- How to Use Python ‘SimpleHTTPServer’ to Create Webserver or Serve Files Instantly
- Step 1: Check for Python Installation
- Step 2: Create a Test Directory and Enable SimpleHTTPServer
- Step 3: Changing SimpleHTTPServer Port
- Step 4: Serve Files from Different Location
- Step 5: Serve HTML Files
- Hi all. SimpleHTTPServer works fine.
- How to Use Python SimpleHTTPServer
- Run the Web Server from the terminal
- Run the Web Server using Python script
- testHTML.html
- Example-1: Run the webserver in the specific port number
- Output
- Example-2: Run the webserver with the port number defined by command-line
- Output
- Example-3: Run the webserver with the HTML file
- Output
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Fahmida Yesmin
- Запуск простого HTTP сервера из Python
How to Use Python ‘SimpleHTTPServer’ to Create Webserver or Serve Files Instantly
SimpleHTTPServer is a python module which allows you to instantly create a web server or serve your files in a snap. Main advantage of python’s SimpleHTTPServer is you don’t need to install anything since you have python interpreter installed. You don’t have to worry about python interpreter because almost all Linux distributions, python interpreter come handy by default.
You also can use SimpleHTTPServer as a file sharing method. You just have to enable the module within the location of your shareable files are located. I will show you several demonstrations in this article by using various options.
Step 1: Check for Python Installation
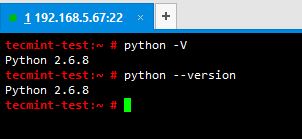
1. Check whether python is installed in your server or not, by issuing below command.
# python –V OR # python --version
It will show you the version of the python interpreter you’ve got and it will give you an error message if it is not installed.
2. You’re lucky if it was there by default. Less work actually. If it was not installed by any chance, install it following below commands.
If you have a SUSE distribution, type yast in the terminal –> Go to Software Management –> Type ‘python’ without quotes –> select python interpreter –> press space key and select it –> and then install it.
Simple as that. For that, you need to have SUSE ISO mounted and configured it as a repo by YaST or you can simple install python from the web.
If you’re using different operating systems like RHEL, CentOS, Debian, Ubuntu or other Linux operating systems, you can just install python using yum or apt.
In my case I use SLES 11 SP3 OS and python interpreter comes installed by default in it. Most of the case you won’t have to worry about installing python interpreter on your server.
Step 2: Create a Test Directory and Enable SimpleHTTPServer
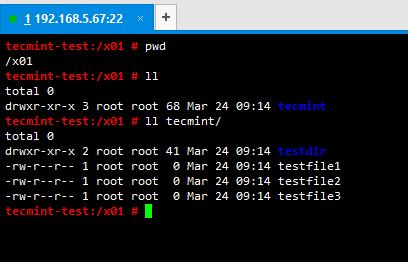
3. Create a test directory where you don’t mess with system files. In my case I have a partition called /x01 and I have created a directory called tecmint in there and also I have added some test files for testing.
4. Your prerequisites are ready now. All you have to do is try python’s SimpleHTTPServer module by issuing below command within your test directory (In my case, /x01//).
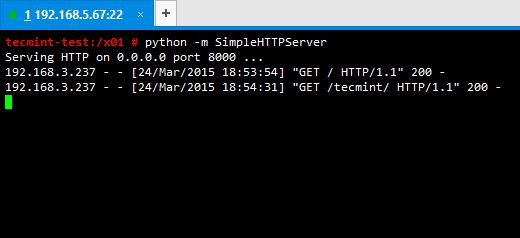
# python –m SimpleHTTPServer
5. After enabling SimpleHTTPServer successfully, it will start serving files through port number 8000. You just have to open up a web browser and enter ip_address:port_number (in my case its 192.168.5.67:8000).
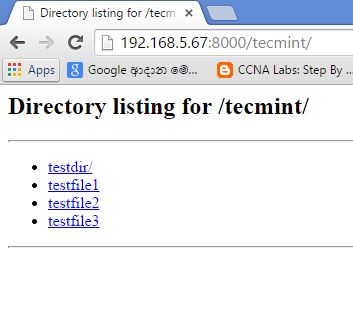
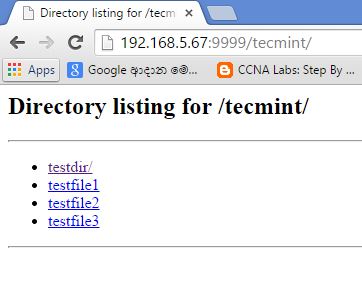
6. Now click on link ‘tecmint’ to browse files and directories of tecmint directory, see the screen below for reference.
7. SimpleHTTPServer serves your files successfully. You can see what has happened at the terminal, after you accessed your server through web browser by having a look at where you executed your command.
Step 3: Changing SimpleHTTPServer Port
8. By default python’s SimpleHTTPServer serves files and directories through port 8000, but you can define a different port number (Here I am using port 9999) as you desire with the python command as shown below.
# python –m SimpleHTTPServer 9999

Step 4: Serve Files from Different Location
9. Now as you tried it, you might like to serve your files in a specific location without actually going to the path.
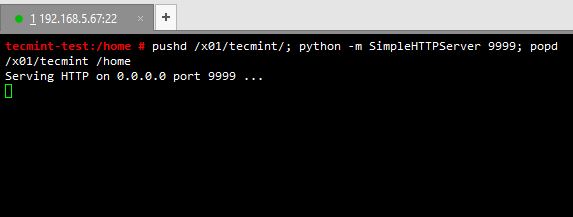
As an example, if you are in your home directory and you want to server your files in /x01/tecmint/ directory without cd in to /x01/tecmint, Let’s see, how we will do this.
# pushd /x01/tecmint/; python –m SimpleHTTPServer 9999; popd;
Step 5: Serve HTML Files
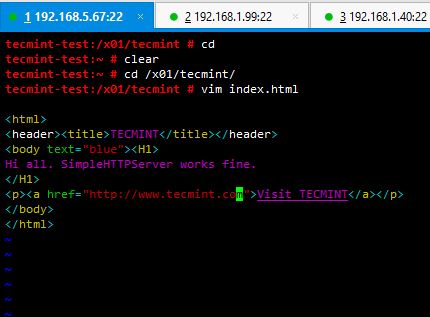
10. If there’s a index.html file located in your serving location, python interpreter will automatically detect it and serve the html file instead of serving your files.
Let’s have a look at it. In my case I include a simple html script in the file named index.html and locate it in /x01/tecmint/.
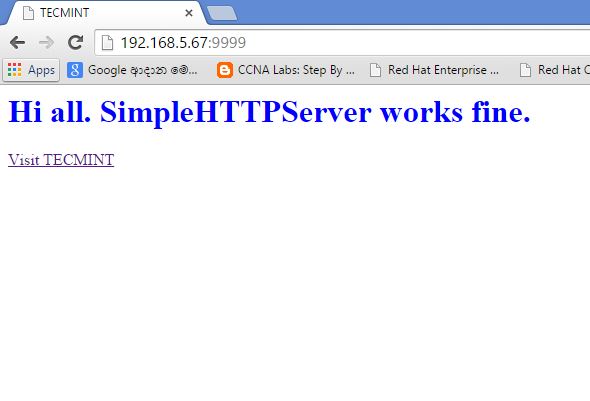
Hi all. SimpleHTTPServer works fine.
Visit TECMINT
Now save it and run SimpleHTTPServer on /x01/tecmint and go to the location from a web browser.
# pushd /x01/tecmint/; python –m SimpleHTTPServer 9999; popd;
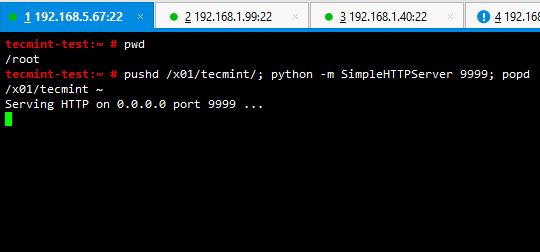
Very simple and handy. You can serve your files or your own html code in a snap. Best thing is you won’t have to worry about installing anything at all. In a scenario like you want to share a file with someone, you don’t have to copy the file to a shared location or making your directories shareable.
Just run SimpleHTTPServer on it and it is done. There is a few things you have to keep in mind when using this python module. When it serves files it runs on the terminal and prints out what happens in there. When you’re accessing it from the browser or download a file from it, it shows IP address accessed it and file downloaded etc. Very handy isn’t it?
If you want to stop serving, you will have to stop the running module by pressing ctrl+c. So now you know how to use python’s SimpleHTTPServer module as a quick solution to serve your files. Commenting below for the suggestions and new findings would be a great favour to enhance future articles and learn new things.
How to Use Python SimpleHTTPServer
The main task of the webserver is to handle the HTTP requests from the client. It waits for the HTTP requests coming from the particular IP address and port number, handles the request, and sends the client’s response back. Python uses the SimpleHTTPServer module to create a web server instantly and easily serve the content of the file from the server. It can be used for file sharing also. For this, you have to enable this module with the location of the shareable files. This module comes with the Python interpreter. You don’t need to install it. Since this module is merged with the http.server module in python3, so you have to run http.server to run the webserver in python3. How web server can be used to handle HTTP request and share files, have been shown in this tutorial.
Run the Web Server from the terminal
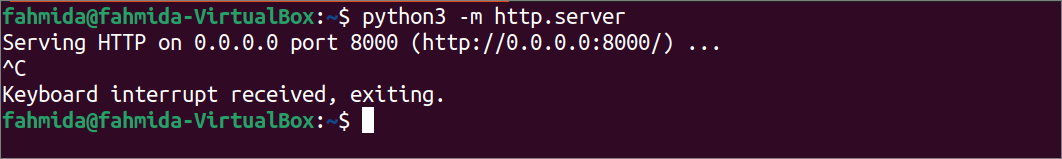
Run the following command to run the webserver from the terminal. If no port number is defined in the command, the webserver will start at 8000 port by default.
The following output will appear if the webserver is started properly. CTRL+C is pressed to stop the server.
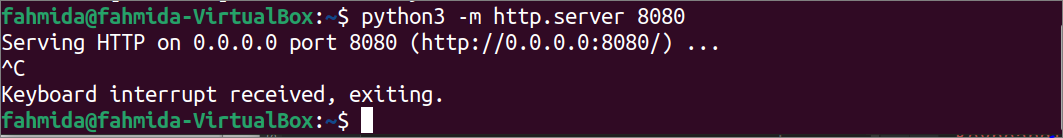
Run the following command to start the webserver at 8080 port.
The following output will appear if the webserver is started at the 8080 port.
Run the Web Server using Python script
Run the following commands to create a folder named web and go to the folder. All the script files and HTML files of this tutorial will be created inside this folder.
Create an HTML file named testHTML.html inside the web folder with the following script. This file will be served from the webserver later.
testHTML.html
Example-1: Run the webserver in the specific port number
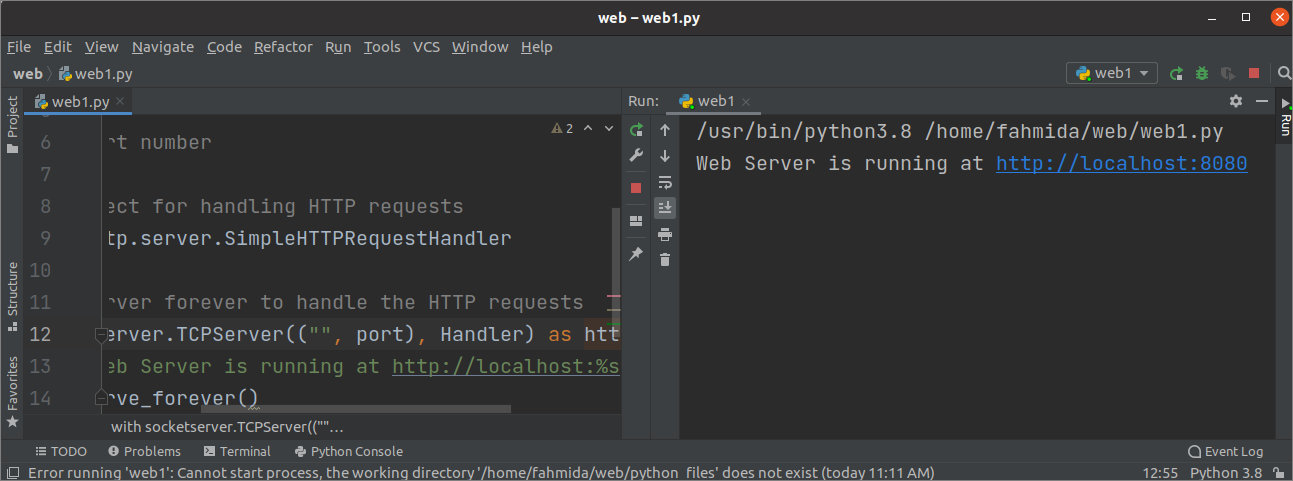
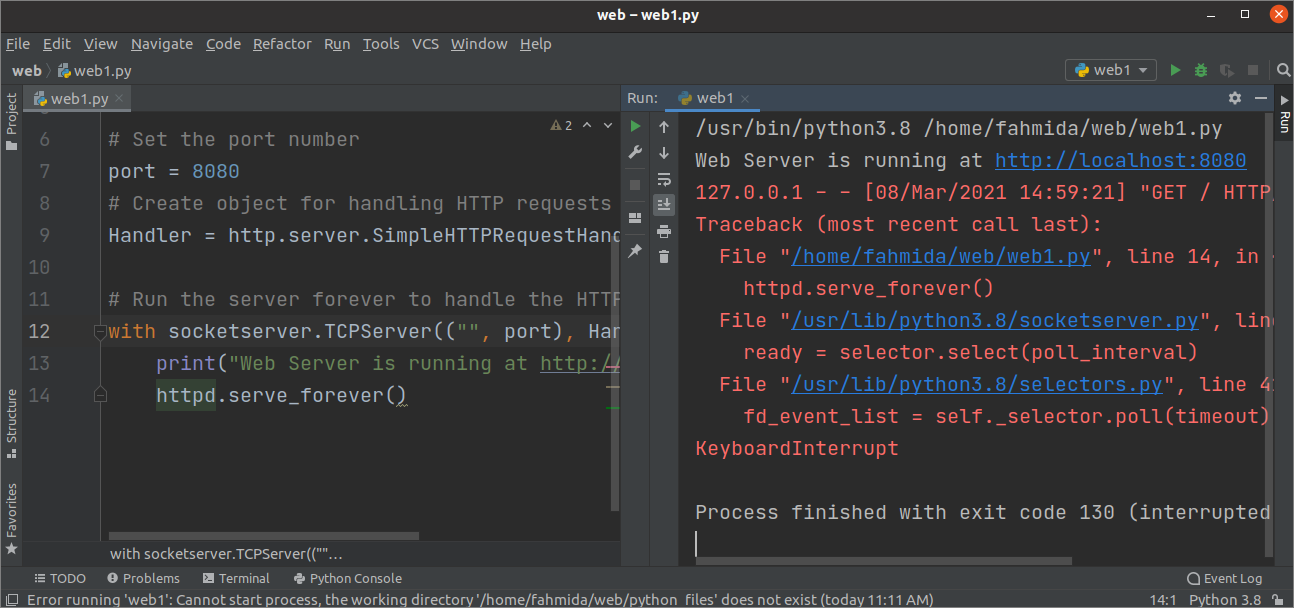
Create a python file with the following script to run the webserver at 8008 port. http.server module has been imported to run the webserver, and the SocketServer module has been imported to handle the HTTP request coming from the 8080 port. An object named Handler has been created to handle the HTTP requests. forever() function is called to run the webserver. No termination condition has been added to the script. So, the script will generate an error when the user tries to stop the server.
# Import server module
import http. server
# Import SocketServer module
import socketserver
# Set the port number
port = 8080
# Create object for handling HTTP requests
Handler = http. server . SimpleHTTPRequestHandler
# Run the server forever to handle the HTTP requests
with socketserver. TCPServer ( ( «» , port ) , Handler ) as httpd:
print ( «Web Server is running at http://localhost:%s» %port )
httpd. serve_forever ( )
Output
The following output will be appeared after executing the above script.
The list of the files and folder of the script location will be shown if the following URL is executed from the browser.
If the user presses CTRL+C from the terminal or presses the stop button from the PyCharm editor, the following error message will be displayed. This problem has solved in the next example of this tutorial.
Example-2: Run the webserver with the port number defined by command-line
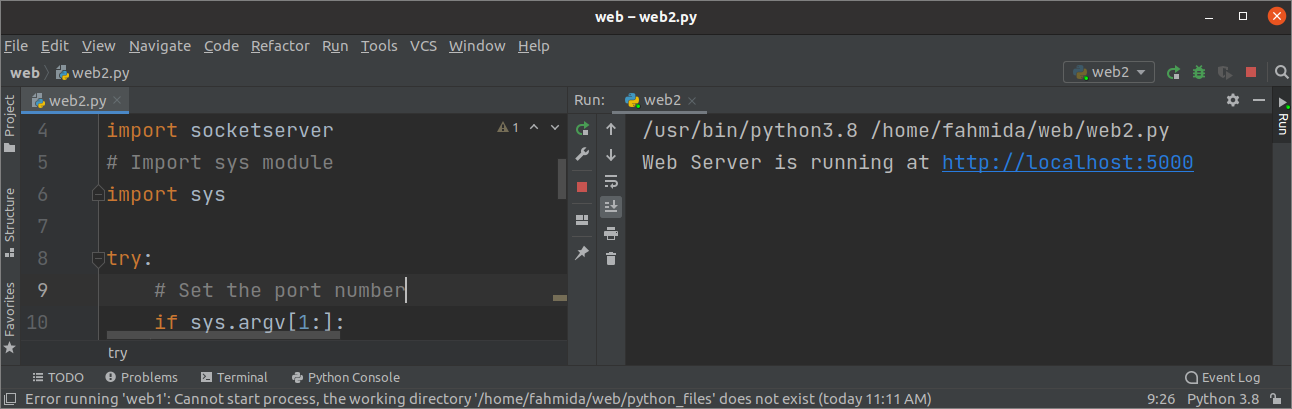
Create a python file with the following script to run a web server at the particular port if the command-line argument gives the port number; otherwise, 5000 will be used as the default port. sys module has been imported in the script to read the command-line argument values. try-except block has been added in the script to handle the error when the user tries to stop the server. If the KeyboardInterrupt exception appears after running the server, then the close() function will be called to stop the webserver.
# Import server module
import http. server
# Import SocketServer module
import socketserver
# Import sys module
import sys
# Set the port number
if sys . argv [ 1 : ] :
port = int ( sys . argv [ 1 ] )
# Set the IP address
server_address = ( ‘127.0.0.1’ , port )
# Create object for handling HTTP requests
Handler = http. server . SimpleHTTPRequestHandler
# Run the web server forever to handle the HTTP requests
with socketserver. TCPServer ( ( «» , port ) , Handler ) as httpd:
print ( «Web Server is running at http://localhost:%s» %port )
httpd. serve_forever ( )
# Stopped the server
except KeyboardInterrupt :
httpd. server_close ( )
print ( «The server is stopped.» )
Output
The following output will be appeared after executing the above script without command-line argument value.
The following output will appear if the run the HTML file that is created in the previous step from the webserver.
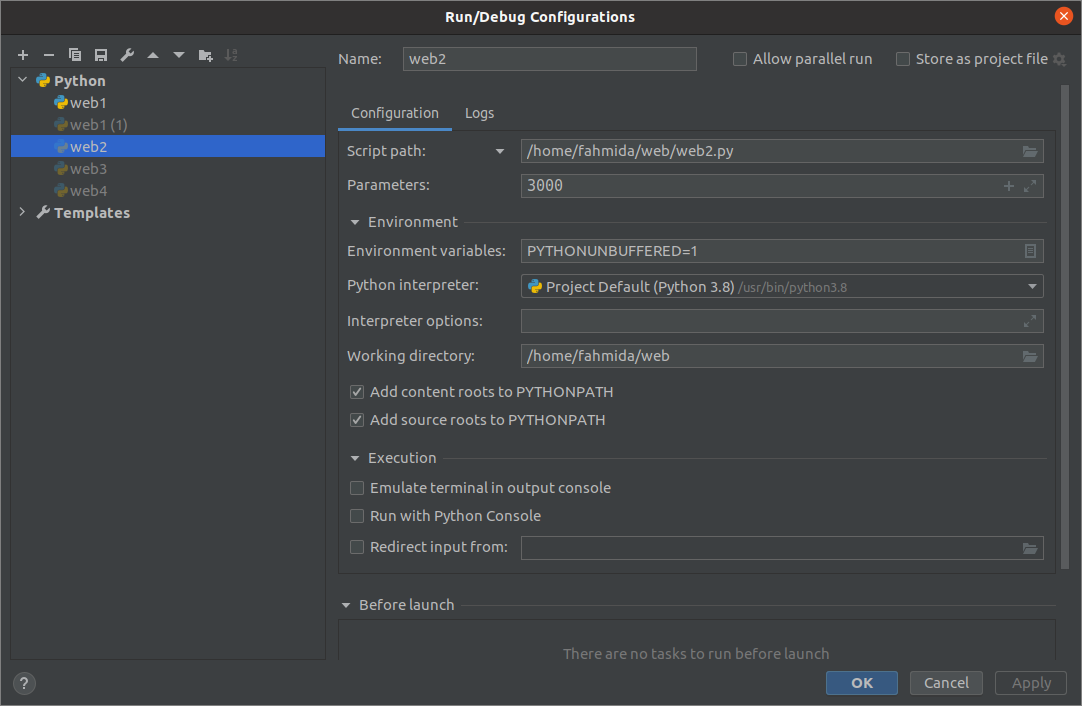
Open the configuration dialog box from the Run menu of the PyCharm editor to set the command-line argument value. Parameters field is used to set the command-line argument, and 3000 is set here as the argument value.
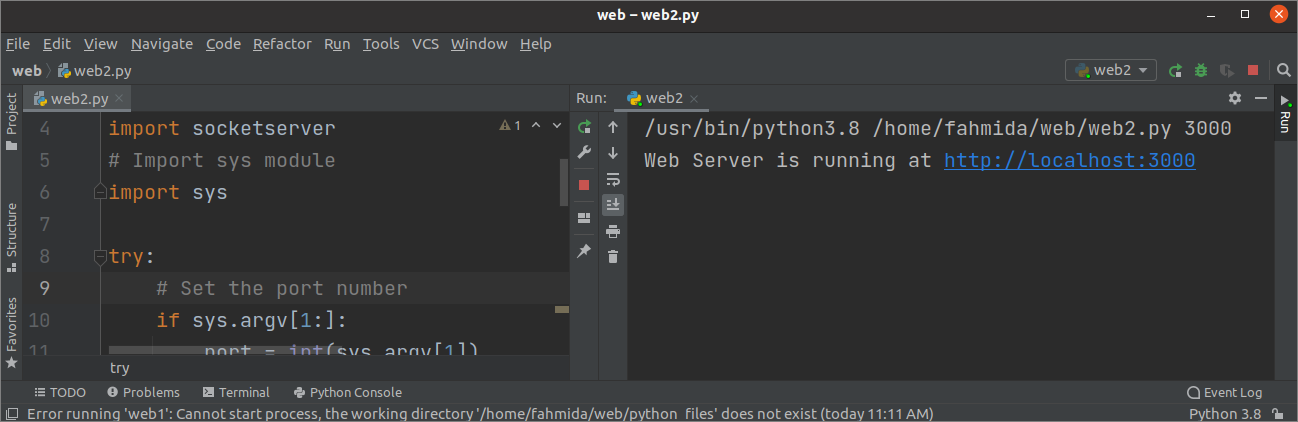
The following output will appear if you run the script again after setting the argument value.
Example-3: Run the webserver with the HTML file
Create a python file with the following script to run the webserver by defining the HTML file for the base URL. The hostname and the port number have defined at the beginning of the script. PythonServer class has defined in the script to display the HTML file in the browser when the web server starts running.
# Import the server module
import http. server
# Set the hostname
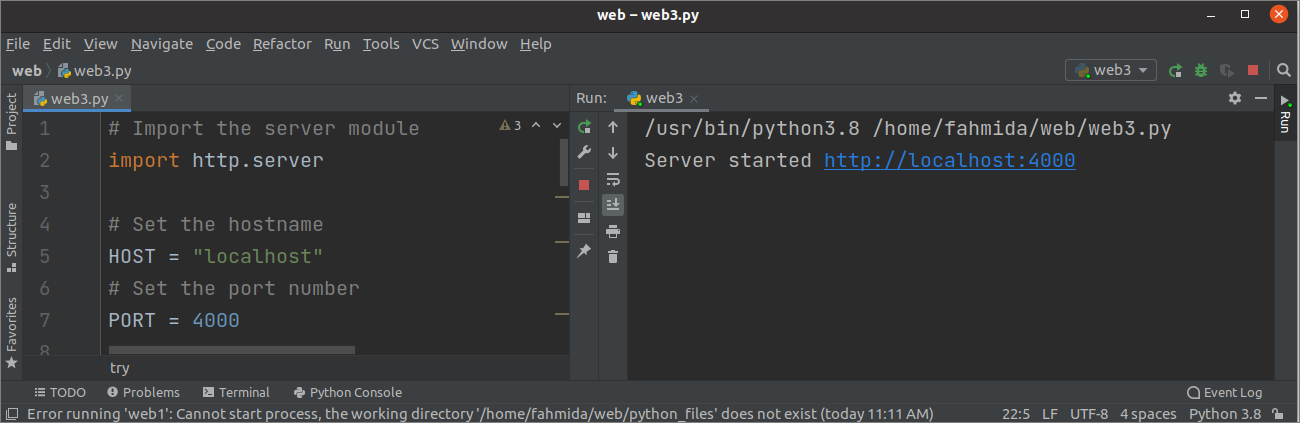
HOST = «localhost»
# Set the port number
PORT = 4000
# Define class to display the index page of the web server
class PythonServer ( http. server . SimpleHTTPRequestHandler ) :
def do_GET ( self ) :
if self . path == ‘/’ :
self . path = ‘testHTML.html’
return http. server . SimpleHTTPRequestHandler . do_GET ( self )
# Declare object of the class
webServer = http. server . HTTPServer ( ( HOST , PORT ) , PythonServer )
# Print the URL of the webserver
print ( «Server started http://%s:%s» % ( HOST , PORT ) )
# Run the web server
webServer. serve_forever ( )
# Stop the web server
webServer. server_close ( )
print ( «The server is stopped.» )
Output
The following output will appear executing the above script.
The following page will appear in the browser if the browser’s base URL of the webserver executes.
Conclusion
The different ways of implementing web servers by using http. server module has shown in this tutorial to help python users to create a simple web server in Python.
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.
Запуск простого HTTP сервера из Python
В python есть встроенный модуль для быстрого запуска простого HTTP сервера. Для запуска достаточно выполнить одну команду.
№ python -m SimpleHTTPServer
По умолчанию это запустит HTTP сервер на порту 8000. Данный HTTP сервер опубликует содержимого текущего каталога.
Чаще всего я использую этот способ, чтобы быстро опубликовать файлы из произвольного каталога хоста Linux по HTTP, и скачать файлы на другое устройство. Например, мне нужно скачать определенный лог файл из каталога /var/log.
Для этого нужно перейти в указанный каталог:
И запустить HTTP сервер python:
$ python3 -m http.server 8080
Если этот порт закрыт файерволом, нужно предварительно временно открыть его:
$ sudo firewall-cmd —add-port=8080/tcp
Теперь на другом устройства откройте браузер, перейдите по адресу http://192.168.79.128:8080 и скачайте нужные файлы.
HTTP сервер пишет в консоль лог всех обращений к файлам (HTTP GET).
Затем вернитесь в консоль Linux и завершите процесс веб сервера Python, нажав Ctrl+C .
Этот трюк можно использовать в том числе для передачи файлов из WSL в Windows.