- Утилиты Traceroute и Tracert
- Как работают Tracert и Traceroute
- Как использовать Traceroute и Tracert
- How to Run a Traceroute on Linux, Windows & macOS
- What Is Traceroute?
- How Does Traceroute Work?
- How to Run a Traceroute?
- Run a Traceroute on Linux
- Run a Traceroute in Windows
- Run a Traceroute on macOS
- How to Read a Traceroute?
Утилиты Traceroute и Tracert
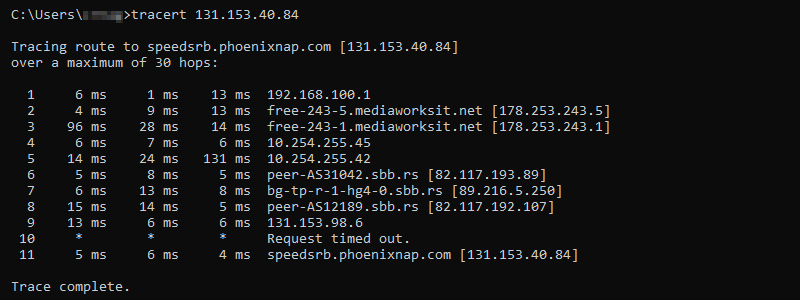
Traceroute — это утилита, которая позволяет проследить маршрут следования данных до удалённого адресата в сетях TCP/IP. В Linux используется команда Traceroute, а в Windows — Tracert. При помощи этих команд можно увидеть путь пакета данных от вашего компьютера до целевого сервера или сайта.
Как работают Tracert и Traceroute
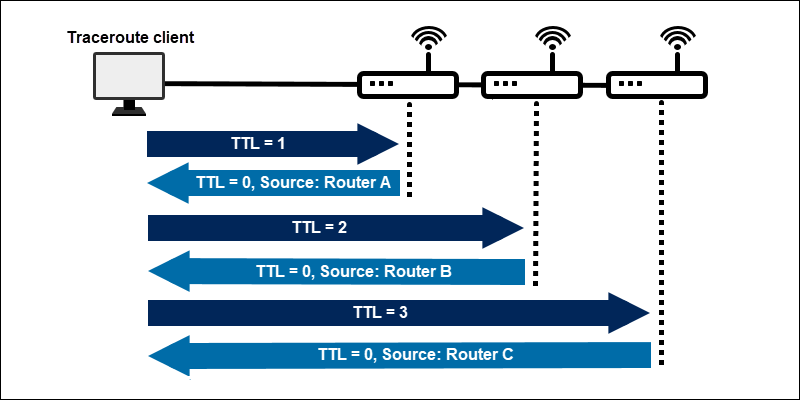
Когда вы пытаетесь открыть сайт, браузер отправляет сообщение (запрос) серверу, на котором этот сайт находится. Сообщение на своём пути проходит через маршрутизаторы. Они решают, куда дальше передать сообщение, чтобы гарантированно его доставить адресату. В трассировке маршрутизаторы ещё называют хопами (хоп — прыжок) или узлами. Количество узлов, через которые на своём пути пройдёт запрос, можно узнать при помощи утилит Tracert и Traceroute. Узлы, которые не являются целевыми для запроса, называют транзитными.
Утилита Traceroute формирует UDP-датаграмму (сообщение, которое нужно доставить целевому серверу), упаковывает её в IP-пакет и передаёт первому транзитному узлу. В заголовке такого IP-пакета есть поле TTL (Time To Live) — время жизни пакета. Оно определяет количество хопов, через которые пакет может пройти. На каждом узле TTL уменьшается на единицу. Если на пути к удалённому адресату время жизни пакета станет равно 0, маршрутизатор отбросит пакет и отправит источнику ICMP-сообщение об ошибке «Time Exceeded» (время истекло).
Этот принцип лежит в основе работы утилит Tracert и Traceroute, однако между ними есть отличия. Рассмотрим каждую утилиту отдельно.
Tracert отправляет на хост назначения ICPM-запрос «Echo Request» с TTL=1. Первый маршрутизатор, который получит запрос, проверяет, кому он предназначен. Если маршрутизатор не является целевым хостом, он уменьшает TTL на 1, отбрасывает пакет и отправляет ICMP-сообщение источнику, так как время жизни теперь равно 0. В этом сообщении маршрутизатор указывает информацию о себе и причину дропа пакета. Получив сообщение, Tracert запоминает этот маршрутизатор как первый хоп (прыжок) и отправляет следующий пакет, но уже с TTL=2. Первый хоп успешно обрабатывает новый пакет, уменьшает время его жизни на 1 и передаёт дальше. Следующий маршрутизатор тоже выполняет проверку хоста назначения и, если пакет предназначен не ему, уменьшает TTL, отбрасывает пакет и отправляет ICMP-сообщение источнику. Tracert запоминает второй хоп, снова увеличивает TTL на 1 и отправляет следующий пакет. Эти действия будут повторяться до тех пор, пока пакет не достигнет целевого хоста. Когда запрос попадёт к целевому хосту, этот хост в ответ направит ICMP «Echo Reply». Источник воспримет это как завершение трассировки.
Утилита Traceroute вместо ICMP-запроса отправляет 3 UDP-пакета на определенный порт целевого хоста и ожидает ответа о недоступности этого порта. Первый пакет отправляется с TTL=1, второй с TTL=2 и так далее, пока запрос не попадёт адресату. Отличие от Tracert в том, как Traceroute понимает, что трассировка завершена. Так как вместо ICMP-запроса он отправляет UDP-запрос, в каждом запросе есть порт отправителя (Sourсe) и порт получателя (Destination). По умолчанию запрос отправляется на закрытый порт 34434. Когда запрос попадёт на хост назначения, этот хост отправит ответ о недоступности порта «Destination port unreachable» (порт назначения недоступен). Это значит, что адресат получил запрос. Traceroute воспримет этот ответ как завершение трассировки.
Если Tracert работает по протоколу ICMP, то какой протокол используется командой Traceroute? По умолчанию используется протокол UDP, но traceroute может отправить и ICMP-запрос «Echo Request», как Tracert. Такой способ пригодится, если хоп не отвечает на UDP-пакет.
Как использовать Traceroute и Tracert
Кириллические домены необходимо вводить в формате Punycode. Для перевода домена в Punycode воспользуйтесь сервисом.
How to Run a Traceroute on Linux, Windows & macOS
Traceroute is a crucial tool in network diagnostics. Together with other Linux commands such as ping, ip, and netstat (or the newer alternative ss), Traceroute identifies the path packets take from source to destination. The tool is universally available for Linux, Windows, and macOS.
This article explains the traceroute or tracert command, how it works, and how to run and read a traceroute on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
- Access to the command line/terminal.
- Network connection.
- A website or IP address to trace (optional, provided in examples).
What Is Traceroute?
traceroute is a command used in network troubleshooting for mapping the path packets travel through the network. The tool aids in the discovery of possible routes of information from source to destination. Additionally, the command also helps calculate the transfer times between points.
When applied to network troubleshooting, traceroute helps locate where traffic slows down between the source and destination.
How Does Traceroute Work?
The protocol sends ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) packets to every router transferring between the source and destination. When you run a traceroute, the output displays:
- The IP address of the router that successfully received the packet.
- The travel latency, or the amount of time it took to get a response for each of the three probes.
Traceroute acts as a series of ping commands. While ping requests a response from the destination, traceroute gathers the intermediate information as well.
To gather the information available between the source and destination, a traceroute lowers the packet’s TTL (time to live) to a minimum (1). When a router receives the information, it decrements the TTL value to 0, indicating it should send information back to the source. The source gathers the intermediate router information, resets the TTL value to 1, and increments it.
This way, the packet reaches the next router in the network. The iterative process repeats until the final package reaches the destination IP. Then, traceroute recognizes the destination IP and outputs all the intermediate information gathered.
The command sends out three probes by default for each TTL value and prints out the round-trip time for each packet.
How to Run a Traceroute?
Traceroute is available on most modern machines. The program is a command line tool with different options and syntax depending on the operating system.
By default, a traceroute is 30 hops for a packet size of 60 bytes for IPv4 and 80 bytes for IPv6.
Note: Learn about the difference between IPv4 and IPv6.
Run a Traceroute on Linux
On Ubuntu, the traceroute command is not available by default. Install the tool using the apt package manager.
1. Open the terminal (CTLR+ALT+T) and install traceroute with:
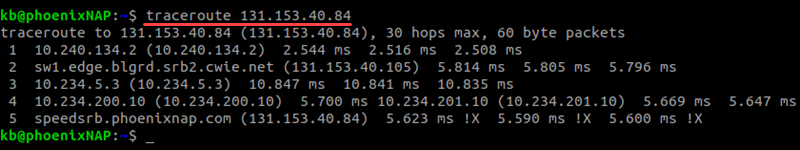
sudo apt install traceroute2. In the terminal, run a traceroute with:
traceroute [options] [packet length]Alternatively, use a hostname:
Note: A similar command called tracepath is available for Linux. The main difference between the two is that traceroute offers more options, some of which require root privilege. On the other hand, tracepath is available for all users and outputs less information.
Advanced Options for Traceroute on Linux
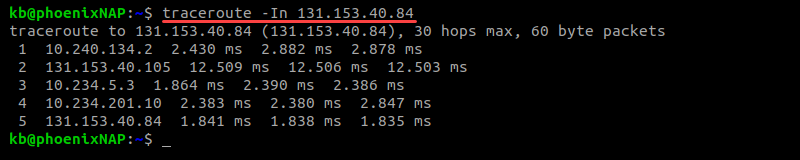
By default, a traceroute sends UDP packets. Add the option -I for ICMP probe packets:
Include the -n option to hide the device names for a cleaner output:
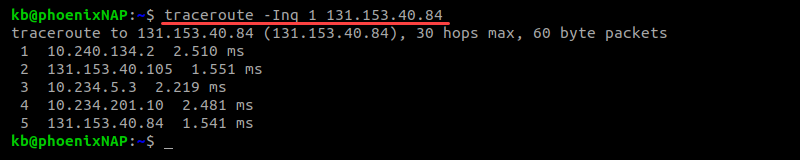
By default, the number of packets sent is three. Change the number with the -q option followed by the number of packets:
Lowering the number of packets to one increases the speed of a traceroute.
For all additional options of traceroute , check the manual page in the terminal with the man command:
The manual contains information on all available command options and how to apply them to the command.
Run a Traceroute in Windows
Traceroute is available for Windows using the shorter name tracert . To run a traceroute on Windows, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key and type CMD.
2. Press Enter and open the command prompt.
3. Lastly, run traceroute with:
The output prints Trace complete to the console when the traceroute completes.
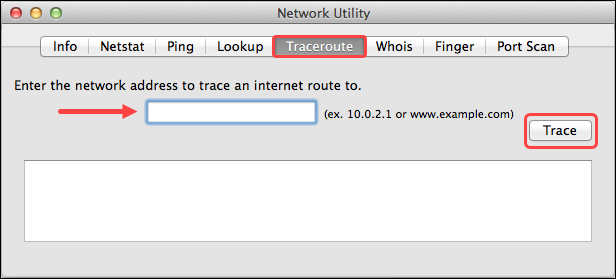
Run a Traceroute on macOS
To run a traceroute on macOS using the GUI, follow the steps below:
1. Click the Spotlight (magnifying glass) icon.
2. Next, search for Network Utility in the search field.
3. Double-click the Network Utility from the search result.
4. Locate and click the Traceroute tab.
5. Lastly, enter the IP address or host of the destination and click Trace. The textbox below the Trace button outputs the Traceroute results.
How to Read a Traceroute?
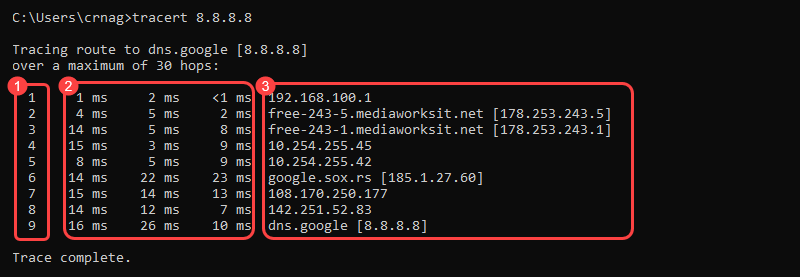
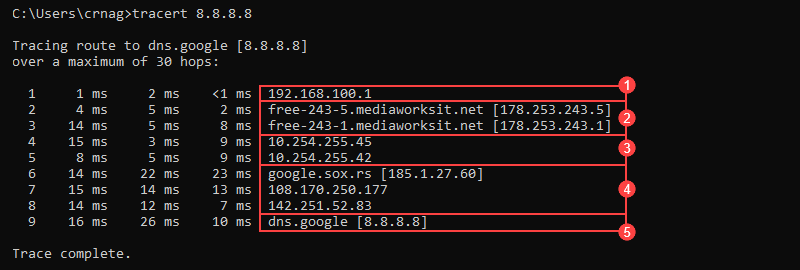
When running a traceroute, the output shows the path packets take when traveling to a destination point. The printed result divides into three general columns:
1. Each line indicates a router hop. The first column shows the hop number.
2. The following three columns show the round-trip time (RTT) for a total of three packets:
- For nearby networks, these numbers are usually below 100ms.
- For distant networks in other countries, typical RTT values go up to 300ms.
Three asterisk symbols (* * *) instead of numbers followed by a «Request timed out» message can indicate:
- The router is down.
- The router is configured not to return traceroute results.
- A firewall is enabled on the router.
- A time-out for one of the previous routers.
3. The last column displays the destination IP address and, whenever possible, the resolved domain name.
The traceroute output rows group into a total of five units:
4. The network of the destination’s host.
5. The destination address.
Note: The results are different for everyone. The general categories still apply to every situation, though. Figure out each address by looking up the reverse DNS.
Add > .txt at the end of the traceroute or tracert command to save the results into a text file for later use and analysis. For example, on Linux and macOS:
traceroute 8.8.8.8 > results.txtWindows users can follow the same steps:
In both cases, the output does not print anything out and returns to the regular command line input. The file saves to the location where the command runs.
At the end of this tutorial, you know how to use and read the output of the traceroute or tracert command. Traceroute is a crucial tool for network troubleshooting and pinpointing bottlenecks in the connection.
If you want to learn more about traceroute comparing to other terminal programs, read our article tracepath vs. traceroute.
For more networking commands, check out our guide on the nmap network scanner tool. It’s a useful tool for scanning for open ports.