- Linux show hidden files and folders with simple commands
- Create hidden Files
- Create hidden folder or directory
- Linux show hidden files and folders with ‘ls’ command
- Linux show hidden files and folders with ‘find’ command
- Check size of hidden files and folders
- Hide Folders and Show Hidden Files in Ubuntu Linux
- Show hidden files in Linux terminal
- Display hidden files in the file manager (for desktop users)
- Hide files and folders in Ubuntu
- Bonus Tip: Hiding multiple files and folders without renaming them (valid for GUI only)
- Hide it or lock it?
Linux show hidden files and folders with simple commands
The commands from this article to view hidden files and folders can be used across any Linux platform such as Ubuntu, Debian, Linux Mint, RHEL, CentOS, SuSE etc or any Unix node such as HP-UX, Solaris, etc.
I am using RHEL/CentOS 8 node installed on Oracle VirtualBox . Please do let me know via comment section if you face any issues following the commands from this article to view hidden files or folders in Linux or Unix.
I would recommend to configure one click installation using Network PXE Boot Server. Using PXE server you can install Oracle VirtualBox Virtual Machines or KVM based Virtual Machines or any type of physical server without any manual intervention saving time and effort.
Create hidden Files
To create hidden files you just need to make sure the filename starts with dot character ( . ). In Linux any filename which starts with dot ( . ) character is considered as hidden file. For example here I create a normal file using touch command
You can also create your own man page with a list of instructions for a script or a custom tool which you have created. In real time production environment it is always recommended to also create and release a man page for every script or tool we develop.
To list the file, as you see since the filename does not starts with dot ( . ) character, it is not hidden
# ls -l total 0 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 21 18:51 hidden_file
Next we rename the file and make it .hidden_file starting with (.)
# mv hidden_file .hidden_file Next if you try to list the available files, we don’t see hidden_file anymore.
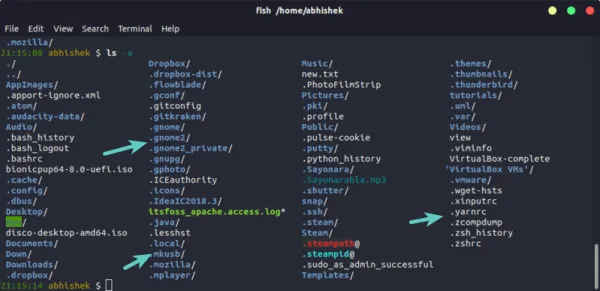
In some Linux or Unix environment it is possible that ls command has an alias to » ls -a «, so in such case even if you execute ls or ls -l , this will show hidden files. For example here ls command without -a will show hidden files
In such case execute alias command from the terminal
# ls -l total 68 drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4096 Jan 21 19:05 . dr-xr-x---. 6 root root 4096 Jan 21 18:51 .. drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Jan 21 19:51 .hidden_directory -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 54894 Jan 21 19:28 .hidden_file -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 21 19:05 normal_directory -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 21 19:05 normal_file
As you see there is an alias for ls command so by default it is configured to hidden files and folders. To remove this temporarily execute » unlias ls «
Next show hidden files and folders using ls , now this works as expected as we don’t see hidden folders or files.
# ls -l total 0 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 21 19:05 normal_directory -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 21 19:05 normal_file
This is temporary fix only for the current session, you need to check where this setting is configured for alias , it may be /etc/profile or /etc/bashrc some other system file based on your distribution.
Similarly to create hidden files you can just put a ( . ) infront of the filename, for example to create hidden files with filename » my_file «:
Create hidden folder or directory
The steps to create hidden folder or directory in Linux or Unix is similar to create hidden files. We just need to make sure the folder name starts with dot ( . ) character.
[root@server3 test]# mkdir .hidden_directory Now list the available files in current directory, as expected we don’t see any directory/folder since the folder is hidden. So we were able to create hidden folder here.
[root@server3 test]# ls -l total 0 Linux show hidden files and folders with ‘ls’ command
- In this example we will use ls command in Linux show hidden files and folders.
- We can use ls command with » -a » to show all files including hidden files and folder.
- With -a «we do not ignore entries starting with . » that means also Linux show hidden files and folders.
- For example to show hidden files and folders which we created in above steps, navigate to your directory and execute ls -a
- We have also used -l to give us a long list so we use ls -al to show all files under test directory in long list format
[root@server3 test]# ls -al total 12 drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4096 Jan 21 19:05 . dr-xr-x---. 6 root root 4096 Jan 21 18:51 .. drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Jan 21 19:02 .hidden_directory -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 21 18:51 .hidden_file
As you see we were able to show hidden folders and files with » ls -a » which we had created earlier in this article.
[root@server3 test]# ls -al total 8 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Jan 21 18:53 . dr-xr-x---. 6 root root 4096 Jan 21 18:51 .. -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 21 18:51 .hidden_file Linux show hidden files and folders with ‘find’ command
Now with ls command we were able to show hidden files in one directory or may be multiple directories in Linux and Unix. But with ls it is little tricky to show hidden folders and files across all partitions. Here we can find hidden files using find command in Linux or Unix.
Now from our chapter » create hidden files » and » create hidden directory «, we know that hidden files start with dot ( . ) character. So we can use this trick with find command to find hidden files.
For example to find hidden files use -type f under /etc/ directory we can use below command
# find /etc/ -type f -name '.*' /etc/selinux/targeted/.policy.sha512 /etc/skel/.kshrc /etc/skel/.bash_profile /etc/skel/.bashrc /etc/skel/.bash_logout /etc/.pwd.lock /etc/.updated
Here we are only search of files using » -type f » and any filename starting with dot ( . )
With Linux show hidden files and folders we can use the same command with -type d to find hidden folders under /usr
# find /usr/ -type d -name '.*' /usr/java/jre1.8.0_172-amd64/.java /usr/java/jre1.8.0_172-amd64/.java/.systemPrefs /usr/local/avamar/etc/.tmp
Here we could not have used » ls -a » to show hidden files in all these directories without using extra commands, so find is a better alternative to find hidden folder and files in Linux or Unix.
Check size of hidden files and folders
Now once you find hidden files or folders, you may also wish to check size of hidden files or folders.
For example we will find hidden files under our ~/test directory
[root@server3 test]# find . -type f -name '.*' ./.hidden_file ./.hidden_directory/.hidden_file_2 So we have two hidden files, we can use ls with -Sh to check size of hidden files but it again has it’s own challenges.
- -S means sort by file size
- -h means print sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K 234M 2G)
We use ls -lSha to show and check size of hidden file but as you see ls could only identify .hidden_file in the current folder but missed .hidden_file_2 available inside .hidden_directory
[root@server3 test]# ls -lSha total 68K -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 54K Jan 21 19:28 .hidden_file drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4.0K Jan 21 19:05 . dr-xr-x---. 6 root root 4.0K Jan 21 18:51 .. drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4.0K Jan 21 19:51 .hidden_directory -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 21 19:05 normal_directory -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 21 19:05 normal_file
Alternatively you can use ls -lSha .* which shall also check child directory for hidden files and print it’s size but again this tool is not very convenient.
We will use du command to check size of hidden files in Linux or Unix. du command is used to estimate file space usage. We must combine du with find commands to first we find hidden files and folders and then we check size of hidden files using du command
For example to check size of hidden files under /test folder
[root@server3 test]# find ~/test/ -type f -name '.*' -exec du -ah <> + 56K /root/test/.hidden_file 984M /root/test/.hidden_directory/.hidden_file_2
Similarly to check size of hidden files under /tmp folder
# find /tmp/ -type f -name '.*' -exec du -ah <> + 4.0K /tmp/smem/smem-1.4/.hg_archival.txt 4.0K /tmp/smem/smem-1.4/.hgtags 4.0K /tmp/test1/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/firmware-cna-emulex-2018.02.01-1.24/.cpq_package.inc 1.6M /tmp/test1/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/firmware-cna-emulex-2018.02.01-1.24/.setup
Lastly I hope the steps from this article to Linux show hidden files and folders, create hidden files, create hidden folder and find hidden files and folders in Linux and Unix was helpful. So, let me know your suggestions and feedback using the comment section.
Didn’t find what you were looking for? Perform a quick search across GoLinuxCloud
If my articles on GoLinuxCloud has helped you, kindly consider buying me a coffee as a token of appreciation.

For any other feedbacks or questions you can either use the comments section or contact me form.
Thank You for your support!!
Hide Folders and Show Hidden Files in Ubuntu Linux
Wondering how to see or hide files in Ubuntu Linux? Its damn easy to do so. Here’s how to show hidden files in Ubuntu and other Linux distributions.
You are probably familiar with the concept of “hiding” a folder or file in Windows. Hiding a folder or file just “removes” the folder from the normal view, and then you can choose to display “hidden files” to see it. So how do you see the hidden files in Linux, then? Let me show you that.
Show hidden files in Linux terminal
If you are in a terminal, you can use the ls command to display all the files, including the hidden ones:
You can recognize the hidden files and folders with the dot (.) before their names.
You can also use the -A option of the ls command to show hidden files but without the . and .. files.
Display hidden files in the file manager (for desktop users)
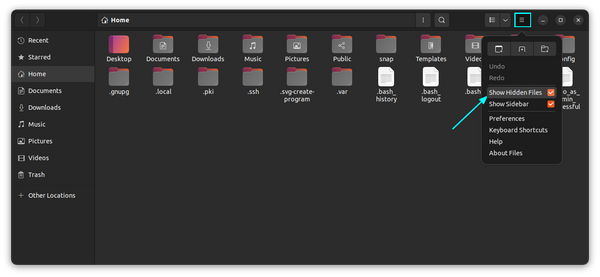
If you are in the file manager, you can use the Ctrl+H keyboard shortcut in Ubuntu and I presume other distributions also display all the files, including the hidden ones. Pressing Ctrl+H again will hide the files. If you are not a fan of keyboard shortcuts, you can use the file manager GUI to display the hidden folders and files. To see a hidden file or hidden folder in Ubuntu, go to the file manager (Ubuntu’s counterpart of Windows Explorer and the default is Nautilus). Now go to the top-right hamburger menu → Show hidden files:
Hide files and folders in Ubuntu
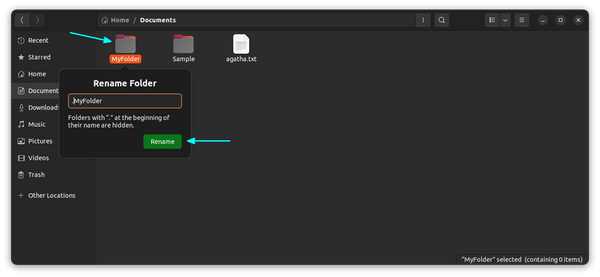
Now that you have learned to see hidden files in Ubuntu, let’s now see how you can hide files and folders in Linux. In Linux, if a file name starts with . (dot), it is considered a hidden file. Now if you want to hide a file or folder, let’s say MyFolder, just rename it to .MyFolder and it will be taken as a hidden file or folder. I hope you know how to rename files in Linux command line using mv command.
If you are using a Linux desktop, right-click and choose the rename option and add the dot before the name. Unfortunately/interestingly, there is no similar way as in Windows to hide a folder. In Windows, you right-click on a file and choose the option of making it hidden. But this option is not available in Ubuntu.
Bonus Tip: Hiding multiple files and folders without renaming them (valid for GUI only)
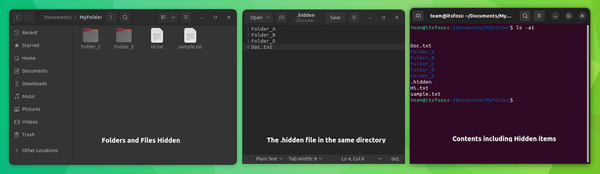
This is a neat little trick that will let you hide several files and folders from the normal view in your desktop Linux’s file manager. Traditionally, if you create a new file named .hidden and add the name of the folders in this file; those folders will be hidden from normal view when you close your file manager and open it again. Keep in mind that this trick works with only the current directory you are in. It won’t work for nested directories. You can create the .hidden file in any directory to hide files and folders in it.
Hide it or lock it?
This .hidden file is one of the many lesser-known tweaks of the Nautilus file manager. Here are a few more. This was about hiding files in Linux. There are separate methods for locking a folder in Linux. I hope you like this little bit of Linux knowledge.