How to check for errors in RAM via Ubuntu?
I have Ubuntu 11 running off a 3.6GB USB flash/stick drive. System has 4GB RAM and blank hard disk (wiped using DBAN tool). How do I check if there are no errors in my RAM? Is there a guaranteed way to check that via some Linux command? If not, it would be great to know why.
You can use memtester once booted into linux.. e.g. sudo memtester 1024 5 This should allocate 1024MB of memory, and repeat the test 5 times.
6 Answers 6
By installing the memtester package, you can check your system for errors while it’s still running. No need for a restart, just run that application.
To install it, open a terminal and type:
sudo apt install memtester You can then use it like so:
This should allocate 1024MB of memory, and repeat the test 5 times.
Update
- If you have more RAM like 4GB or 8GB, it is up to you how much memory you want to allocate for testing.
- As your operating system, current running process might take some amount of RAM, Please check available free RAM and assign that too memtester.
- If you are using a 32 Bit System, you can’t test more than 4 GB even though you have more RAM (32 bit systems doesn’t support more than 3.5 GB RAM).
- If your system is very busy and you still assigned higher than available amount of RAM, then the test might get your system into a deadlock, and leads to system to halt, be aware of this.
- Run the memtester as root user, so that memtester process can malloc the memory, once its gets hold on that memory it will try to apply lock. if specified memory is not available, it will try to reduce required RAM automatically and try to lock it with mlock.
- If you run it as a regular user, it can’t auto reduce the required amount of RAM, so it can’t lock it, it tries to get hold on that specified memory and starts exhausting all system resources.
Does this somehow mean that only a part of the memory is tested, and the rest remains untested? How can I make sure that all of the memory is tested?
Upvoted, but unless I’ve missed something it is not possible to do a thorough test of the entire memory using memtester as the system becomes totally unresponsive (or even memtester fails to claim the full extent of memory you are asking for). So I guess memtester ‘s use case is when you are trying to test a particular area of memory using some advanced arguments which I haven’t explored. Otherwise for a through scan use UNetbootin that runs before loading the operating system and any user programs (so the responsiveness issues becomes moot).
How to Check RAM on Ubuntu 18.04
Random Access Memory or RAM in short, is a very important part of any computer. If you’ve bought a new pre-configured Ubuntu computer or a Virtual Private Server (VPS) and you don’t know any information about how much RAM it has, how much of it is used, the speed of the RAM installed, the type of the RAM, then this article is for you. In this article, I will show you how to find out information about your installed RAM or memory on Ubuntu 18.04 and also find out if you have any problems in your installed RAM. Let’s get started.
Checking Size and Availability of RAM
You can check how much RAM you have installed on your Ubuntu 18.04 machine using the following command:
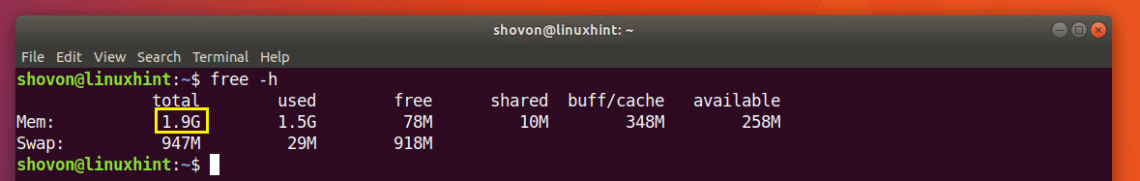
As you can see from the marked section of the screenshot below, the total installed RAM on my Ubuntu 18.04 machine is 1.9 Giga Bytes (GB).
You can also find out how much RAM is used and how much RAM is available using free command.
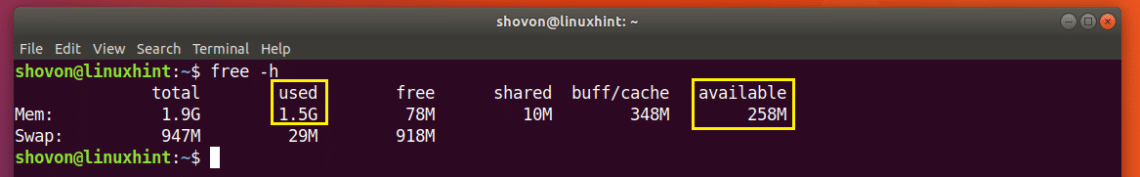
As you can see from the marked section of the screenshot below, the RAM used on my Ubuntu 18.04 machine is 1.5 Giga Bytes (GB) and the RAM available or free is 258 Mega Bytes (MB).
Checking the Type and Speed of RAM
There are different types of RAM available in the market. For example, DDR1, DDR2, DDR3 and DDR4. DDR here means Double Data Rate. At the time of this writing, the most widely used RAM type is DDR3 and DDR4. There are other types of memory for portable devices as well such as SDRAM, DRAM etc.
Every RAM or memory module these days has different profiles. Each of these profile define the clock speed at which the RAM should be running.
You can check the type of RAM you have installed on your Ubuntu 18.04 machine using the following command:
You should see the following window as shown in the screenshot below. This is a lot of information. You can press the and arrow keys to navigate this information.
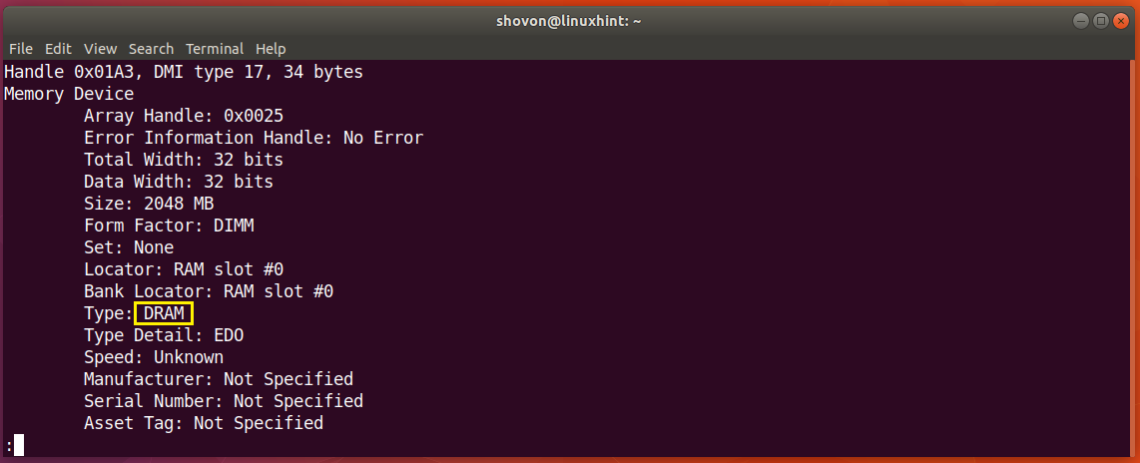
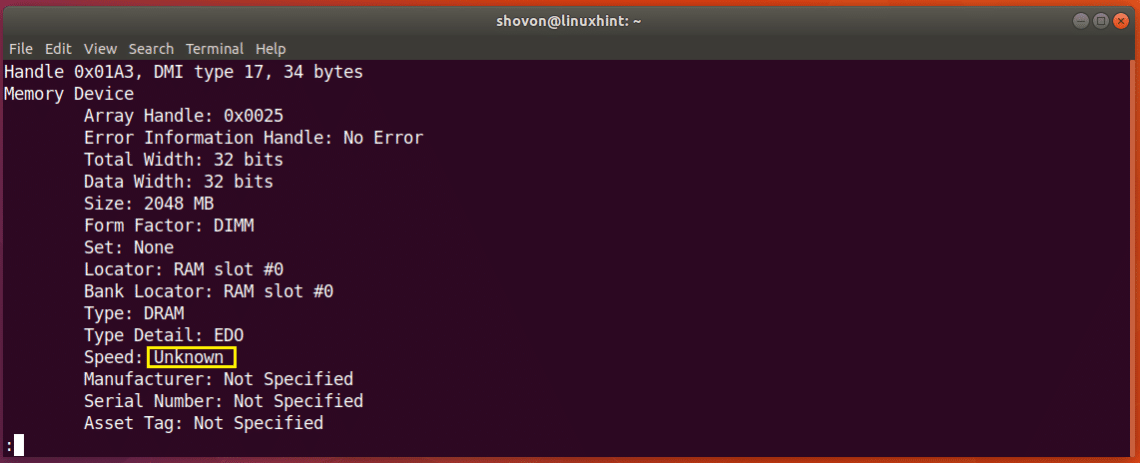
Just scroll down a little bit and you should find information about your RAM. As you can see from the screenshot below, the type of RAM installed on my Ubuntu 18.04 machine is DRAM.
You can also find out the clock speed or speed of the RAM installed on your machine using the dmidecode command. As you see from the marked section of the screenshot below. I don’t have the speed of my RAM listed here as I am using a Virtual Machine. But on real computers, it should be something like 1333 MHz or something like that.
Checking RAM for Errors
At times your RAM may suffer many issues as semiconductor devices like RAM are very fragile. You can check your RAM for errors.
On Ubuntu 18.04, you can use memtester command line utility to check your RAM for errors. memtester is not installed on Ubuntu 18.04 by default. But it is available in the official package repository of Ubuntu 18.04.
First update the package repository cache of your Ubuntu 18.04 machine with the following command:
The package repository cache should be updated.
Now you can install memtester on Ubuntu 18.04 with the following command:
memtester should be installed.
Now you can run memtester command to check memory as follows:
Here SIZE is the amount of memory to allocate and test using memtester utility. ITERATIONS is a number that specifies how many times you want memtester to test the allocated memory.
As SIZE you can use B for Bytes, K for Kilobytes, M for Megabytes and G for Gigabytes.
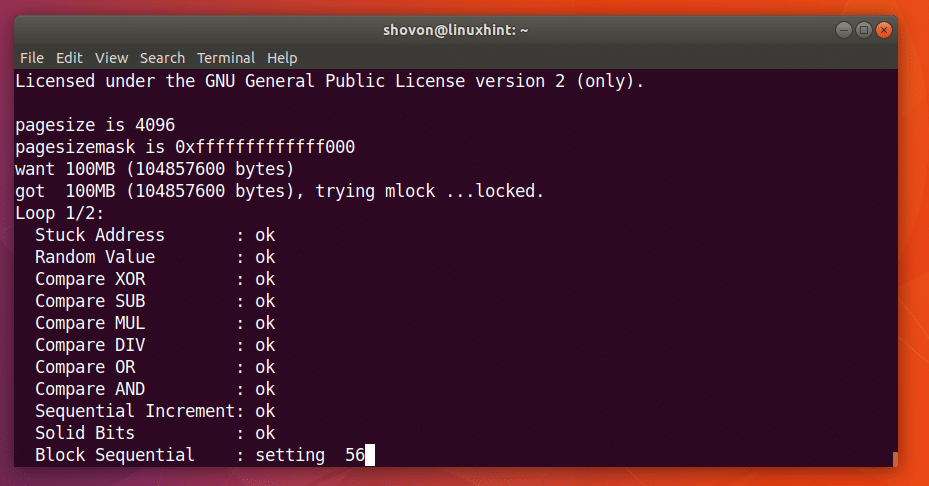
Let’s say you can to allocate 100 Megabytes in RAM and check it twice. You can run the following command to do that:
As you can see from the screenshot below, the memtester program is testing the RAM.
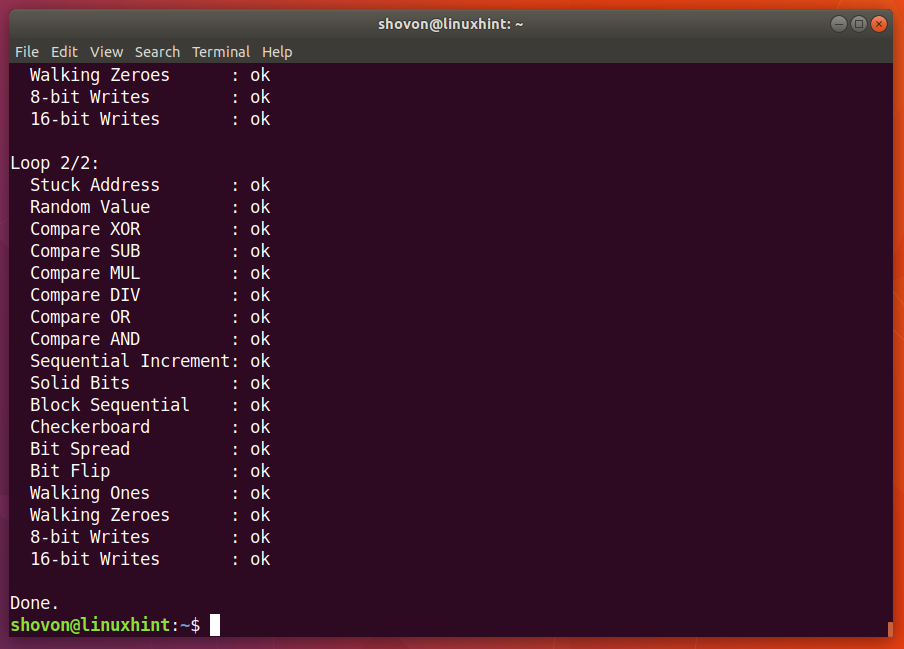
When memtester command is complete, as you can see from the screenshot below, all the tests are successful. It means the RAM has no errors. You can of course allocate more memory at once to perform a thorough test.
The only downside of memtester utility is that you can’t allocate more RAM than you have available as free.
You can use memtest86+ to do a more thorough check of your RAM. It has no such limitations as memtester. It is installed by default on Ubuntu 18.04.
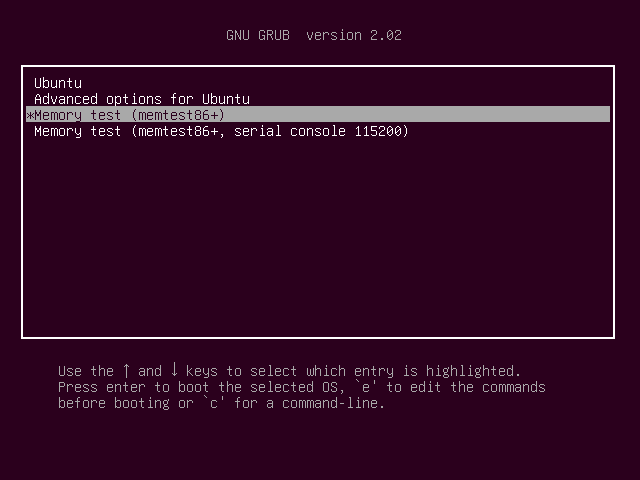
Just reboot your Ubuntu machine and from the GRUB menu, select Memory test (memtest86+).
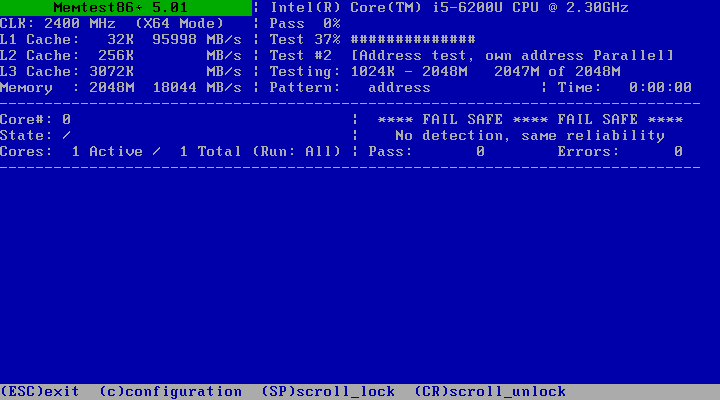
You should see the following window. Now press F1 to go to Fail-Safe Mode.
memtest86+ should start checking your RAM for errors as you can see from the screenshot below.
That’s how you find out different information about RAM and check RAM for errors on Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic Beaver. Thanks for reading this article.
About the author
Shahriar Shovon
Freelancer & Linux System Administrator. Also loves Web API development with Node.js and JavaScript. I was born in Bangladesh. I am currently studying Electronics and Communication Engineering at Khulna University of Engineering & Technology (KUET), one of the demanding public engineering universities of Bangladesh.
Testing whether memory is accessible in Linux
Given an untrusted memory address, is there a way in Linux to test whether it points to valid, accessible memory? For example, in mach you can use vm_read_overwrite() to attempt to copy data from the specified location. If the address is invalid or inaccessible, it will return an error code rather than crashing the process.
3 Answers 3
write from that memory (into /dev/null , for example (EDIT: with /dev/null it might not work as expected, use a pipe)), and you’ll receive EFAULT error if the address is unaccessible.
I have no idea how to test for writable memory without destroying its content if it is writable.
«I have no idea how to test for writable memory without destroying its content if it is writable» If you do it from userspace, you won’t destroy its content but get a segfault!
This a typical case of TOCTOU — you check at some point that the memory is writeable, then later on you try to write to it, and somehow (e.g. because the application deallocated it), the memory is no longer accessible.
There is only one valid way to actually do this, and that is, trap the fault you get from writing to it when you actually need to use it.
Of course, you can use tricks to try to figure out if the memory «may be writeable», but there is no way you can actually ensure it is writeable.
You may want to explain slightly more what you are actually trying to do, and maybe we can have some better ideas if you are more specific.