- Как разбить файл на части Linux
- Синтаксис и опции split
- Как разбить файл на части Linux
- 1. Разбить по размеру
- 2. Разбить по количеству строк
- 4. Настройка имени частей файла
- Как объединить части файла
- Выводы
- How do I split a file into parts in Linux
- How to split files by size in Linux:
- How to split files by content in Linux using csplit:
- How to combine or join files back:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- David Adams
Как разбить файл на части Linux
В некоторых случаях один файл нужно разбить на несколько частей, например, для более удобного хранения или для загрузки в случае слишком большого размера. Проще всего это сделать с помощью утилиты split в терминале Linux.
В данной статье мы расскажем о том, как работает команда split Linux. А затем разберемся с конкретными сценариями использования, например, как разбить файл на части Linux по определенным критериям. А затем рассмотрим как объединить обратно получившиеся части.
Синтаксис и опции split
Данная команда разбивает один большой файл на несколько маленьких. У неё достаточно понятный синтаксис. Для запуска следует указать опции, путь к большому файлу и путь создания новых файлов с общим префиксом имени:
$ split опции /местоположение/исходного/файла /путь/к/конечной/папке/префикс_имени
- -a, —suffix-length – задать длину суффикса (количество символов) в имени части файла. По умолчанию это 2 символа.
- —additional-suffix – указать дополнительный суффикс.
- -b, —bytes – разбить файл на части равного указанного размера. Единица измерения – 1 байт, 1000 байт записывается как KB, 1024 как K. По аналогии есть MB (M), GB (G) и так далее.
- -C, —line-bytes – разбить файл на части не более указанного размера, не разделяя строки/записи внутри него.
- -d – использовать числовой суффикс в имени конечного файла вместо алфавитного. Отсчет начинается с нуля.
- —numeric-suffixes – то же самое, что и -d, но еще задаётся начальное число для отсчета.
- -x – использовать hex-префикс вместо алфавитного. Начальное значение – 0.
- —hex-suffixes – то же самое, что и -x, но начальное значение задаётся вручную.
- -e, —elide-empty-files – не создавать пустые файлы при выполнении опции -n.
- -l, —lines – установить максимальное количество строк/записей итогового файла. По умолчанию команда split разбивает файл на 1000 строк.
- -n, —number – разбить файл на чанки (указанное количество частей).
- -t, —separator – установить свой разделительный символ вместо новой строки.
- —verbose – выводить информацию о новых файлах перед их созданием.
- —version – посмотреть версию утилиты.
В список включены не все опции. Чтобы посмотреть полную информацию, выполните в терминале команду:
Как разбить файл на части Linux
Теперь перейдем к практической части статьи и на конкретных примерах посмотрим, как используется команда split Linux для разбивания файлов по размеру, по количеству строк и на заданное количество частей. Заодно мы упомянем нюансы выбора имени для частей файла.
1. Разбить по размеру
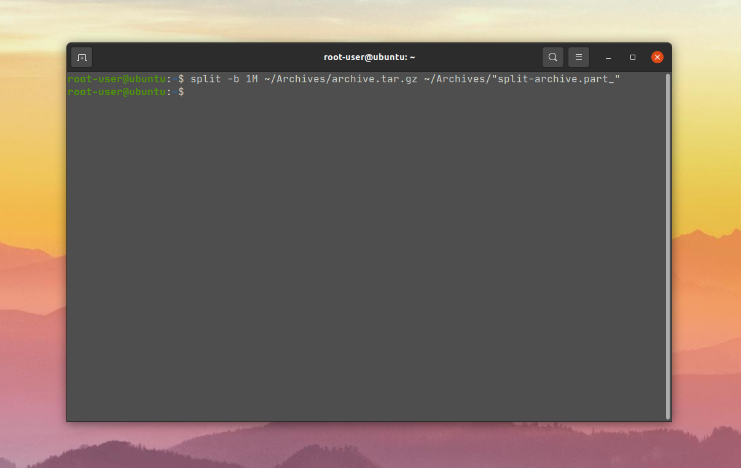
В данном случае поможет опция -b, определяющая максимальный размер конечного файла. За основу возьмем архив в 5.3 Мб, который находится по пути ~/Archives/archive.tar.gz. Его нужно разбить на несколько файлов по 1 Мб, например, чтобы потом переслать по почте. Для удобства зададим ему префикс имени split-archive.part_, а после нижнего подчеркивания будет идти суффикс, обозначающий номер конечного файла. Команда выглядит следующим образом:
split -b 10M ~/Archives/archive.tar.gz ~/Archives/split-archive.part_
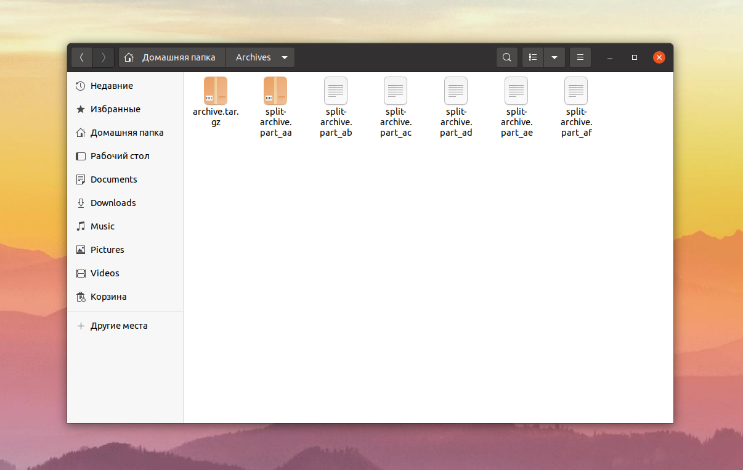
Вот как будет выглядеть конечная папка:
Помимо самого архива, в ней есть еще 6 файлов. Вы можете пропустить ввод конечного местоположения и префикса. Тогда файлы автоматически создадутся в текущей папке.
2. Разбить по количеству строк
Иногда нужно разбить один текстовый документ на несколько, например, с количеством строк не больше установленного числа. В этом вопросе полезной окажется опция -l. Команда для разбития будет выглядеть следующим образом:
split -l 1000 ~/Logs/log ~/Logs/Split/divided-log_
Возьмем большой log-файл с данными на 219 тысяч строк. Для более удобной работы его нужно разбить на документы по 10 тысяч строк в каждом и поместить во вложенный каталог.
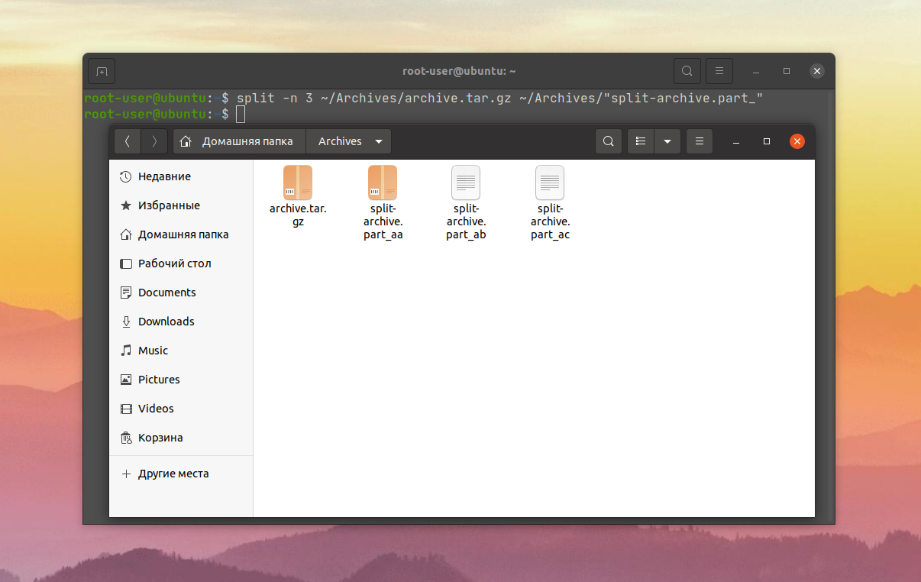
Еще одна достаточно интересная задача, в решении которой поможет опция -n. Достаточно прописать для неё итоговое количество файлов и запустить команду:
split -n 3 ~/Archives/archive.tar.gz ~/Archives/archive/split-archive.part_
Вот как это выглядит для рассмотренного ранее архива:
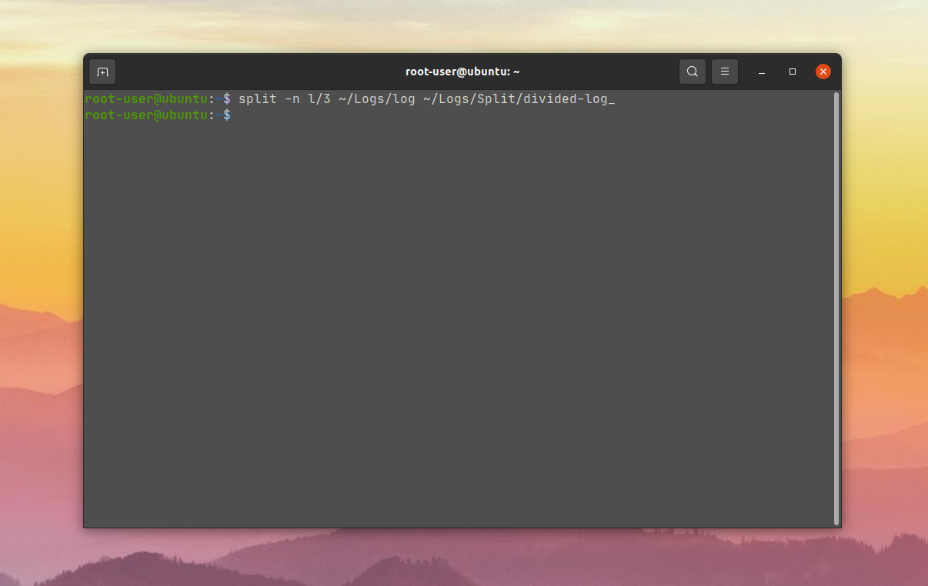
Если вы хотите разбить файл на несколько частей, не разделяя строки/записи внутри него, то понадобится модификатор l. Например, для того чтобы разбить файл на три части выполните такую команду:
split -n l/3 ~/Logs/Log ~/Logs/Split/divided-log_
4. Настройка имени частей файла
Как мы уже писали ранее, для команды split префикс определяет название части файла. А после него по умолчанию идет суффикс из двух латинских букв. С помощью дополнительных опций можно изменить его длину (опция -a), переключиться на числа (опция -d) или hex-символы (опция -x). В последних двух сценариях получится выбрать начальную точку отчета (опция —numeric-suffixes для чисел и —hex-suffixes для hex-символов).
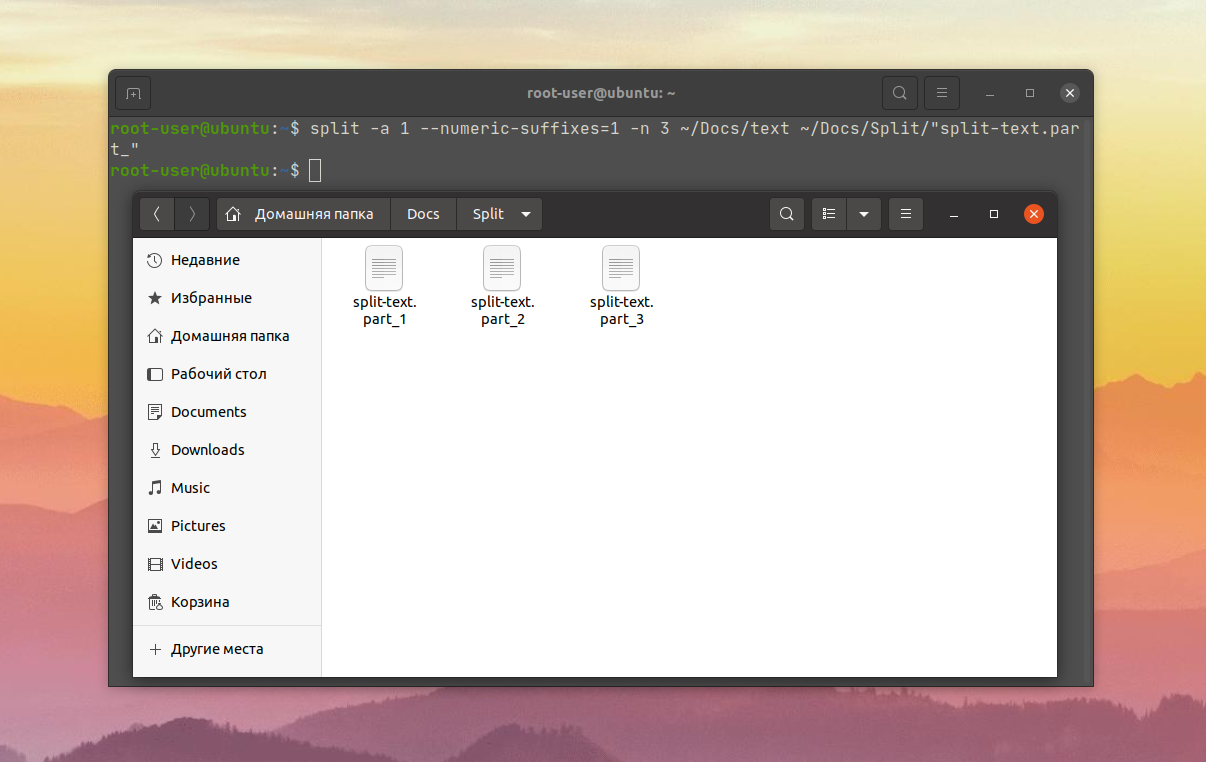
Возьмем такую задачу – разделить текстовый документ на 3 файла равного размера, чтобы каждый из них имел префикс split-text.part_ и числовой суффикс из одного символа, начиная с единицы:
split -a 1 —numeric-suffixes=1 -n 3 ~/Docs/text ~/Docs/Split/split-text.part_
Как объединить части файла
Теперь вы знаете как разбить файл на части в Linux с помощью команды split. Следующий шаг – объединение нескольких частей в единый файл. Для этих целей отлично подойдет утилита cat. Сначала нужно задать имена самых частей, а потом итоговый файл:
$ cat /путь/к/1/части /путь/ко/2/части … > /местоположение/объединенного/файла
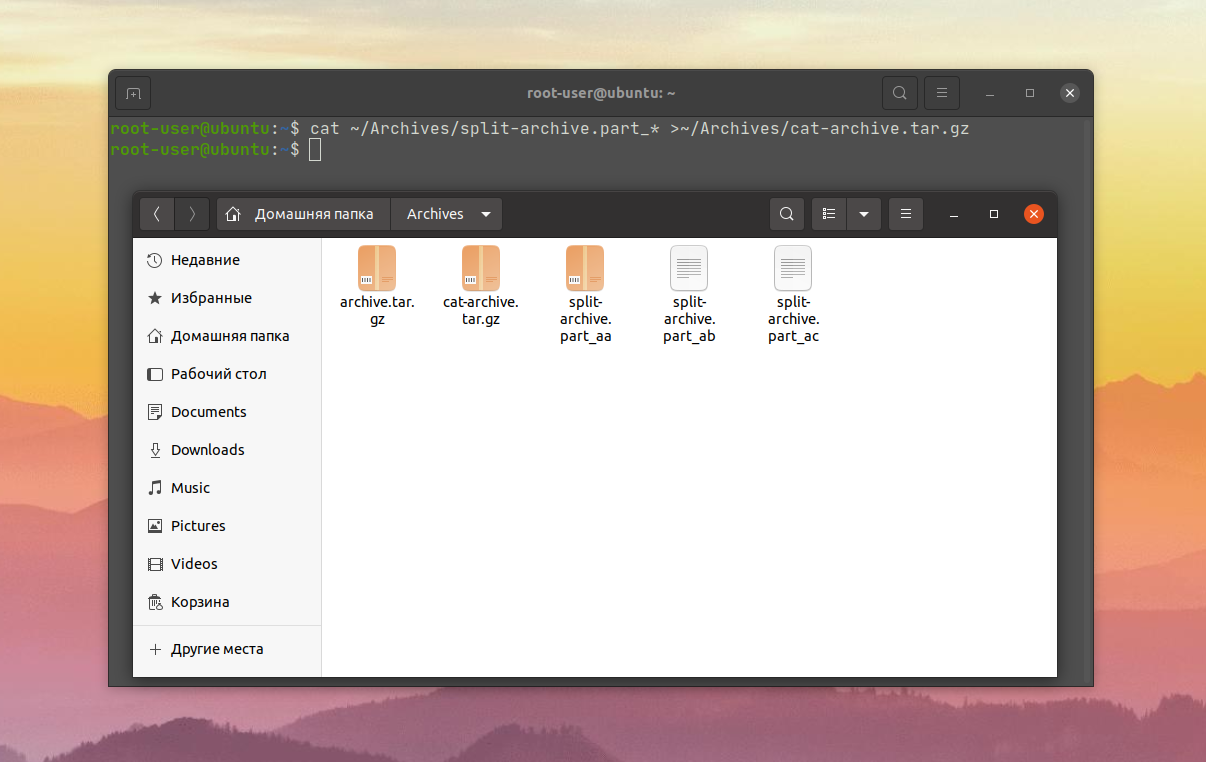
Поскольку все части имеют схожее имя, и различается только суффикс, можно упростить команду до такого вида:
cat ~/Archive/split-archive.part_* > ~/Archives/cat-archive.tar.gz
Рассмотрим объединение ранее разбитого на части архива.
Выводы
Утилита split в некоторых ситуациях окажется очень полезной. Она позволяет разбить один большой файл на несколько маленьких, указав при этом определенные критерии разделения. Мы рассмотрели несколько популярных сценариев для её использования. Но на деле их гораздо больше. Разбитый файл можно объединить, например, с помощью утилиты cat. Мы упомянули ее ближе к концу статьи.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How do I split a file into parts in Linux
This tutorial explains how to split files into parts in Linux by size easily, several files, content, and more options. After reading this article, you’ll know how to split files using both the split and csplit commands and how to combine or join file pieces back.
How to split files by size in Linux:
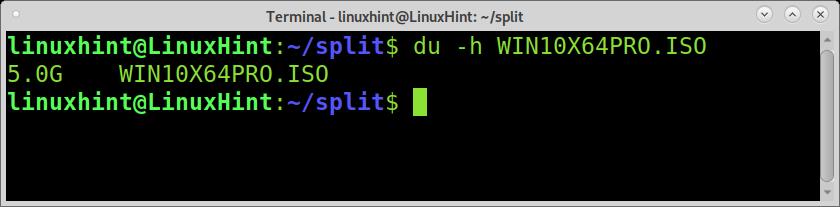
For the first example of this tutorial, I will use a 5GB Windows ISO image named WIN10X64.ISO. To learn the file size you want to split, you can use the du -h command, as shown in the screenshot below.
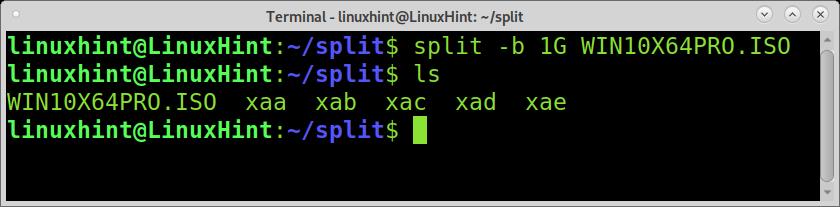
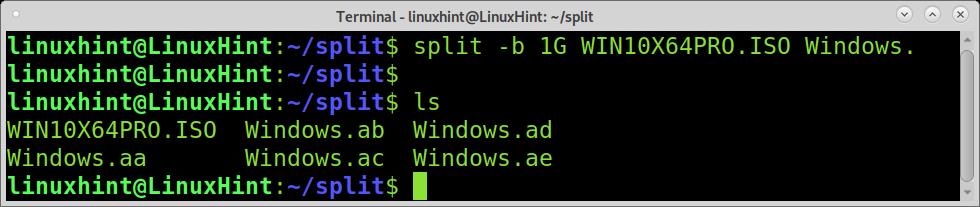
As you can see, the file size is 5GB. To split it into 5 files of 1GB each, you can use the split command followed by the -b flag and the splitted files size you want. The G defining the size unit for GB can be replaced by M for megabytes or B for bytes.
As you can see, the ISO was splitted into 5 files named xaa, xab, xac, xad, and xae.
By default, the split command names generated files in the previous example, where xaa is the first part, xab the second part, xac the third, etc. As shown in the example below, you can change this and define a name, leaving the default name as an extension.
As you can see, all files are named Windows.* , the extension of the name given by the split command, which allows us to know the order of the files.
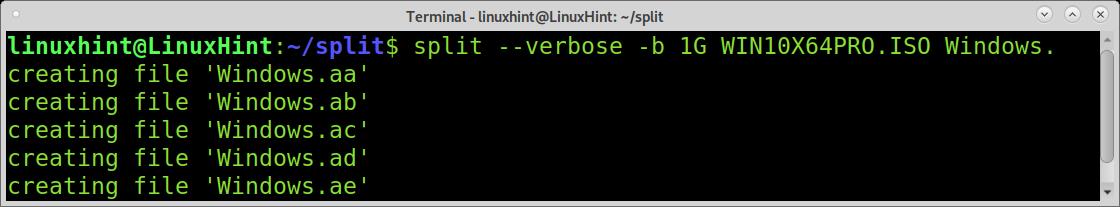
When using the split command, you can implement verbosity for the command to print the progress, as shown in the following screenshot.
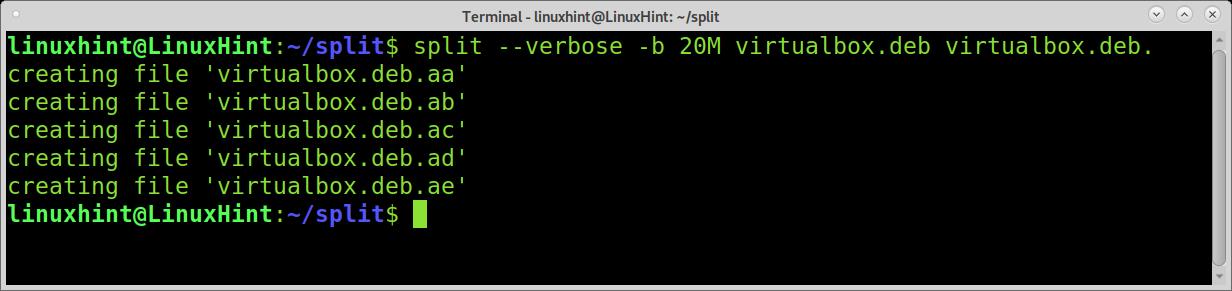
As you can see, the progress output shows the phase of file division. The next example shows how to split the files into MB units. The file is an 85MB file.
The split command includes additional interesting features which aren’t explained in this tutorial. You can get additional information on the split command at https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/split.1.html.
How to split files by content in Linux using csplit:
In some cases, users may want to split files based on their content. For such situations, the previously explained split command isn’t useful. The alternative to achieve this is the csplit command.
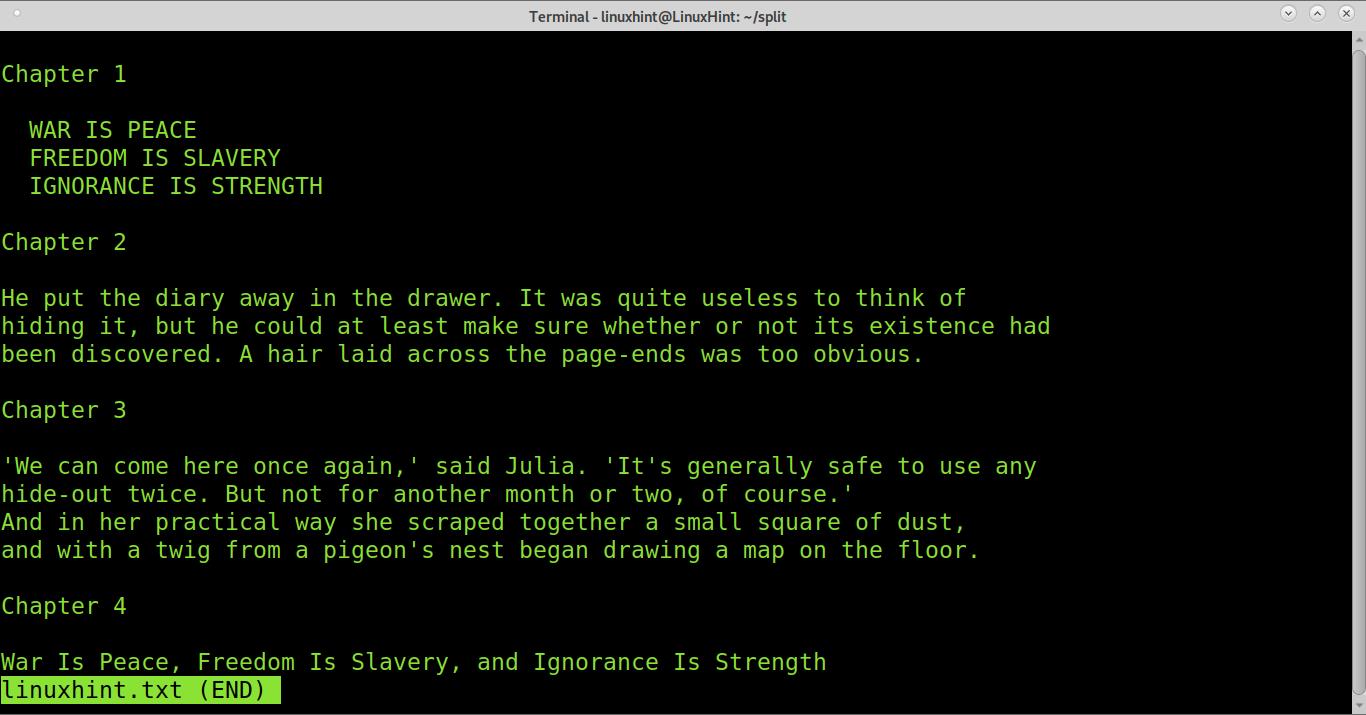
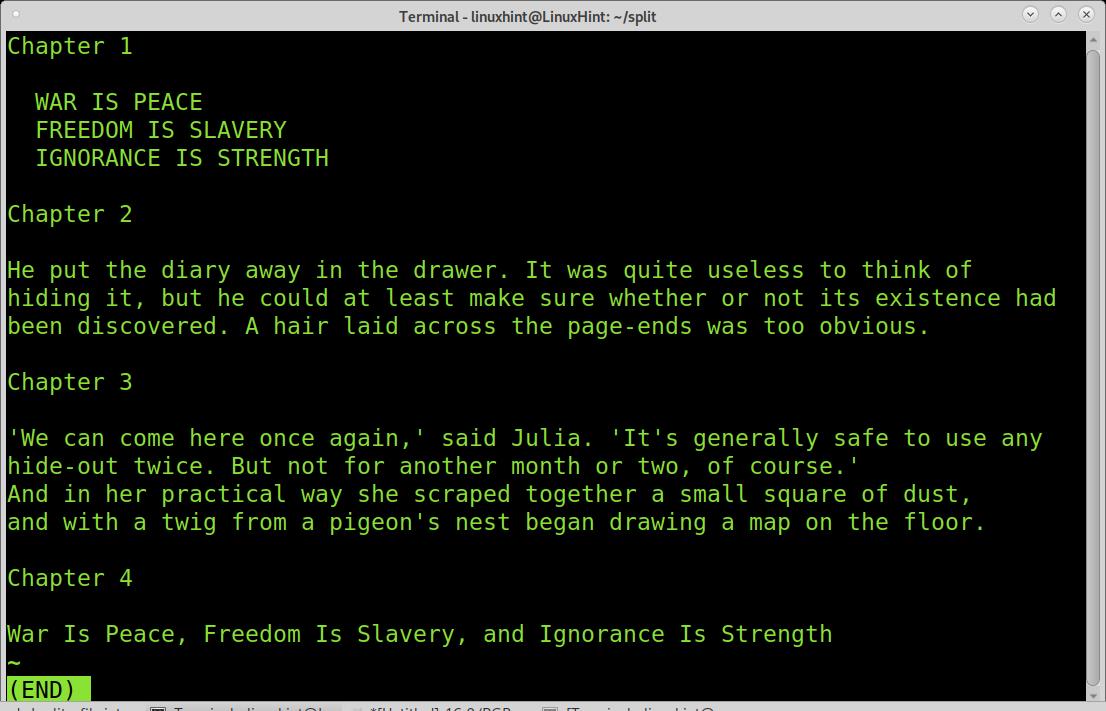
In this tutorial section, you’ll learn how to split a file every time a specific regular expression is found. We will use a book, and we will divide it into chapters.
As you can see in the image below, we have 4 chapters (they were edited to allow you to see the chapter divisions). Let’s say you want each chapter into a different file. For this, the regular expression we’ll use is “Chapter“.
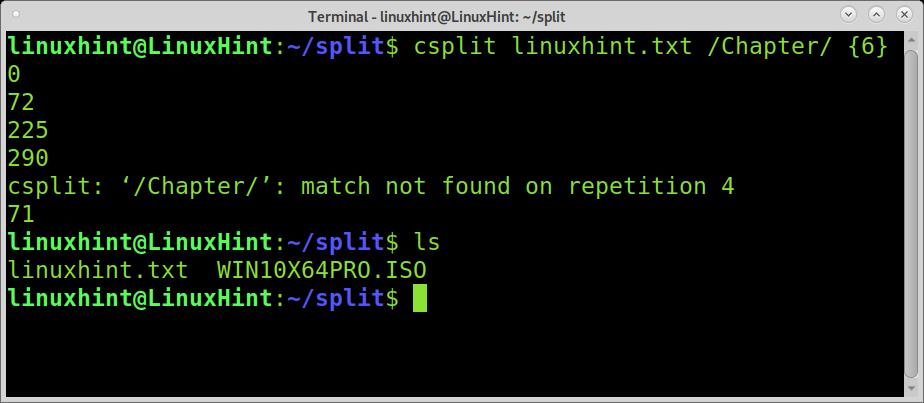
I know there are 4 Chapters in this book, so we need to specify the number of splits we want to prevent errors. In the examples below, I explain how to split without knowing the number of regular expressions or splits. But in this case, we know there are 4 chapters; thus, we need to split the file 3 times.
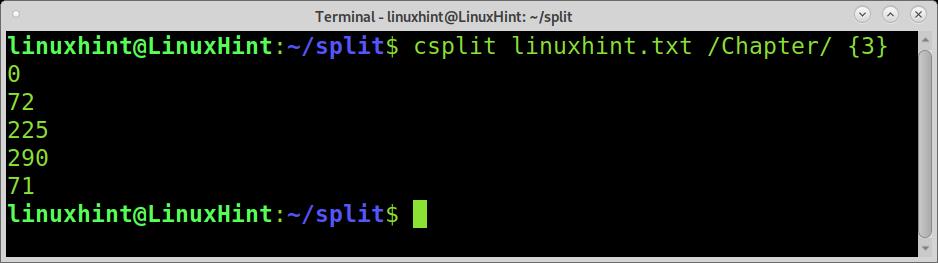
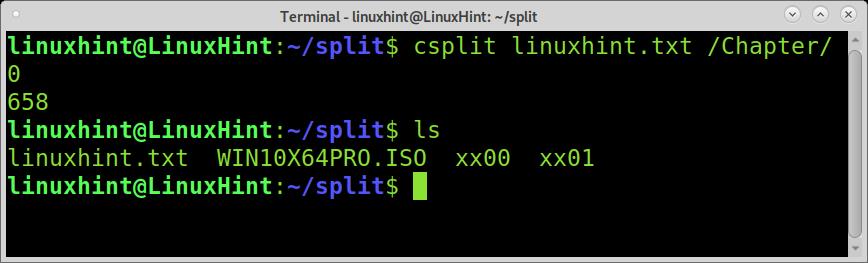
Run csplit followed by the file you want the split, the regular expression between slashes, and the number of splits between braces, as shown in the example below.
The output we see is the bytes count for each file piece.
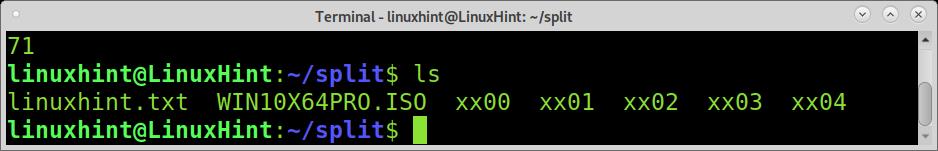
As you can see, 5 files were created, the empty space before Chapter 1 was also divided.
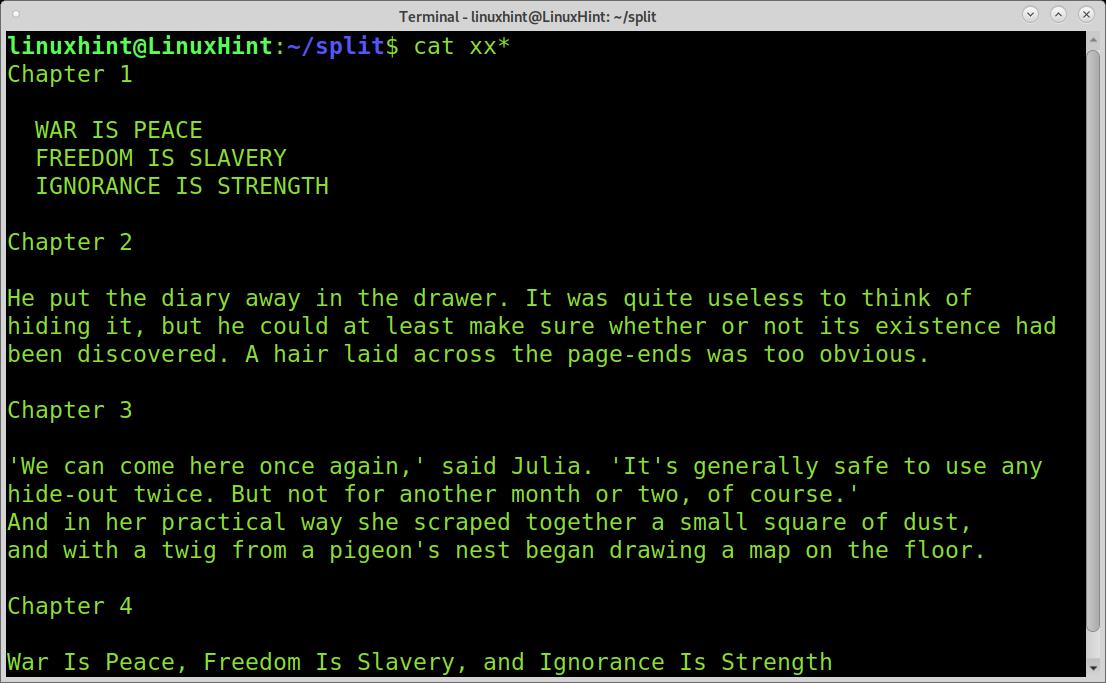
The files are named as when using the previously explained split command. Let’s see how they were divided.
The first file, xx00 is empty, it is the empty space before the first time the “Chapter” regular expression appears, and the file gets splitted.
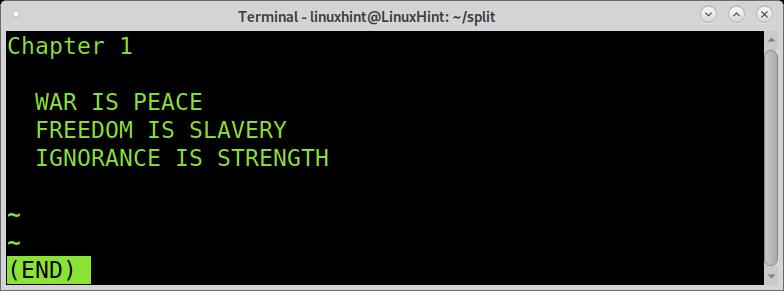
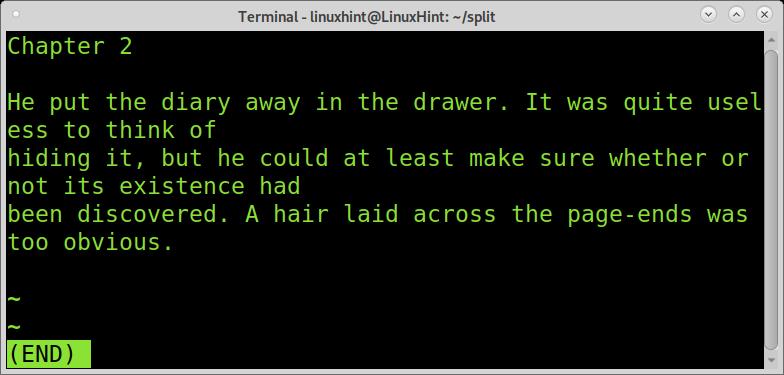
The second piece shows only the first chapter correctly.
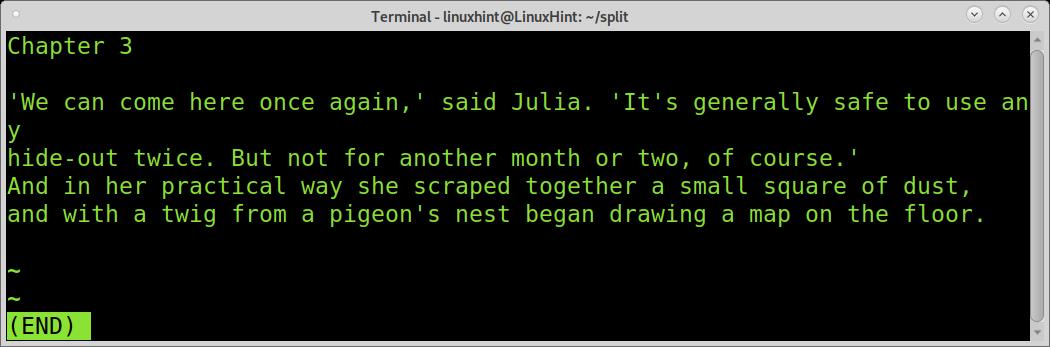
The third piece shows chapter 2.
The fourth piece shows chapter three.
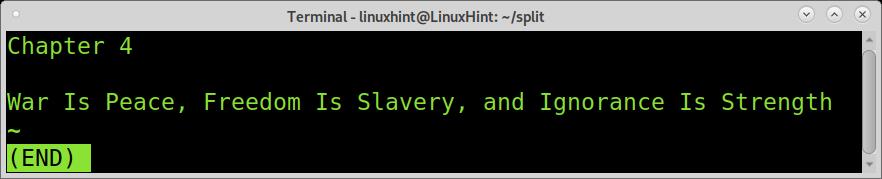
And the last piece shows chapter 4.
As explained previously, the number of regular expressions was specified to prevent a wrong result. By default, if we don’t specify the number of splits, csplit will only cut the file one time.
The following example shows the execution of the previous command without specifying the number of splits.
As you can see, only one split and two files were produced because we didn’t specify the number of splits.
Also, if you type a wrong number of splits, for example, 6 splits with only 4 regular expressions, you’ll get an error, and no split will occur, as shown in the example below.
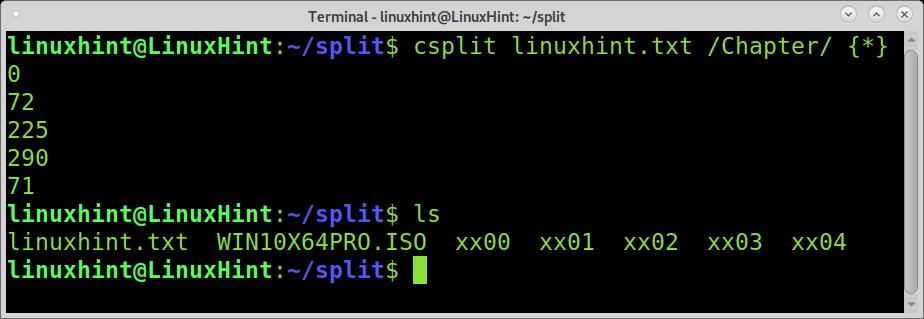
So what to do when the content is too long, and you don’t know how many regular expressions to split you have in the content?. In such a situation, we need to implement the wildcard.
The wildcard will produce many pieces as regular expressions found in the document without the need for you to specify them.
As you can see, the file was splitted properly.
The csplit command includes additional interesting features which aren’t explained in this tutorial. You can get additional information on the split command at https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/csplit.1.html.
How to combine or join files back:
Now you know how to split files based on size or content. The next step is to combine or join files back. An easy task using the cat command.
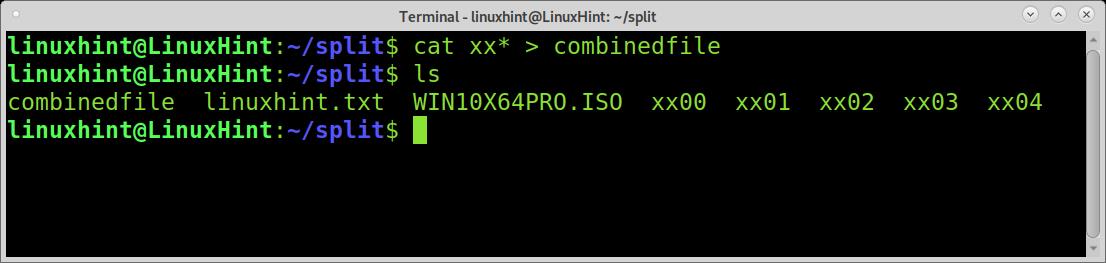
As you can see below, if we read all file’s pieces using cat and the wildcard, the cat command will order them by the alphabetical order of their names.
As you can see, cats are capable of ordering the files properly. Joining or merging the files consists of exporting this result; you can do it as shown in the example below, where the combinedfile is the name for the combined file.
As you can see in the following picture, the file was properly merged.
Conclusion:
As you can see, splitting files into parts in Linux is pretty easy, and you only need to be aware of what is the proper tool for your task. It is worthwhile for any Linux user to learn these commands and their advantages, for example, when sharing files through an unstable connection or through channels limiting file size. Both tools have many additional features that weren’t explained in this tutorial, and you can read on their man pages.
I hope this tutorial explaining how to split a file into parts in Linux was useful. Keep following this site for more Linux tips and tutorials.
About the author
David Adams
David Adams is a System Admin and writer that is focused on open source technologies, security software, and computer systems.