- How do I start/stop mysql server?
- 11 Answers 11
- How to Start, Stop, and Restart MySQL Server
- How to Start, Stop, and Restart MySQL Server in Linux
- How to Start, Stop, and Restart MySQL Server in Windows
- How to Start/Stop MySQL Server on Ubuntu?
- How to Start the MySQL Server on Ubuntu?
- How to Stop the MySQL Server on Ubuntu?
- Conclusion
How do I start/stop mysql server?
I tried to find in some articles describing how to correctly start & stop mysql server. I found this link: How to start/stop MySql server on Ubuntu 8.04 | Abhi’s Blogging World I ran this command:
ERROR 1045 (28000) Access denied for user. sudo /etc/init.d/mysql - root -p start ERROR 1049 (42000) Unknown database 'start'. MySQL server success started. Cool! So, what’s wrong with the other commands? Why do they result in error?
In fact, even with sudo it didn’t work for me, but then I found in the script the following hint: Rather than invoking init scripts through /etc/init.d, use the service(8) and it was ok
Generally you can use sudo -l to see what your specific user on your specific system is allowed to do with sudo. (Your permissions are configured in /etc/sudoers.) However I don’t know for sure if it would help in this particular case. EDIT: Wait, never mind, the access denied error looks like it is coming from MySQL or something, not sudo.
11 Answers 11
Your first two commands weren’t run as root so that is expected behaviour. You need to be root to stop/start mysql.
should work. Indeed it does, for me:
kojan:~> sudo /etc/init.d/mysql restart [sudo] password for chris: Stopping MySQL database server: mysqld. Starting MySQL database server: mysqld. Checking for corrupt, not cleanly closed and upgrade needing tables.. I used restart rather than start, since it was already running, but the effect is the same. Are you sure you entered your password correctly? 🙂 Have you edited your sudo config at all which would stop this working?
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql - root -p start The arguments are wrong. an init.d script only takes start or stop or restart — just one word telling it what to do. You cannot give it multiple arguments as you were trying to do.
Anyway, the short answer is the one you actually got to work, is the recommended way. service is replacing all the init.d scripts over time, so you should get into the habit of using service . The page you link to was written in 2008, so has to be taken with some salt 🙂
How to Start, Stop, and Restart MySQL Server
When using MySQL, there are times when it’s important to know how to start, stop, or restart your MySQL server. Luckily, there are multiple, easy ways to do this. Which methods are available to you however, will depend on the operating system your running.
Read on to learn how to start, stop, and restart MySQL server in both Linux and Windows.
How to Start, Stop, and Restart MySQL Server in Linux
If you need to stop or restart your MySQL server on a Linux system, there are three different commands that can be used:
- Depending on your Linux distribution, you can change the state of MySQL using the service command.
- To start MySQL server:
sudo service mysqld start
- To stop MySQL server:
sudo service mysqld stop
- To restart MySQL server:
sudo service mysqld restart
- To start MySQL server:
- If you don’t have the service command available or would prefer to make changes to MySQL using a different method, you can also use the init.d command to start/stop your MySQL server.
- To start MySQL server:
sudo /etc/init.d/mysqld start
- To stop MySQL server:
sudo /etc/init.d/mysqld stop
- To restart MySQL server:
sudo /etc/init.d/mysqld restart
- To start MySQL server:
- Lastly, you can also use the systemctl command to start, stop, and restart applications on Linux, including MySQL.
- To start MySQL server:
sudo systemctl start mysqld
- To stop MySQL server:
sudo systemctl stop mysqld
- To restart MySQL server:
sudo systemctl restart mysqld
- To start MySQL server:
How to Start, Stop, and Restart MySQL Server in Windows
If you’re trying to start, stop, or restart your MySQL server on a Windows-based system, you can do so easily from the command line. Just follow these 3 steps:
- To start, you’ll first need to open a terminal window. If you don’t have this somewhere easily accessible, you can find it quickly using the Windows’ Run dialog. To open the Run dialog, just press the Windows Key + R .
- Next, type in “ cmd ” and press the Enter key. This will open a new terminal window.
- Once you’ve opened a terminal window, just type the following commands to start or stop MySQL server:
- To start MySQL server:
mysqld start
- To stop MySQL server:
mysqld stop
- To start MySQL server:
*Note: depending on which version of Windows you are running, you may need the specific name of the MySQL version number you are running in order to start or stop the service. To find this, go to the start menu and search for Services . Locate the version of MySQL you are using and try the following commands, replacing “##” with your version number:
net start MySQL##
net stop MySQL##
For instance, if you’re running MySQL 8.0, replace “MySQL##” with “MySQL80”.
And there you have it! You now have several different methods for starting, stopping, and restarting MySQL server as needed.
Looking for more information on MySQL ? Search our Knowledge Base !
Interested in more articles about Databases ? Navigate to our Categories page using the bar on the left or check out these popular articles:
Popular tags within this category include: MySQL , MSSQL , phpMyAdmin , PostgreSQL , and more.
Don’t see what you’re looking for? Use the search bar at the top to search our entire Knowledge Base.
The Hivelocity Difference
Seeking a better Dedicated Server solution? In the market for Private Cloud or Colocation services? Check out Hivelocity’s extensive list of products for great deals and offers.
With best-in-class customer service, affordable pricing, a wide-range of fully-customizable options, and a network like no other, Hivelocity is the hosting solution you’ve been waiting for.
Unsure which of our services is best for your particular needs? Call or live chat with one of our sales agents today and see the difference Hivelocity can make for you.
How to Start/Stop MySQL Server on Ubuntu?
MySQL Server is a free and open-source relational database management system that is utilized to store and manage data. Ubuntu allows users to install, run, start, or stop MySQL Server services to manage their databases, tables, queries, and many more.
This article will provide a detailed explanation to start and stop the MySQL Server service on Ubuntu:
Note: To install MySQL on Ubuntu, follow the link.
How to Start the MySQL Server on Ubuntu?
The “systemctl” command is utilized to manage system services by starting or stopping. To start the MySQL Server service, follow these steps:
Step 1: Start the MySQL Server Service
To start the MySQL Server service, use the “systemctl” command with the “start” option in the terminal window:
$ sudo systemctl start mysql
The output command shows that the MySQL Server service has been started and makes it available for use.
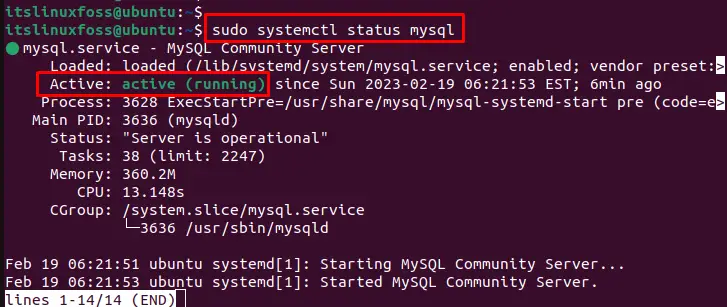
Step 2: Verify the Status of the MySQL Server Service
To verify that the MySQL Server service is running, utilize the “systemctl” command with the “status” option. It displays information about the current status of the MySQL Server service, including whether it is running or stopped:
$ sudo systemctl status mysql
This output indicates that the MySQL Server service is running and has been active for a certain amount of time.
How to Stop the MySQL Server on Ubuntu?
To stop the MySQL Server service, follow the step-by-step instructions which are given below:
Step 1: Stop the MySQL Server Service
To stop the MySQL Server service, specify the “systemctl” command with the “stop” option by specifying the “mysql” in the terminal window:
$ sudo systemctl stop mysql
It stops the MySQL Server service and prevents any further access to the server until the service is started again.
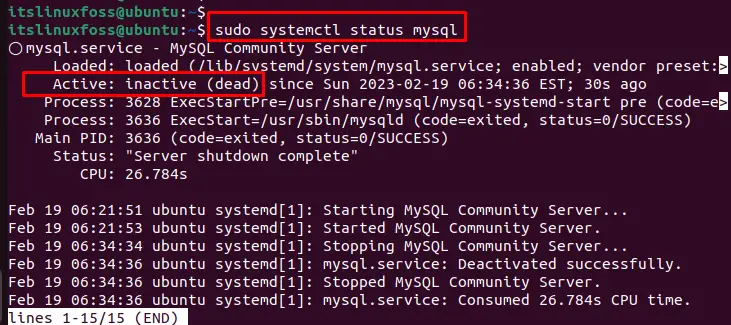
Step 2: Verify the MySQL Server Service
Users can now verify that the MySQL Server service is no longer running by typing the “systemctl” command with the “status” option in the terminal:
$ sudo systemctl status mysql
This output indicates that the MySQL Server service is not running and has been inactive since a certain time.
Conclusion
To start and stop the MySQL server on Ubuntu, execute the “sudo systemctl start mysql” and “sudo systemctl stop mysql” commands. After the start/stop, it is recommended to check the status of the MySQL Server service using the “sudo systemctl status mysql” command. This article has briefly demonstrated methods to start and stop the MySQL server’s service on Ubuntu.