syslog(3) — Linux man page
closelog() closes the descriptor being used to write to the system logger. The use of closelog() is optional.
openlog() opens a connection to the system logger for a program. The string pointed to by ident is prepended to every message, and is typically set to the program name. If ident is NULL, the program name is used. (POSIX.1-2008 does not specify the behavior when ident is NULL.)
The option argument specifies flags which control the operation of openlog() and subsequent calls to syslog(). The facility argument establishes a default to be used if none is specified in subsequent calls to syslog(). Values for option and facility are given below. The use of openlog() is optional; it will automatically be called by syslog() if necessary, in which case ident will default to NULL.
syslog() generates a log message, which will be distributed by syslogd(8). The priority argument is formed by ORing the facility and the level values (explained below). The remaining arguments are a format, as in printf(3) and any arguments required by the format, except that the two character sequence %m will be replaced by the error message string strerror(errno). A trailing newline may be added if needed.
The function vsyslog() performs the same task as syslog() with the difference that it takes a set of arguments which have been obtained using the stdarg(3) variable argument list macros.
The subsections below list the parameters used to set the values of option, facility, and priority.
option The option argument to openlog() is an OR of any of these: LOG_CONS
Write directly to system console if there is an error while sending to system logger.
Open the connection immediately (normally, the connection is opened when the first message is logged).
Don’t wait for child processes that may have been created while logging the message. (The GNU C library does not create a child process, so this option has no effect on Linux.)
The converse of LOG_NDELAY; opening of the connection is delayed until syslog() is called. (This is the default, and need not be specified.)
(Not in POSIX.1-2001 or POSIX.1-2008.) Print to stderr as well.
Include PID with each message.
facility The facility argument is used to specify what type of program is logging the message. This lets the configuration file specify that messages from different facilities will be handled differently. LOG_AUTH
security/authorization messages (private)
clock daemon (cron and at)
system daemons without separate facility value
kernel messages (these can’t be generated from user processes) LOG_LOCAL0 through LOG_LOCAL7
reserved for local use LOG_LPR
messages generated internally by syslogd(8) LOG_USER (default)
generic user-level messages LOG_UUCP
level This determines the importance of the message. The levels are, in order of decreasing importance: LOG_EMERG
action must be taken immediately
normal, but significant, condition
debug-level message The function setlogmask(3) can be used to restrict logging to specified levels only.
Conforming To
The functions openlog(), closelog(), and syslog() (but not vsyslog()) are specified in SUSv2, POSIX.1-2001, and POSIX.1-2008. POSIX.1-2001 specifies only the LOG_USER and LOG_LOCAL* values for facility. However, with the exception of LOG_AUTHPRIV and LOG_FTP, the other facility values appear on most UNIX systems. The LOG_PERROR value for option is not specified by POSIX.1-2001 or POSIX.1-2008, but is available in most versions of UNIX.
Notes
The argument ident in the call of openlog() is probably stored as-is. Thus, if the string it points to is changed, syslog() may start prepending the changed string, and if the string it points to ceases to exist, the results are undefined. Most portable is to use a string constant.
Never pass a string with user-supplied data as a format, use the following instead:
Beginner’s Guide to Syslogs in Linux
The good old syslogs are still relevant in the systemd age of journal logs. Learn the basics of logging with syslogd in this guide.
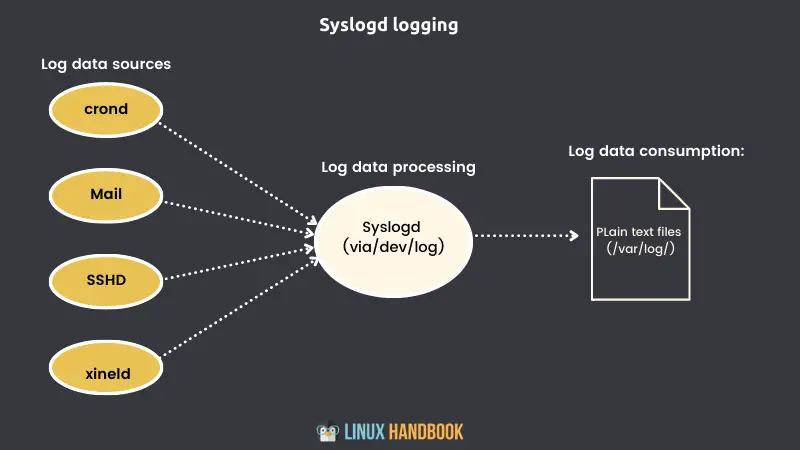
For decades, Linux logging has been managed by the syslogd daemon.
Syslogd would collect the log messages that system processes and applications sent to the /dev/log pseudo device. Then it would direct the messages to appropriate plain text log files in the /var/log/ directory.
Syslogd would know where to send the messages because each one includes headers containing metadata fields (including a time-stamp, and the message origin and priority).
In the wake of systemd’s relentless, world-conquering juggernaut, Linux logging is now also handled by journald. I say also because syslogd hasn’t gone anywhere, and you can still find most of its traditional log files in /var/log/. But you need to be aware that there’s a new sheriff in town whose (command line) name is journalctl.
But this article is not about journald. The focus here is on systemd so let’s dig it a bit more.
Logging with syslogd
All the logs generated by events on a syslogd system are added to the /var/log/syslog file. But, depending on their identifying characteristics, they might also be sent to one or more other files in the same directory.
With syslogd, the way messages are distributed is determined by the contents of the 50-default.conf file that lives in the /etc/rsyslog.d/ directory.
This example from 50-default.conf shows how log messages marked as cron-related will be written to the cron.log file. In this case, the asterisk (*) tells syslogd to send entries with any priority level (as opposed to a single level like emerg or err):
Working with syslogd log files doesn’t require any special tools like journalctl. But if you want to get good at this, you’ll need to know what kind of information is kept in each of the standard log files.
The table below lists the most common syslogd log files and
their purposes.
| Filename | Purpose |
|---|---|
| auth.log | System authentication and security events |
| boot.log | A record of boot-related events |
| dmesg | Kernel-ring buffer events related to device drivers |
| dpkg.log | Software package-management events |
| kern.log | Linux kernel events |
| syslog | A collection of all logs |
| wtmp | Tracks user sessions (accessed through the who and last commands) |
In addition, individual applications will sometimes write to their own log files. You’ll often also see entire directories like /var/log/apache2/ or /var/log/mysql/ created to receive application data.
Log redirection can also be controlled through any one of eight priority levels, in addition to the * symbol (for all priority levels) you saw before.
| Level | Description |
|---|---|
| debug | Helpful for debugging |
| info | Informational |
| notice | Normal conditions |
| warn | Conditions requiring warnings |
| err | Error conditions |
| crit | Critical conditions |
| alert | Immediate action required |
| emerg | System unusable |
Managing log files with sysglogd
By default, syslogd handles log rotation, compression, and deletion behind the scenes without any help from you. But you should know how it’s done in case you ever have logs needing special treatment.
What kind of special treatment could a simple log ever require? Well, suppose your company has to be compliant with the transaction reporting rules associated with regulatory or industry standards like Sarbanes-Oxley or PCI-DSS. If your IT infrastructure records must remain accessible for longer periods of time, then you’ll definitely want
to know how to find your way through the key files.
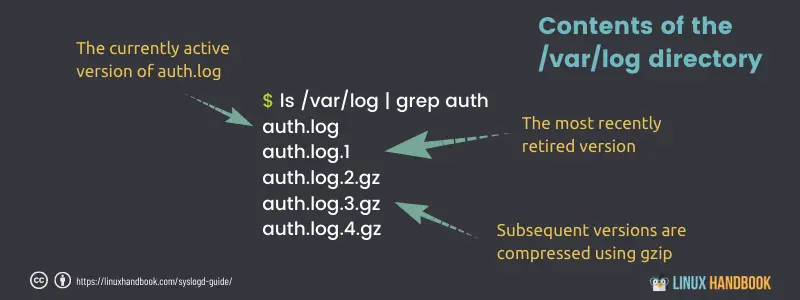
To see the logrotate system in action, list some of the contents of the /var/log/ directory. The auth.log file, for instance, appears in three different formats:
- auth.log — The version that’s currently active, with new auth messages being written to it.
- auth.log.1 — The most recent file to have been rotated out of service. It’s maintained in uncompressed format to make it easier to quickly call it back into action should it be necessary.
- auth.log.2.gz — An older collection (as you can see from the .gz file extension in the following listing) that has been compressed to save space.
After seven days, when the next rotation date arrives, auth.log.2.gz will be renamed auth.log.3.gz, auth.log.1 will be compressed and renamed auth.log.2.gz, auth.log will become auth.log.1, and a new file will be created and given the name auth.log.
The default log rotation cycle is controlled in the /etc/logrotate.conf file. The values illustrated in this listing rotate files after a single active week and delete old files after four weeks.
# rotate log files weekly weekly # keep 4 weeks worth of backlogs rotate 4 # create new (empty) log files after rotating old ones create # packages drop log rotation information into this directory include /etc/logrotate.The /etc/logrotate.d/ directory also contains customized configuration files for managing the log rotation of individual services or applications. Listing the contents of that directory, you see these config files:
$ ls /etc/logrotate.d/ apache2 apt dpkg mysql-server rsyslog samba unattended-upgradeYou can view their content to see what kind of configuration they have on log rotation.
Many admins choose to redirect log entries to purpose-built remote log servers where the data can receive all the specialized attention it deserves. This can free up application servers for their immediate tasks and consolidate log data in a single, easily accessible central location.
How to read the syslog files
You know you’ve got better things to do with your time than read through millions of lines of log entries.
Using cat should be avoided entirely here. It will simply dump thousands of lines on your screen.
I suggest using grep for filtering text through the files.
Using tail -f command allows you to read the current log file in real time. You may combine it with grep to filter on desired text.
In some cases, you may require to access the old, compressed logs. You may always extract the file first and then use grep, less and other commands to read its content, however, there is a better option. There are z commands like zcat, zless etc that let you work on the compressed files without explicitly extracting them.
A practical example of log analysis
Here’s an obvious example that will search through the auth.log file for evidence of failed login attempts. Searching for the word failure will
return any line containing the phrase authentication failure.
Checking this once in a while can help you spot attempts to compromise an account by guessing at the correct password. Anyone can mess up a password once or twice, but too many failed attempts should make you suspicious:
$ cat /var/log/auth.log | grep 'Authentication failure' Sep 6 09:22:21 workstation su[21153]: pam_authenticate: Authentication failureIf you’re the kind of admin who never makes mistakes, then this search might come up empty. You can guarantee yourself at least one result by manually generating a log entry using a program called logger. Try it out doing something like this:
logger "Authentication failure"You could also pre-seed a genuine error by logging in to a user account and entering the wrong password.
As you can tell, grep did the job for you, but all you can see from the results is that there was an authentication failure. Wouldn’t it be useful to know whose account was involved? You can expand the results grep returns by telling it to include the lines immediately before and after the match.
This example prints the match along with the lines around it. It tells you that someone using the account david tried unsuccessfully to use su (switch user) to log in to the studio account:
$ cat /var/log/auth.log | grep -C1 failure Sep 6 09:22:19 workstation su[21153]: pam_unix(su:auth): authentication failure; logname= uid=1000 euid=0 tty=/dev/pts/4 ruser=david rhost= user=studio Sep 6 09:22:21 workstation su[21153]: pam_authenticate: Authentication failure Sep 6 09:22:21 workstation su[21153]: FAILED su for studio by davidWhat next?
Knowing the basics is one thing and applying the knowledge is a different thing. However, the knowledge of the fundamentals helps in various situations.
Now that you know the essentials of syslogs in Linux, you may have a slight better time while dealing with logs.
This article is an excerpt from the book Linux in Action by David Clinton. It is published by Manning Publication and you can get 30% discount on any Manning books using the code nlitsfoss22 at checkout time.