- Как создать каталог в Linux
- Терминал
- Файловый менеджер
- Заключение
- Создать новую директорию линукс
- NAME
- SYNOPSIS
- DESCRIPTION
- AUTHOR
- REPORTING BUGS
- COPYRIGHT
- SEE ALSO
- Создать новую директорию линукс
- NAME
- SYNOPSIS
- DESCRIPTION
- OPTIONS
- OPERANDS
- STDIN
- INPUT FILES
- ENVIRONMENT VARIABLES
- ASYNCHRONOUS EVENTS
- STDOUT
- STDERR
- OUTPUT FILES
- EXTENDED DESCRIPTION
- EXIT STATUS
- CONSEQUENCES OF ERRORS
- APPLICATION USAGE
- EXAMPLES
- RATIONALE
- FUTURE DIRECTIONS
- SEE ALSO
Как создать каталог в Linux
Операционная система Linux существенно отличается от некоторых своих аналогов. В этом может убедиться каждый новичок, который впервые имеет дело с непростым дистрибутивом Ubuntu. Переход на ОС Линукс всегда становится испытанием для любителей Windows, но опыт и понимание специфики такого устройства приходит со временем. В большинстве случае базового количества стандартных папок не хватает для хранения всех необходимых файлов, а сбрасывать их в один каталог – крайне неразумная затея. Это неудобно. Также не стоит забывать о временных файлах или отдельно взятых программах на компьютере. Они нуждаются в автономных хранилищах. Как минимум для того, чтобы соблюдать порядок на ПК. В данной статье мы разберемся, как создать новую папку в Линукс посредством самых простых и доступных способов.
Терминал
К сожалению, столь универсальный инструмент управления системой, как терминал, часто игнорируется неопытными пользователями. Они его попросту боятся, но это лишь вопрос времени и привычки. Имея дело с ОС Линукс, всё же придется сделать этот отважный шаг. Для создания новой папки на ПК понадобится специальная утилита – mkdir. Можно сказать, это и есть её основная задача. Синтаксическая структура mkdir выглядит следующим образом:
Данная программа не наделена широким функционалом, но в данном вопросе он и не понадобится. Итак, приступаем к созданию нового каталога. Запустите окно терминала, используя клавиатуру своего ПК. А именно – комбинацию Ctrl+Alt+T. Пропишите в нем команду в виде: Создадим новый каталог «new-papka». $ mkdir new-papka После этого в текущей директории появится новый каталог «new-papka». Новую папку можно создать и в любой иной директории. Для этого дополнительно необходимо указать полный или относительный путь. Создадим директорию «test» в «usr». # mkdir /usr/test Все еще сомневается в уникальных возможностях терминала по сравнению с графическими программами? Тогда мы выделим для вас еще несколько заманчивых опций для создания нового каталога в Линукс. Чтобы создать сразу несколько новых папок, не придется выполнять этот процесс вручную, повторяя одни и те же действия раз за разом. С терминалом все делается намного проще и быстрее! Нужно лишь знать специальную команду: $ mkdir И еще одна полезная подсказка! Для создания папки с подпапками примените команду с опцией «-p». $ mkdir –p ~/каталог/подкаталог Здесь ~ — доманий каталог пользователя.
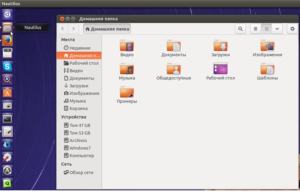
Файловый менеджер
Чтобы создать новую папку данным способом, найдите ярлык файлового менеджера (Nautilus) в меню Dash или на панели Unity. Кликните мышкой по этому ярлыку. В перечне доступных каталогов выберите тот, в котором планируете создать новую папку. Вам необходимо перейти в него для выполнения актуальной задачи. Предлагаем вашему вниманию альтернативный вариант: в окне файлового менеджера кликните правой кнопкой мыши для вызова контекстного меню. В списке доступных опций выберите вариант «Создать папку». Так будет еще быстрее. Придумайте наименование для новой папки. Используйте любые цифры, символы или буквы для ввода названия в специальной графе. Единственным исключением из правила является символ косой черточки. Его использование запрещено для подобных целей. В этом плане операционная система Linux не так строга и взыскательна, как операционная система Windows. Если внимательнее присмотреться, то можно понять без сомнений: Линукс имеет множество преимуществ в работе. После того, как наименование будет прописано, нужно сохранить внесенные изменения. Для этого следует один раз кликнуть мышкой в окне файлового менеджера – там, где остается свободное место. Как видите, ничего сложного в этом нет.
Заключение
В данной статье представлены сразу несколько альтернативных способов создания новой папки в Линукс. Неопытному пользователю остается лишь выбрать максимально удобный вариант. Работа с консольными командами станет для новичка сущим удовольствием, как только он отважится иметь делом с терминалом.
Создать новую директорию линукс
NAME
SYNOPSIS
mkdir [OPTION]. DIRECTORY.
DESCRIPTION
Create the DIRECTORY(ies), if they do not already exist. Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too. -m, --mode=MODE set file mode (as in chmod), not a=rwx - umask -p, --parents no error if existing, make parent directories as needed -v, --verbose print a message for each created directory -Z set SELinux security context of each created directory to the default type --context[=CTX] like -Z, or if CTX is specified then set the SELinux or SMACK security context to CTX --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exit
AUTHOR
Written by David MacKenzie.
REPORTING BUGS
GNU coreutils online help: http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/> Report mkdir translation bugs to http://translationproject.org/team/>
COPYRIGHT
Copyright © 2016 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>. This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
SEE ALSO
mkdir(2) Full documentation at: http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/mkdir> or available locally via: info '(coreutils) mkdir invocation'
© 2019 Canonical Ltd. Ubuntu and Canonical are registered trademarks of Canonical Ltd.
Создать новую директорию линукс
NAME
SYNOPSIS
mkdir [-p][-m mode] dir.
DESCRIPTION
The mkdir utility shall create the directories specified by the operands, in the order specified. For each dir operand, the mkdir utility shall perform actions equivalent to the mkdir() function defined in the System Interfaces volume of IEEE Std 1003.1-2001, called with the following arguments: 1. The dir operand is used as the path argument. 2. The value of the bitwise-inclusive OR of S_IRWXU, S_IRWXG, and S_IRWXO is used as the mode argument. (If the -m option is specified, the mode option-argument overrides this default.)
OPTIONS
The mkdir utility shall conform to the Base Definitions volume of IEEE Std 1003.1-2001, Section 12.2, Utility Syntax Guidelines. The following options shall be supported: -m mode Set the file permission bits of the newly-created directory to the specified mode value. The mode option-argument shall be the same as the mode operand defined for the chmod utility. In the symbolic_mode strings, the op characters '+' and '-' shall be interpreted relative to an assumed initial mode of a= rwx; '+' shall add permissions to the default mode, '-' shall delete permissions from the default mode. -p Create any missing intermediate pathname components. For each dir operand that does not name an existing directory, effects equivalent to those caused by the following command shall occur: mkdir -p -m $(umask -S),u+wx $(dirname dir) && mkdir [-m mode] dir where the -m mode option represents that option supplied to the original invocation of mkdir, if any. Each dir operand that names an existing directory shall be ignored without error.
OPERANDS
The following operand shall be supported: dir A pathname of a directory to be created.
STDIN
INPUT FILES
ENVIRONMENT VARIABLES
The following environment variables shall affect the execution of mkdir: LANG Provide a default value for the internationalization variables that are unset or null. (See the Base Definitions volume of IEEE Std 1003.1-2001, Section 8.2, Internationalization Variables for the precedence of internationalization variables used to determine the values of locale categories.) LC_ALL If set to a non-empty string value, override the values of all the other internationalization variables. LC_CTYPE Determine the locale for the interpretation of sequences of bytes of text data as characters (for example, single-byte as opposed to multi-byte characters in arguments). LC_MESSAGES Determine the locale that should be used to affect the format and contents of diagnostic messages written to standard error. NLSPATH Determine the location of message catalogs for the processing of LC_MESSAGES .
ASYNCHRONOUS EVENTS
STDOUT
STDERR
The standard error shall be used only for diagnostic messages.
OUTPUT FILES
EXTENDED DESCRIPTION
EXIT STATUS
The following exit values shall be returned: 0 All the specified directories were created successfully or the -p option was specified and all the specified directories now exist. >0 An error occurred.
CONSEQUENCES OF ERRORS
Default. The following sections are informative.
APPLICATION USAGE
The default file mode for directories is a= rwx (777 on most systems) with selected permissions removed in accordance with the file mode creation mask. For intermediate pathname components created by mkdir, the mode is the default modified by u+ wx so that the subdirectories can always be created regardless of the file mode creation mask; if different ultimate permissions are desired for the intermediate directories, they can be changed afterwards with chmod. Note that some of the requested directories may have been created even if an error occurs.
EXAMPLES
RATIONALE
The System V -m option was included to control the file mode. The System V -p option was included to create any needed intermediate directories and to complement the functionality provided by rmdir for removing directories in the path prefix as they become empty. Because no error is produced if any path component already exists, the -p option is also useful to ensure that a particular directory exists. The functionality of mkdir is described substantially through a reference to the mkdir() function in the System Interfaces volume of IEEE Std 1003.1-2001. For example, by default, the mode of the directory is affected by the file mode creation mask in accordance with the specified behavior of the mkdir() function. In this way, there is less duplication of effort required for describing details of the directory creation.
FUTURE DIRECTIONS
SEE ALSO
chmod() , rm , rmdir() , umask() , the System Interfaces volume of IEEE Std 1003.1-2001, mkdir()