- How to start, restart & stop Apache & MySQL server on Ubuntu
- Start Apache on Ubuntu Linux
- Stop Apache server on Ubuntu Linux
- Restart Apache server on Ubuntu Linux
- Stop MySQL on Ubuntu Linux
- Start MySQL on Ubuntu Linux
- Restart MySQL on Ubuntu Linux
- How to Start/Stop and Restart Apache Server Commands
- Start/Stop/Restart Apache Web Server on Ubuntu/Debian Linux
- Commands for Debian Linux version 7.x or Ubuntu Linux version Ubuntu 14.10 or older
- Commands for Debian Linux version 8.x+ or Ubuntu Linux version Ubuntu 15.04+ or above
- Start/Stop/Restart Apache Web Server on CentOS/RHEL
- Commands for CentOS/RHEL version 4.x/5.x/6.x or older
- Commands for CentOS/RHEL version 7.x or newer
- start/stop/restart Apache webserver with Generic Method
- Conclusion
- Recent Posts
- How to Start, Stop, and Restart Nginx (systemctl & Nginx Commands)
- Start, Stop, and Restart Nginx with systemctl
- How to View Status of Your Nginx Server
- Stop and Start Nginx
- How to Restart Nginx
- Gracefully Restart Nginx
- Force Restart Nginx
- Restart vs Reload Nginx
- Configure Nginx to Launch on Boot
- Start, Stop, and Reload Nginx with the Nginx Command
- Nginx Start
- Nginx Restart
- Nginx Stop
- Nginx Reload
- Nginx Quit
How to start, restart & stop Apache & MySQL server on Ubuntu
The Apache web server is the light and most popular open source web server use worldwide on Linux based operating system. It can be installed on Ubuntu with a single command to handle both dynamic and static content web pages. Most of the WordPress and other popular CMS uses it as a Web server.
Furthermore, when you want to create some online application or website then you also need a database software to store all your content and here the MySQL comes in. It is also an open source database system software that can install on any Linux operating system with ease. If you are new to both then you can look at our tutorial which let you know how to install Apache, MySQL, and PHP on Ubuntu Linux.
The below-given commands will work on all Ubuntu and Debian based Linux operating systems no matter where they are, it could be on your local PC system or a hosting or cloud services like AWS, DigitalOcean, google cloud and more..
Start Apache on Ubuntu Linux
The command to start the Apache web server on Ubuntu is:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 start or sudo service apache2 start
Stop Apache server on Ubuntu Linux
Command on the terminal to stop the web server Apache2
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 stop OR sudo service apache2 stop
Restart Apache server on Ubuntu Linux
Commands to execute on Ubuntu terminal to restart the Apache web server.
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart OR sudo service apache2 restart
If you are using the Ubuntu 15.04 or above then you can also use the below commands to start/restart and stop the Apache web server.
To start Apache systemctl start apache2.service To stop Apache systemctl stop apache2.service To Restart Apache systemctl restart apache2.service
For start/Stop and restart the MySQL server on Ubuntu use the below mentioned commands:
Stop MySQL on Ubuntu Linux
Terminal commands to stop MySQL
sudo stop mysql or sudo service mysql stop or sudo /etc/inid.d/mysql stop
Start MySQL on Ubuntu Linux
Use any of one given below to start the MySQL, if it in a stop state.
sudo start mysql or sudo service mysql start or sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start
Restart MySQL on Ubuntu Linux
To restart the MySQL Ubuntu Linux server use the commands in terminal.
sudo restart mysql or sudo service mysql restart or sudo /etc/init.d/mysql restart
How to Start/Stop and Restart Apache Server Commands
The Apache web server is an open-source web application that can be used for deploying dynamic websites and web-based applications. It is fast, secure, stable, reliable and one of the most widely-used web server in the world.
It can be run on Linux and Windows operating systems.
There are several ways to start, stop and restart Apache web server in various Linux-based operating systems.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to start, stop and restart Apache webserver on Debian, Ubuntu and CentOS operating system.
Start/Stop/Restart Apache Web Server on Ubuntu/Debian Linux
There are different commands to start, stop and restart Apache webserver on a different version of Ubuntu/Debian operating system.
Commands for Debian Linux version 7.x or Ubuntu Linux version Ubuntu 14.10 or older
You can start the Apache webserver with the following command:
You can restart the Apache webserver with the following command:
You can stop the Apache webserver with the following command:
You can also check the status of Apache webserver whether it is running or not with the following command:
Commands for Debian Linux version 8.x+ or Ubuntu Linux version Ubuntu 15.04+ or above
Debian version 8.x+ and Ubuntu version 15.04+ uses systemd to start, stop and restart Apache web server.
To start the Apache webserver run the following command:
To restart the Apache webserver run the following command:
systemctl restart apache2
To stop the Apache webserver run the following command:
To check the status of Apache webserver run the following command:
Start/Stop/Restart Apache Web Server on CentOS/RHEL
There are different commands to start, stop and restart Apache webserver on a different version of CentOS/RHEL operating system.
Commands for CentOS/RHEL version 4.x/5.x/6.x or older
To start the Apache webserver run the following command:
To restart the Apache webserver run the following command:
To stop the Apache webserver run the following command:
To check the status of the Apache webserver run the following command:
Commands for CentOS/RHEL version 7.x or newer
To start the Apache webserver run the following command:
To restart the Apache webserver run the following command:
To stop the Apache webserver run the following command:
To check the status of the Apache webserver run the following command:
start/stop/restart Apache webserver with Generic Method
You can start the Apache webserver on CentOS/RHEL operating system by running the following command:
apachectl -f /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
You can start the Apache webserver on Ubuntu/Debian operating system by running the following command:
apachectl -f /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
You can restart the Apache webserver on Ubuntu, Debian, RHEL and CentOS operating system by running the following command:
You can stop the Apache webserver on Ubuntu, Debian, RHEL and CentOS operating system by running the following command:
Conclusion
In the above tutorial, we learned how to start, stop and restart Apache webserver on different Unix-based operating systems. I hope you have now enough knowledge to manage Apache web service.
Recent Posts
- Forcepoint Next-Gen Firewall Review & Alternatives
- 7 Best JMX Monitoring Tools
- Best PostgreSQL Backup Tools
- Best CSPM Tools
- Best Cloud Workload Security Platforms
- Best Automated Browser Testing Tools
- Event Log Forwarding Guide
- Best LogMeIn Alternatives
- Citrix ShareFile Alternatives
- SQL Server Security Basics
- Cloud Security Posture Management Guide
- Cloud Workload Security Guide
- The Best JBoss Monitoring Tools
- ITL Guide And Tools
- 10 Best Enterprise Password Management Solutions
How to Start, Stop, and Restart Nginx (systemctl & Nginx Commands)
Nginx is a powerful server application that routes network traffic. It’s often used as a reverse proxy server, but can also be configured as a regular web server.
One of the most common operations you will encounter is starting, stopping, and restarting the Nginx web server.
In this tutorial, learn how to start, stop, and restart the Nginx service.
- A system with Nginx installed and configured
- Access to a terminal window or command line
- A user account with sudo or root privileges
- An existing SSH connection to a remote system (if you’re working remotely)
Note: If you haven’t installed Nginx yet, refer to our guides on Installing Nginx on Ubuntu or Installing Nginx on CentOS 8.
Start, Stop, and Restart Nginx with systemctl
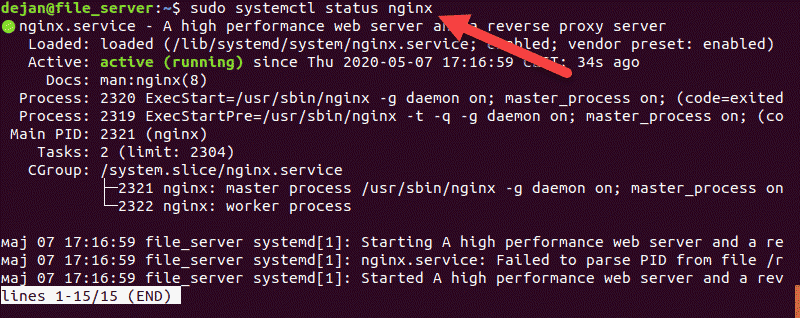
How to View Status of Your Nginx Server
Nginx runs as a service on your server. That means that it should be actively running in the background, even if you don’t see anything on the screen. You can display the status of the Nginx service by entering the following command in a terminal window:
sudo systemctl status nginxThe system will switch into a status mode, displaying lots of information about the Nginx service.
- If the service is running (active), you’ll see a green active (running) status in the third line.
- If Nginx is not running, it will display as inactive in standard white.
- If something went wrong and Nginx couldn’t load, you’ll see a red status failed, with some information about the failure.
Press q to reactivate the bash prompt.
SystemD is the default service manager on modern versions of Linux distributions (Ubuntu 20.04/18.04/16.04, CentOS 7/7, and Debian 9/10). The SystemD manager functions through the systemctl command.
The systemctl command is a base Linux command. That means that it can be used for any Linux service.
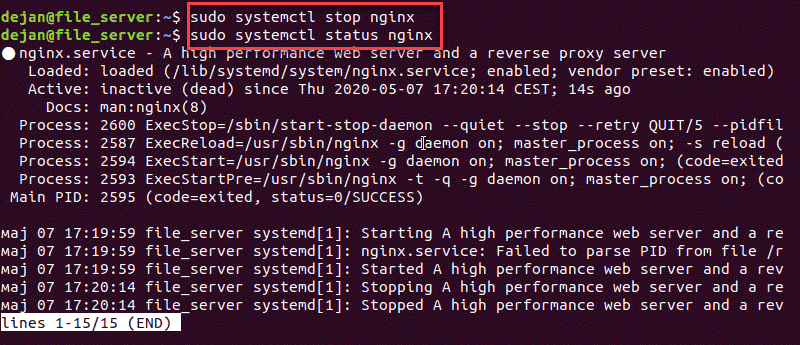
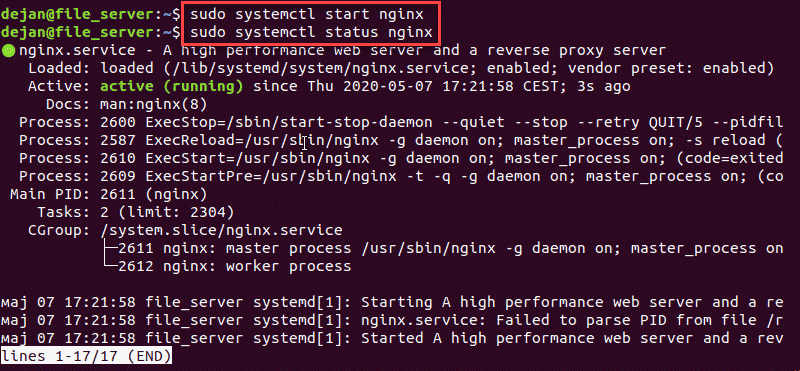
Stop and Start Nginx
systemctl can be used to start and stop the Nginx service.
To stop Nginx, run the following command:
sudo systemctl stop nginxTo start Nginx, execute the systemctl command with the start option:
sudo systemctl start nginxHow to Restart Nginx
Gracefully Restart Nginx
If you’re refreshing Nginx after changing the configuration, it’s best to gracefully reload the service. That shuts down old processes and restarts new ones with the new configuration.
Use the systemctl Linux command to reload the Nginx service. Run the following command:
sudo systemctl reload nginxNote: Nginx cannot be reloaded if the the Nginx service is not active.
Force Restart Nginx
For major configuration changes, you can force a full restart of Nginx. This force-closes the whole service and sub-processes, and restarts the whole package.
Enter the following command:
sudo systemctl restart nginxRestart vs Reload Nginx
The reload command keeps the Nginx server running as it reloads updated configuration files. If Nginx notices a syntax error in any of the configuration files, the reload is aborted and the server keeps running based on old config files. Reloading is safer than restarting Nginx.
The restart command will shut down the server including all related services and power it on again. Restart Nginx only when making significant configuration updates, such as changing ports or interfaces. This command will force shut down all worker processes.
Configure Nginx to Launch on Boot
Use the enable option with the systemctl command to enable Nginx:
sudo systemctl enable nginxUse the disable option with the systemctl command to disable Nginx:
sudo systemctl disable nginxStart, Stop, and Reload Nginx with the Nginx Command
Nginx has a set of built-in tools for managing the service that can be accessed using the Nginx command.
Nginx Start
To start Nginx and related processes, enter the following:
If run successfully, the terminal output will display the following:
Output [ ok ] Starting nginx (via systemctl): nginx.service.Nginx Restart
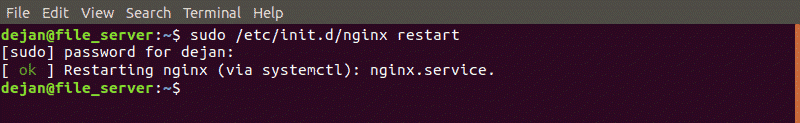
To force close and restart Nginx and related processes:
sudo /etc/init.d/nginx restartAs an alternative, use the nginx -s command:
Nginx Stop
To disable or stop the Nginx service, enter the following:
Nginx Reload
To gracefully stop and restart Nginx and related processes, use the command:
sudo /etc/init.d/nginx reloadAlternately, you can use the nginx -s command to pass instructions directly to Nginx:
Nginx Quit
Force close the Nginx service by using the quit instruction with the nginx -s command:
This article has outlined several methods to start, stop, and restart Nginx on your server. Use these commands for the most common operations when managing an Nginx web server.
Dejan is the Head of Content at phoenixNAP with over 8 years of experience in Web publishing and technical writing. Prior to joining PNAP, he was Chief Editor of several websites striving to advocate for emerging technologies. He is dedicated to simplifying complex notions and providing meaningful insight into data center and cloud technology.
In most modern Linux operating systems, managing a service is quite simple when it comes to basic commands.
Nginx (pronounced as «engine-x») is a Linux-based web server and reverse proxy application. Learn how to set it up as a reverse proxy.