- Bluetoothctl: Management of Bluetooth Devices in Linux
- Table of Contents
- Installation and Early Preparation
- Step 1: Get into Bluetoothctl’s Interactive Mode
- Step 2: Turn on Bluetooth in Linux
- Step 3: Scan for Available Bluetooth Devices
- Step 4: Connect to Your Bluetooth Device
- 1. Pair and Connect
- 2. Trust and Connect
- Scripting using bluetoothctl in non-interactive mode
- Other Bluetoothctl Commands
- Conclusion
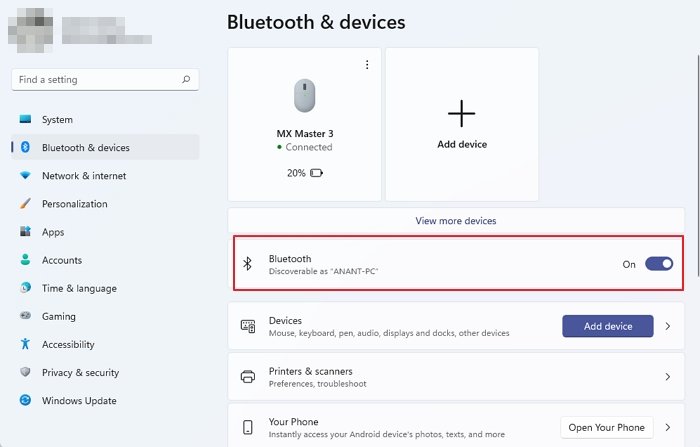
- Toggle to turn Bluetooth On or Off is missing in Windows 11/10
- The toggle to turn Bluetooth On or Off is missing
- 1] Update, Rollback or Reinstall the Bluetooth driver
- 2] Enable Bluetooth from the Device Manager
- 3] Enable Services for Bluetooth
- Where is the Check for Bluetooth Hardware button?
- How do I turn on Bluetooth on my computer if there is no option?
- Why is there no Bluetooth on my Device Manager?
Bluetoothctl: Management of Bluetooth Devices in Linux
This article is about the Management of Bluetooth devices in Linux using a command-line tool called bluetoothctl. In this, I will talk about how to connect with a Bluetooth device in Linux. I have also given a little hint in the end about how to automate this whole scanning, connecting, and other processes just with a script.
Alternatively, we can use Graphical Tools like GNOME Bluetooth, Bluedevil, Blueman. But like all other Graphical Tools, they are bloated, they lack the ability of scripting, and they cannot be used without X11 or Wayland. These restrictions are mitigated by using a command-line utility called bluetoothctl .
Table of Contents
Installation and Early Preparation
~$ sudo pacman -S bluez bluez-utils ~$ sudo dnf install bluez bluez-toolsNow, enable the bluetooth.service using following systemd‘s command
~$ sudo systemctl enable bluetooth.serviceThe above is to enable the Bluetooth service in the background. But it requires restarting your system. If you do not want to restart, execute the following command as well:
~$ sudo systemctl start bluetooth.serviceNote: Make sure that kernel module btusb is loaded into the system. Kernel modules are equivalent to drivers in Windows OS. If it is not loaded, load it using
Now, I will be describing how to connect to a Bluetooth device using my smartphone as an example in the following steps.
Step 1: Get into Bluetoothctl’s Interactive Mode
Like nmtui, bluetoothctl’s interactive mode is easier to work with during the first-time connection. And like nmcli, the non-interactive mode is good for scripting.
To get into interactive mode, use
Output may look like this:
Agent registered [CHG] Controller F8:89:D6:C8:2E:54 Pairable: yes [bluetooth]# Notice, how the prompt is changing from ~$ to [bluetooth]# . Now, you can execute any command like help after the # symbol. Use help to find all existing commands and their one-liner explanations.
After following all the steps, you can quit using
Step 2: Turn on Bluetooth in Linux
To turn on the Bluetooth, use power on command:
In my system, I get the following output:
[CHG] Controller F8:89:D2:C8:2E:54 Class: 0x006c010c Changing power on succeededSimilarly, to turn it off, you can use the power off command.
Step 3: Scan for Available Bluetooth Devices
First list available devices using
[bluetooth]# devices Device 40:45:DA:B8:AB:BB 34SUPER Device 04:C8:07:12:D0:2D LG Q3If you cannot find your device in the output, use the following command:
As you turn on your Bluetooth device (in the above example, my new smartphone), bluetoothctl will list it in the output. After you have found your device, copy its address for future use.
If you want your Linux computer to be discoverable by other devices, use the command given below. But for my tutorial, it is not necessary.
[bluetooth]# discoverable onStep 4: Connect to Your Bluetooth Device
We can do it in two ways:
1. Pair and then Connect.
2. Trust and then Connect. I find it simpler, less confusing and it works for me with all kinds of devices. Hence, I will be describing this in detail.
1. Pair and Connect
Turn on the pairing in your Bluetooth device (ex – smartphone). Then, Turn on the pairing in your Linux computer using
[bluetooth]# pair 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8[bluetooth]# connect 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8Now, you might get a prompt to accept the connection. Just say yes.
2. Trust and Connect
First, you need to trust your device using the following :
[bluetooth]# trust 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8[CHG] Device 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8 Trusted: yes Changing 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8 trust succeededNow, bluetoothctl saves your device’s address on your computer. In the future, you will not be needing to trust the device anymore. This saving is preserved even over system-restart. Now, you can connect with the device using:
[bluetooth]# connect 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8Now, you might get a prompt to accept the connection. Just say yes. It might even ask you to match passkey/pin. For my smartphone, the output is
Request confirmation [agent] Confirm passkey 989960 (yes/no): yes [CHG] Device 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8 Paired: yes Connection successfulScripting using bluetoothctl in non-interactive mode
We can execute the above-mentioned commands in non-interactive mode as well by prepending bluetoothctl with them. For example, power on command becomes
So, if you want to connect to your Bluetooth device using a single command, use the following:
~$ bluetoothctl power on && bluetoothctl connect 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8Note: As stated above, don’t forget to trust your device 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8 before executing the above command – We need to do this only once in our lifetime.
Scripting is one of the things I love about Linux – You can merge one command with another and boost your productivity.
This can be seen with my current usage of the above command with the nmcli command to share my smartphone’s internet with the computer. It is reasonably fast – it can play Youtube videos at 720p. at the same time, Bluetooth consumes much less energy than Wi-Fi.
~$ bluetoothctl power on && bluetoothctl connect 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8 && nmcli connection up id 'Mi A3 Network'Other Bluetoothctl Commands
When we used the devices command, we got a list of devices. If you want to remove your device from the list due to privacy reasons, use the following in interactive mode:
[bluetooth]# remove 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8And if you no longer want your device to be trusted any more use:
[bluetooth]# untrust 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8To disconnect, there are many methods:
1. Toggle the Bluetooth switch on your Bluetooth device and/or computer.
2. Use bluetoothctl power off command from your terminal.
3. Or, use the standard method bluetoothctl disconnect 90:78:B2:C7:8F:A8
Conclusion
There are many more options to explore in bluetoothctl, just read them in bluetoothctl help. Now you can use Bluetooth for sharing files/internet/audio.
Occasionally, you might face a few bugs. Sometimes, restarting the computer might fix them. And if the problem still persists, put them in the comment section below. I have a few solutions and putting them here will make the article lengthy.
That’s all. And also do not forget to notify me any mistakes committed by me in this article if any.
Toggle to turn Bluetooth On or Off is missing in Windows 11/10
Windows 11/10 has always included support for Bluetooth hardware. Well, this support has been here for a while now. And with support for the latest version of Bluetooth 5.0 LE, it keeps getting even better. But at times, some users have found that when they go on to use Bluetooth, they find that the option to turn on Bluetooth is missing in the Windows Settings app or the Action Center. If you face this issue, then this post will help you fix the problem.
The toggle to turn Bluetooth On or Off is missing
- No option to turn on Bluetooth
- The device does not have Bluetooth.
- Bluetooth won’t turn on
- Bluetooth missing toggle
- No Bluetooth toggle
- No Bluetooth switch
- The option to turn Bluetooth on or off is missing.
- Update, Rollback, or Reinstall the Bluetooth driver.
- Enable Bluetooth from Device Manager.
- Enable Services for Bluetooth.
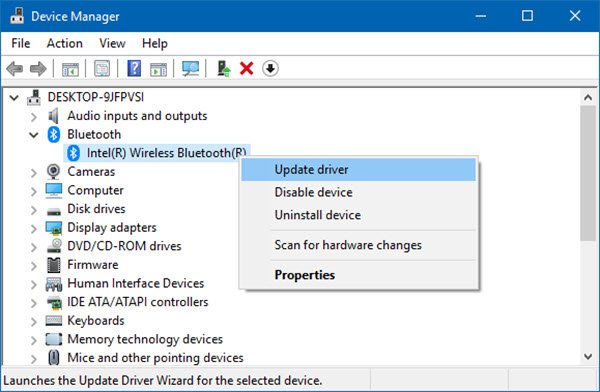
1] Update, Rollback or Reinstall the Bluetooth driver
If you recently updated your drivers, maybe you could uninstall or rollback any drivers and see if that helps. If you did not, you could, via Device Manager, either update or uninstall and fresh install the Bluetooth driver. It could be the Bluetooth Generic Adapter driver, Intel(R) Wireless Bluetooth, etc.
2] Enable Bluetooth from the Device Manager
Start by hitting the WINKEY + R button combination to launch the Run utility. Now type in devmgmt.msc and hit Enter. It will open the Device Manager for you.
Now, click on the entry labeled as Bluetooth and expand it.
Then, right-click on all the Bluetooth driver entries. It could be labeled as Bluetooth USB Module, Intel(R) Wireless Bluetooth, etc. If you see it disabled, then click on Enable device.
Restart your computer to check if the issue is fixed or not.
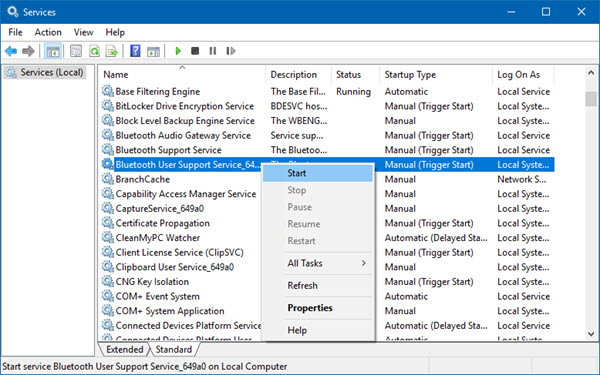
3] Enable Services for Bluetooth
Press the WINKEY+R button combination, type in Services.msc, and then hit Enter to open the Windows Services Manager.
- Bluetooth Handsfree Service.
- Bluetooth Audio Gateway Service.
- Bluetooth Support Service.
- Bluetooth User Support Service.
Right-click on the services listed above and click on Properties.
Make sure that the Startup Type of all is set to Manual. Click on Apply and then click on OK.
If the above services are not running, right-click on the service and click on Start.
Where is the Check for Bluetooth Hardware button?
Some laptops offer a hardware button that can turn off WiFi and Bluetooth, and you will not be able to turn it on from Windows Settings. So check if that’s the case, and turn on the hardware button, also called as Airplane mode button.
How do I turn on Bluetooth on my computer if there is no option?
If your PC doesn’t show a Bluetooth option at all, you may not have a Bluetooth device. Check if your motherboard has a Bluetooth device on it. If not, you will need to install a Bluetooth adaptor. That said, you can also invest in a PCIe card that supports WiFi and Bluetooth.
Why is there no Bluetooth on my Device Manager?
If your Device Manager doesn’t display any Bluetooth, click File and select Scan for Hardware changes. If the device is physically connected to the PC, then it should be able to detect it. If this doesn’t work, you can restart the PC, get into BIOS, and check if the Bluetooth is disabled. Enable it, reboot, and you should be able to see the Bluetooth option once you log in to the computer.