- Start a jar file like service in linux [closed]
- 3 Answers 3
- How to Create and Execute a .Jar File in Linux Terminal
- How to Create a JAR File in Linux
- How to Run Jar File in Ubuntu Linux
- Run jar files in Ubuntu
- Method 1: Using GUI
- Method 2: Using the Terminal
- Here’s how to set up the JAVA_HOME variable
- Как запустить jar в Linux
- Как запустить jar Linux
- Выводы
Start a jar file like service in linux [closed]
Closed. This question does not meet Stack Overflow guidelines. It is not currently accepting answers.
Questions asking us to recommend or find a tool, library or favorite off-site resource are off-topic for Stack Overflow as they tend to attract opinionated answers and spam. Instead, describe the problem and what has been done so far to solve it.
I want to start and stop my jar file as follows service myService start service myService stop my current jar file running as follows
cd /home/alex/IdeaProjects/myService java -jar target/myService-SNAPSHOT-1.jar server config.yml Implement a wrapper service. A little search will show up some 3rd party implementation you could use.
3 Answers 3
You need a Service Wrapper to run the Jar file.
There are examples and instructions for init.d here. or for systemd (ubuntu 16+) here
Just an info for people who are on Ubuntu 16+. This doesn’t work with Ubuntu 16+. You will get ‘Failed to start MyService.service: Unit MyService.service not found’
I prefer a light weight, free, bash script rather than a more elaborate system that requires licensing.
If you want to try the DIY way, you can place a startup script in your /etc/init.d directory as said here.
However, to implement a clean yourScript stop command, I would recommend that you split your functionality into a launcher and a daemon, and make your launcher able to start or communicate with your existing daemon in order to send orders to it. Then your startup script would only invoke your launcher, which in its turn would start a new daemon, or send orders to the existing one.
How to Create and Execute a .Jar File in Linux Terminal
A JAR (Java ARchive) is platform-independent file format used to aggregate many Java class files and associated metadata and resources such as text, images, etc, into a single file for distribution.
It allows Java runtimes to efficiently deploy an entire application in one archive file, and provides many benefits such as security, its elements may be compressed, shortening download times, allows for package sealing and versioning, supports portability. It also supports packaging for extensions.
In this article, we will show how to create a simple Java application and bundle it into a JAR file, and demonstrate how to execute a .jar file from the Linux terminal.
To do this, you must have java command line tool installed to launche a Java application, and the -jar flag to execute a program encapsulated in a JAR file. When this flag is used, the specified JAR file is the source of all user classes, and other class path settings are ignored.
How to Create a JAR File in Linux
1. First start by writing a simple Java class with a main method for an application called TecmintApp, for demonstration purpose.
Copy and paste the following code to TecmintApp.java file.
Save the file and close it.
2. Next, we need to compile and pack the class into a JAR file using the javac and jar utilities as shown.
$ javac -d . TecmintApp.java $ ls $ jar cvf tecmintapp.jar TecmintApp.class $ ls
3. Once tecmintapp.jar created, now you can excute the file using java command as shown.
$ java -jar tecmintapp.jar no main manifest attribute, in tecmintapp.jar
From the output of the above command, we encountered an error. The JVM (Java Virtual Machine) couldn’t find our main manifest attribute, thus it could not locate the main class containing the main method (public static void main (String[] args)).
The JAR file should have a manifest that contains a line in the form Main-Class:classname that defines the class with the main method that serves as our application’s starting point.
4. To fix the above error, we will need to update the JAR file to include a manifest attribute together with our code. Let’s create a MANIFEST.MF file.
Copy and paste the following line to MANIFEST.MF file.
Save the file and let’s add the file MANIFEST.MF to our tecmintapp.jar using following command.
$ jar cvmf MANIFEST.MF tecmintapp.jar TecmintApp.class
5. Finally, when we executed the JAR file again, it should produce the expected result as shown in the output.
$ java -jar tecmintapp.jar Just executed TecmintApp!
For more information, see the java, javac and jar command man pages.
$ man java $ man javac $ man jar
That’s all! In this short article, we have explained how to create a simple Java application and bundle it into a JAR file, and demonstrated how to execute a .jar file from the terminal. If you have any questions or supplementary ideas to share, use the feedback form below.
How to Run Jar File in Ubuntu Linux
Downloaded a JAR file and don’t know how to use it? Learn how to run JAR files in Ubuntu based Linux distributions.
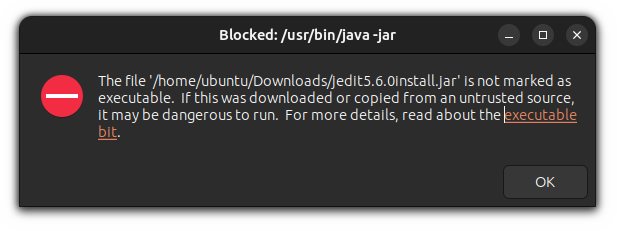
If you install any package having the .jar extension and try to execute it, it may throw an error saying «The file is not marked as executable»: And in this tutorial, I will walk you through how you can install its prerequisites and run Jar files in Ubuntu and other Linux with multiple methods.
Run jar files in Ubuntu
If you don’t know, JAR stands for Java ARchive so you must have a working Java environment. If you have Java installed, you should be able to run it. Check if Java is installed with:
If you see an error instead of the version number, install Java runtime environment using the following command:
sudo apt install default-jreSo let’s start with the first one.
Method 1: Using GUI
The first step is to open the file manager from the system menu and navigate to the jar file which you want to run.
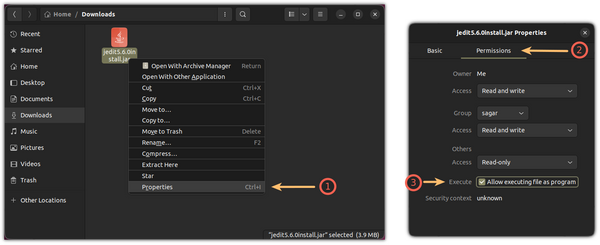
Then, right-click on the jar app and select Properties .
From there, select Permissions and enable Allow executing file as program :
That made the file executable.
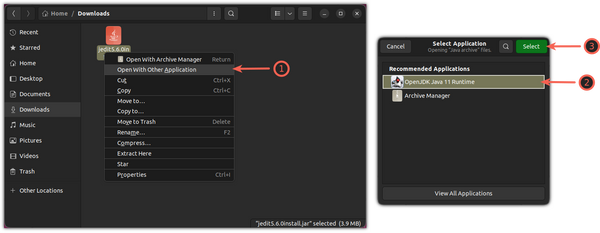
But you have yet to select which app it should use to run the jar files.
To select an Application to start the jar files, again, click on the jar file and choose the second option Open with Other Application and choose the OpenJDK Java Runtime option:
Now, you can start the jar application like you do with any other files by pressing the Enter key.
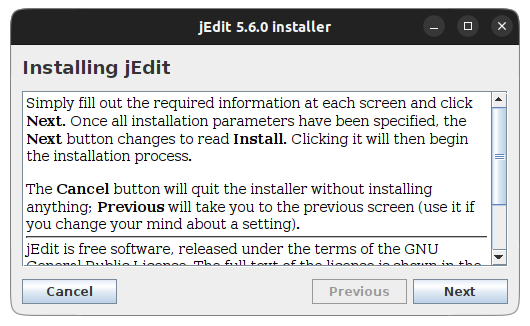
In my case, it was an installer and it started as it should:
Method 2: Using the Terminal
If you believe in efficiency, I’m about to show you the terminal method will complete the task in only three commands.
First, open the terminal and navigate to the directory where the jar file is located using the cd command:
Once done, use the chmod command with the +x flag to make the file executable:
And finally, you can use the Java command with the -jar flag to run the jar file:
Here’s how to set up the JAVA_HOME variable
Most of the users set the JAVA_HOME variable incorrectly. So we thought, why not make a dedicated guide to get things done correctly?
I hope you will find this guide helpful.
Как запустить jar в Linux
Java — это кроссплатформенный язык программирования, благодаря которому программы, написанные один раз, можно запускать в большинстве операционных систем: в Windows, Linux и даже MacOS. И всё это без каких-либо изменений.
Но программы, написанные на Java, распространяются в собственном формате .jar, и для их запуска необходимо специальное ПО — Java-машина. В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим, как запустить jar-файл в Linux.
Как запустить jar Linux
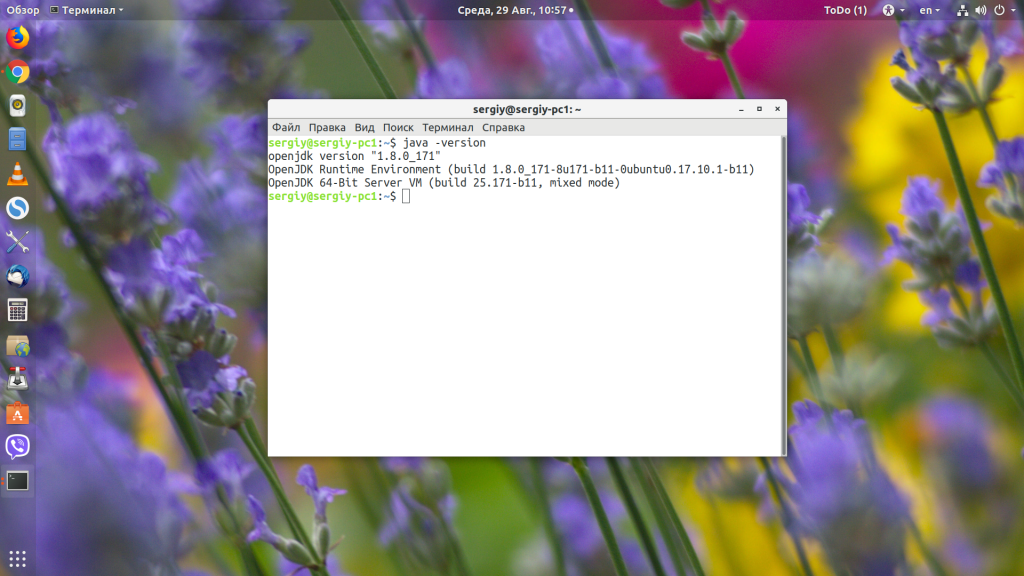
Как я уже сказал, для запуска jar-файлов нам необходимо, чтобы на компьютере была установлена Java-машина. Если вы не собираетесь ничего разрабатывать, вам будет достаточно Java Runtime Environment или JRE. Что касается версии, то, обычно, большинство программ работают с 7 или 8 версией. Если нужна только восьмая, то разработчики прямо об этом сообщают. Посмотреть версию Java и заодно убедиться, что она установлена в вашей системе, можно с помощью команды:
У меня установлена восьмая версия, с пакетом обновлений 171. Если вы получаете ошибку, что команда не найдена, то это значит, что вам нужно установить java. В Ubuntu OpenJDK JRE можно установить командой:
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jre
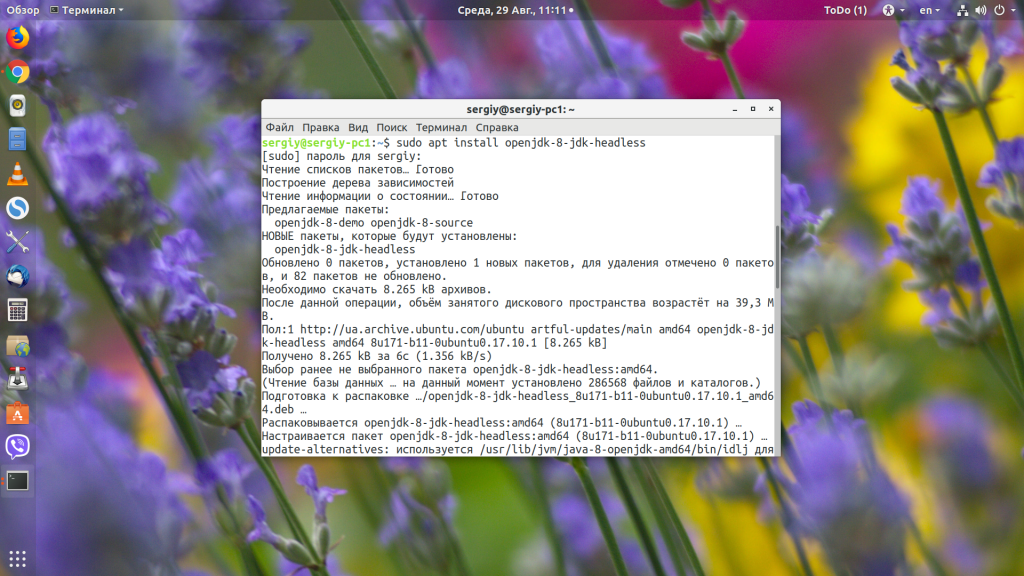
Если вы хотите скомпилировать пример из этой статьи, то вам понадобиться не JRE, а JDK, её можно установить командой:
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk-headless
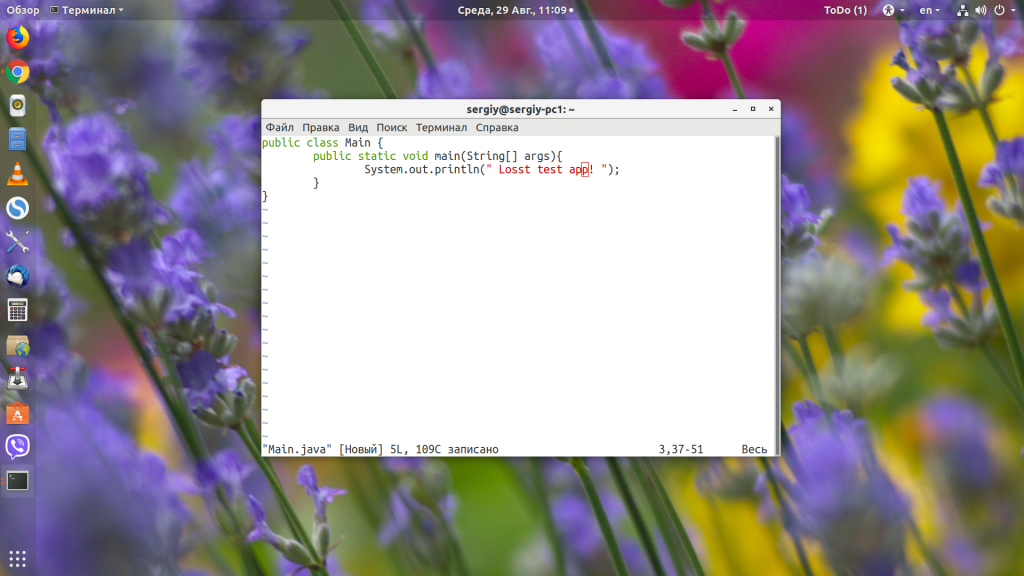
Чтобы узнать, как установить Java в других дистрибутивах, смотрите статью по ссылке выше. Когда Java будет установлена, вы можете очень просто запустить любой jar-файл в Linux, передав путь к нему в качестве параметра Java-машине. Давайте для примера создадим небольшое приложение:
public class Main public static void main(String[] args) System.out.println(» Losst test app! «);
>
>
Затем скомпилируем наше приложение в jar-файл:
javac -d . Main.java
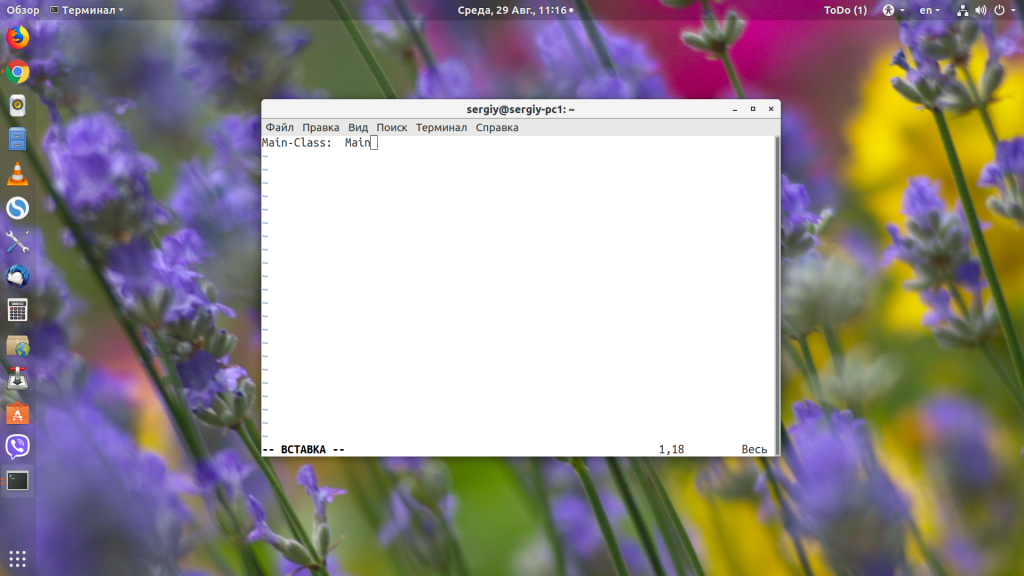
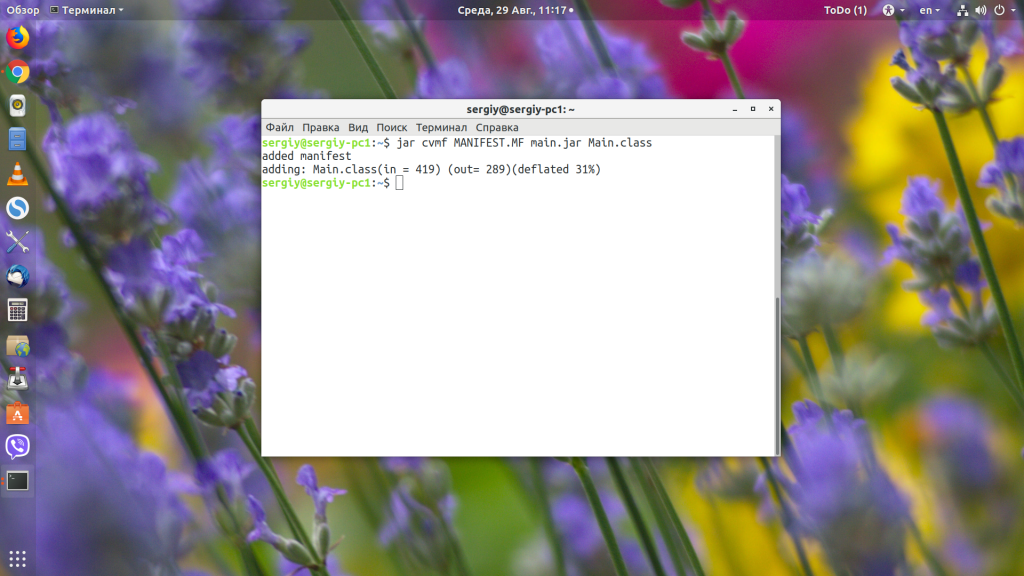
jar cvmf MANIFEST.MF main.jar Main.class
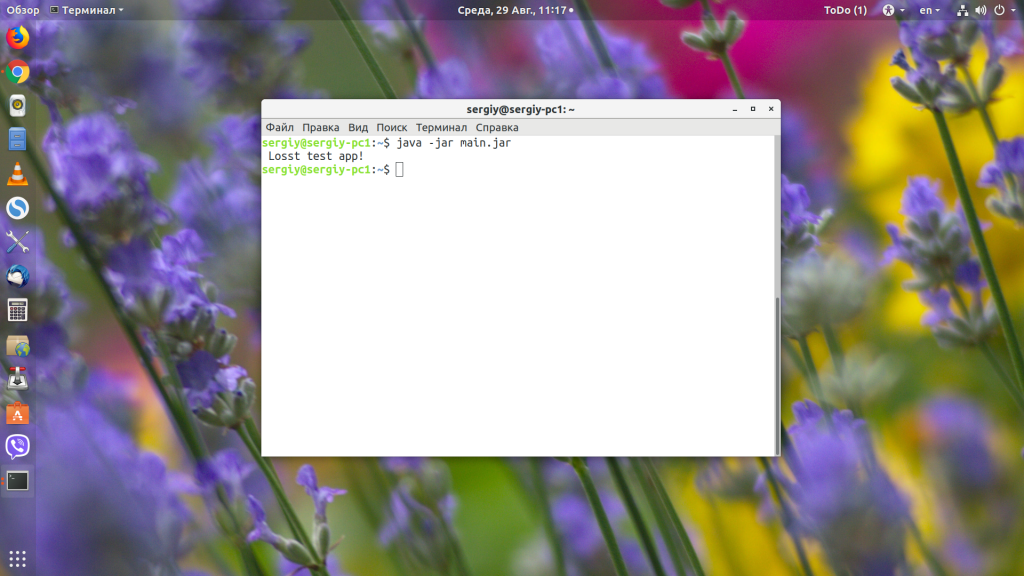
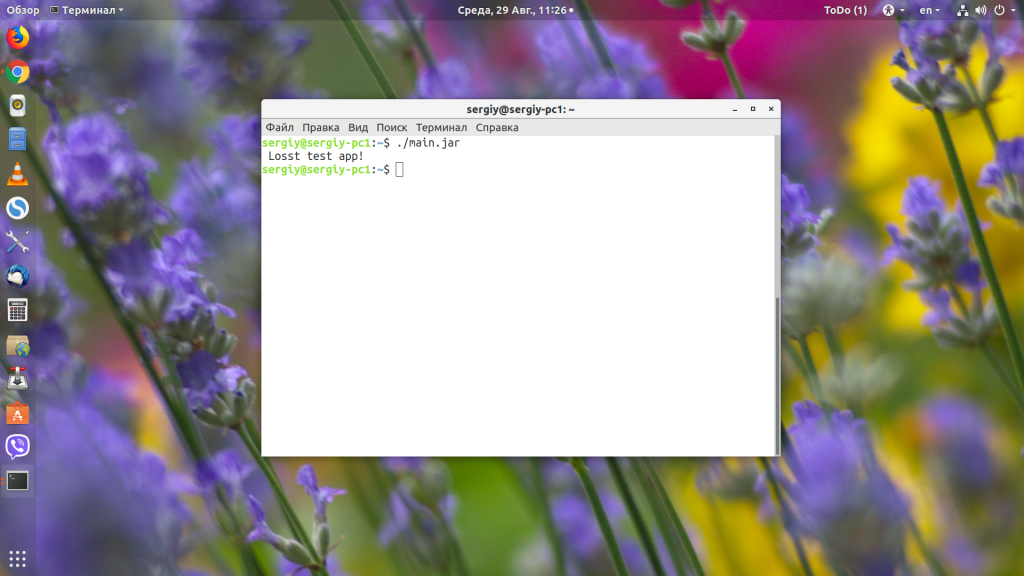
Теперь можно запустить наш jar-файл командой java с параметром -jar:
Таким образом вы можете запустить любой jar-файл, который собран для вашей версии Java. Но не очень удобно каждый раз открывать терминал и прописывать какую-либо команду. Хотелось бы запускать программу по щелчку мышки или как любую другую Linux-программу — по имени файла.
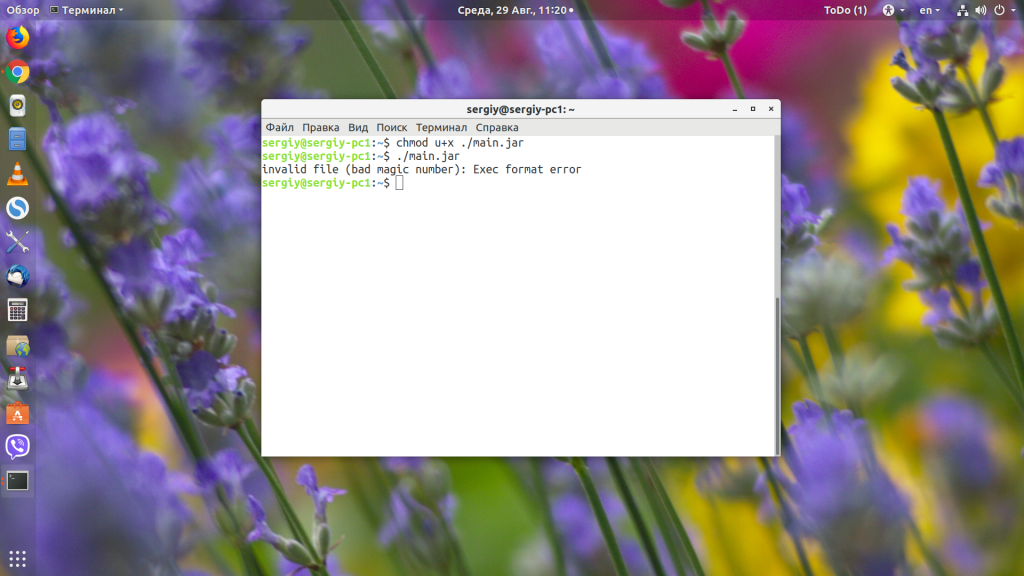
Если мы дадим программе право на выполнение:
И попытаемся её запустить, то получим ошибку:
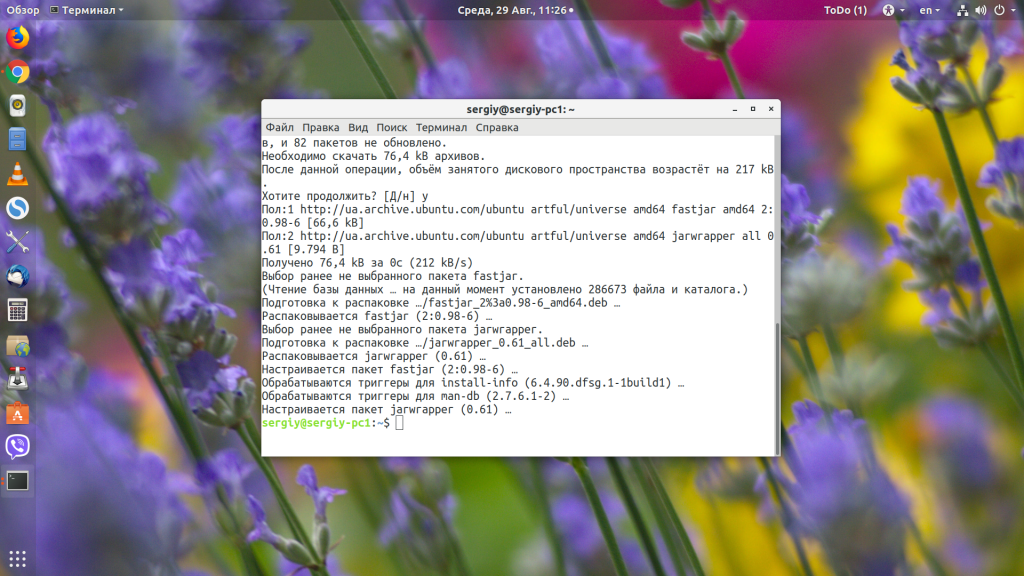
Чтобы её исправить, нам понадобиться пакет jarwrapper:
sudo apt install jarwrapper
Теперь можно запускать java в Linux по щелчку мыши или просто командой.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрели, как запустить jar Linux с помощью java-машины, а также как упростить команду запуска. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.