- Смена порта SSH
- Как изменить порт SSH?
- How to Change the Default SSH Port in Linux [Properly and Safely]
- Why change the default SSH port?
- Allow traffic on the new port by changing the firewall settings
- Changing the default SSH port
- How to Change SSH Port in Ubuntu 18.04
- Change SSH Port on Ubuntu 20.04 Linux System — Best Method ?
- How to Change SSH Port on Ubuntu OS ?
- [Need assistance in fixing Missing Software Installation packages on Debian System? We can help you . ]
- Conclusion
Смена порта SSH
Удалённое администрирование Linux, как правило, осуществляется при помощи SSH (Secure Shell) — сетевого протокола прикладного уровня, позволяющего производить туннелирование TCP-соединений. Вышедший в 1995-м году SSH широко используется и в наши дни. С помощью этого протокола, помимо администрирования операционной системы с помощью командной оболочки, можно выполнять файловые операции и монтировать удалённые файловые системы.
SSH-сервер по умолчанию работает с использованием 22-го TCP-порта. Иногда бывают ситуации когда необходимо изменить этот порт. Например, для превентивной защиты от bruteforce-атак, направленных именно на 22-й порт, или для освобождения этого порта, занятого другим приложением. В этом случае можно изменить порт SSH на любой другой свободный TCP-порт.
Как изменить порт SSH?
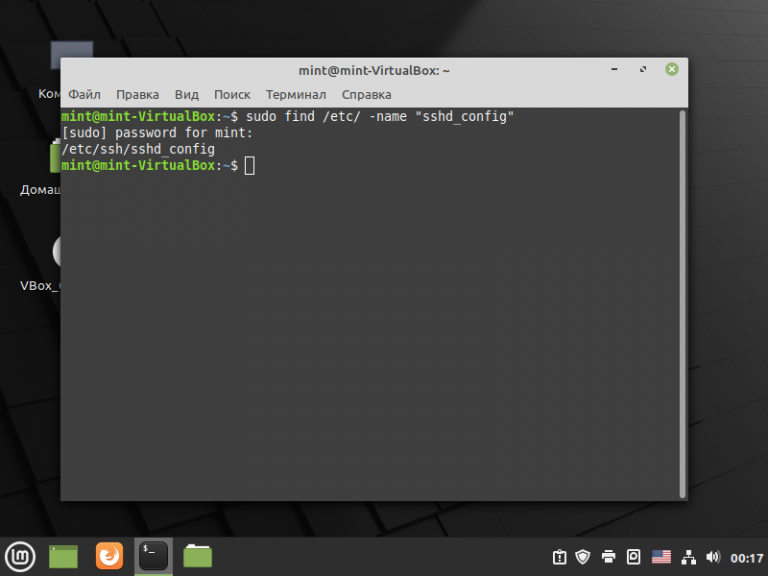
В большинстве разновидностей Linux конфигурационный файл SSH-сервера располагается по пути /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Тем не менее, можно воспользоваться и поиском для того, чтобы узнать наверняка. Воспользуйтесь командой:
sudo find /etc/ -name «sshd_config»
В данном случае файл там, где и должен быть. Откройте в текстовом редакторе файл sshd_config:
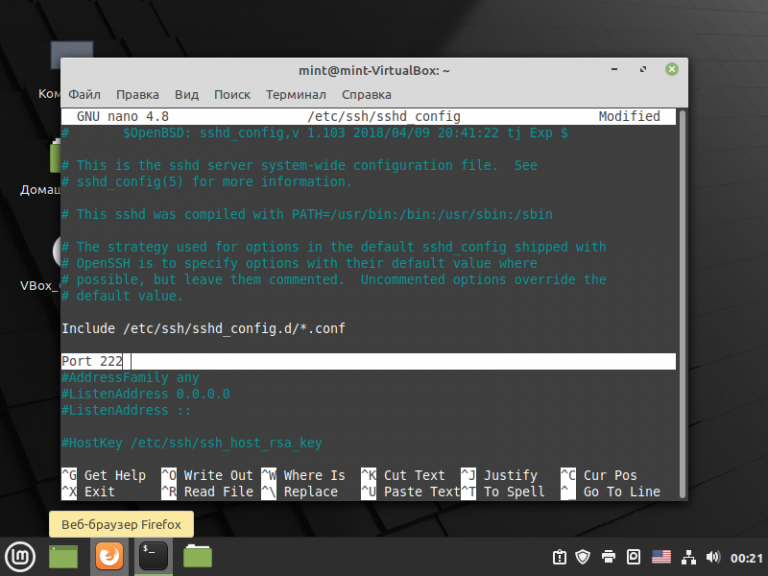
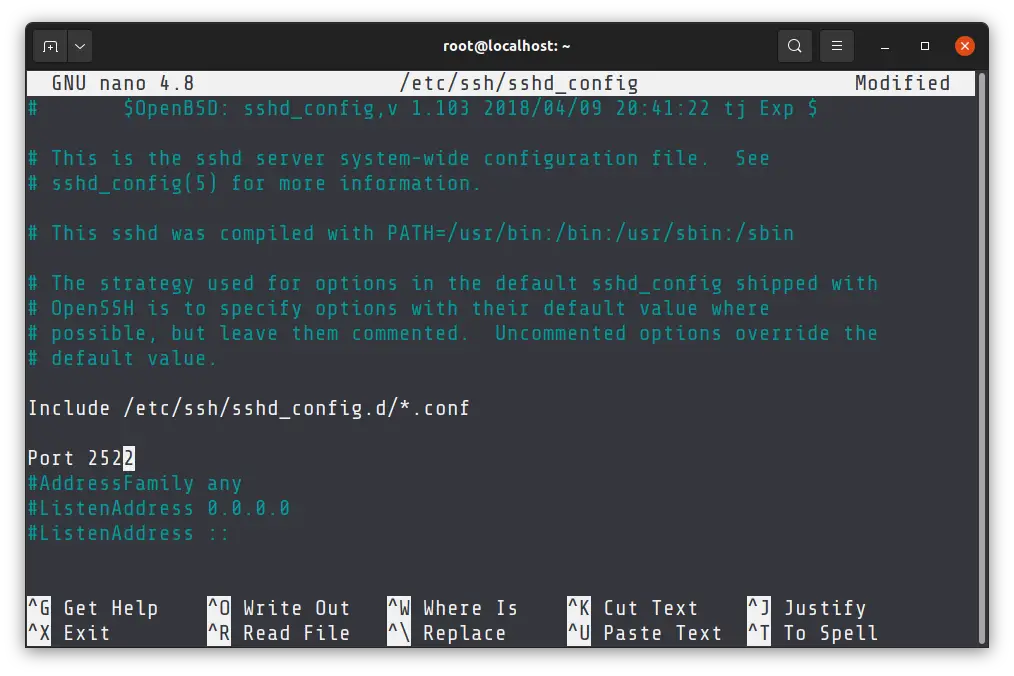
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Найдите строку Port 22 и измените значение (в нашем примере на Port 222). Возможно в вашем конфигурационном файле эта строка будет закомментирована, то есть выглядит вот так — #Port 22.
В этом случае нужно убрать символ # и выполнить действия, описанные выше:
Сохраните файл. Далее следует перезапустить демон SSH. Выполните команду:
sudo systemctl restart sshd
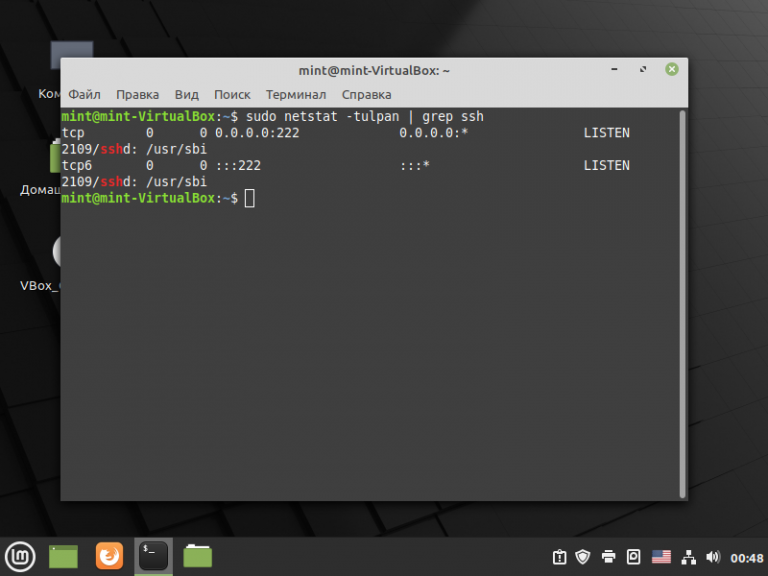
Для того, чтобы проверить прошла ли удачно смена порта SSH сервера, выполните следующую команду:
sudo netstat -tupln | grep ssh
Будут показаны открытые порты SSH на вашем компьютере:
Строка tcp 0.0.0.0:222 LISTEN говорит о том, что 222-й порт, который назначенный для SSH-демона, успешно используется. В SSH-клиентах, подключаемых к вашему компьютеру, нужно будет изменить порт по умолчанию на назначенный SSH-серверу.
Если на вашем компьютере работает файрвол, не забудьте добавить в его исключения новый порт, назначенный SSH-серверу. Если вы изначально работаете удалённо по SSH-протоколу, сделать это нужно ещё до того, как вы перезапустите демон SSH на сервере, к которому подключены.
Если у вас в качестве файрвола установлен UFV, выполните команду:
Для тех, кто использует iptables, необходимо разрешить новый порт с помощью команды:
sudo /sbin/iptables -A INPUT -m state —state NEW -m tcp -p tcp —dport 222 -j ACCEPT
В операционных системах, использующих firewalld, выполните такую команду:
sudo firewall-cmd —permanent —add-port=222/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd reload
Здесь порт 222 — это порт SSH, назначенный мною для примера. Теперь вы знаете как поменять порт SSH чтобы его не трогали боты. А какие методы защиты от ботов используете вы? Напишите в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to Change the Default SSH Port in Linux [Properly and Safely]
Changing the default SSH port is one of the several ways to enhance SSH server security. Learn how to do it properly and safely.
If you are aware of the SSH basics, you already know that SSH uses port 22 by default.
When you connect to a server via SSH, most of the time you don’t provide any port information. And in such cases, your connection goes to the port 22 of the SSH server.
You can change the default port from 22 a port number of your choice using the following steps:
- Open the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file for editing.
- Locate the line that has Port 22 (if it is commented out with #, remove the # as well).
- Change the line to Port 2522 (or any number of your choice between 1024 and 65535).
- Make sure that the new port is allowed by the firewalls (if you have any).
- Restart ssh daemon with sudo systemctl restart sshd .
- From now onwards, you’ll have to specify the port to make the ssh connection ssh [email protected]_address_of_server -p 2522 .
Let me show you the steps in details and also tell you why you may consider changing the
Why change the default SSH port?
One of the most elementary tricks for securing SSH server is to change the default SSH port number 22.
Why? Because a number of bot scripts try the brute force attacks on the default port 22. Most of these scripts don’t always scan for open ports, and they target the default ports for various known services like SSH.
Changing the default SSH port reduces number of such attacks. There are other ways to improve the security of your SSH server. If interested, please follow these actionable tips for improving SSH server security.
Now that you know why you would change the default SSH port, let’s see how to do it.
Allow traffic on the new port by changing the firewall settings
If you have a firewall set or custom ipconfig or ifconfig or if you are using SELinux, you must allow the new ssh port before making the changes. Otherwise you may lock yourself out without an SSH access.
Now this part depends upon what kind of firewall or routing you are using.
If you are using UFW, you can use the following command to allow port 2522:
If you are using iptables, you should use this command:
sudo iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 2522 -j ACCEPTOn Fedora, CentOS, Red Hat, the firewall is managed by firewalld and you can use this command:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=2522/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --reloadOn CentOS and Red Hat, you may also have to change the SELinux rules:
sudo semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 2522Now that you have put the correct firewall settings, let’s move on to changing the SSH port.
Changing the default SSH port
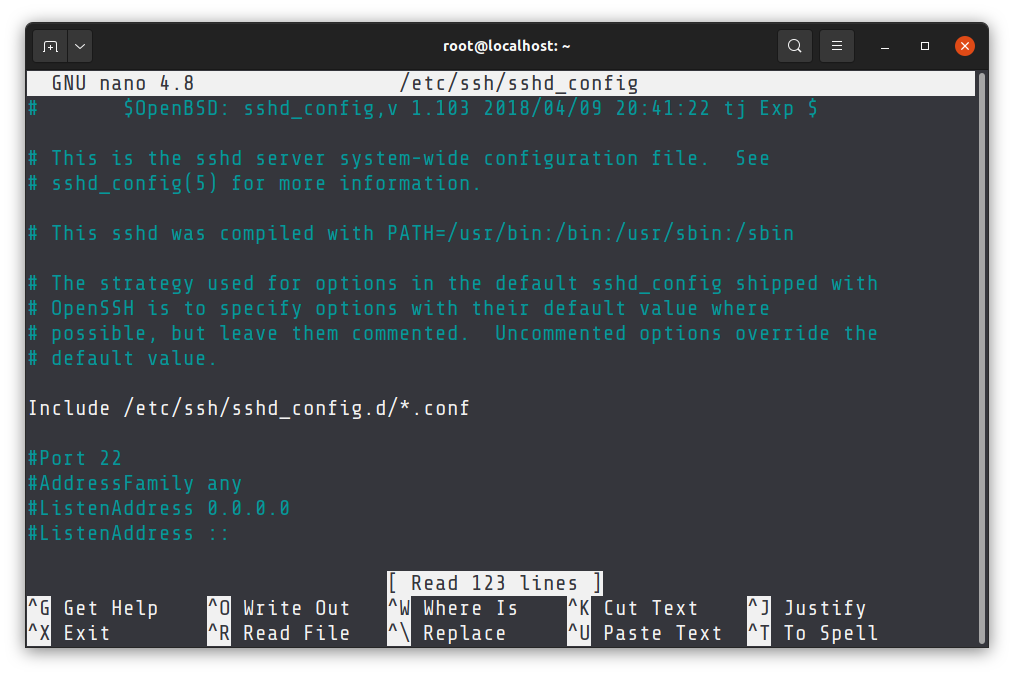
Usually, the ssh configuration file is located at /etc/ssh/sshd_config . You’ll have to use a terminal-based editor like Vim or Nano or Emacs to edit the file.
Distributions like Ubuntu have Nano installed by default so you can use it for opening the file in edit mode like this:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_configAs you can see, you’ll have to be a sudo user or root to edit the ssh configuration.
Scroll down a bit and you’ll see a line with Port 22 . If it starts with # , it means the line is commented out. The commented out lines gives you the default settings.
So if you see # Port 22 , it means that default port is 22.
Change this line with a port number of your choice. In Linux, port number 0-1023 are usually reserved for various services. It will be good to avoid using anything between 0 and 1023 to avoid conflicts.
You can use any other port number between 1024 and 65535. I am using 2522 in the example. Make sure to remove the # before the Port line.
Save your changes and exit the editor. If you are using Nano, use Ctrl+X to save and exit.
The next step is to restart the ssh service. Most modern system use systemd services so you can use the following command:
sudo systemctl restart sshdNow if you want to access the SSH server, you’ll have to specify the port number:
ssh [email protected]_address_of_server -p 2522Was it helpful?
I hope you find this tutorial helpful in changing the SSH port. Now that you have changed the port, you’ll have to use it all the time you want to connect to the server via SSH and that could be annoying.
This is why I recommend using SSH config file to save the settings for easy and quick access.
How to Change SSH Port in Ubuntu 18.04
This tutorial explains how to configure Ubuntu OpenSSH server to run on some specific port number rather than the default port number 22, in order to increase the overall security of your Ubuntu server.
The SSH server on Ubuntu listen on TCP port 22 by default. You can run the netstat command to check ssh port currently running on:
As you can see, the SSH daemon is currently running on TCP port 22.
In Ubuntu 18.04, the Port directive of the sshd_config config file specifies the port number that ssh server listens on. You can check the current configuration with following command:
grep -i port /etc/ssh/sshd_configThe Port directive is commented out by default, which means SSH daemon listens on the default port 22.
If you want to change the default SSH port in Ubuntu, perform the following steps with root privileges:
- Open the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file and locate the line:
After that, run the netstat command and make sure that the ssh daemon now listen on the new ssh port:
When connecting to the server using the ssh command, you need to specify the port to connect using the -p flag:
Note that if the Firewall is enabled, you need to add a rule to allow new SSH port.
Change SSH Port on Ubuntu 20.04 Linux System — Best Method ?
By default, SSH protocol is known to listen to port 22. While it’s perfectly OK, in a security sense, it’s recommended to change the default port to another port. This greatly minimizes the risks of hackers launching automated brute-force attacks using SSH.
Here at LinuxAPT , as part of our Server Management Services , we regularly help our Customers to perform related System SSH queries.
In this context, we shall look into how you can change the default SSH port to something else on Ubuntu Linux System.
How to Change SSH Port on Ubuntu OS ?
To begin, Ensure that you also have an SSH client ( such as Putty ) or even a client Linux system to set the connection to the server using the new port. Then with a sudo privileged user follow the steps below.
1. Check if SSH is running on the default port
Firstly, we need to verify that the SSH service is running on the server. To accomplish this, run the following command:
$ sudo systemctl status ssh The output is a confirmation that the SSH service is active. Let’s even go further and ensure that it is running on the default port. Run the following netstat command:
$ sudo netstat -pnltu | grep 22 2. Select a port and configure SSH
As you might know, TCP ports range from port 0 – 65535. However, the ports from 0 – 1024 are regarded as privileged ports designated for special services such as HTTP ( Port 80 ), FTP ( 21 ), and SMTP ( 25 ) to mention just a few.
To avoid any conflict with privileged ports, we are going to pick a port that’s above port 1024. In this example, we have chosen to change the default port to port 5466. To enable this, we will modify the /etc/ssh/sshd_config SSH configuration file:
$ sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config Locate the line that starts with #Port 22 .
Then, Uncomment and specify the port number.
Thereafter, save the changes made and exit the configuration file. For the changes to persist, restart the SSH service:
$ sudo systemctl restart ssh To verify that SSH is listening to the newly configured port, run:
$ sudo netstat -pnltu | grep 5466 3. Allow the new SSH port on the UFW firewall
If the UFW firewall is enabled, be sure to open the configured port as shown below:
$ sudo ufw allow 5466/tcp
$ sudo ufw reload For CentOS / RHEL, open the port as follows:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=5466/tcp --add-zone=public --permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload At this point, you can remotely access the server.
4. Logging in using the new port
To log in to the server, head over to the SSH client. Specify the port number using the -p option followed by the SSH port and the remote server identity:
$ ssh -p 5466 linuxapt@192.168.2.101 As expected, you will be prompted to provide the password after which you will be granted access to the remote server.
[Need assistance in fixing Missing Software Installation packages on Debian System? We can help you . ]
Conclusion
This article covers how to change the ssh port on Ubuntu Linux server. You can easily change the SSH Port for Your Linux server. For better security, consider using SSH passwordless authentication with SSH public/private key pair.
The ssh port defined in sshd_config file. This file located in /etc/ssh/sshd_config location.
To open the new port run the following commands on Fedora/CentOS/RHEL/Oracle Linux using FirewallD:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=2222/tcp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload How to Restart the sshd service ?
Type the following command on a CentOS/RHEL/Fedora Linux:
$ sudo service sshd restart OR if you are using CentOS/RHEL/Fedora Linux with systemd:
$ sudo systemctl restart sshd OR if you are using Ubuntu/Debian/Mint Linux:
OR if you are using Ubuntu/Debian/Mint Linux with systemd:
$ sudo systemctl restart ssh Or if you are using FreeBSD Unix, enter:
$ sudo service sshd restart