- slapt-src Command Examples in Linux
- slapt-src Command Examples
- Summary
- Some more articles you might also be interested in …
- How to Create Hard and Soft (symlink) Links on Linux Systems
- Soft-link :
- Hard Link :
- Symbolic Link :
- Creating Hard Link
- Creating Soft Link:
- Removing Soft Link / Symbolic Links
- 3 thoughts on “How to Create Hard and Soft (symlink) Links on Linux Systems”
- Leave a Comment Cancel reply
- Recent Posts
- Pages
slapt-src Command Examples in Linux
slapt-src is a command-line tool that helps automate the building and installation of SlackBuilds in Slackware Linux. SlackBuilds are scripts that automate the process of building a package from source code. While they are powerful tools, SlackBuilds can be time-consuming to set up and maintain, especially when working with many packages or dependencies.
slapt-src automates this process by fetching the source code, configuring the build, and building the package. It is similar to slapt-get, which manages pre-built binary packages, but slapt-src works with source packages instead. By using slapt-src, Slackware users can easily install, update, and manage software packages that are not included in the official repositories.
To use slapt-src, you need to configure the sources in the slapt-srcrc configuration file. This file contains information about the sources, including the URLs of the source repositories, the versions of the source code, and the build options. You can edit the slapt-srcrc file using a text editor like nano or vi.
slapt-src Command Examples
1. Update the list of available slackbuilds and versions:
2. List all available slackbuilds:
3. Fetch, build and install the specified slackbuild(s):
4. Locate slackbuilds by their name or description:
5. Display information about a slackbuild:
Summary
In summary, slapt-src is a powerful tool that can automate the process of building and installing SlackBuild packages in Slackware Linux. By using slapt-src, Slackware users can easily manage software packages that are not available in the official repositories, without having to manually configure and build each package themselves.
Some more articles you might also be interested in …
How to Create Hard and Soft (symlink) Links on Linux Systems
Many a times in any Linux/Unix based Operating Systems it is wise to understand the underlying concepts then only one can appreciate the beauty of commands and how they are implemented.
Some small details will help us a lot in debugging and troubleshooting many challenging situations if we know well in advance about these commands and related concepts.

In this topic, I will be covering what are links, different types, distinguishing characters and how they can be better used along with concepts required.

By executing “man ln” command you can see that this says “make link between files” and doesn’t say about soft or hard links.
Similarly the command “man link” describes as “call link function to create a file”.
Soft-link :
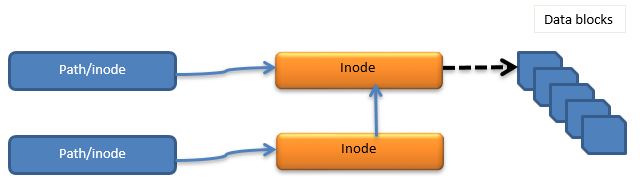
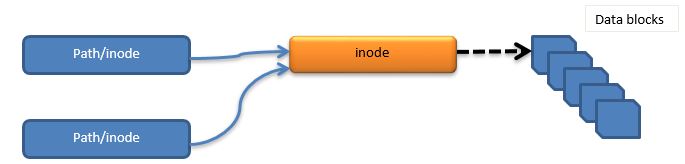
Soft link as the name suggests is a just a new link created to the new file. In this case the new file’s inode number will be pointing to the old file.
Hard Link :
In this case the old and new file both will be pointing to same inode number.
Symbolic Link :
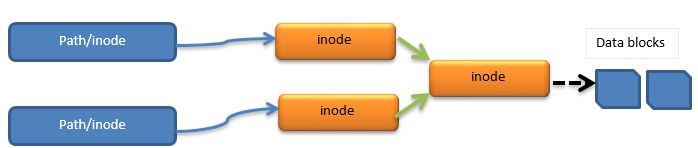
In some Unix/Linux flavors both the symbolic and soft links are treated as same. But actual difference is that both the inode numbers of new and old file will be pointing to a new inode number. This will be completely depending on the implementation.
Note 1 :- In many cases symbolic and soft link terminologies are used interchangeably. But one has to be aware of when to use what.
Usage of “ln” command for creating hard links and soft links
Creating Hard Link
1) “man ln” command will provide the following output.
[email protected] ~>$ man ln ln - make links between files
2) When “ln” command is passed without any arguments, “missing file operand” error is thrown.
[email protected] ~>$ln ln: missing file operand Try 'ln --help' for more information.
3) Creating the hard link between two files. First check for any existing files if any, else create the file/files freshly and then link them. Following is the step-by-step approach,
[email protected] ~>$ ls -la total 24 drwx------ 4 root root 4096 Feb 6 15:23 . drwxr-xr-x 23 root root 4096 Jan 25 16:39 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3122 Jan 25 16:41 .bashrc drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Feb 6 15:23 .cache -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 25 16:41 .hushlogin -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 148 Aug 17 2015 .profile drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 25 16:41 .ssh
i) Create the file using “touch” command
[email protected] ~>$ touch 123.txt [email protected] ~>$ ls -l total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 6 15:51 123.txt
ii) Enter contents into the file using “cat” command, and hit “ctrl+c” to save and exit.
[email protected] ~>$ cat > 123.txt Welcome to this World! ^C
iii) Create the hard link between the files “123.txt” and “321.txt”. In this case the “123.txt” already existed with contents “Welcome to this World”.
[email protected] ~>$ ln 123.txt 321.txt [email protected] ~>$ ls -l total 8 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 123.txt -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 321.txt
iv) Check the inode(index node) numbers of the files. For both the files the inode number is same and which is 794583. Also check the contents of new file “321.txt” which is also same as “123.txt”.
[email protected] ~>$ ls -li total 8 794583 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 123.txt 794583 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 321.txt $ cat 321.txt Welcome to this World!
Note 2 :- Inode number is a unique index number generated for any file that is being created in Linux/unix Operating systems. These inode numbers are stored in directory/file attributes in /proc directory. But in case of links these inode numbers are shared b/w the files and only path is updated in file table.
v) Create one more file called “456.txt” and link this using ln command to “321.txt”. Now all the three files have the same inode numbers. Contents of “456.txt” will be as same as that of original file.
[email protected] ~>$ ls -li total 12 794583 -rw-r--r-- 3 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 123.txt 794583 -rw-r--r-- 3 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 321.txt 794583 -rw-r--r-- 3 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 456.txt $ cat 456.txt Welcome to this World! [email protected] ~>$ ls -l total 12 -rw-r--r-- 3 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 123.txt -rw-r--r-- 3 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 321.txt -rw-r--r-- 3 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 456.txt
vi) When the source file or any of these files are removed, it will not impact other files. The source file can be removed using “rm” command. Contents of other file will not have any impact either.
[email protected] ~>$ rm 123.txt [email protected] ~>$ ls -l total 8 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 321.txt -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 456.txt [email protected] ~>$ ls -li total 8 794583 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 321.txt 794583 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 456.txt [email protected] ~>$ cat 456.txt Welcome to this World!
vii) Hard link creation across directories is not allowed.
[email protected] ~>$ls -l total 8 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 321.txt -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 23 Feb 6 15:52 456.txt [email protected] ~>$ mkdir abc [email protected] ~>$ ln abc def ln: abc: hard link not allowed for directory
viii) Any changes to the content of one file will impact and change the content of other file accordingly, following are the steps explained,
[email protected] ~>$ vi 321.txt Welcome to this World! You are welcomed to this new world :wq [email protected] ~>$ ls -l total 12 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 59 Feb 6 16:24 321.txt -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 59 Feb 6 16:24 456.txt drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Feb 6 16:18 abc [email protected] ~>$ cat 456.txt Welcome to this World! You are welcomed to this new world
Creating Soft Link:
1) Create the file “src.txt” using “touch” command and enter contents as “Hello World” using cat command and then hit “ctrl+c” to save and exit.
[email protected] ~>$ touch src.txt [email protected] ~>$ cat > src.txt Hello World ^C [email protected] ~>$ ls -l total 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 12 Feb 6 16:32 src.txt
2) Create the destination file as “dst.txt” and using “ln -s” command line options create the symbolic link (also called as soft link). Check the contents of “dst.txt” file and same contents as that of “src.txt” can be seen.
[email protected] ~>$ ln -s src.txt dst.txt [email protected] ~>$ ls -l total 4 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Feb 6 16:33 dst.txt -> src.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 12 Feb 6 16:32 src.txt [email protected] ~>$ cat dst.txt Hello World
3) In case of symbolic links the inode number of source file and destination file differs. Also, in the permissions letter “l” appears indicating that these are links. “dst.txt–>src.txt” will be the new link established now.
[email protected] ~>$ ls -li total 4 794584 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Feb 6 16:33 dst.txt -> src.txt 794583 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 12 Feb 6 16:32 src.txt
4) Symbolic creation for directories is allowed. This is explained as below in the steps
[email protected] ~>$ mkdir abc [email protected] ~>$ ln -s abc def $ ls -l total 8 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Feb 6 16:34 abc lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 3 Feb 6 16:34 def -> abc lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Feb 6 16:33 dst.txt -> src.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 12 Feb 6 16:32 src.txt
5) Inode number for all the files/directories (source and destination are different)
[email protected] ~>$ ls -li total 8 794585 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Feb 6 16:34 abc 794586 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 3 Feb 6 16:34 def -> abc 794584 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Feb 6 16:33 dst.txt -> src.txt 794583 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 12 Feb 6 16:32 src.txt
6) Symbolic links can be created for directories as explained earlier. Once these directories with symbolic link are created, inside these directories files can be created. This will make it more interesting to know how this behaves now. When the files are created in the source directory, the same is reflected in destination directory as well. The following steps explains this clearly.
[email protected] ~>$ $ cd abc [email protected] ~>$ touch 123.txt [email protected] ~>$ vi 123.txt Hello :wq! [email protected] ~>$ touch 456.txt [email protected] ~>$ cd .. [email protected] ~>$ ls -l total 8 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Feb 6 16:36 abc lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 3 Feb 6 16:34 def -> abc lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Feb 6 16:33 dst.txt -> src.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 12 Feb 6 16:32 src.txt [email protected] ~>$ cd def [email protected] ~>$ ls -l total 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6 Feb 6 16:37 123.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 6 16:36 456.txt [email protected] ~>$ cat 123.txt Hello
Note 3 :- We can have any number of nested links. But the user/admin who creates these symbolic links should be aware of the fact that these will lead to confusion. Sometimes may be forgotten and may create unwanted results. So they have to be careful.
Note 4 :- There are some possibilities of “symbolic” or “soft” link pointing to a non-existing link. This is called as “Dangling link”. This will be pointing to no-where.
Note 5 :- there are system calls used in linux/unix to create symbolic OR hard links at programming level (using system level C/C++ programs). These are 1) symlink 2) symlinkat.
These should not be confused with command line utilities that I have described above.
Removing Soft Link / Symbolic Links
Soft or symbolic links are removed using the ‘rm’ and unlink commands.
Removing Soft Link directories
Conclusions:
Creating links whether hard or soft will be very helpful for admins and developers. The above reference material will come handy while understanding what type of link we are creating and how it is helpful. Also this article will help in understanding the differences and utilization of links.
3 thoughts on “How to Create Hard and Soft (symlink) Links on Linux Systems”
Hi,
Very detailed article.
There is an advice to add procedure to remove hard/soft links as well, for the sake of completeness of your article. Reply
Hi Ahmer, We have added the commands that are are used for removing the soft link files and directories. Reply
Hi, Nice article, but lacks description about permissions of files for symlinked folder. Could permissions of symlinked folder files could be changed, how to do that if possible? Reply
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Recent Posts
- How to Install PHP 8 on RHEL 8 / Rocky Linux 8 / CentOS 8
- How to Install and Use Wireshark in Ubuntu 22.04
- Top 10 Things to Do After Installing Debian 12 (Bookworm)
- How to Install Debian 12 (Bookworm) Step-by-Step
- How to Upgrade Debian 11 to Debian 12 (Bookworm) via CLI
- How to Setup Dynamic NFS Provisioning in Kubernetes Cluster
- How to Install Nagios on Rocky Linux 9 / Alma Linux 9
- How to Install Ansible AWX on Kubernetes Cluster
- How to Install Docker on Fedora 38/37 Step-by-Step
- How to Setup High Availability Apache (HTTP) Cluster on RHEL 9/8