- 10 Amazing Tips & Tricks to Work with Linux
- 1. Removing Larger Files
- 2. Copying in Multiple Directories
- 3. Minimizing Keystrokes
- 4. Searching Files Made Easy
- 5. Turning Off Your System
- 6. Using the Right Command
- 7. Executing Multiple Commands
- 8. Multiple Commands: When First One Fails
- 9. Creating Directory Trees
- 10. Moving to End or Starting of Line
- Inference
- 10 Interesting Linux Command Line Tricks and Tips Worth Knowing
- 1. Lock or Hide a File or Directory in Linux
- 2. Translate rwx Permissions into Octal Format in Linux
- 3. How to Use ‘su’ When ‘sudo’ Fails
- 4. Kill a Process in Linux
- 5. Delete File Permanently in Linux
- 6. Rename Multiple Files in Linux
- 7. Check for Spelling of Words in Linux
- 8. Search for Description of Keyword in Manual Page
- 9. Watch Logs in Real-Time in Linux
- 10. List All Shell builtin Commands
10 Amazing Tips & Tricks to Work with Linux
Linux terminal can seem quite overwhelming for new users and even for experienced users without the knowledge of Linux tips & tricks. Linux is an incredibly flexible operating system.
However, it is difficult to remember all the commands and their appropriate usage. Our amazing tricks will allow you to use Linux like a pro!
Take a look at these 10 tips & tricks to scale-up your Linux game:
1. Removing Larger Files
Because of poor administrative skills files can get “heavy”, sometimes as large as 250 GB! In that case, rm utility is not of much use due to the massive amount of data involved.
Therefore, removing a single log file of that size using rm utility should be avoided. You should rather opt for an easier solution:
You would be required to change file names and the path that matches your case. As a result, the empty output will be generated for that particular file.
2. Copying in Multiple Directories
In general, when you want to copy a file, you use cp command which looks like this:
cp /path-to-file/my_file.txt /path-to-new-dir Right? What if you want to copy that into multiple directories? You usually go for something like this:
cp /home/user/my_file.txt /home/user/1cp /home/user/my_file.txt /home/user/2cp /home/user/my_file.txt /home/user/3
Writing these commands over and over again is not only time consuming but frustrating as well. What if we tell you that you can still execute this process in a single-line command? Don’t believe us? Try this:
echo /home/user/1/ /home/user/2/ /home/user/3/ | xargs -n 1 cp -v /home/user/my_file.txt 3. Minimizing Keystrokes
The more you press keys on your keyboard, the longer it will take to get things done. If you are aware of certain time-saving commands, you can increase your work efficiency by manifolds.
In order to execute your last command, you should make use of the UNIX bash shell.
Instead of typing the whole command again, just use Ctrl+R and change a few lines if you want to. That will save you a lot of time and speed-up your work.
4. Searching Files Made Easy
This may seem easier than you think. Following is an example of the command used for searching files:
Once you run this command, it will locate all files in /home/user. This is a powerful command but you may want to refine your search and make it more directed.
For instance, let’s suppose you want to include an option to search files greater than 10 MB. You can do this by:
Be careful not to use the root directory, failing which can cause high I/O on the system.
5. Turning Off Your System
Did you know you can use certain commands to turn off your system at a specific time? You may or may not be physically present to shut down your computer but you can choose when to. Configure the shutdown time using this command:
Your system will shut down exactly at 21:00! Instead of hours, you can also choose minutes.
For example:
Your computer will automatically turn off after 15 minutes.
6. Using the Right Command
With several command lines at your disposal, it’s extremely difficult to recall them when needed. Not only do you need to have the right command in mind, but also execute it effectively.
What you are looking for is this:
Just replace “description” with the actual command description that you are searching for.
Take a look at this example:
With this trick, you don’t need to recall the required command at all. You just need to search for one!
7. Executing Multiple Commands
Quite often you have to wait for the previous command to run successfully in order to run the next one. This again consumes a lot of your precious time.
There’s an efficient way to do it. You can use a single command to execute multiple ones and your waiting time is over!
The command looks like this:
command_1; command_2; command_3
This separator is a lifesaver when it comes to finishing your job within a stipulated time.
8. Multiple Commands: When First One Fails
In the previous section, we talked about how to use a single command for running several commands. But what should you do in case the first command does not run successfully? You want to run the subsequent command only if the previous one was successful.
For this use “||” separator like shown below:
After this, command 2 will run only after the command 1 when you use the above single-line command.
9. Creating Directory Trees
You generally use the mkdir command to create new directories in Linux.
The usual command for creating directories goes like this:
How about creating 7 sub folders within the new folder? Repeating the above command 7 times is not an ideal solution. You can instead use this command:
With the help of the above command, you can easily create 7 subfolders without having to run mkdir multiple times.
10. Moving to End or Starting of Line
You have typed a lengthy command but realize that you need to move to the beginning of it in order to make some changes.
What do you do? Strike that left arrow key several times until you reach the starting of command?
There is a better way.
Apart from using End and Home keys, you can opt for Ctrl+E to reach the end and Ctrl+A to reach the beginning.
Inference
Mastering these tips and tricks will make your transition to Linux hassle-free.
The aforementioned commands are quite easy for everyone to comprehend even if they are not Linux experts. That’s the beauty of it!
These useful tricks can work wonders for your efficiency. Wish you all the best for your Linux journey!
10 Interesting Linux Command Line Tricks and Tips Worth Knowing
I passionately enjoy working with commands as they offer more control over a Linux system than GUIs (Graphical User Interfaces) applications, therefore am always on the lookout to discover or figure out interesting ways and ideas to make Linux so easy and fun to operate, primarily from the terminal.
It is always thrilling when we discover new tricks or tips while using Linux especially a command line geek like myself.
And the feeling of wanting to share newly learned practices or commands with millions of Linux users out there, particularly the newbies who are still getting their way around this exciting operating system normally sets in.
In this article, we will review a number of useful command line tricks and tips that can significantly enhance your Linux usage skills.
1. Lock or Hide a File or Directory in Linux
The simplest way of locking a file or directory is by using Linux file permissions. In case your the owner of a file or directory, you can block (remove read, write and execute privileges) other users and groups from accessing it as follows:
$ chmod 700 tecmint.info OR $ chmod go-rwx tecmint.info
To know more about Linux file permissions, read this article Managing Users & Groups, File Permissions & Attributes in Linux.
To hide the file/directory from other system users, rename it with a (.) at the start of the file or directory:
2. Translate rwx Permissions into Octal Format in Linux
By default, when you run the ls command, it displays file permissions in rwx format, but to understand the equivalence of this format and the octal format, you can learn how to translate rwx permissions into Octal format in Linux.
3. How to Use ‘su’ When ‘sudo’ Fails
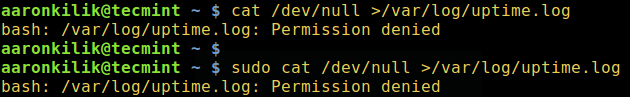
Although sudo command is used to execute commands with superuser privileges, there are moments when it fails to work as in the example below.
Here, I want to empty the contents of a large file named uptime.log but the operation has failed even when I used sudo.
$ cat /dev/null >/var/log/uptime.log $ sudo cat /dev/null >/var/log/uptime.log
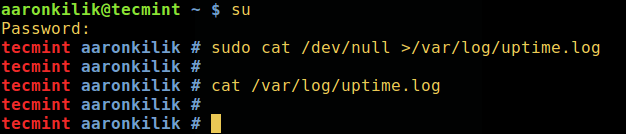
In such as case, you need to switch to the root user account using su command to perform the operation like so:
$ su $ sudo cat /dev/null >/var/log/uptime.log $ cat /var/log/uptime.log
Try to understand the difference between su and sudo, in addition, read through their man pages for more guidelines:
4. Kill a Process in Linux
Sometimes when you want to terminate a process using kill or killall or pkill commands, it may fail to work, you realize that the process still continues to run on the system.
In order to destructively kill a process, send the -KILL siganl to it.
First determine its process ID and then kill it like so:
$ pidof vlc $ sudo kill -KILL 10279
Check the kill command for additional usage options and information.
5. Delete File Permanently in Linux
Normally, we use the rm command to delete files from a Linux system, however, these files do not completely get deleted, they are simply stored and hidden on the hard disk and can still be recovered these files in Linux and viewed by another person.
To prevent this, we can use the shred command which overwrites the file content and optionally deletes the file as well.
The options used in the above command:
- -z – adds a final overwrite with zeros to hide shredding.
- -u – helps to truncate and remove file after overwriting.
- -v – shows progress.
Read through shred man page for additional usage instructions:
6. Rename Multiple Files in Linux
You can rename multiple files in Linux on the go by invoking the rename command.
It renames the filenames supplied according to a rule specified in the first argument.
The command below renames all .pdf files to .doc , here ‘s/\.pdf$/\.doc/’ is the rule:
The next example renames all files matching «*.bak» to strip the extension, where ‘s/\e.bak$//’ is the rule.
7. Check for Spelling of Words in Linux
The look command displays lines beginning with a given string, it can help you to check for the spelling of word from within the command line. Although it is not so effective and reliable, look is still a useful alternative to other powerful spelling-checkers:
8. Search for Description of Keyword in Manual Page
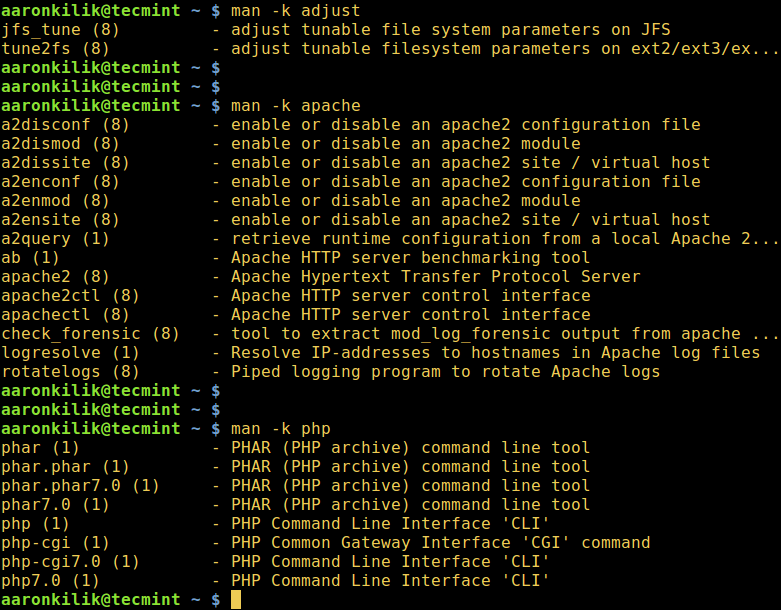
The man command is used to display manual entry pages of commands, when used with the -k switch, it searches the short descriptions and manual page names for the keyword printf (such as adjust, apache and php in the commands below) as regular expression.
$ man -k adjust $ man -k apache $ man -k php
9. Watch Logs in Real-Time in Linux
With watch command, you can run another Linux command periodically while displaying its output on fullscreen and alongside tail command which is used to view the last parts of a file, it is possible to watch the recording of log entries in a logfile.
In the example below, you will watch the system authentication logfile. Open two terminal windows, display the log file for watching in real-time in the first window like so:
$ sudo watch tail /var/log/auth.log
You can also use tail command which shows the last parts of a file. Its -f flag enables watching changes in a file in real-time, therefore it is possible to watch the recording of log entries in a log file.
$ sudo tail -f /var/log/auth.log
And run the commands below in the second terminal as you observe the logfile content from the first window:
$ sudo mkdir -p /etc/test $ sudo rm -rf /etc/test
10. List All Shell builtin Commands
A shell builtin is a command or a function, called from within and executed directly in the shell itself, instead of an external executable program which the shell would load from the hard disk and execute.
To list all shell builtins and their usage syntax, run:
As a concluding remark, command line tricks and tips always come in handy and make learning and using Linux easy and fun especially for newbies.
You can as well share with us other useful and interesting command line tricks or tips in Linux that you have come across via the comment form below.