TP-Link WN722N V2/3 Monitor Mode & Packet Injection Support
TP-Link WN722N is a very popular WiFi adapter for wireless auditing. It is low budget and beginner friendly so cybersecurity students and new learners always look for it. Now it becomes a problem because TP-Link WN722N Version 1 comes with Atheros AR9002U chipset and supports monitor mode and packet injection. Version 2/3 has the Realtek RTL8188EUS chipset and doesn’t support monitor mode or packet injection. Also TP Link N150 TL-WN722N version 1 have low availability in the market right now.
So in our this article we are going to cover how we can set TP-Link WN722N Version 2 or Version 3 on our Kali Linux and for Monitor Mode & Packet Injection. In that way we can use this affordable and reliable WiFi adapter for WiFi security testing.
We got a TP-Link WN722N Version 2 WiFi adapter on our hand (shown in the following picture) and we will show how to use Monitor Mode and Packet Injection on it.
| We can see the Model and Version on the back of the device |
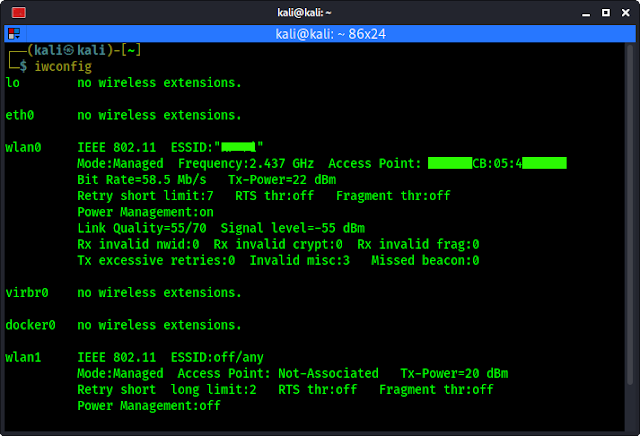
Now we are going to connect it on our system. After connecting it we can see it is working and we can connect to our WiFi networks with it (plug and play), but that is not our intention we need Monitor Mode and Packet Injection. Lets fire up our terminal and run following command to check our wireless network interfaces:
In the above screenshot we can see that in our case wlan0 is our system’s inbuilt wireless interface and wlan1 is our TP-Link WN722N’s network interface ( wlan0 and wlan1 etc depends on the system, confused what is yours? Then unplug the TP-Link WN722N and run ifconfig and check then again plug it in and check again you will get it ).
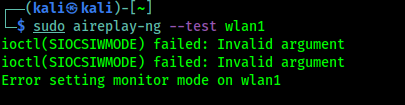
Now we run the following command to check if Packet Injection is supported or not on our TP-Link WN722N WiFi adapter by using following command:
sudo aireplay-ng --test wlan1
The output shown in the following screenshot:
In the above screenshot we can see that our external WiFi adapter don’t support Monitor Mode. So, we need to change the driver of this TP-Link WN722N adapter.
TP-Link WN722N V 2/3 Monitor Mode on Kali Linux
First of all we need to have an updated Kali Linux system ( sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade ), We are on all updated Kali Linux box. Then we need to install some dependencies on our system by applying following command:
sudo apt install dkms bc build-essential libelf-dev -y
After applying the above command above programs will be installed on our system as we can see in the following screenshot:
sudo apt install linux-headers-$(uname -r)
In the following screenshot we can see that we are already on a updated kernel:
Now we remove the current driver of RTL8188EUS driver by using following command:
Then we need to be the root user by applying following command:
We can see the results of the above commands in the following screenshot:
Now we need to blacklist old drivers by using following commands one by one:
echo "blacklist 8188eu" >> "/etc/modprob.d/realtek.conf"
echo "blacklist r8188eu" >> "/etc/modprob.d/realtek.conf"
After it is done our old drivers are removed. Here we need a reboot, rebooting our system will prevent errors for the rest of this setup. So we must need to Reboot.
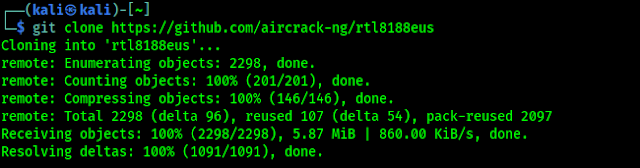
After a reboot we need to install that driver which one supports Monitor Mode & Packet Injection on TP-Link WN722N. To do that we need to clone a driver built by aircrack-ng form GitHub by using following command on our terminal window:
git clone https://github.com/aircrack-ng/rtl8188eus
We can see cloning process on the following screenshot:
After the installation process is done, we need to navigate to our cloned directory by applying following command:
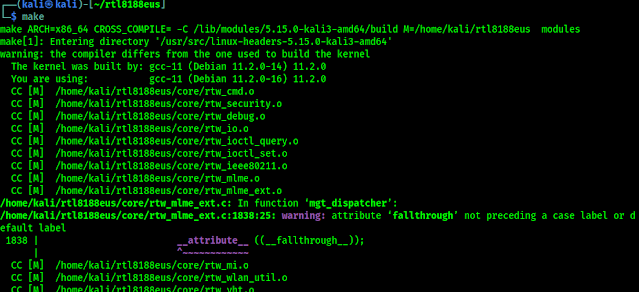
Then we need compile this driver by using following command:
Following screenshot shows the output of the compilation process:
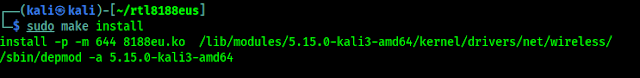
This compilation process may take couple of minutes depending on our system performance. Then we need to run following command to install the compiled driver:
Following screenshot shows the output of the command:
Now we need to run following command to set all up:
Now we are almost set, we just need a reboot. If everything was right then we are ready to rock after reboot. After the reboot is done let’s again check our network interfaces using following command:
Here we can see that the mode is still not showing Monitor Mode. Wait a bit, we need to turn on Monitor Mode on our wlan1 interface. To do that we run following commands on our terminal one by one:
sudo iwconfig wlan1 mode monitor
Now we can check our network interfaces status by using following command:
We can see the output in the following screenshot:
In the above screenshot we can see that our wlan1 got Monitor Mode (highlighted in red). BINGO
Let’s check it it is working well or not by scanning WiFi networks around us. To do so we need to run following command:
We can see the output on the following screenshot:
In the above screenshot we can see that we can scan for targets with our TP-Link WN722N Version 2 WiFi adapter on our Kali Linux system.
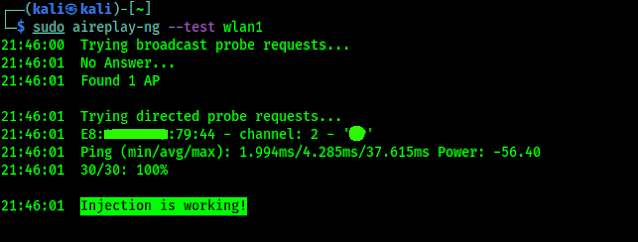
Let we check for packet injection by using following command (We tried this on the beginning):
sudo aireplay-ng --test wlan1
In the following screenshot we can see the output of the applied command:
In the above screenshot we can see that Packet Injection is working» on our TP-Link WN722N Version 2 WiFi adapter on our Kali Linux system.
Video Tutorial
Our article is inspired from David Bombal’s Youtube video. We can check his following video for a video tutorial:

This is how we can get monitor mode and packet injection support on TP-Link WN722N version 2 and 3 (same process) on our Kali Linux system.
Love our articles? Make sure to follow us on Twitter and GitHub , we post article updates there. To join our KaliLinuxIn family, join our Telegram Group . We are trying to build a community for Linux and Cybersecurity. For anything we always happy to help everyone on the comment section . As we know our comment section is always open to everyone. We read each and every comment and we always reply .
Tp link 722n v2 kali linux
There are many WLAN adapter on the market that has the option of running in monitor mode. The TP-Link TL-WN722N WLAN adapter is one of the more accessible and cheap adapters in Scandinavia. Unfortunately, it’s a bit of a pain to get up and running in Kali Linux. Especially the versions you can buy in stores today (v2/v3).
In this article, I will guide you through the process of installing the needed kernel module, and making it run in monitor mode in Kali Linux on a Virtual Machine in VirtualBox.
Enable adapter in VM
Make the Wi-Fi adapter accessable in the VM
Before the adapter can be used by Kali Linux, the adapter has to be enabled or attached to the VM. Open the settings for the VM, navigate to the USB menu, and add the Wi-Fi adapter to the VM. This way only the VM will be able to use the Wi-Fi adapter, and no other VM or your host OS.
Add the Wi-Fi NIC to the Kali Linux Virtual Machine
To make the adapter appear in the VM you might have to restart it. To check if it’s available you run the iwconfig command. If it’s discovered by the Operating System it will appear in the output.
iwconfig lo no wireless extensions. eth0 no wireless extensions. wlan0 IEEE 802.11g ESSID:"haxor" Mode:Managed Frequency:2.427 GHz Access Point: 00:0D:9D:FF:FF:FF Bit Rate=48 Mb/s Tx-Power=20 dBm Sensitivity=8/0 Retry limit:7 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off Power Management:off Link Quality=91/100 Signal level=-39 dBm Noise level=-87 dBm Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:860 Rx invalid frag:0 Tx excessive retries:0 Invalid misc:39 Missed beacon:8As you can see from the output above the adapter was discovered. To enable monitor mode and start using it for ethical hacking you need to install a custom kernel module, and enable monitor mode.
Kernel module
Install the needed packages for your Kali VM
Before anything can be done, you need to have a fully updated version of Kali Linux. In my experience, the 2021 versions of Kali Linux do not break during updates. But proceed with caution! You might not be as lucky. Your best bet might be to download the newest VirtualBox image and proceed from there. To update Kali run these commands.
sudo apt update sudo apt upgradeNow you must install the Linux kernel header files and the bc programming language packet. Both are necessary dependencies that are needed to compile the driver for the Wi-Fi adapter.
sudo apt install linux-headers-amd64 sudo apt install bcBefore we can use the new driver we must blacklist the default realtech kernel module (driver). To do this you first need to login as the root user. Please note that this is not possible to do with sudo privileges.
Once logged in as root you can blacklist the kernel module.
echo "blacklist r8188eu" > "/etc/modprobe.d/realtek.conf" exitNow you are ready to download the sourcecode to the custom kernel modules for the Wi-Fi adapter.
cd ~/Downloads git clone https://github.com/aircrack-ng/rtl8188eus cd rtl8188eusOnce downloaded you can compile the kernel module and install it.
make sudo make install sudo modprobe rtl8188eusAfter the installation, you can use the Wi-Fi adapter for ethical hacking.
WLAN sniffing
Make sure the adapter is running the new kernel module run this command
sudo airmon-ng PHY Interface Driver Chipset phy0 wlan0 8188eu TP-Link TL-WN722N v2/v3 [Realtek RTL8188EUS]As you can see from the output — the kernel module was successfully installed and running. To enable monitor mode on the adapter run this command:
sudo airmon-ng --verbose start wlan0 Found 2 processes that could cause trouble. Kill them using 'airmon-ng check kill' before putting the card in monitor mode, they will interfere by changing channels and sometimes putting the interface back in managed mode PID Name 485 NetworkManager 3847 wpa_supplicant No LSB modules are available. Distributor ID: Kali Description: Kali GNU/Linux Rolling Release: 2021.4 Codename: kali-rolling Linux kali 5.14.0-kali4-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 5.14.16-1kali1 (2021-11-05) x86_64 GNU/Linux Regulatory Domain appears to be unset, please consider setting it with 'iw reg set XX' https://wireless.wiki.kernel.org/en/users/documentation/iw#updating_your_regulatory_domain Detected VM using lspci This appears to be a VirtualBox Virtual Machine If your system supports VT-d, it may be possible to use PCI devices If your system does not support VT-d, you can only use USB wifi cards K indicates driver is from 5.14.0-kali4-amd64 V indicates driver comes directly from the vendor, almost certainly a bad thing S indicates driver comes from the staging tree, these drivers are meant for reference not actual use, BEWARE ? indicates we do not know where the driver comes from. report this X[PHY]Interface Driver[Stack]-FirmwareRev Chipset Extended Info K[phy0]wlan0 8188eu[mac80211]-unavailable TP-Link TL-WN722N v2/v3 [Realtek RTL8188EUS] mode managed (monitor mode enabled)From the verbose output for the command, you can see that it got activated in monitor mode. Another method of verifying that it is running in monitor mode is to run iwconfig:
iwconfig lo no wireless extensions. eth0 no wireless extensions. wlan0 unassociated Nickname:"" Mode:Monitor Frequency=2.457 GHz Access Point: Not-Associated Sensitivity:0/0 Retry:off RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off Power Management:off Link Quality=0/100 Signal level=0 dBm Noise level=0 dBm Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:0 Rx invalid frag:0 Tx excessive retries:0 Invalid misc:0 Missed beacon:0As you can see from the output — the NIC is in monitor mode. You are now able to use it with wireshark and a lot of other fun networking tools. As a starter you can start running scan for access points and endpoints using airodump-ng:
sudo airodump-ng wlan0 CH 13 ][ Elapsed: 36 s ][ 2021-12-12 16:48 BSSID PWR Beacons #Data, #/s CH MB ENC CIPHER AUTH ESSID 72:02:71:7C:FF:FF -82 5 0 0 9 130 WPA2 CCMP PSK Victim_AP_01 72:02:71:7C:FF:FF -69 16 0 0 1 130 WPA2 CCMP PSK Victim_AP_02 50:C7:BF:4F:FF:FF -57 15 2 0 9 405 WPA2 CCMP PSK Victim_AP_03 BSSID STATION PWR Rate Lost Frames Notes Probes (not associated) 7E:45:E3:FF:FF:FF -38 0 - 5 0 3 Victim_AP_04The Wi-Fi sniffer program airodump-ng will listen in on every channel looking for access points and devices. After a couple of minutes, you should have a list of all devices in the area. If you were able to successfully run airodump-ng using the Wi-Fi adapter you have verified that monitor mode is working correctly.
Congratulations. You now have a working Wi-Fi packet sniffing solution using the TP-Link TL-WN722N. Now, go ahead and use this for good!
Skarshaug Solutions © 2010 — 2023