directory. Since no other directory was specified, the touch command created the file in the current directory.
If there’s already a file with the name you chose, the touch command will update the timestamp.
Create a New File With the Redirect Operator
A redirection operator is a name for a character that changes the destination where the results are displayed.
Right angle bracket >
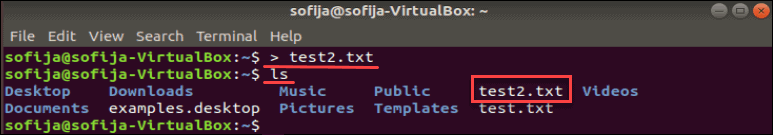
This symbol tells the system to output results into whatever you specify next. The target is usually a filename. You can use this symbol by itself to create a new file:
This creates a new empty file.
Use the ls command to list the contents of the current directory and find the file test2.txt.
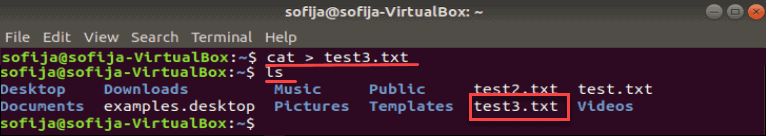
Create File with cat Command
The cat command is short for concatenate. It can be used to output the contents of several files, one file, or even part of a file. If the file doesn’t exist, the Linux cat command will create it.
To create an empty file using cat , enter the following:
Note the redirection operator. Typically, the command displays the contents of test2.txt on the screen. The redirection operator > tells the system to place it in the test2.txt file.
Verify that the file was created:
The system should now have test.txt, test2.txt, and test3.txt in the list.
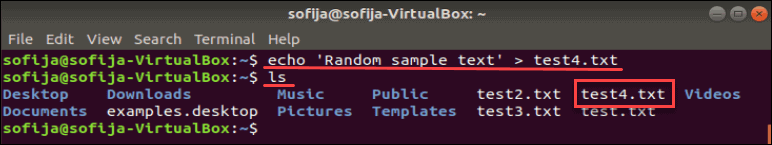
Create File with echo Command
The echo command will duplicate whatever you specify in the command, and put the copy into a file.
echo 'Random sample text' > test4.txtVerify that the file was created:
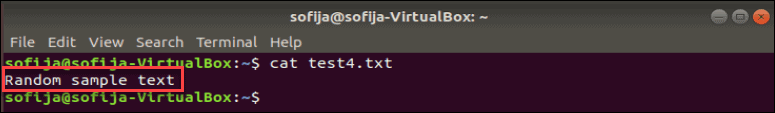
You should see the test4.txt file added to the list. Use the cat command to display the contents of the new file:
The system should display Random sample text (or whatever you entered with the echo command.)
Create File with printf Command
The printf command works like the echo command, and it adds some formatting functionality. To add a single line of text, enter:
printf 'First line of text\n' test5.txtTo add two lines of text, separate each line with the \n option:
printf 'First line of text\n Second line of text' test6.txtYou can use the cat command on either of these files to display their contents.
Note: To use several terminal instances in a single window manager, consider using Linux screen. It enables additional features and an enhanced command line for working with Linux files.
Using Text Editors to Create a Linux File
All Linux distributions have at least one text editor. Some have multiple editors. Each editor has different strengths and features. This will show you three of the most popular.
Vi Text Editor
Vi is the oldest text editor in Linux. It was created alongside the Linux operating system for directly editing text files. Since it’s unlikely you’ll see a Linux distribution without it, it’s a safe editor to know.
To create a file using Vi, enter the following:
Your screen will change. Now you’re in the text editor. Press the letter i to switch to insert mode, then type a few words to try it out.
To save and exit press Esc 😡 and hit Enter .
Vim Text Editor
You may have noticed that the Vi editor wasn’t very user-friendly. Vim is a newer version, which stands for Vi editor, Modified.
Use vim to create a new text file:
This screen will look similar to the Vi editor screen. Press i to insert text, and type a few words. Save file and exit by entering:
(Escape, colon wq, then Enter.)
Nano Text Editor
Nano is a newer and much easier text editor to navigate.
Create a new file by entering the command:
By default, Nano puts you directly into editing mode. It also displays a helpful list of commands at the bottom of the screen.
Enter some text, then press Ctrl+O to save the changes.
Press Ctrl+X to exit the editor.
Note: Learn all you need about Nano in the Install and Use Nano in Linux article.
Now you have several options to create new files in Linux from the command line. Next, learn how to copy files and directories in Linux to manage your files more efficiently.