- CommandLine¶
- Starting NGINX¶
- Basic Example of Starting NGINX¶
- Advanced Example of Starting NGINX¶
- Options¶
- Stopping or Restarting NGINX¶
- Loading a New Configuration Using Signals¶
- Upgrading To a New Binary On The Fly¶
- References¶
- How to Start, Stop and Restart Nginx (Built-in, Systemctl and SysVinit Commands)
- Prerequisites
- Start, Stop, and Restart Nginx Web Server
- Start, Stop, and Restart Nginx using Systemctl
- Check Status of Nginx
- Stop and Start Nginx
- Reload Nginx
- Restart Nginx
- Start, Stop, and Restart Nginx Server using Built-in Commands
- Nginx start
- Nginx stop
- Nginx reload
- Nginx restart
- Nginx Restart vs Reload
- Conclusion
CommandLine¶
This page shows you how to start NGINX, and once it’s running, how to control it so that it will stop or restart.
Starting NGINX¶
NGINX is invoked from the command line, usually from /usr/bin/nginx .
Basic Example of Starting NGINX¶
Advanced Example of Starting NGINX¶
/usr/bin/nginx -t -c ~/mynginx.conf -g "pid /var/run/nginx.pid; worker_processes 2;" Options¶
| -?, -h | Print help. |
| -v | Print version. |
| -V | Print NGINX version, compiler version and configure parameters. |
| -t | Don’t run, just test the configuration file. NGINX checks configuration for correct syntax and then try to open files referred in configuration. |
| -q | Suppress non-error messages during configuration testing. |
| -s signal | Send signal to a master process: stop, quit, reopen, reload. (version >= 0.7.53) |
| -p prefix | Set prefix path (default: /usr/local/nginx/ ). (version >= 0.7.53) |
| -c filename | Specify which configuration file NGINX should use instead of the default. |
| -g directives | Set global directives. (version >= 0.7.4) |
NGINX has only a few command-line parameters. Unlike many other software systems, the configuration is done entirely via the configuration file (imagine that).
Stopping or Restarting NGINX¶
There are two ways to control NGINX once it’s already running. The first is to call NGINX again with the -s command line parameter. For example, /usr/bin/nginx -s stop will stop the NGINX server. (other -s options are given in the previous section)
The second way to control NGINX is to send a signal to the NGINX master process… By default NGINX writes its master process id to /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid . You can change this by passing parameter with ./configure at compile-time or by using pid directive in the configuration file.
Here’s how to send the QUIT (Graceful Shutdown) signal to the NGINX master process:
kill -QUIT $( cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid )
The master process can handle the following signals:
Start the new worker processes with a new configuration
Gracefully shutdown the old worker processes
There’s no need to control the worker processes yourself. However, they support some signals, too:
| TERM, INT | Quick shutdown |
| QUIT | Graceful shutdown |
| USR1 | Reopen the log files |
Loading a New Configuration Using Signals¶
NGINX supports a few signals that you can use to control it’s operation while it’s running.
The most common of these is 15, which just stops the running process:
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 2213 0.0 0.0 6784 2036 ? Ss 03:01 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
The more interesting option however, is being able to change the NGINX configuration on the fly (notice that we test the configuration prior to reloading it):
2006/09/16 13:07:10 [info] 15686#0: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok 2006/09/16 13:07:10 [info] 15686#0: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf was tested successfully USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 2213 0.0 0.0 6784 2036 ? Ss 03:01 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
What happens is that when NGINX receives the HUP signal, it tries to parse the configuration file (the specified one, if present, otherwise the default), and if successful, tries to apply a new configuration (i.e. re-open the log files and listen sockets). If successful, NGINX runs new worker processes and signals graceful shutdown to old workers. Notified workers close listen sockets but continue to serve current clients. After serving all clients old workers shutdown. If NGINX couldn’t successfully apply the new configuration, it continues to work with an old configuration.
RequestForReviewCategory – (Request For Review: Just What Happens With The Worker Processes at a HUP? -Olle)
Upgrading To a New Binary On The Fly¶
If you need to replace NGINX binary with a new one (when upgrading to a new version or adding/removing server modules), you can do it without any service downtime — no incoming requests will be lost.
First, replace old binary with a new one, then send USR2 signal to the master process. It renames its .pid file to .oldbin (e.g. /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid.oldbin ), then executes a new binary, which in turn starts a new master process and the new worker processes:
: PID PPID USER %CPU VSZ WCHAN COMMAND 33126 1 root 0.0 1164 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx 33134 33126 nobody 0.0 1368 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx) 33135 33126 nobody 0.0 1380 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx) 33136 33126 nobody 0.0 1368 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx) 36264 33126 root 0.0 1148 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx 36265 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx) 36266 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx) 36267 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
At this point, two instances of NGINX are running, handling the incoming requests together. To phase the old instance out, you have to send WINCH signal to the old master process, and its worker processes will start to gracefully shut down:
: PID PPID USER %CPU VSZ WCHAN COMMAND 33126 1 root 0.0 1164 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx 33135 33126 nobody 0.0 1380 kqread nginx: worker process is shutting down (nginx) 36264 33126 root 0.0 1148 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx 36265 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx) 36266 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx) 36267 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
After some time, old worker processes all quit and only new worker processes are handling the incoming requests:
: PID PPID USER %CPU VSZ WCHAN COMMAND 33126 1 root 0.0 1164 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx 36264 33126 root 0.0 1148 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx 36265 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx) 36266 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx) 36267 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
At this point you can still revert to the old server because it hasn’t closed its listen sockets yet, by following these steps:
- Send HUP signal to the old master process — it will start the worker processes without reloading a configuration file
- Send QUIT signal to the new master process to gracefully shut down its worker processes
- Send TERM signal to the new master process to force it quit
- If for some reason new worker processes do not quit, send KILL signal to them
After new master process quits, the old master process removes .oldbin suffix from its .pid file, and everything is exactly as before the upgrade attempt.
If an update is successful and you want to keep the new server, send QUIT signal to the old master process to leave only new server running:
: PID PPID USER %CPU VSZ WCHAN COMMAND : 36264 1 root 0.0 1148 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx : 36265 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx) : 36266 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx) : 36267 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
References¶
How to Start, Stop and Restart Nginx (Built-in, Systemctl and SysVinit Commands)
Nginx is an open-source high-performance robust web server used on Linux. It is one of the most stable and reliable web servers. It is very often used as a reverse proxy server that sits in front of one or more web servers.
System administrators have to regularly start, stop, restart, or reload the Nginx web server as part of the configuration changes.
In this guide, we will learn how to start, stop, and restart Nginx on Linux servers.
Prerequisites
- A Linux system with Nginx installed.
- Fundamental understanding of Linux commands.
- A user account with root or sudo privileges.
Start, Stop, and Restart Nginx Web Server
A regular task when administering Nginx is to start, stop, and restart the nginx service. For example, if you update a configuration file, install updates or change server blocks, then you need to restart the Nginx service to apply these changes.
You can use systemctl or in-built commands to manage the Nginx service. On Older versions of Ubuntu, Debian, and CentOS you can use SysVinit based commands.
The following table lists different commands to start, stop, and restart the Nginx service on the Linux server:
| Argument | Systemctl | Built-in Commands | SysVinit |
|---|---|---|---|
| start | sudo systemctl start nginx | sudo /etc/init.d/nginx start | sudo service nginx start |
| stop | sudo systemctl stop nginx | sudo /etc/init.d/nginx stop | sudo service nginx stop |
| reload | sudo systemctl reload nginx | sudo /etc/init.d/nginx reload | sudo service nginx reload |
| restart | sudo systemctl restart nginx | sudo /etc/init.d/nginx restart | sudo service nginx restart |
Use any of the above commands based on your Linux distribution and preferences.
Start, Stop, and Restart Nginx using Systemctl
Almost all modern Linux distributions adopted using Systemd as the default service manager. Systemctl is a built-in Linux command-line tool that is used to manage and control systemd services. You can use Systemctl to perform various operations on Nginx.
You can use systemctl on distro versions such as Ubuntu 20.04/18.04/16.04, CentOS Stream, and Debian 9/10/11.
The following examples show you how to use the systemctl commands on Nginx.
Check Status of Nginx
Nginx runs as a service on your Linux computer and it keeps running in the background even if it does not display anything on the screen.
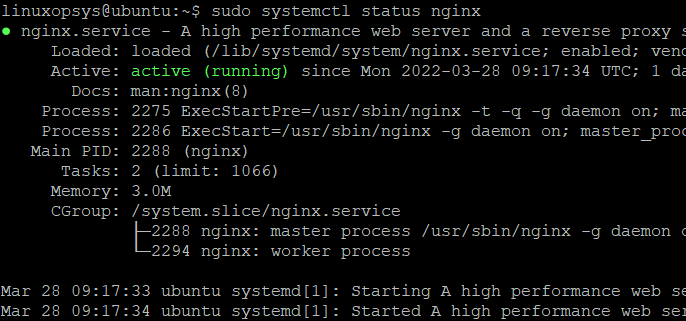
Use the following example to check the status of the Nginx service:
sudo systemctl status nginxPress q from the keyboard to return to the command prompt.
The status can be any of the following:
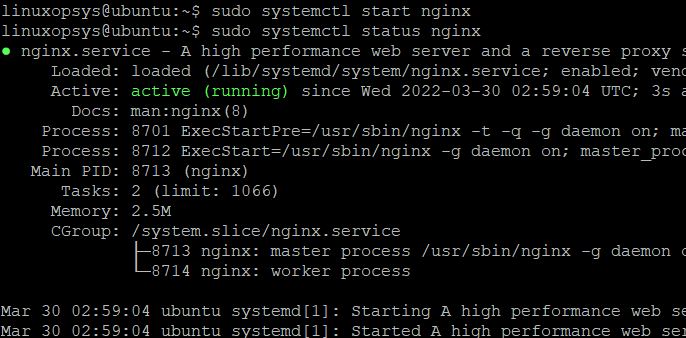
- If the service is running, then you will see active (running) with other information.
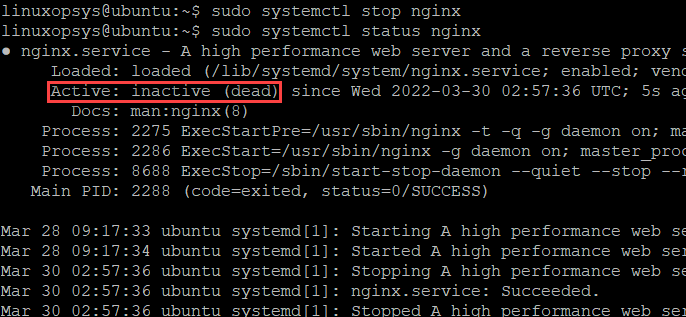
- If it is not running, then the status will be inactive (dead).
- If the service fails to load for some reason, then the status will be failed.
Stop and Start Nginx
If the service is active and running, then you can use the following command to stop the service:
sudo systemctl stop nginxTo start an inactive Nginx service, run the following command:
sudo systemctl start nginxReload Nginx
Nginx reload first checks the configuration syntax and apply the new configuration. Nginx reload doesn’t cause downtime as Nginx starts new worker processes and sends messages to old worker processes requesting them to shut down gracefully.
Use the following command to gracefully reload Nginx service after updating the configuration file or other parameters:
sudo systemctl reload nginxIf successful, Nginx reload won’t show any output.
Restart Nginx
Restarting Nginx stops all active services and starts them again. Use the following command to forcefully restart the Nginx service after making configuration file changes:
sudo systemctl restart nginxAfter you forcefully restart the nginx service, the service active timestamp changes. But it does not change after a reload.
Start, Stop, and Restart Nginx Server using Built-in Commands
Nginx provides a set of in-built command-line utilities to manage the services. These examples will show you how to use the nginx commands to manage the Nginx service.
Nginx start
To start the Nginx services using the nginx command, type:
Nginx stop
To stop the Nginx server quickly use the following command:
The -s signal sends a signal to the master process -quit shutdown gracefully:
Nginx reload
To gracefully shut down old worker processes and start Nginx, use the following command:
sudo /etc/init.d/nginx reloadIf the service is not actively running, then you will get a failed status and message. To reload the service, you must first start it.
Nginx restart
Use the sudo /etc/init.d/nginx restart command to close the Nginx service and start it again:
Nginx Restart vs Reload
With Nginx reload command, the server operations keep running and reload the updated configuration files. If there is any syntax error during reloading, the server keeps running on the old configuration. On the other hand, the restart command will terminate all the worker processes and will start them again.
The good thing about Nignix reload is that it shows the error on the terminal and at the same time keeps the webserver running. You can fix the error and reload again.
Restarting Nginx is required when you make major configuration changes, such as installing bug fixes, updates, and updating interface and port configuration. For the safe side check the Nginx configuration syntax using nginx -t before doing a restart.
Conclusion
This tutorial walks you through different commands to start, stop, reload, and restart Nginx. Use these commands to manage your remote server running Nginx.
If this resource helped you, let us know your care by a Thanks Tweet. Tweet a thanks