- Как создавать каталоги в Linux (команда mkdir)
- Синтаксис команды Linux mkdir
- Как создать новый каталог
- Как создать родительские каталоги
- Как установить разрешения при создании каталога
- Как создать несколько каталогов
- Выводы
- Создать папку linux mkdir
- NAME
- SYNOPSIS
- DESCRIPTION
- OPTIONS
- OPERANDS
- STDIN
- INPUT FILES
- ENVIRONMENT VARIABLES
- ASYNCHRONOUS EVENTS
- STDOUT
- STDERR
- OUTPUT FILES
- EXTENDED DESCRIPTION
- EXIT STATUS
- CONSEQUENCES OF ERRORS
- APPLICATION USAGE
- EXAMPLES
- RATIONALE
- FUTURE DIRECTIONS
- SEE ALSO
- How to Use mkdir Command to Make or Create a Linux Directory
- mkdir Command Syntax in Linux
- How to Make a New Directory In Linux
- How to Create Multiple Directories with mkdir
- How to Make Parent Directories
- How to Set Permissions When Making a Directory
- How to Verify Directories
- mkdir Command Options and Syntax Summary
Как создавать каталоги в Linux (команда mkdir)
В системах Linux вы можете создавать новые каталоги либо из командной строки, либо с помощью файлового менеджера вашего рабочего стола. Команда, позволяющая создавать каталоги (также известные как папки), — это mkdir .
В этом руководстве рассматриваются основы использования команды mkdir , включая повседневные примеры.
Синтаксис команды Linux mkdir
Синтаксис команды mkdir следующий:
Команда принимает в качестве аргументов одно или несколько имен каталогов.
Как создать новый каталог
Чтобы создать каталог в Linux, передайте имя каталога в качестве аргумента команды mkdir . Например, чтобы создать новый каталог newdir вы должны выполнить следующую команду:
Вы можете убедиться, что каталог был создан, перечислив его содержимое с помощью команды ls :
drwxrwxr-x 2 username username 4096 Jan 20 03:39 newdir При указании только имени каталога без полного пути он создается в текущем рабочем каталоге.
Текущий рабочий каталог — это каталог, из которого вы запускаете команды. Чтобы изменить текущий рабочий каталог, используйте команду cd .
Чтобы создать каталог в другом месте, вам необходимо указать абсолютный или относительный путь к файлу родительского каталога. Например, чтобы создать новый каталог в каталоге /tmp вы должны ввести:
Если вы попытаетесь создать каталог в родительском каталоге, в котором у пользователя недостаточно прав, вы получите сообщение об ошибке Permission denied :
mkdir: cannot create directory '/root/newdir': Permission denied Параметр -v ( —verbose ) указывает mkdir печатать сообщение для каждого созданного каталога.
Как создать родительские каталоги
Родительский каталог — это каталог, который находится над другим каталогом в дереве каталогов. Чтобы создать родительские каталоги, используйте параметр -p .
Допустим, вы хотите создать каталог /home/linuxize/Music/Rock/Gothic :
mkdir /home/linuxize/Music/Rock/GothicЕсли какой-либо из родительских каталогов не существует, вы получите сообщение об ошибке, как показано ниже:
mkdir: cannot create directory '/home/linuxize/Music/Rock/Gothic': No such file or directory Вместо того, чтобы создавать недостающие родительские каталоги один за другим, вызовите команду mkdir с параметром -p :
mkdir -p /home/linuxize/Music/Rock/GothicКогда используется опция -p , команда создает каталог, только если он не существует.
Если вы попытаетесь создать каталог, который уже существует, а параметр -p не mkdir , mkdir выведет сообщение об ошибке File exists :
mkdir: cannot create directory 'newdir': File exists Как установить разрешения при создании каталога
Чтобы создать каталог с определенными разрешениями, используйте параметр -m ( -mode ). Синтаксис для назначения разрешений такой же, как и для команды chmod .
В следующем примере мы создаем новый каталог с разрешениями 700 , что означает, что только пользователь, создавший каталог, сможет получить к нему доступ:
Когда опция -m не используется, вновь созданные каталоги обычно имеют права доступа 775 или 755 , в зависимости от значения umask .
Как создать несколько каталогов
Чтобы создать несколько каталогов, укажите имена каталогов в качестве аргументов команды, разделенные пробелом:
Команда mkdir также позволяет создать сложное дерево каталогов с помощью одной команды:
mkdir -p Music/,Classical/Baroque/Early>Приведенная выше команда создает следующее дерево каталогов :
Music/ |-- Classical | `-- Baroque | `-- Early |-- Disco |-- Folk |-- Jazz | `-- Blues `-- Rock |-- Gothic |-- Progressive `-- Punk Выводы
Команда mkdir в Linux используется для создания новых каталогов.
Для получения дополнительной информации о mkdir посетите страницу руководства mkdir .
Если у вас есть вопросы, не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии ниже.
Создать папку linux mkdir
NAME
SYNOPSIS
mkdir [-p][-m mode] dir.
DESCRIPTION
The mkdir utility shall create the directories specified by the operands, in the order specified. For each dir operand, the mkdir utility shall perform actions equivalent to the mkdir() function defined in the System Interfaces volume of IEEE Std 1003.1-2001, called with the following arguments: 1. The dir operand is used as the path argument. 2. The value of the bitwise-inclusive OR of S_IRWXU, S_IRWXG, and S_IRWXO is used as the mode argument. (If the -m option is specified, the mode option-argument overrides this default.)
OPTIONS
The mkdir utility shall conform to the Base Definitions volume of IEEE Std 1003.1-2001, Section 12.2, Utility Syntax Guidelines. The following options shall be supported: -m mode Set the file permission bits of the newly-created directory to the specified mode value. The mode option-argument shall be the same as the mode operand defined for the chmod utility. In the symbolic_mode strings, the op characters '+' and '-' shall be interpreted relative to an assumed initial mode of a= rwx; '+' shall add permissions to the default mode, '-' shall delete permissions from the default mode. -p Create any missing intermediate pathname components. For each dir operand that does not name an existing directory, effects equivalent to those caused by the following command shall occur: mkdir -p -m $(umask -S),u+wx $(dirname dir) && mkdir [-m mode] dir where the -m mode option represents that option supplied to the original invocation of mkdir, if any. Each dir operand that names an existing directory shall be ignored without error.
OPERANDS
The following operand shall be supported: dir A pathname of a directory to be created.
STDIN
INPUT FILES
ENVIRONMENT VARIABLES
The following environment variables shall affect the execution of mkdir: LANG Provide a default value for the internationalization variables that are unset or null. (See the Base Definitions volume of IEEE Std 1003.1-2001, Section 8.2, Internationalization Variables for the precedence of internationalization variables used to determine the values of locale categories.) LC_ALL If set to a non-empty string value, override the values of all the other internationalization variables. LC_CTYPE Determine the locale for the interpretation of sequences of bytes of text data as characters (for example, single-byte as opposed to multi-byte characters in arguments). LC_MESSAGES Determine the locale that should be used to affect the format and contents of diagnostic messages written to standard error. NLSPATH Determine the location of message catalogs for the processing of LC_MESSAGES .
ASYNCHRONOUS EVENTS
STDOUT
STDERR
The standard error shall be used only for diagnostic messages.
OUTPUT FILES
EXTENDED DESCRIPTION
EXIT STATUS
The following exit values shall be returned: 0 All the specified directories were created successfully or the -p option was specified and all the specified directories now exist. >0 An error occurred.
CONSEQUENCES OF ERRORS
Default. The following sections are informative.
APPLICATION USAGE
The default file mode for directories is a= rwx (777 on most systems) with selected permissions removed in accordance with the file mode creation mask. For intermediate pathname components created by mkdir, the mode is the default modified by u+ wx so that the subdirectories can always be created regardless of the file mode creation mask; if different ultimate permissions are desired for the intermediate directories, they can be changed afterwards with chmod. Note that some of the requested directories may have been created even if an error occurs.
EXAMPLES
RATIONALE
The System V -m option was included to control the file mode. The System V -p option was included to create any needed intermediate directories and to complement the functionality provided by rmdir for removing directories in the path prefix as they become empty. Because no error is produced if any path component already exists, the -p option is also useful to ensure that a particular directory exists. The functionality of mkdir is described substantially through a reference to the mkdir() function in the System Interfaces volume of IEEE Std 1003.1-2001. For example, by default, the mode of the directory is affected by the file mode creation mask in accordance with the specified behavior of the mkdir() function. In this way, there is less duplication of effort required for describing details of the directory creation.
FUTURE DIRECTIONS
SEE ALSO
chmod() , rm , rmdir() , umask() , the System Interfaces volume of IEEE Std 1003.1-2001, mkdir()
How to Use mkdir Command to Make or Create a Linux Directory
With mkdir , you can also set permissions, create multiple directories (folders) at once, and much more.
This tutorial will show you how to use the mkdir command in Linux.
- Linux or UNIX-like system.
- Access to a terminal/command line.
- A user with permissions to create and change directory settings.
mkdir Command Syntax in Linux
The basic command for creating directories in Linux consists of the mkdir command and the name of the directory. As you can add options to this command, the syntax looks like this:
To understand better how to use mkdir , refer to the examples we provide in the rest of the guide.
Tip: Use cd to navigate to the directory where you want to create a sub-directory. You can also use the direct path. Use ls to list the directories in the current location.
How to Make a New Directory In Linux
To create a directory using the terminal, pass the desired name to the mkdir command.
In this example, we created a directory Linux on the desktop. Remember commands in Linux and options are case sensitive.
If the operation is successful, the terminal returns an empty line.
To verify, use ls .
Note: To create a hidden directory, follow our guide on how to show and create hidden files in Linux.
How to Create Multiple Directories with mkdir
You can create directories one by one with mkdir, but this can be time-consuming. To avoid that, you can run a single mkdir command to create multiple directories at once.
To do so, use the curly brackets <> with mkdir and state the directory names, separated by a comma.
Do not add any spaces in the curly brackets for the directory names. If you do, the names in question will include the extra characters:
How to Make Parent Directories
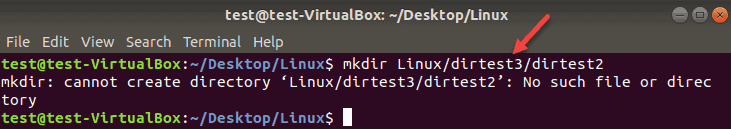
Building a structure with multiple subdirectories using mkdir requires adding the -p option. This makes sure that mkdir adds any missing parent directories in the process.
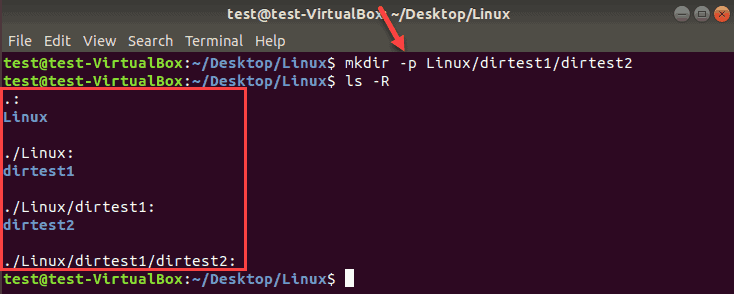
For example, if you want to create “dirtest2” in “dirtest1” inside the Linux directory (i.e., Linux/dirtest1/dirtest2), run the command:
mkdir –p Linux/dirtest1/dirtest2Use ls -R to show the recursive directory tree.
Without the -p option, the terminal returns an error if one of the directories in the string does not exist.
How to Set Permissions When Making a Directory
The mkdir command by default gives rwx permissions for the current user only.
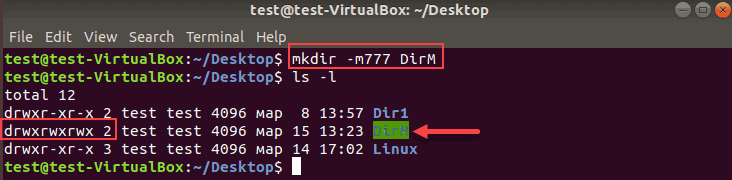
To add read, write, and execute permission for all users, add the -m option with the user 777 when creating a directory.
To create a directory DirM with rwx permissions:
To list all directories and show the permissions sets: -l
The directory with rwx permissions for all users is highlighted. As you can see on the image above, two other directories by default have rwx permission for the owner, xr for the group and x for other users.
How to Verify Directories
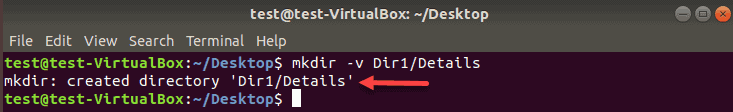
When executing mkdir commands, there is no feedback for successful operations. To see the details of the mkdir process, append the -v option to the terminal command.
Let’s create a Details directory inside Dir1 and print the operation status:
By getting the feedback from the process, you do not have to run the ls command to verify the directory was created.
mkdir Command Options and Syntax Summary
| Option / Syntax | Description |
|---|---|
| mkdir directory_name | Creates a directory in the current location |
| mkdir | Creates multiple directories in the current location. Do not use spaces inside <> |
| mkdir –p directory/path/newdir | Creates a directory structure with the missing parent directories (if any) |
| mkdir –m777 directory_name | Creates a directory and sets full read, write, execute permissions for all users |
| mkdir –v directory_name(s) | Creates a directory in the current location |
Note: Learn to fully manage directories by learning to move a directory in a system running a Linux distribution.
This guide covered all commands you need to create directories in Linux.
Now you understand how to use the Linux mkdir command. It’s straightforward and simple to use.
If you have the necessary permissions, there should be no error messages when you follow the instructions in this article.