- How to Set Date, Time and Timezone in RHEL 8
- Set Date and Time in RHEL 8
- timedatectl Command
- Check Date and Time in RHEL
- Change Time in RHEL
- Change Date in RHEL
- Change Timezone in RHEL
- How to Change Timezone on CentOS & RHEL-based Systems
- Step 1: View the Current Time Zone
- Step 2: List Available Time Zones
- Step 3: Change the Time Zone
- Step 4: Verify the Change
- Conclusion
- Chapter 2. Date and Time Configuration
- 2.1. Date/Time Properties Tool
- 2.1.1. Date and Time Properties
- 2.1.2. Network Time Protocol Properties
- 2.1.3. Time Zone Properties
How to Set Date, Time and Timezone in RHEL 8
When it comes to Date and Time configurations, all operating systems are familiar with two types of clocks; real-time clock (RTC) and system clock.
RTC/hardware clock is tied to the computer’s integrated circuit, which remains active even when the computer is not running. On the other hand, the operability of the system/software clock depends on the system kernel. The system clock takes the hardware clock’s value as its initial value.
When an operating system is brought to life for the first time, the software clock value becomes independent of the hardware clock value making it possible for a user to set this value to a new one based on their preferred Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) or local time. However, most operating systems like RHEL 8 recommend users to go with UTC.
Set Date and Time in RHEL 8
There are several Date and Time configuration approaches supported by RHEL 8. All these system Date and Time configuration approaches are accessible from the command line.
For this article guide, we are going to look at the timedatectl command.
timedatectl Command
The systemd system and service manager are responsible for this Date and Time command-line utility. This command is used to alter the system/software clock values.
The timedatectl command achieves the following functionalities:
- Synchronizing the system clock of a local server/machine with that of a remote server/machine.
- Editing the currently set timezone.
- Configuring the current date and time.
Check Date and Time in RHEL
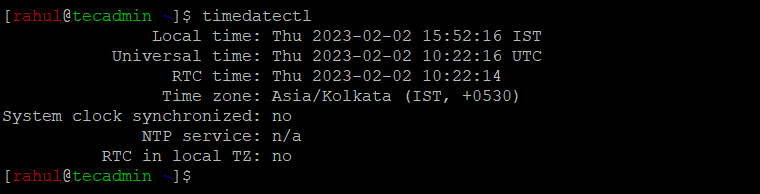
To display the current date and time setting on your RHEL 8 system, execute the following command on your terminal:
The command outputs the Local time, Universal time, RTC time, and associated Time zone.
Change Time in RHEL
Before you can change the date and time settings on your RHEL system, you need to temporarily disable the NTP service.
$ sudo timedatectl set-ntp no
To change the current local time, we must adhere to the following syntax rule:
$ sudo timedatectl set-time HH:MM:SS
Where HH is for hours, MM for minutes, and SS for seconds.
An example implementation is as follows:
$ sudo timedatectl set-time 18:05:00
Confirm that the set time:
As you can see, the Universal time and the RTC time were also automatically adjusted.
Change Date in RHEL
To change the current date, adhere to the following command syntax:
$ sudo timedatectl set-time YYYY-MM-DD
Where YYYY is for a year, MM for a month, and DD for a day.
A practical implementation of the above command is as follows:
$ sudo timedatectl set-time 2021-11-17
While changing the current date, the current time might be altered. To avoid such inconvenience, first, change the date and then the local time.
Change Timezone in RHEL
To change/edit the Time Zone you are under, adhere to the following command syntax:
$ sudo timedatectl set-timezone your_preferred_time_zone
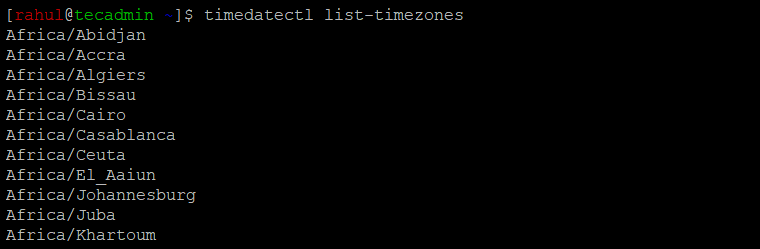
However, it is advisable to get a sneak peek of available and supported timezones under RHEL 8 using the following command.
$ timedatectl list-timezones
From here, you can implement the timezone of your choice:
$ sudo timedatectl set-timezone America/Aruba
Confirm that the timezone was successfully added.
These date and time configuration changes you have made on your local rhel system can also be automatically synchronized with remote machines and servers you might be using.
Since remote servers and machines understand the NTP protocol, you only need to enable it for your remote servers/machines to be in-sync with your system/software clock.
$ sudo timedatectl set-ntp yes
The timedatectl command is flexible enough to meet all your RHEL 8 date and time configuration needs. It is easy to memorize and implement making your date and time associated system tasks manageable.
How to Change Timezone on CentOS & RHEL-based Systems
Time zones play a crucial role in ensuring that the system clock displays the correct time, particularly in a multi-user environment. Keeping the system time in sync with the right time zone helps to avoid confusion, reduce errors, and enhance the reliability of your systems.
In this article, we will cover the steps involved in configuring the time zone in CentOS Steam 9/8 and other RHEL-based systems, which is a popular Linux distribution used in enterprise environments.
Before we get started, it is important to note that you will need root access to your system to perform the steps outlined in this guide.
Step 1: View the Current Time Zone
Before making any changes to the time zone, it’s always a good idea to check the current time zone of your system. You can do this by running the following command in your terminal:
The above output showing that the current timezone is set to “Asia/Kolkata” alsoing with the current system time, date, and time zone information.
Step 2: List Available Time Zones
The CentOS Steam 9/8 and other RHEL-based system supports a large number of time zones, and you can view a list of all available time zones by running the following command:
timedatectl list-timezones This command will display a list of all the supported time zones, which you can use to determine the correct time zone for your system.
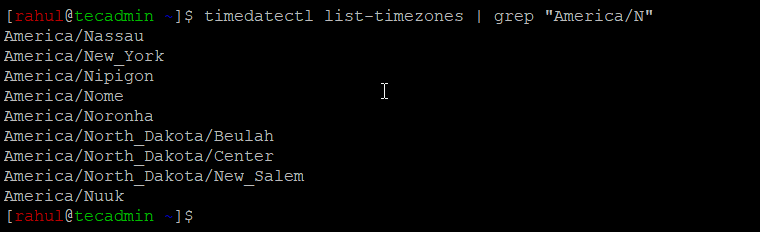
timedatectl list-timezones | grep "America/N" In the above output, you will get a long list of available packages. You can also filter the output with grep command.
Step 3: Change the Time Zone
To change the time zone in RHEL/CentOS Steam 9/8, you can use the `timedatectl set-timezone` command. For example, to change the time zone to “America/New_York”, you would run the following command:
timedatectl set-timezone America/New_York Its always recommended to use the universal timezone (UTC) for the servers and then manager your applications accordingly. This way its easier to handle application between cross regions and timezones.
timedatectl set-timezone "UTC" The above commands replaces the link for the /etc/localtime file and set them to requested timezone file available udner /usr/share/zoneinfo directory. Which you can also do manaully, instead of using the above commands. For example, to change timezone to the “America/New_York” time zone, you would run the following command:
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/New_York /etc/localtime After running this command, the time zone change will persist across reboots.
Step 4: Verify the Change
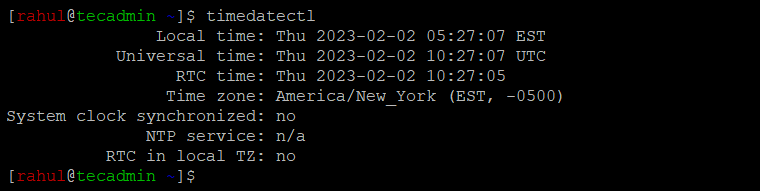
After changing the time zone, you can verify the change by running the timedatectl command again. The output should display the updated time zone information.
You should see the updated timezone.
Conclusion
In conclusion, configuring the time zone in CentOS Steam 9/8 other RHEL-based systems is a straightforward process that can be performed by following these simple steps. Keeping the system time in sync with the correct time zone helps to enhance the reliability of your systems and avoid confusion.
Chapter 2. Date and Time Configuration
This chapter covers setting the system date and time in Red Hat Enterprise Linux, both manually and using the Network Time Protocol ( NTP ), as well as setting the adequate time zone. Two methods are covered: setting the date and time using the Date/Time Properties tool, and doing so on the command line.
2.1. Date/Time Properties Tool
The Date/Time Properties tool allows the user to change the system date and time, to configure the time zone used by the system, and to set up the Network Time Protocol daemon to synchronize the system clock with a time server. Note that to use this application, you must be running the X Window System (see Appendix C, The X Window System for more information on this topic).
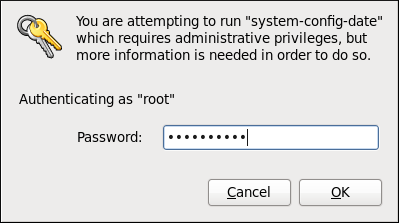
To start the tool, select System → Administration → Date & Time from the panel, or type the system-config-date command at a shell prompt (e.g., xterm or GNOME Terminal ). Unless you are already authenticated, you will be prompted to enter the superuser password.
Figure 2.1. Authentication Query
2.1.1. Date and Time Properties
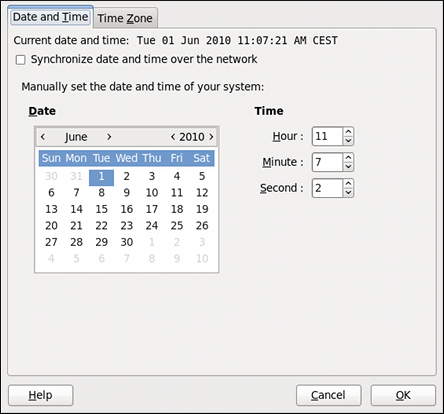
As shown in Figure 2.2, “Date and Time Properties”, the Date/Time Properties tool is divided into two separate tabs. The tab containing the configuration of the current date and time is shown by default.
Figure 2.2. Date and Time Properties
Change the current date. Use the arrows to the left and right of the month and year to change the month and year respectively. Then click inside the calendar to select the day of the month.
Change the current time. Use the up and down arrow buttons beside the Hour , Minute , and Second , or replace the values directly.
2.1.2. Network Time Protocol Properties
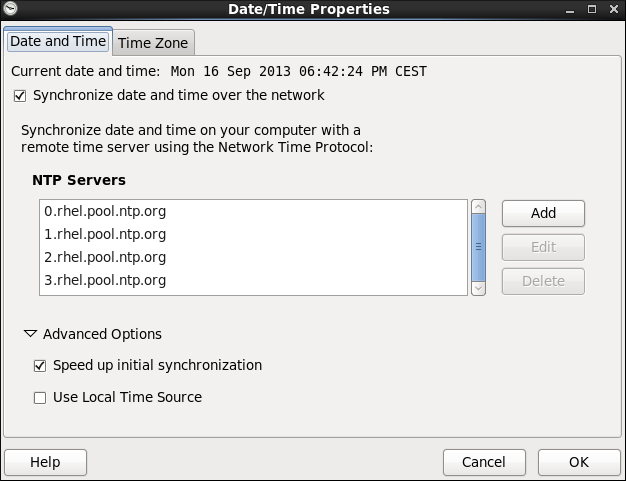
If you prefer an automatic setup, select the check box labeled Synchronize date and time over the network instead. This will display the list of available NTP servers as shown in Figure 2.3, “Network Time Protocol Properties”.
Figure 2.3. Network Time Protocol Properties
Here you can choose one of the predefined servers, edit a predefined server by clicking the Edit button, or add a new server name by clicking Add . In the Advanced Options , you can also select whether you want to speed up the initial synchronization of the system clock, or if you want to use a local time source.
Your system does not start synchronizing with the NTP server until you click the OK button at the bottom of the window to confirm your changes.
Click the OK button to apply any changes made to the date and time settings and exit the application.
2.1.3. Time Zone Properties
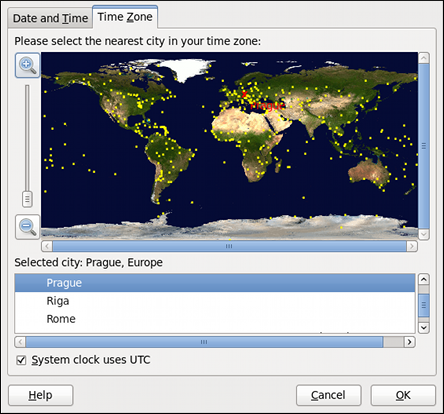
To configure the system time zone, click the Time Zone tab as shown in Figure 2.4, “Time Zone Properties”.
Figure 2.4. Time Zone Properties
Using the interactive map. Click “zoom in” and “zoom out” buttons next to the map, or click on the map itself to zoom into the selected region. Then choose the city specific to your time zone. A red X appears and the time zone selection changes in the list below the map.
Use the list below the map. To make the selection easier, cities and countries are grouped within their specific continents. Note that non-geographic time zones have also been added to address needs in the scientific community.
If your system clock is set to use UTC , select the System clock uses UTC option. UTC stands for the Universal Time, Coordinated, also known as Greenwich Mean Time ( GMT ). Other time zones are determined by adding or subtracting from the UTC time.