- Tftp сервер linux debian
- 4.5.1. Настройка DHCP сервера
- 4.5.1.1. Включение загрузки PXE в конфигурацию DHCP
- 4.5.2. Настройка BOOTP сервера
- 4.5.3. Включение TFTP сервера
- 4.5.4. Копирование TFTP образов в каталог TFTP сервера
- How to install tftp server on Debian 11
- Installing TFTP server and client:
- Configuring the TFTP server:
- Upload and Download files using TFTP:
- TFTP vs FTP vs SFTP:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- David Adams
Tftp сервер linux debian
Если ваша машина подключена к локальной сети, то вы можете загрузить её по сети с другой машины через TFTP. Для этого на удалённую машину в определённое место вам нужно поместить загрузочные файлы и настроить поддержку загрузки вашей машины.
Вам нужно настроить TFTP сервер, а если машин много, то DHCP сервер .
BOOTP — это IP протокол, который информирует компьютер о его IP-адресе и где в сети получить загрузочный образ. DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) более гибок и обратно совместим с BOOTP. Некоторые системы могут быть настроены только через DHCP.
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) используется для загрузки загрузочного образа на клиентскую машину. Теоретически, можно использовать любой сервер на любой платформе, которая реализует эти протоколы. В примерах этого раздела мы используем команды из SunOS 4.x, SunOS 5.x (так называемый Solaris) и GNU/Linux.
Для сервера Debian GNU/Linux мы рекомендуем tftpd-hpa . Он написан автором системного загрузчика syslinux и поэтому, скорее всего, не вызовет проблем. Также неплох atftpd .
4.5.1. Настройка DHCP сервера
Одним из свободных DHCP серверов является ISC dhcpd . В Debian GNU/Linux он доступен из пакета isc-dhcp-server . Вот пример его конфигурационного файла (обычно /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf ):
option domain-name "example.com"; option domain-name-servers ns1.example.com; option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0; default-lease-time 600; max-lease-time 7200; server-name "servername"; subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 < range 192.168.1.200 192.168.1.253; option routers 192.168.1.1; >host clientname < filename "/tftpboot.img"; server-name "servername"; next-server servername; hardware ethernet 01:23:45:67:89:AB; fixed-address 192.168.1.90; >
В этом примере определён единственный сервер servername , который работает в качестве DHCP, TFTP серверов и шлюза сети. Вам почти наверняка нужно изменить опцию domain-name, а также имя сервера и аппаратный адрес клиента. Опция filename должна содержать имя файла, который нужно получить по TFTP.
После редактирования конфигурационного файла для dhcpd , перезагрузите сервер командой /etc/init.d/isc-dhcp-server restart .
4.5.1.1. Включение загрузки PXE в конфигурацию DHCP
Вот другой пример dhcp.conf , который можно использовать, если включён метод предстартового выполнения среды (PXE) по TFTP.
option domain-name "example.com"; default-lease-time 600; max-lease-time 7200; allow booting; allow bootp; # нужно изменить согласно вашим настройкам subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 < range 192.168.1.200 192.168.1.253; option broadcast-address 192.168.1.255; # адрес шлюза, который может быть другим # (для доступа в интернет, например) option routers 192.168.1.1; # используемый dns option domain-name-servers 192.168.1.3; >group < next-server 192.168.1.3; host tftpclient < # аппаратный адрес клиента tftp hardware ethernet 00:10:DC:27:6C:15; filename "pxelinux.0"; >>
Заметим, что для PXE загрузки в filename клиента pxelinux.0 записан системный загрузчик, а не образ ядра (смотрите ниже Раздел 4.5.4, «Копирование TFTP образов в каталог TFTP сервера»).
If your machine uses UEFI to boot, you will have to specify a boot loader appropriate for UEFI machines, for example
4.5.2. Настройка BOOTP сервера
Для GNU/Linux есть два BOOTP сервера. Первый — CMU bootpd . Второй, на самом деле являющийся сервером DHCP — ISC dhcpd . В Debian GNU/Linux они находятся в пакетах bootp и isc-dhcp-server соответственно.
Чтобы использовать CMU bootpd , во-первых, вы должны раскомментировать (или добавить) соответствующую строку в /etc/inetd.conf . Для этого в Debian GNU/Linux вы можете запустить update-inetd —enable bootps , затем /etc/init.d/inetd reload . Если BOOTP сервер работает не под Debian, то строка выглядит так:
bootps dgram udp wait root /usr/sbin/bootpd bootpd -i -t 120
Теперь вы должны создать файл /etc/bootptab . Внутри он напоминает хорошо знакомый и загадочный формат старых добрых BSD файлов printcap , termcap и disktab . Подробности смотрите в справочной странице bootptab . Для CMU bootpd вам нужно знать аппаратный адрес (MAC) клиента. Вот пример /etc/bootptab :
client:\ hd=/tftpboot:\ bf=tftpboot.img:\ ip=192.168.1.90:\ sm=255.255.255.0:\ sa=192.168.1.1:\ ha=0123456789AB:
Вам нужно изменить, по крайней мере, параметр « ha » , который содержит аппаратный адрес клиента. Параметр « bf » содержит файл, который клиент должен получить по TFTP; подробности смотрите в Раздел 4.5.4, «Копирование TFTP образов в каталог TFTP сервера».
Напротив, настройка BOOTP в ISC dhcpd очень проста, так как здесь клиенты BOOTP считаются одним из вариантов клиентов DHCP. Некоторые архитектуры требуют сложной настройки для загрузки клиентов по BOOTP. Если у вас один из таких случаев, прочитайте раздел Раздел 4.5.1, «Настройка DHCP сервера». Если нет, то достаточно просто добавить директиву allow bootp в блок настройки подсети, содержащей клиента, в /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf и перезапустить dhcpd командой /etc/init.d/isc-dhcp-server restart .
4.5.3. Включение TFTP сервера
Чтобы сервер TFTP заработал, во-первых нужно проверить что включена tftpd .
Программа tftpd-hpa может быть запущена двумя способами. Она может запускаться по требованию службой inetd , или может быть настроена для работы как независимая служба. Выбор метода происходит при при установке пакета, и его можно изменить через перенастройку пакета.
Исторически, TFTP-серверы используют каталог /tftpboot для хранения образов. Однако, пакеты Debian GNU/Linux могут использовать другие каталоги, чтобы соответствовать Filesystem Hierarchy Standard. Например, tftpd-hpa по умолчанию использует /srv/tftp . Вам может потребоваться изменить примеры конфигурации для соответствия.
По умолчанию, все альтернативные программы in.tftpd , доступные в Debian, протоколируют запросы TFTP в системный журнал. Некоторые из них имеют параметр -v , позволяющий включить более подробный протокол. Рекомендуется проверить эти сообщения в журнале в случае возникновения проблем с загрузкой; это хорошая отправная точка при поиске причин ошибок.
4.5.4. Копирование TFTP образов в каталог TFTP сервера
Далее, поместите нужный загрузочный образ TFTP из Раздел 4.2.1, «Где искать установочные образы» в каталог загрузочных образов tftpd . Вы можете сделать ссылку на этот файл для файла, который tftpd будет передавать для загрузки определённому клиенту. К сожалению, имя файла зависит от клиента TFTP и никак не стандартизовано.
For PXE booting, everything you should need is set up in the netboot/netboot.tar.gz tarball. Simply extract this tarball into the tftpd boot image directory. Make sure your dhcp server is configured to pass pxelinux.0 to tftpd as the filename to boot. For UEFI machines, you will need to pass an appropriate EFI boot image name (such as /debian-installer/amd64/bootnetx64.efi ).
How to install tftp server on Debian 11
This tutorial explains how to set up a TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server on Debian 11 and Linux-based distributions.
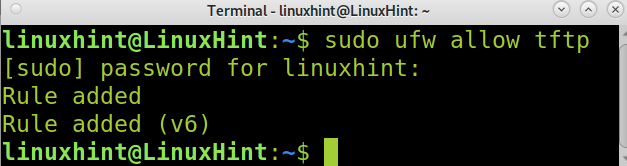
Before starting, let’s open the tftp port (69) using UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall), as shown in the following image.
Once the port is open, we can proceed with the TFTP installation.
Installing TFTP server and client:
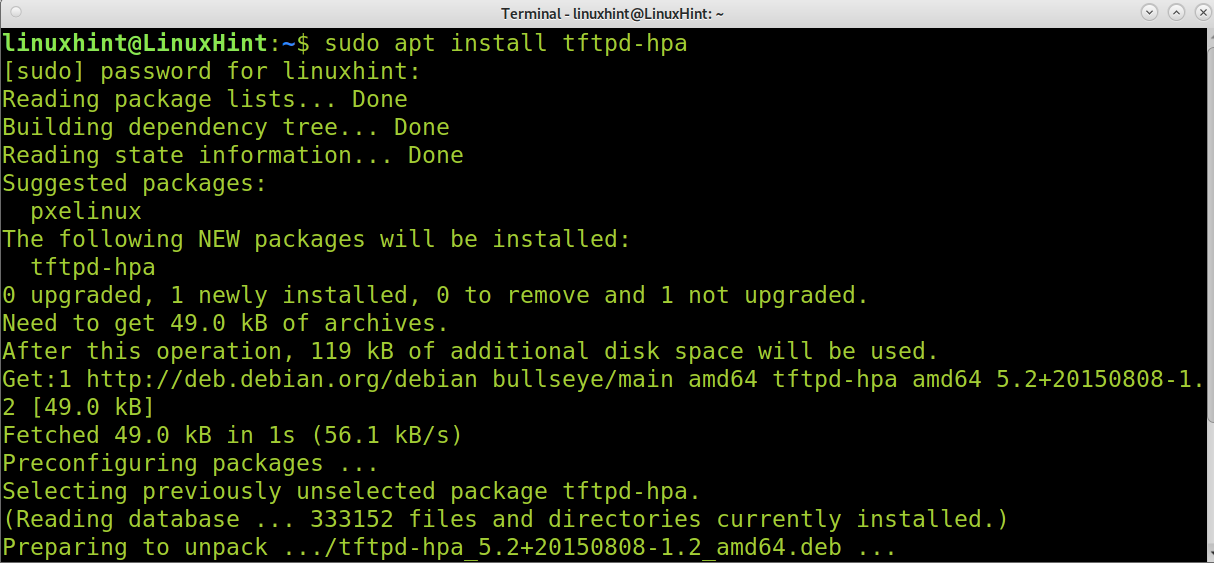
To begin installing the TFTP service, use apt as shown in the screenshot below.
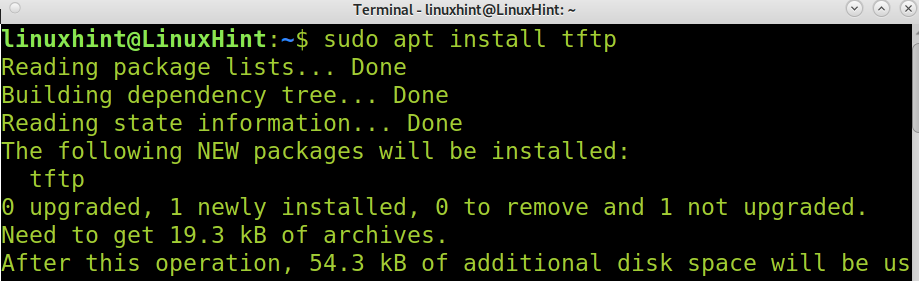
As said, the previous command installed the TFTP service. To install the TFTP client using apt, run the following command.
Configuring the TFTP server:
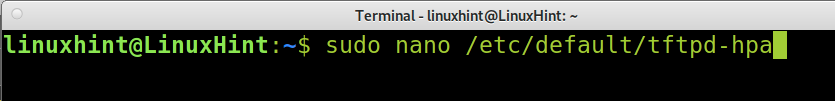
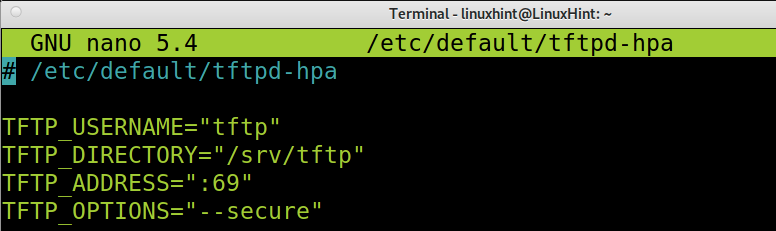
Once the TFTP server is installed, you need to configure it. The TFTP configuration file is located at /etc/default/tftpd-hpa. You can edit the configuration file using nano, as shown in the example below. On debian, run the following command.
The default configuration file seems like the image below where:
- TFTP_USERNAME: Here, you can specify the TFTP user; the default user is tftp.
- TFTP_DIRECTORY: Here, you can specify the TFTP directory to upload or download files from. By default, the directory /srv/tftp is created; you can leave it or define a new one (in such case, you’ll need to create it using the mkdir command).
- TFTP_ADDRESS: Here, you specify the TFTP IP address and port, which by default for TFTP is port 69
- TFTP_OPTIONS: Here, you can specify options; we’ll add the needed option to upload files to the TFTP server in our following examples.
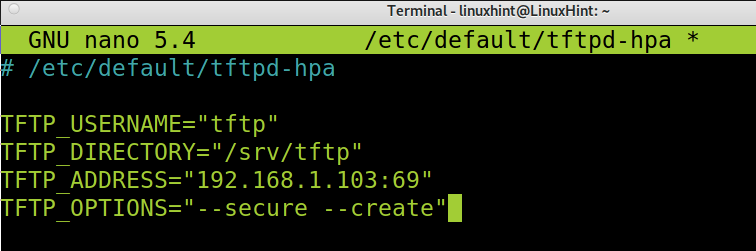
In the screenshot below, you can see I only edited TFTP_ADDRESS to define the server IP and TFTP_OPTIONS to allow uploading files by adding the —create option.
After editing the configuration file, exit saving changes (For nano, press Ctrl+X and Y)
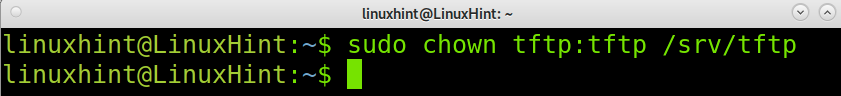
As you can see, the default tftp directory is where files are stored in /srv/ftp. On Debian 11, this directory is created by default when installing tftp. You can create a different one if needed. But you’ll need to change the user and group ownership to allow the defined user in the configuration file (By default, the tftp user) to store files inside.
To change the directory ownership to the tftp user, use the chown command as shown below.
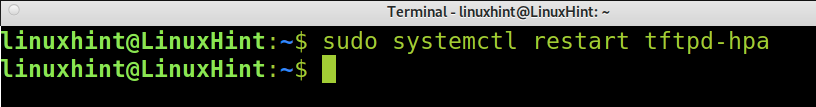
Once reconfigured, restart the tftp service; you can do it using systemctl, as shown in the following example.
Upload and Download files using TFTP:
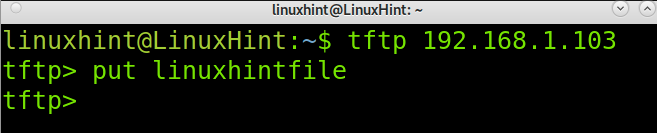
To connect to a TFTP server, just run tftp followed by the server IP address as shown in the following screenshot, in which tftp is used to connect to the server with IP address 192.168.1.103.
Once connected, to upload a file, you can use the put command followed by the file name you want to upload. In the example below, the file named linuxhintfile is uploaded to the server with IP address 192.168.1.103.
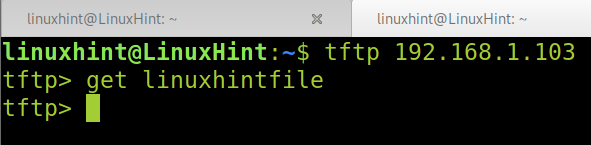
To download files, use the get command followed by the file name you want to download, as shown in the image below.
TFTP vs FTP vs SFTP:
Unlike FTP and SFTP, TFTP works under the UDP protocol; it is a faster but less secure and flexible alternative. TFTP doesn’t allow authentication, and users can’t modify files. Even the regular FTP protocol (Port 21) is the safest alternative. TFTP is mainly used for network boot processes and is almost unused.
The TFTP server doesn’t allow to show the TFTP directory content; users must know the file name they want to download.
Conclusion:
As you can see, the main advantage of the TFTP protocol is the simplicity of implementing it. Any Linux user level can easily set up a TFTP server. It is important to remember that TFTP is an unsafe implementation, and SFTP must be considered the main alternative to transfer files and filter unwanted access. Users must remember to open port 69 to allow TFTP traffic; this can be achieved using Iptables or UFW, as shown in the first step of this article.
You can get additional information on TFTP at https://linux.die.net/man/1/tftp.
I hope this tutorial explaining how to install a TFTP server on Debian 11 was useful. Keep following Linux Hint for additional Linux tips and tutorials.
About the author
David Adams
David Adams is a System Admin and writer that is focused on open source technologies, security software, and computer systems.