- How do I type on the next line in the Terminal?
- 6 Answers 6
- 13 Linux Terminal Shortcuts Every Power Linux User Must Know
- Must Know Linux Shortcuts
- 1. Tab
- 2. Ctrl + C
- 3. Ctrl + Z
- 4. Ctrl + D
- 5. Ctrl + L
- 6. Ctrl + A
- 7. Ctrl + E
- 8. Ctrl + U
- 9. Ctrl + K
- 10. Ctrl + W
- 11. Ctrl + Y
- 12. Ctrl + P
- 13. Ctrl + N
- Bonus shortcut: Ctrl + R to search in command history
- Download FREE terminal shortcut cheatsheet
How do I type on the next line in the Terminal?
I am using Ubuntu 12.10 and want to run a set of commands in the terminal, and from what i see in the instructions, these commands each start on a new line. I don’t know how to do this in the terminal. I can’t find what key to press to do the carriage-return to the next line.
@LnxSlck: Though, it’s often preferable to separate commands with && instead of ; . This way, if one of the commands fail, the remaining commands will not be run. So, using your example, if home doesn’t exist, you won’t accidentally create a test directory in the current directory.
6 Answers 6
As Web-E explains the most direct way to do what you want with two different commands, I thought I’d show that there are a number of ways to execute multiple commands or to continue commands onto another line without immediately executing them.
Continuing long commands:
1) The most common way to construct one long command is to enter your commands, then use a backslash \ , press return, and then Bash will provide another prompt for you instead of executing the command. This secondary prompt is called PS2 and waits for your input:
find /home/mike/Downloads -type f -iname '*.jpg' \ > You can keep on adding backslashes and pressing return as long as you want, as long as you think the overall command will make sense.
You can cancel this secondary prompt with the usual Ctrl + C .
2) Bash recognises some commands such as for loops (for i in. ) and the prompt will appear immediately; just as it will if you miss a quotation mark off a command:
Multiple Commands:
3) As Lxnslck notes, you can separate commands with semicolons:
which vlc; whereis vlc /usr/bin/vlc vlc: /usr/bin/vlc /etc/vlc /usr/lib/vlc /usr/bin/X11/vlc /usr/share/vlc /usr/share/man/man1/vlc.1.gz 4) Or you can use the ampersand && to join two commands:
The commands you see in each line are to be executed one by one.
So after entering a line, press enter to execute then execute next command.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade These are two commands to be executed one by one.
To execute at once it will be like sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade (there are other methods also), but these thing doesn’t require generally . So don’t worry. Type one line and press enter it will do it’s job.
You can press the ENTER key after each line and if the command is not terminated (mutiline commands like for loops for example), the terminal will wait for you to enter the rest of the command. If the command is terminated, it will be executed and you enter next command after, no problem.
If you are copying the commands from a tutorial, you can copy the whole group of commands and paste it directly in the terminal and it will work.
When it’s a set of commands you expect to be using more than once, you should put them in a bash script file. For instance,
xrandr --newmode "1280x960_80.00" 139.25 1280 1368 1504 1728 960 963 967 1008 -hsync +vsync xrandr --verbose --addmode VGA1 "1280x960_80.00" xrandr --output HDMI1 --off --output LVDS1 --mode 1366x768 --pos 1280x512 --rotate normal --output DP1 --off --output VGA1 --mode "1280x960_80.00" --pos 0x0 --rotate normal sleep 3 xfce4-panel -r is nothing you’d like to type ever again, but I happen to need this particular sequence of commands very often. So it goes in a file called 1280×980-2head.sh , you can create that with any editor of your choice. To make that script executable, you put the line #!/bin/bash in front of everything (a shebang), and set the execution-permission: chmod +x 1280×980-2head.sh . Then, just typing ./128 (auto-completion) and executes all the commands.
13 Linux Terminal Shortcuts Every Power Linux User Must Know
Use Linux command line like a pro by mastering these Linux terminal shortcuts and increase your productivity. It’s a must for any power Linux user.
You know what sets apart a pro user from a regular user? Mastery over the keyboard shortcuts.
Alright! That’s not the only thing but it is undoubtedly a factor.
Shortcuts help you to be more productive and efficient with whatever tool you use. Just think about it. If someone holds the mouse all the way down to copy entire text instead of Ctrl+A, how would you feel about it?
Linux terminal is not an exception. There are certain Linux terminal shortcuts that every user must know and practice.
Trust me; once you master these shortcuts, you’ll notice how good you are with using the Linux command line.
Must Know Linux Shortcuts
I would like to mention that some of these shortcuts may depend upon the Shell you are using. Bash is the most popular shell, so the list is focused on Bash. If you want, you may call it Bash shortcut list as well.
Do note that I have used the capital letters in the keyboard shortcuts but this does NOT mean that you have to press the shift key while using these shortcuts.
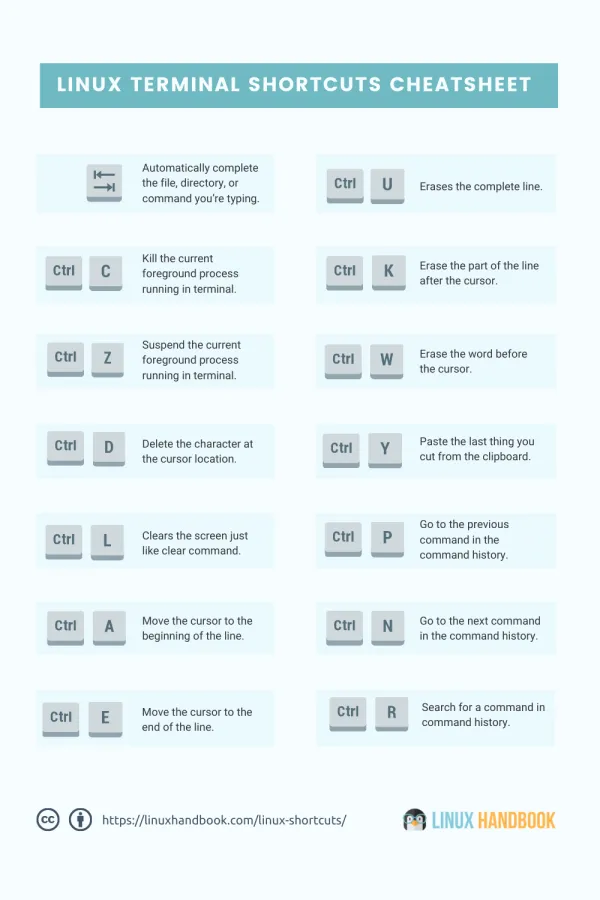
1. Tab
This is the Linux shortcut you cannot live without. It will save you so much time in the Linux command line.
Just start typing a command, filename, directory name or even command options and hit the tab key. It will either automatically complete what you were typing or it will show all the possible results for you.
If you could only remember one shortcut, this would be the chosen one.
2. Ctrl + C
These are the keys you should press in order to break out of a command or process on a terminal. This will stop (terminate) a running program immediately.
If you want to stop using a program running in the foreground, just press this key combination.
3. Ctrl + Z
This shortcut will suspend a running program and gives you control of the shell. You can see the stopped program in background jobs and even resume to run it using the fg command.
4. Ctrl + D
This keyboard shortcut will log you out of the current terminal. If you are using an SSH connection, it will be closed. If you are using a terminal directly, the application will be closed immediately.
Consider it equivalent to the ‘exit’ command.
5. Ctrl + L
How do you clear your terminal screen? I guess using the clear command.
Instead of writing C-L-E-A-R, you can simply use Ctrl+L to clear the terminal. Handy, isn’t it?
6. Ctrl + A
This shortcut will move the cursor to the beginning of the line.
Suppose you typed a long command or path in the terminal and you want to go to the beginning of it, using the arrow key to move the cursor will take plenty of time. Do note that you cannot use the mouse to move the cursor to the beginning of the line.
This is where Ctrl+A saves the day.
7. Ctrl + E
This shortcut is sort of opposite to Ctrl+A. Ctrl+A sends the cursor to the beginning of the line whereas Ctrl+E moves the cursor to the end of the line.
Note: If you have the Home and End keys on your keyboard, you can also use them. Home is equivalent to Ctrl +A and End is equivalent to Ctrl + E.
8. Ctrl + U
Typed a wrong command? Instead of using the backspace to discard the current command, use Ctrl+U shortcut in the Linux terminal. This shortcut erases everything from the current cursor position to the beginning of the line.
9. Ctrl + K
This one is similar to the Ctrl+U shortcut. The only difference is that instead of the beginning of the line, it erases everything from the current cursor position to the end of the line.
10. Ctrl + W
You just learned about erasing text till the beginning and the end of the line. But what if you just need to delete a single word? Use the Ctrl+W shortcut.
Using Ctrl+W shortcut, you can erase the word preceding to the cursor position. If the cursor is on a word itself, it will erase all letters from the cursor position to the beginning of the word.
The best way to use it to move the cursor to the next space after the targetted word and then use the Ctrl+W keyboard shortcut.
11. Ctrl + Y
This will paste the erased text that you saw with Ctrl + W, Ctrl + U and Ctrl + K shortcuts. Comes handy in case you erased wrong text or if you need to use the erased text someplace else.
12. Ctrl + P
You can use this shortcut to view the previous command. You can press it repeatedly to keep on going back in the command history. In a lot of terminals, the same can be achieved with PgUp key.
13. Ctrl + N
You can use this shortcut in conjugation with Ctrl+P. Ctrl+N displays the next command. If you are viewing previous commands with Ctrl+P, you can use Ctrl+N to navigate back and forth. Many terminals have this shortcut mapped to the PgDn key.
Bonus shortcut: Ctrl + R to search in command history
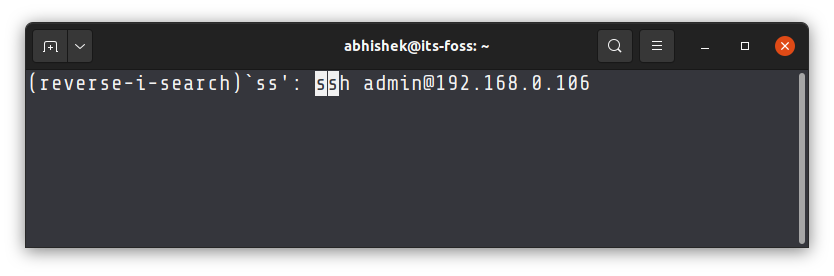
You typed some command but cannot remember what it was exactly? Meet Ctrl + R.
This keyboard shortcut allows you to perform a search in your command history. Just press Ctrl+R and start typing. It will show the last command that matches the string you typed. Note that the typed string could be anywhere in the command. How cool is that?
If you want to see more commands for the same string, just keep pressing Ctrl + R.
You can press enter to run the command selected or press Esc to come out of the search with the last search result.
Download FREE terminal shortcut cheatsheet
The best way to learn new keyboard shortcuts is by keeping a cheat sheet pinned to your disk. You cannot possibly remember the new shortcuts so having the shortcuts in front of you gives the ability to look at it at a quick glance. This way you’ll use them more often and eventually, it gets added to your muscle memory.
To help you with that, I have added a one-page PDF. You can print it and keep it at your desk.