- Как запустить / остановить и включить / отключить FirewallD и Iptables Firewall в Linux
- Как запустить / остановить и включить / отключить службу FirewallD
- If you’re using CentOS/RHEL 7 or Fedora 18+ versions, you should follow below instructions to manage FirewallD service.
- Как запустить / остановить и включить / отключить службу IPtables
- On RHEL / CentOS 6/5/4 and Fedora 12-18 iptables firewall comes as pre and later, the iptables service can be installed via:
- How to Enable/Disable UFW Firewall on Ubuntu 18.04 & 20.04
- Check Ubuntu Firewall Status
- Disable Ubuntu Firewall
- Enable Firewall
- Using UFW to Set Firewall Rules
- Reseting UFW Firewall Rules
- How to Start/Stop and Enable/Disable FirewallD and Iptables Firewall in Linux
- What is FirewallD
- What is Iptables
- How to Start/Stop and Enable/Disable FirewallD Service
- How to Start/Stop and Enable/Disable IPtables Service
- Conclusion
Как запустить / остановить и включить / отключить FirewallD и Iptables Firewall в Linux
Как запустить / остановить и включить / отключить службу FirewallD
If you’re using CentOS/RHEL 7 or Fedora 18+ versions, you should follow below instructions to manage FirewallD service.
Start FirewallD Service
# systemctl start firewalld Stop FirewallD Service
Check the Status of FirewallD
# systemctl status firewalld Check the State of FirewallD
As an alternative, you can disable the firewalld service so that it doesn’t apply rules to packets and enable ones needed again.
Disable FirewallD Service
# systemctl disable firewalld Enable FirewallD Service
# systemctl enable firewalld Mask FirewallD Service
Кроме того, вы можете замаскировать службу брандмауэра, которая создает символическую ссылку firewall.service на /dev/ null, тем самым отключая службу.
Unmask FirewallD Service
# systemctl unmask firewalld This is reverse of masking the service. This removes the symlink of the service created during masking, thus re-enabling the service.
Как запустить / остановить и включить / отключить службу IPtables
On RHEL / CentOS 6/5/4 and Fedora 12-18 iptables firewall comes as pre and later, the iptables service can be installed via:
# yum install iptables-services Then, the service can be started, stopped or restarted via following commands:
Start Iptables Service
# systemctl start iptables OR # service iptables start Stop Iptables Service
# systemctl stop iptables OR # service iptables stop Disable Iptables Service
# systemctl disable iptables Or # service iptables save # service iptables stop Enable Iptables Service
# systemctl enable iptables Or # service iptables start Check Status of Iptables Service
# systemctl status iptables OR # service iptables status
On Ubuntu and some other Linux distributions however, ufw is the command which is used to manage the iptables firewall service. Ufw provides an easy interface for the user to handle the iptables firewall service.
Enable Ufw Iptables Firewall
Disable Ufw Iptables Firewall
Check Status of Ufw Iptables Firewall
However, if you want to list chains in iptables which contains all the rules following command can help you achieve the same:
How to Enable/Disable UFW Firewall on Ubuntu 18.04 & 20.04
Ubuntu comes pre-installed with a firewall configuration tool, UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall). UFW is easy to use for managing server firewall settings.
This tutorial shows you how to disable and enable an Ubuntu UFW firewall using the command line.
- A machine running Ubuntu 18.04, 20.04, or 22.04.
- Command line / terminal window
- User with root or sudo privileges
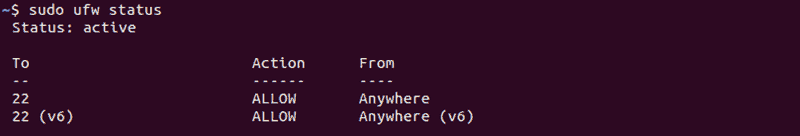
Check Ubuntu Firewall Status
Before disabling the UFW firewall, it is a good idea to check its status first. In Ubuntu, the firewall is disabled by default. How do you know if your firewall is on?
To check the current status of the firewall, execute the command in your command terminal:
In this example below, the output shows that the firewall is active.
As we have determined the current state, now we can proceed to disable the UFW firewall.
Disable Ubuntu Firewall
A firewall is a vital element in a network and server security. However, while testing or troubleshooting, you might need to shut down or stop the firewall.
To disable the firewall on Ubuntu, enter:
The terminal informs you that the service is no longer active.
If you disable the firewall, keep in mind that your firewall rules are still in place. Once you enable the firewall again, the same rules that were set up prior to the deactivation will apply.
Enable Firewall
Learning how to enable the firewall on Ubuntu is vital.
To enable the firewall on Ubuntu, use the command:
As with the ‘disable’ command, the output confirms that the firewall is once again active.
Using UFW to Set Firewall Rules
UFW does not provide complete firewall functionality via its command-line interface. However, it does offer an easy way to add or remove simple rules.
A good example is opening an SSH port.
Once the terminal confirms that the rule is now in place, check the status of the firewall with the ‘status’ command:
The output is going to reflect the fact that an SSH port is now open.
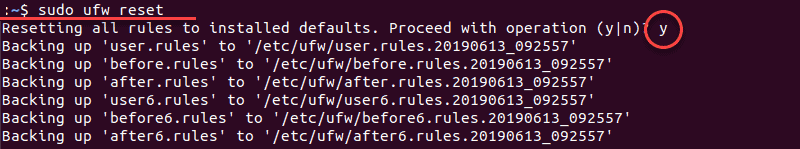
Reseting UFW Firewall Rules
If you need to reset all rules back to default settings, use the reset command:
After confirming the action, by typing y , the firewall settings revert to their default values.
In this guide, you learned how to disable and stop the firewall on Ubuntu. We also showed you how to enable the firewall and reset settings.
Now you know the options available with the UFW tool. These commands provide an excellent foundation to explore firewall functions and settings.
Vladimir is a resident Tech Writer at phoenixNAP. He has more than 7 years of experience in implementing e-commerce and online payment solutions with various global IT services providers. His articles aim to instill a passion for innovative technologies in others by providing practical advice and using an engaging writing style.
UFW is a simple interface implemented on top of iptables that provides an easier way to configure a firewall. Use it to define rules of communication to and from a server and ensure your Ubuntu 18.04 is protected.
This phoenixNAP guide instructs how to enable and start firewalld on CentOS 7. It explains basic firewall zone concepts and teaches you how to work with default firewalld zones.
Apache Tomcat is a free, open-source, lightweight application server used for Java-based web applications. Developers use it to implement Java Servlet and JavaServer.
FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. It is similar to HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol), in that it specifies a language for transferring data over a network. FTP is.
How to Start/Stop and Enable/Disable FirewallD and Iptables Firewall in Linux
Firewall is a software that acts as a shield between user’s system and external network allowing some packets to pass while discarding other’s. Firewall commonly operates on network layer i.e. on IP packets both Ipv4 and Ipv6.
Whether a packet will pass or will be bocked, depends on the rules against such type of packets in the firewall. These rules can be built-in or user-defined ones. Each packet which enters the network has to pass through this shield which verifies it against rules defined in it for such type of packets.
Each rule has a target action which is to be applied in case the packet fails to satisfy it. On Linux systems, firewall as a service is provided by many softwares, most common which are: firewalld and iptables.
In Linux there are many different types of firewalls used, but most standard ones are Iptables and Firewalld, which is going to discuss in this article.
What is FirewallD
FirewallD is the Dynamic Firewall Manager of Linux systems. This service is used to configure the network connections, thus deciding which external network or internal packets to allow traversing the network and which to block.
It allows two types of configurations, permanent and runtime. Runtime configurations will get lost ones the service is restarted while the permanent ones get retained across the system boot so that they are followed every time the service gets active.
Corresponding to these configurations, firewallD has two directories, default/fallback one (/usr/lib/firewall) which is lost ones system is updated and the system configuration (/etc/firewall) which remains permanent and overrides the default one if given. This is found as a default service in RHEL/CentOS 7 and Fedora 18.
What is Iptables
Iptables is another service which decides to allow, drop or return IP packets. Iptables service manages Ipv4 packets while Ip6tables manages Ipv6 packets. This service manages a list of tables where each table is maintained for different purpose like: ‘filter‘ table is for firewall rules, ‘nat‘ table is consulted in case of new connection, ‘mangle‘ in case of packet alterations and so on.
Each table further has chains which can be built-in or user-defined where a chain signifies a set of rules which are applies to a packet, thus deciding what the target action for that packet should be i.e. it must be ALLOWED, BLOCKED or RETURNED. This service is a default service on systems like: RHEL/CentOS 6/5 and Fedora, ArchLinux, Ubuntu etc.
To learn more about firewalls, follow the following links:
In this article we will explain how to start, stop or restart Iptables and FirewallD services in Linux.
How to Start/Stop and Enable/Disable FirewallD Service
If you’re using CentOS/RHEL 7 or Fedora 18+ versions, you should follow below instructions to manage FirewallD service.
Start FirewallD Service
# systemctl start firewalld
Stop FirewallD Service
Check the Status of FirewallD
# systemctl status firewalld
Check the State of FirewallD
As an alternative, you can disable the firewalld service so that it doesn’t apply rules to packets and enable ones needed again.
Disable FirewallD Service
# systemctl disable firewalld
Enable FirewallD Service
# systemctl enable firewalld
Mask FirewallD Service
Also, you can mask the firewall service which creates a symbolic link of the firewall.service to /dev/null , thus disabling the service.
Unmask FirewallD Service
# systemctl unmask firewalld
This is reverse of masking the service. This removes the symlink of the service created during masking, thus re-enabling the service.
How to Start/Stop and Enable/Disable IPtables Service
On RHEL/CentOS 6/5/4 and Fedora 12-18 iptables firewall comes as pre and later, the iptables service can be installed via:
# yum install iptables-services
Then, the service can be started, stopped or restarted via following commands:
Start Iptables Service
# systemctl start iptables OR # service iptables start
Stop Iptables Service
# systemctl stop iptables OR # service iptables stop
Disable Iptables Service
# systemctl disable iptables Or # service iptables save # service iptables stop
Enable Iptables Service
# systemctl enable iptables Or # service iptables start
Check Status of Iptables Service
# systemctl status iptables OR # service iptables status
On Ubuntu and some other Linux distributions however, ufw is the command which is used to manage the iptables firewall service. Ufw provides an easy interface for the user to handle the iptables firewall service.
Enable Ufw Iptables Firewall
Disable Ufw Iptables Firewall
Check Status of Ufw Iptables Firewall
However, if you want to list chains in iptables which contains all the rules following command can help you achieve the same:
Conclusion
These are the techniques which can help you start, stop, disable and enable the packet management services in Linux Based Systems. Different Linux distros can have different services as default, like: Ubuntu can have iptables as the default and pre-installed service, while CentOS can have firewalld as the default configured service for managing incoming and outgoing of IP packets.
Presented in this article are the most common tricks to manage these services on almost all Linux Distros, however, if you find something and would like to add on to this article, your comments are always welcome.