- How to Configure Service to Start Automatically in Linux
- Configuring Services Autostart in Linux
- 1. List Services which are Started Automatically
- 2. Check Service Autostart State
- 3. Enable Autostart for Service
- 4. Disable Autostart for Service
- Configure Autostart for User’s Services
- Wrapping Up
- Use systemd to Start a Linux Service at Boot
- What is systemd?
- Create a Custom systemd Service
- Start and Enable the Service
- Troubleshooting
- More Information
- How to Auto-start Services on Boot in Linux?
- CentOS or RHEL 6.x
- RHEL or CentOS 7.x/8.x
- Ubuntu
How to Configure Service to Start Automatically in Linux
Service in the Linux operating system is just a program which is executing in the background and does not have any windows or other communication channels with a user interface. There are a lot of services which are working in the background. And most of them must be run on the system startup.
The Systemd initialization system handles all of this. It can help you to check which services are running at the moment, view their logs, configure autostart, and other things. In this article, I will explain how to configure the service to start automatically in Linux. I will use Ubuntu for all examples, but this tutorial will work in all distributions that use Systemd.
Configuring Services Autostart in Linux
As I said before, services are regular programs which are running in the background and are not connected to stdin and stdout streams. Each service in Systemd has its configuration file in the filesystem. You can read about this in more detail in previous article. In this article, I will cover only autostart of services.
Linux supports run levels since SysVInit initialization system. Each Run level determines which services must be started. Systemd supports run levels too. But here they exist as targets. Here is the list of supported run levels and targets that correspond to them:
- Run Level 0 (poweroff.target, runlevel0.target) — shut down the system;
- Run Level 1 (rescue.target runlevel1.target) — recovery mode;
- Run Level 3 (multi-user.target, runlevel3.target) — text-only mode;
- Run level 5 (graphical.target) — graphical environment;
- Run level 6 (reboot.target, runlevel6.target) — reboots the system.
When you add service to system startup, Systemd just creates a symbolic link to the service unit in the run level folder. The run level is specified in the service configuration file.
On the system startup, Systemd runs all services which are configured to start with multi-user.target and then graphical.target when it is a desktop system. On servers, Systemd runs only services for multi-user.target. Now, let’s have a look at how to deal with all of this in practice.
1. List Services which are Started Automatically
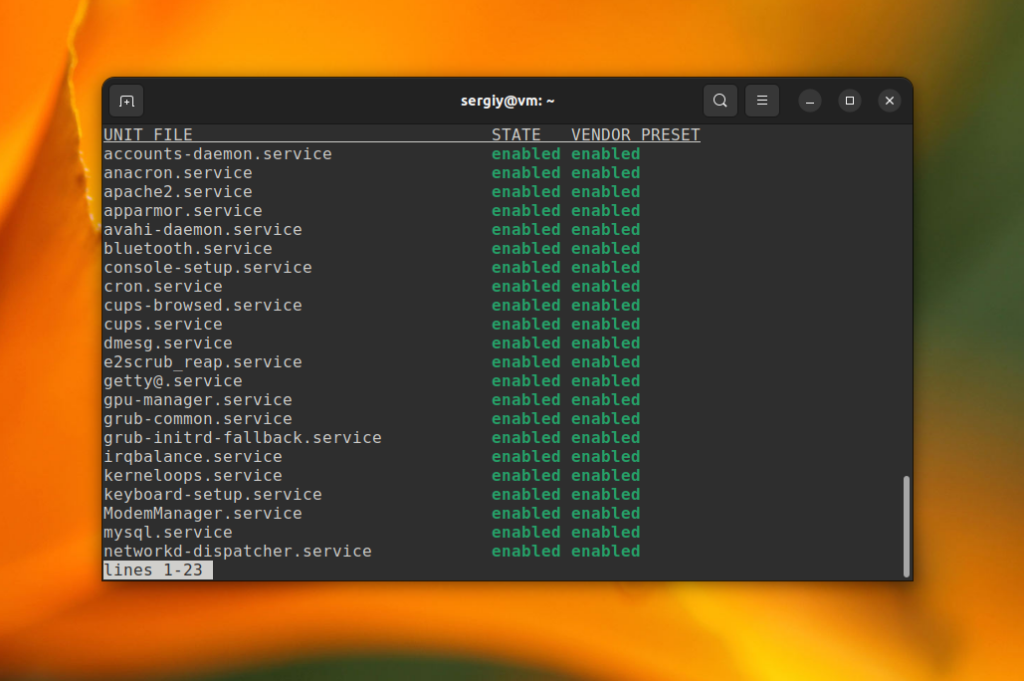
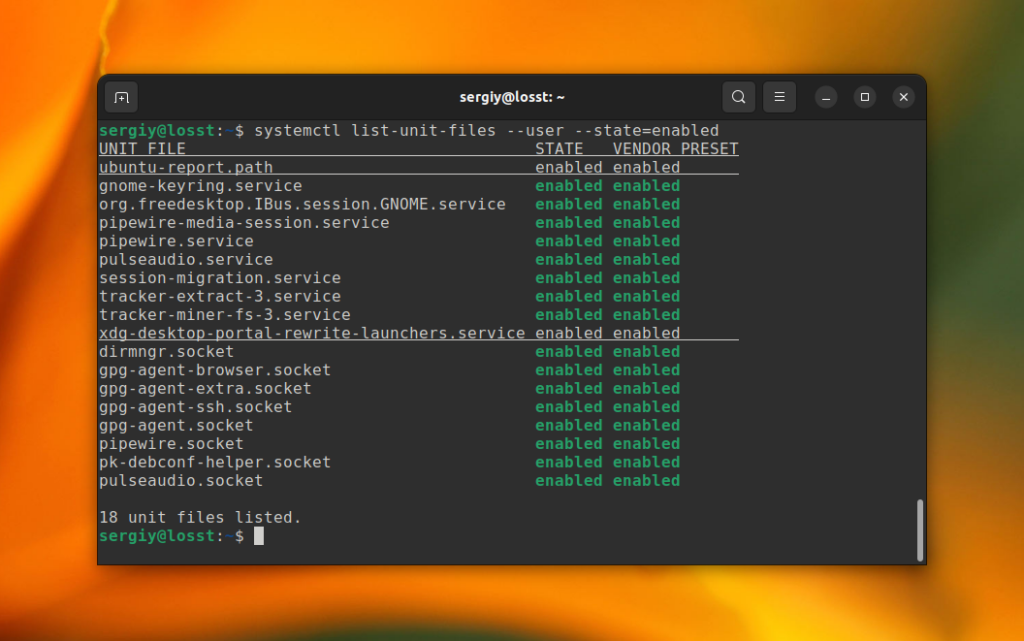
If you want to find which services are added into Systemd autostart, use the list-unit-files command with filtering by state:
systemctl list-unit-files —type=service —state=enabled
2. Check Service Autostart State
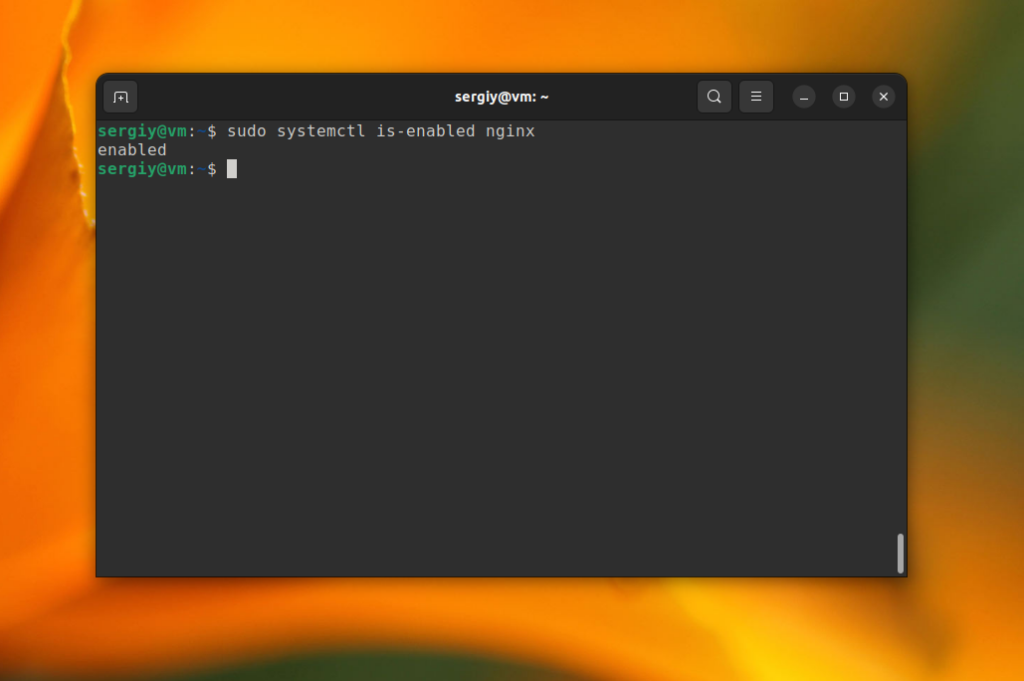
You can use the is-enabled command to check whether the service is already added to autostart. For example:
sudo systemctl is-enabled nginx
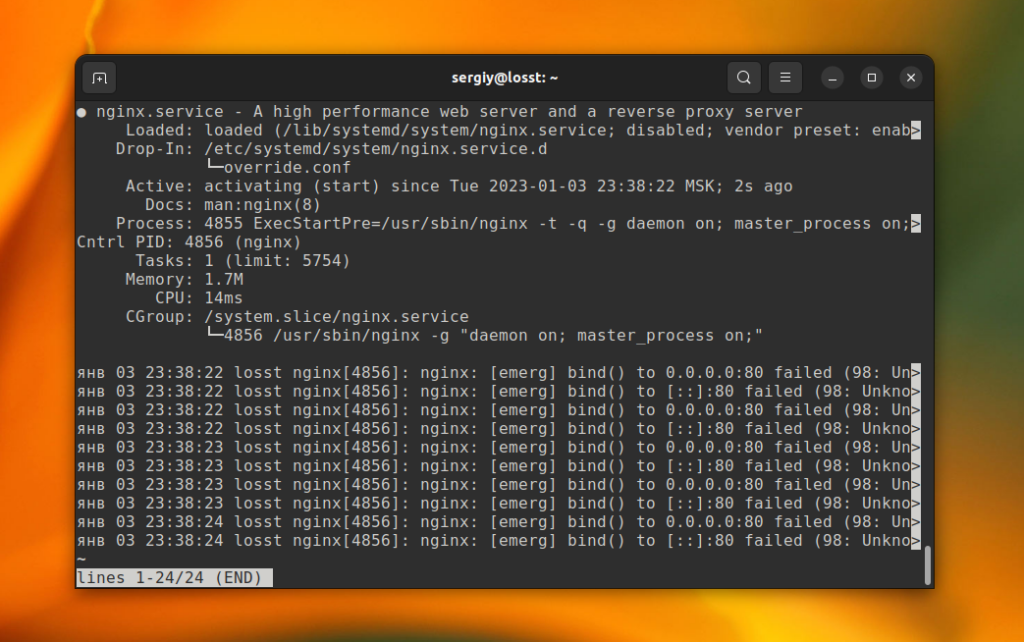
You can use the status command instead of is-enabled. In addition, it displays whether the service is running at the moment and its latest logs:
sudo systemctl status nginx
You can find autostart state in the Loaded line after the path to the service unit file. The state can be enabled, disabled, or static. Services marked as static are added to autostart and can’t be removed.
3. Enable Autostart for Service
Use the enable command to make the service start at the system startup:
For example, run the following command to configure autostart for Nginx web-server:
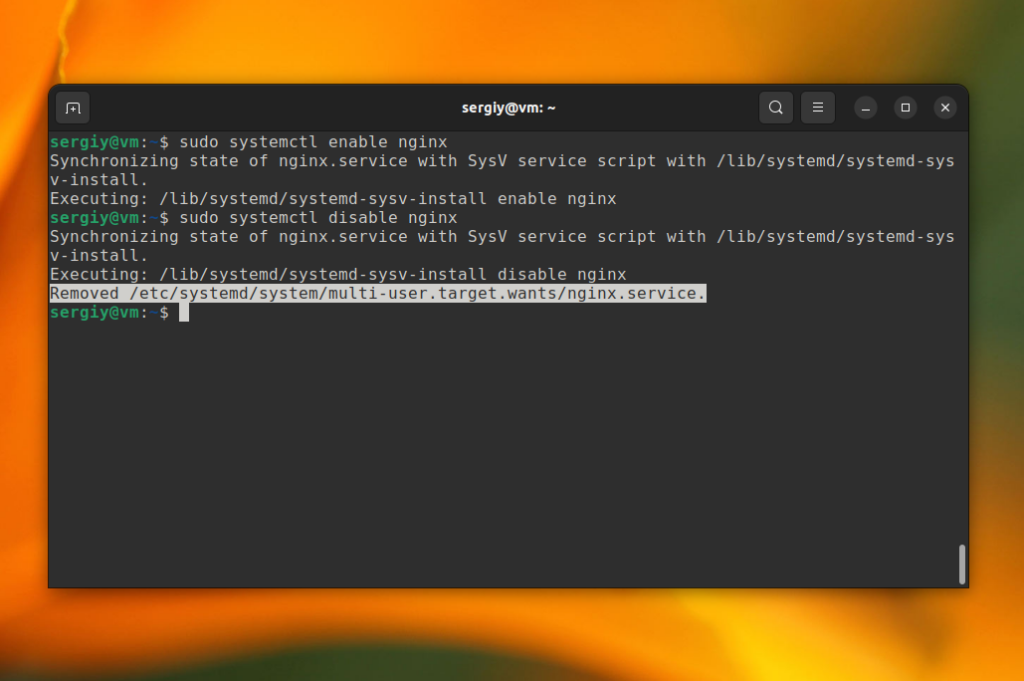
sudo systemctl enable nginx
When the service is not running now and you want to start it now, you can combine the enable command with the —now option. For example:
sudo systemctl enable —now nginx
4. Disable Autostart for Service
If you don’t want the service to start whenever the system boots use the disable command to remove it from autostart:
sudo systemctl disable nginx
Configure Autostart for User’s Services
Systemd supports not only system services but also services which can be started and managed by regular users. You don’t required to have superuser privileges to manage them. Just use the —user option with the systemctl command.
Usually, these services are started when the first user session starts and are stopped when the last user session ends. If you want to get a list of the current user’s services that are started automatically, use the following command:
systemctl list-unit-files —user —type=service —state=enabled
Use the enable command with the —user option to make the service start automatically. For example, if you want pipewire to start automIX-03B-OPatically use this command:
systemctl enable —user pipewire
Disabling autostart for user’s services works similarly:
systemctl disable —user pipewire
If you want autostart services for a specific user not on the first session start but at the system startup you should enable lingering for this user. Run the following command to do this:
sudo loginctl enable-linger
For example, run this command to enable lingering for the user with the name sergiy:
sudo loginctl enable-linger sergiy
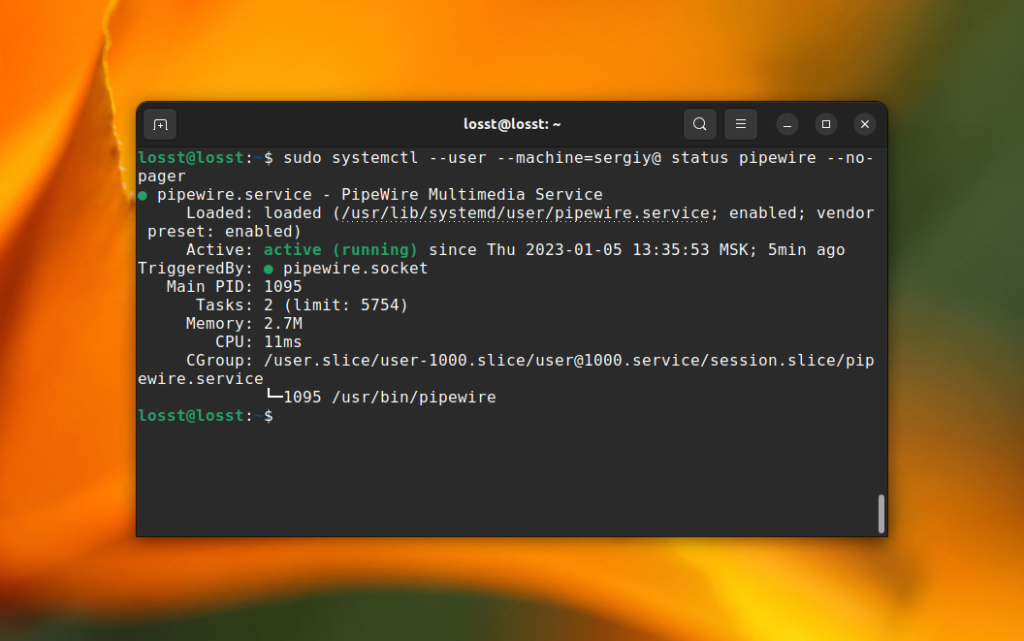
After this you can ensure that this feature works by authorizing from another user and checking the service status for the previous user. For example:
sudo systemctl —user —machine=sergiy@ status pipewire —no-pager
Wrapping Up
In this article, I have explained how to configure the service to start automatically in Linux. As you can see it is pretty straightforward with the Systemd initialization system.
Found a mistake in the text? Let me know about that. Highlight the text with the mistake and press Ctrl+Enter.
Use systemd to Start a Linux Service at Boot
Estamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
What is systemd?
systemd is a Linux system tool initially developed by the Red Hat Linux team. It includes many features, including a bootstrapping system used to start and manage system processes. It is currently the default initialization system on most Linux distributions. Many commonly used software tools, such as SSH and Apache, ship with a systemd service.
It is simple to create a custom systemd service that will run any script or process you choose. Although there are several ways to run a script or start a process when your Linode boots, a custom systemd service makes it easy to start, stop, or restart your script, as well as configure it to start automatically on boot. systemd offers the advantage of using a standardized interface that is consistent across all Linux distributions that support it.
Create a Custom systemd Service
- Create a script or executable that the service will manage. This guide uses a simple Bash script as an example:
sudo cp test_service.sh /usr/bin/test_service.sh sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/test_service.sh [Unit] Description=Example systemd service. [Service] Type=simple ExecStart=/bin/bash /usr/bin/test_service.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.targetsudo cp myservice.service /etc/systemd/system/myservice.service sudo chmod 644 /etc/systemd/system/myservice.service Start and Enable the Service
sudo systemctl start myservice sudo systemctl status myservice ● myservice.service - Example systemd service. Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/myservice.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2018-05-01 18:17:14 UTC; 4s ago Main PID: 16266 (bash) Tasks: 2 Memory: 748.0K CPU: 4ms CGroup: /system.slice/myservice.service ├─16266 /bin/bash /usr/bin/test_service.sh └─16270 sleep 30 May 01 18:17:14 localhost systemd[1]: Started Example systemd service.. May 01 18:17:14 localhost cat[16269]: Example service started at 2018-05-01 18:17:14 May 01 18:17:14 localhost bash[16266]: Looping. sudo systemctl stop myservice sudo systemctl restart myservice sudo systemctl enable myservice Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/myservice.service to /lib/systemd/system/myservice.service.sudo systemctl status myservice ● myservice.service - Example systemd service. Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/myservice.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2018-05-02 15:03:07 UTC; 48s ago Main PID: 2973 (bash) CGroup: /system.slice/myservice.service ├─2973 /bin/bash /usr/bin/test_service.sh └─3371 sleep 30 May 02 15:03:07 localhost systemd[1]: Started Example systemd service.. May 02 15:03:07 localhost systemd[1]: Starting Example systemd service. May 02 15:03:07 localhost bash[2973]: Looping. May 02 15:03:37 localhost bash[2973]: Looping. For more information about using systemctl commands, see the systemctl guide.
Troubleshooting
- “Example service started at …” line does not appear in the output of the status command. The systemd-cat output is not reliable because of a race condition. As a workaround update the test_service.sh file as follows:
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
This page was originally published on Tuesday, May 1, 2018.
How to Auto-start Services on Boot in Linux?
Invicti Web Application Security Scanner – the only solution that delivers automatic verification of vulnerabilities with Proof-Based Scanning™.
One of the essential for a system administrator to know is how to configure service at boot, so when a server gets a reboot, they start automatically.
There could be various reasons for server reboot, including the following.
By doing the right configuration, you don’t have to start them manually each time you reboot.
A little bit of automation. Isn’t it?
The following examples are for two popular distros tested on DigitalOcean servers.
CentOS or RHEL 6.x
In the following example, I have taken an Apache HTTP server, but the procedure remains the same for any other services you wish to start at boot in Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) or CentOS 6 version.
You can keep any script file name, and here I’ve kept httpd
[root@Chandan init.d]# ls -ltr httpd -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 3371 Jan 6 08:56 httpd [root@Chandan init.d]#We will use chkconfig utility which is available default on Linux or CentOS.
[root@Chandan init.d]# chkconfig --add httpd [root@Chandan init.d]# chkconfig httpd on[root@Chandan init.d]# chkconfig --list httpd httpd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off [root@Chandan init.d]#That’s all! httpd script will be called to start services on Linux boot.
In case you need to disable the auto-start service then you can use the following commands
chkconfig httpd off chkconfig --del httpdRHEL or CentOS 7.x/8.x
The procedure to configure services on boot in RHEL 7 is slightly different than RHEL 6. It uses systemd to manage the services.
Most of the software like Apache, PHP, MySQL, Nginx scripts are added in services when you install it.
Let’s take an example of PHP-FPM.
First thing first, let’s see the status of php-fpm (this assume you already have scripts in /usr/lib/systemd/system/ )
[root@instance-1 ~]# systemctl status php-fpm php-fpm.service - The PHP FastCGI Process Manager Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: inactive (dead) [root@instance-1 ~]#As you can see the status is disabled which means it’s not configured to start on boot.
Let’s enable php-fpm to start on boot by using systemctl
[root@instance-1 ~]# systemctl enable php-fpm Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/php-fpm.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service. [root@instance-1 ~]#[root@instance-1 ~]# systemctl status php-fpmphp php-fpm.service - The PHP FastCGI Process Manager Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: inactive (dead) [root@instance-1 ~]#php-fpm is all set to start on boot. Let’s test it by rebooting the server.
If you ever need to disable starting services on boot, then you can use the below command
You may also prefer to check out this post explaining systemd and auto-starting services on boot.
Ubuntu
Configuring auto-start services in Ubuntu is slightly different. Let’s say the script name is Nginx
- Login to Ubuntu server with root
- Copy the script in /etc/init.d/ folder
- Execute the below command
This has helped me and I believe it will be beneficial to you as well.
System administration is always fun and challenging, and if you are looking to supercharge your career in it, then you may refer to this Udemy course.