- How to Create a Basic HTML5 Project in Ubuntu Using Netbeans
- Installing Java JDK in Ubuntu
- Installing Netbeans in Ubuntu
- Creating a Basic HTML5 Project in Ubuntu
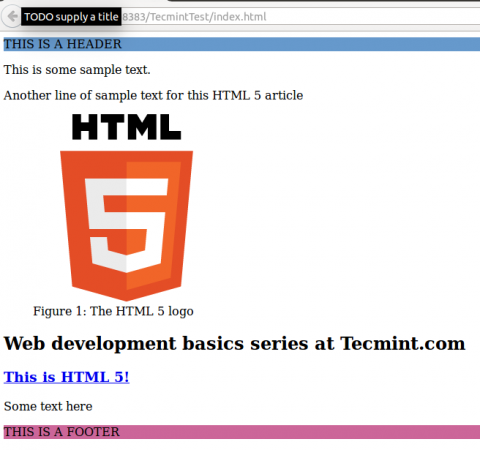
- Web development basics series at Tecmint.com
- This is HTML 5!
- Summary
- 7 Best Free HTML Editors for Linux and Unix
- Best HTML and XML Editor: Komodo Edit
- Best HTML Editor Interface: Aptana Studio
- Most Customizable HTML Editor: NetBeans
- Best for Cross-Platform Development: Eclipse
- Best Browser With an HTML Editor: SeaMonkey
- Best Light-weight HTML Editor: Geany
- The Official W3C HTML Editor: Amaya
How to Create a Basic HTML5 Project in Ubuntu Using Netbeans
In this 4-article mobile web development series, we will walk you through setting up Netbeans as an IDE (also known as Integrated Development Environment) in Ubuntu to start developing mobile-friendly and responsive HTML5 web applications.
Following are the 4-article series about HTML5 Mobile Web Development:
A well-polished work environment (as we will later see), autocompletion for supported languages, and its seamless integration with web browsers are, in our opinion, some of Netbeans, most distinguishing features.
Let us also remember that the HTML 5 specification brought many advantages for developers – to name a few examples: cleaner code thanks to many new elements), built-in video and audio playback capabilities (which replaces the need for Flash), cross-compatibility with major browsers, and optimization for mobile devices.
Although we will initially test our applications on our local development machine, we will eventually move our website to a LAMP server and turn it into a dynamic tool.
Along the way, we will make use of jQuery (a well-known cross-platform Javascript library that greatly simplifies client-side scripting), and Bootstrap (the popular HTML, CSS, and JavaScript framework for developing responsive websites). You will see incoming articles how easy it is to set up a mobile-friendly application using these HTML 5 tools.
After you go through this brief series, you will be able to:
- use the tools described herein to create basic HTML5 dynamic applications, and
- go on to learn more advanced web development skills.
However, please note that even though we will be using Ubuntu for this series, the instructions and procedures are perfectly valid for other desktop distributions as well (Linux Mint, Debian, CentOS, Fedora, you name it).
To that end, we have chosen to install the necessary software (Netbeans and the Java JDK, as you will see in a minute) using a generic tarball (.tar.gz) as an installation method.
That being said – let’s get started with Part 1.
Installing Java JDK in Ubuntu
This tutorial assumes that you already have an Ubuntu desktop installation in place. If you don’t, please refer to the Ubuntu Desktop Installation article, written by our colleague Matei Cezar before proceeding further.
Since the Netbeans version that is available for download from the Ubuntu official repositories is a little outdated, we will download the package from the Oracle website to get a newer version.
To do this, you have two choices:
- Choice 1: Download the bundle that includes Netbeans + JDK, or
- Choice 2: Install both utilities separately.
In this article we will choose #2 because that not only means a download that is a bit smaller (as we will only install Netbeans with support for HTML5 and PHP) but also will allow us to have a standalone JDK installer should we need it for another set that does not require Netbeans nor involve web development (mostly related to other Oracle products).
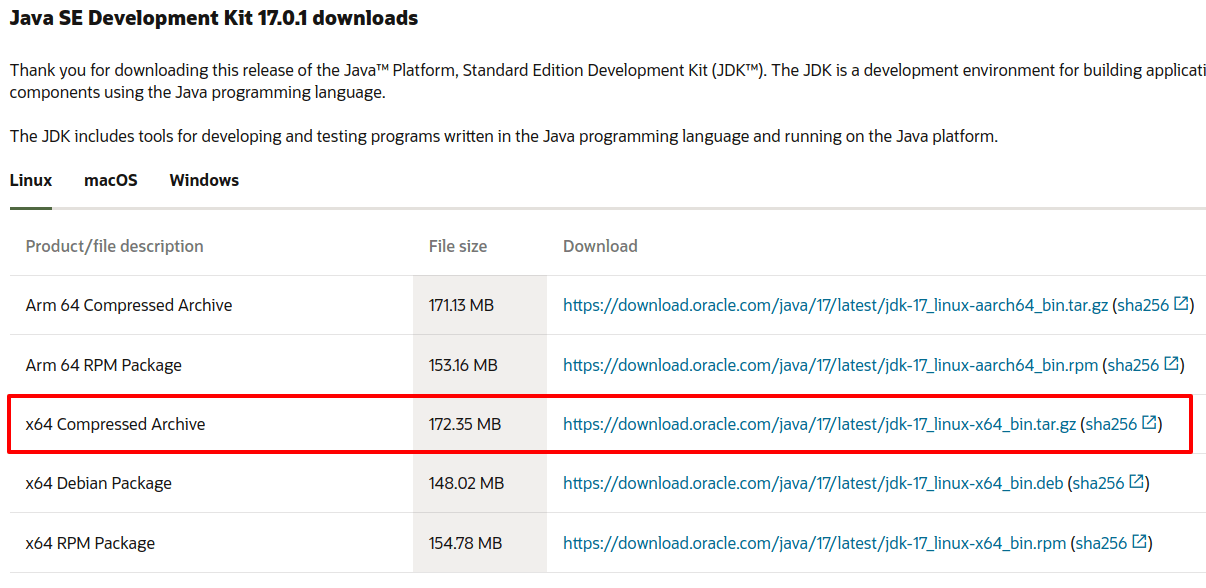
To download JDK, go to the Oracle Technology Network site and navigate to the Java → Java SE → Downloads section.
When you click on the image highlighted below, you will be asked to accept the license agreement and then you will be able to download the necessary JDK version (which in our case is the tarball for 64-bit machines). When prompted by your web browser, choose to save the file instead of opening it.
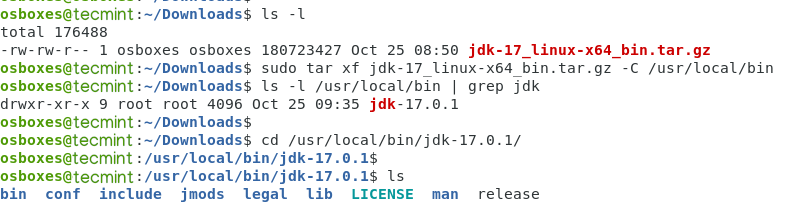
When the download is complete, go to ~/Downloads and extract the tarball to /usr/local/bin :
$ sudo tar xf jdk-17_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin
Installing Netbeans in Ubuntu
To install Netbeans with support for HTML5 and PHP, go to https://netbeans.org/downloads/ and click Download or use the following wget command to download as shown.
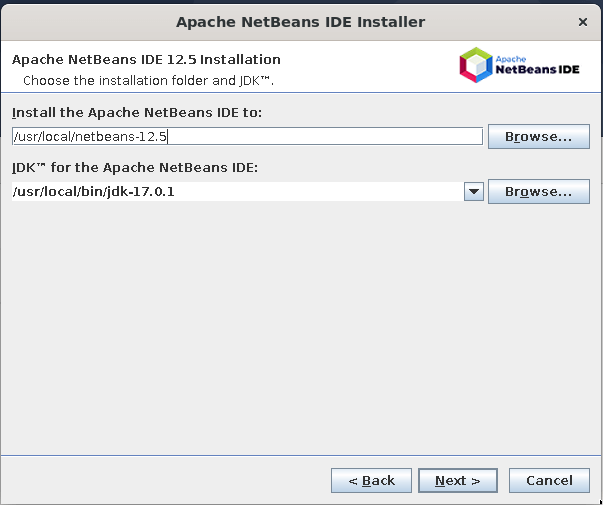
$ cd ~/Downloads $ wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/netbeans/netbeans/12.5/Apache-NetBeans-12.5-bin-linux-x64.sh $ chmod 755 Apache-NetBeans-12.5-bin-linux-x64.sh $ sudo ./Apache-NetBeans-12.5-bin-linux-x64.sh --javahome /usr/local/bin/jdk-17.0.1
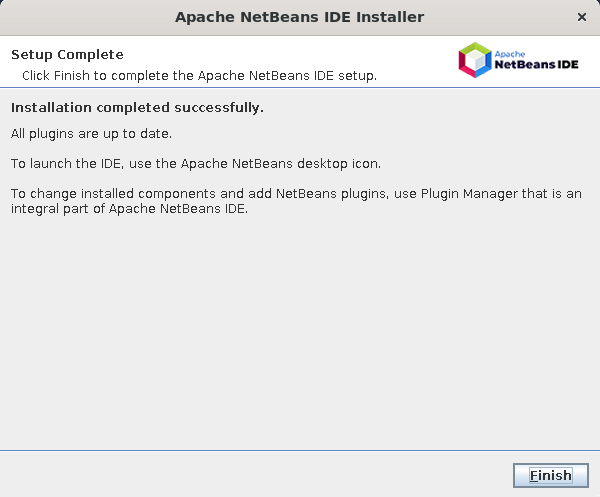
From then on, follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation leaving the default values:
and wait for the installation to complete.
Creating a Basic HTML5 Project in Ubuntu
To open Netbeans, select it from the Dash menu:
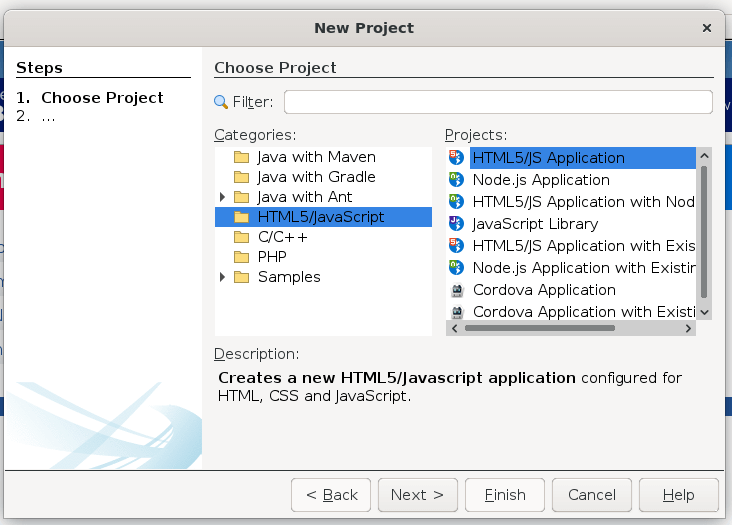
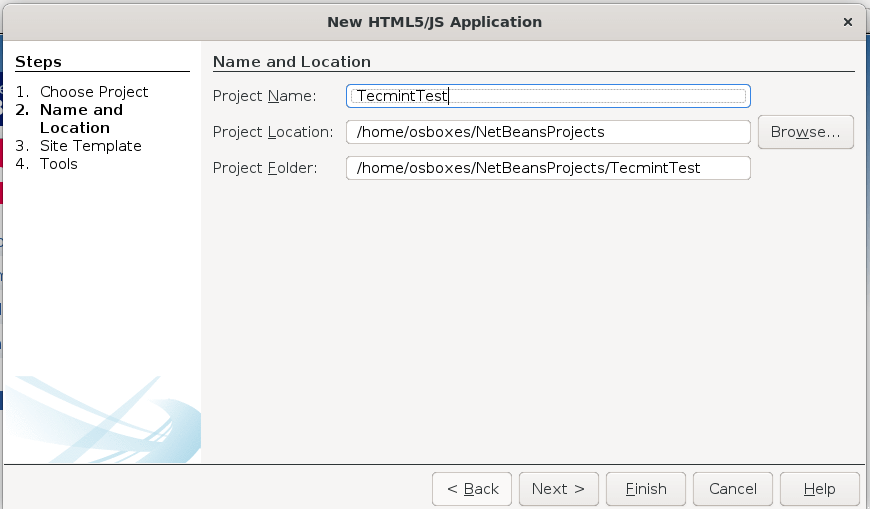
To create a new HTML5 project using the basic template provided by Netbeans, go to File → New project → HTML5 → HTML5 Application. Choose a descriptive name for your project and finally click Finish (do not include an external site template or javascript libraries at this time):
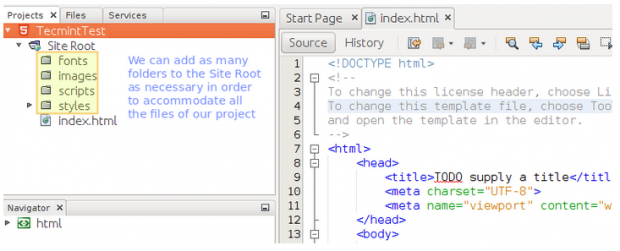
We will then be taken to the Netbeans UI, where we can add folders and files to our Site Root as needed. In our case, this will mean adding folders for fonts, images, Javascript files (scripts), and cascading style sheets (styles) to help us better organize our content in coming articles.
To add a folder or a file, right-click on Site Root and then choose New → Folder or HTML file.
Now let’s introduce some new HTML5 elements and modify the page body:
- and define a header or a footer, respectively, for a document or a section.
- represents the main content of a document, where the central topic or functionality is shown.
- is used for self-contained material, such as images or code, to name a few examples.
- shows a caption for a element, and thus it must be placed within the tags.
- is reserved for contents related somehow to the page content, usually related to it. It can be placed as a sidebar with help from CSS (more on this in coming articles).
.
Now copy the following code snippet to your index.html file in Netbeans.
TIP: Don’t just copy and paste from this window to your development environment, but take the time to type in each tag in order to visualize the auto-completion features of Netbeans, which will come in handy later on.
!DOCTYPE html>THIS IS A HEADER This is some sample text.
Another line of sample text for this HTML 5 article
You can view the page by selecting a web browser (preferably Firefox, as in the below image) and clicking the Play icon:
You can now view the progress of your development so far:
Summary
In this article, we have reviewed some of the advantages of writing your web applications using HTML 5 and set up a development environment with Netbeans in Ubuntu.
We learned that this specification of the language introduced new elements and thus provided us with the possibility of writing cleaner code and replacing resource-hungry components such as Flash movies with built-in controls.
In coming articles, we will introduce jQuery and Bootstrap so that you can not only use these controls and watch your pages load faster, but also make them mobile-friendly.
In the meanwhile, feel free to experiment with other controls in Netbeans, and let us know if you have any questions or comments using the form below.
7 Best Free HTML Editors for Linux and Unix
Jennifer Kyrnin is a professional web developer who assists others in learning web design, HTML, CSS, and XML.
Chris Selph is a CompTIA-certified technology and vocational IT teacher. He also serves as network & server administrator and performs computer maintenance and repair for numerous clients.
Looking for a free HTML editor for Linux? While there are plenty of reasonably priced HTML editors that offer more features and flexibility, these free desktop tools are all you need to design and edit HTML and XML web pages offline.
These apps are available for all Unix-based operating systems, and many are also available for Windows.
Best HTML and XML Editor: Komodo Edit
Komodo Edit is hands down the best free XML editor available, and it includes a lot of great features for HTML and CSS development as well. You can also get extensions to add support for languages or other helpful features like special HTML characters. Komodo Edit comes packaged with Komodo IDE, which is a paid program, but the editor can be downloaded by itself at no cost.
Best HTML Editor Interface: Aptana Studio
Aptana Studio offers an interesting take on web page development. In addition to HTML editing, Aptana focuses on JavaScript and other elements that allow you to create rich internet applications. One great feature is the outline view, which makes it really easy to visualize the Direct Object Model (DOM), making CSS and JavaScript development much more manageable.
Most Customizable HTML Editor: NetBeans
NetBeans IDE is a Java IDE that can help you build robust web applications. Like most IDEs, it has a steep learning curve because it doesn’t work in the same way that web editors do. One nice feature is the version control tool, which is really useful for people working in large development environments.
Best for Cross-Platform Development: Eclipse
- Powerful code refracting capabilities.
- Seamless integration with source control management tools.
Eclipse is a complex development environment that is perfect for people who do a lot of coding on various different platforms and with different languages. If you are creating complex web applications, Eclipse has a lot of features to help make your apps easier to build. There are Java, JavaScript, and PHP plugins, as well as a plugin for mobile developers.
Best Browser With an HTML Editor: SeaMonkey
SeaMonkey is Mozilla’s all-in-one web app development suite. It includes an email and newsgroup client, IRC chat client, and a web page editor called Composer. One of the nice things about using SeaMonkey is that you have the browser built in already, so testing is a breeze. Plus, it has a free WYSIWYG editor with an embedded FTP to publish your web pages.
Best Light-weight HTML Editor: Geany
Geany is a text editor for developers. It should run on any platform that can support the GTK+ Toolkit. It is meant to be a small and fast loading IDE, so you can develop all your projects in one editor. It supports HTML, XML, PHP, and many other web and programming languages.
The Official W3C HTML Editor: Amaya
Amaya is the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) web editor. It validates the HTML as you build your page, and since you can see the tree structure of your web documents, it can be very useful for learning to understand the DOM and how your documents look in the document tree. It has a lot of features that most web designers won’t ever use, but if you want to be 100% sure that your pages work with the W3C standards, Amaya is the obvious choice.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-187039843-5aaad2033418c600363d9e3b.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headshot-00415ba557444a8a9b6bb139498b97c5.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/001_free-html-editors-for-linux-and-unix-3468154-58149635c54b4ac7a984e2cfc22c0ade.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/002_free-html-editors-for-linux-and-unix-3468154-e2dd0da334cb4717a2bbe5dd6d24a6b6.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/003_free-html-editors-for-linux-and-unix-3468154-7f696910059c446d8f8b0fb58dfe78e8.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/005_free-html-editors-for-linux-and-unix-3468154-96a8b7cc14c74d2fbdc34afc0f2f23db.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/006_free-html-editors-for-linux-and-unix-3468154-a9e608d70a6642b6ba42a42682f8c8f5.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/009_free-html-editors-for-linux-and-unix-3468154-07cc8facad134dadad964050e6ea4f36.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/010_free-html-editors-for-linux-and-unix-3468154-5603dc318ea940b38478688139246103.jpg)