- How to Create Bootable USB Drive on Ubuntu / Linux Mint
- Startup Disk Creator
- UNetbootin
- dd (Command line Utility)
- Test Your Bootable Disk
- 7 thoughts on “How to Create Bootable USB Drive on Ubuntu / Linux Mint”
- Create the bootable media¶
- How to make a bootable USB stick¶
- In Linux Mint¶
- In Windows, Mac OS, or other Linux distributions¶
- How to make a bootable DVD¶
- In Linux¶
- In Windows¶
- In Mac OS¶
- How to Create Bootable Linux Mint USB Installer in Linux, Windows, or Mac OS
- Supported Systems:
- Preparation:
- Option 1: Create USB installer from an Ubuntu machine.
- Option 2: Create bootable USB from Windows, Mac OS, or other Linux.
- Conclusion:
How to Create Bootable USB Drive on Ubuntu / Linux Mint
When planning to install any Linux distributions, you definitely need a bootable USB flash drive or bootable DVD. There are several 3 rd party applications that helps you turn the ISO file into a Bootable USB disk. With a Bootable drive, you can not only install distro applications, you can also use the disk to test the desktop experience of Ubuntu without needing to meddle with your computer’s configuration or even help in fixing any configuration issues. In this article, we’ll show you how to create a bootable usb flash drive on Ubuntu / Linux Mint.
When it comes to creating bootable usb drive, there are many tools available and we are going to discuss about the following tools:
Startup Disk Creator
Startup Disk Creator is a utility that is readily available with Ubuntu to help you create bootable disks easily. Whenever we install Ubuntu and Linux Mint then this installed automatically as part of default tools. Refer the beneath steps to Create Bootable USB stick or DVD using startup Disk Creator
Step: 1) Insert the USB disk / DVD into your computer
Step:2 ) Open the Start Disk Creator application in Ubuntu
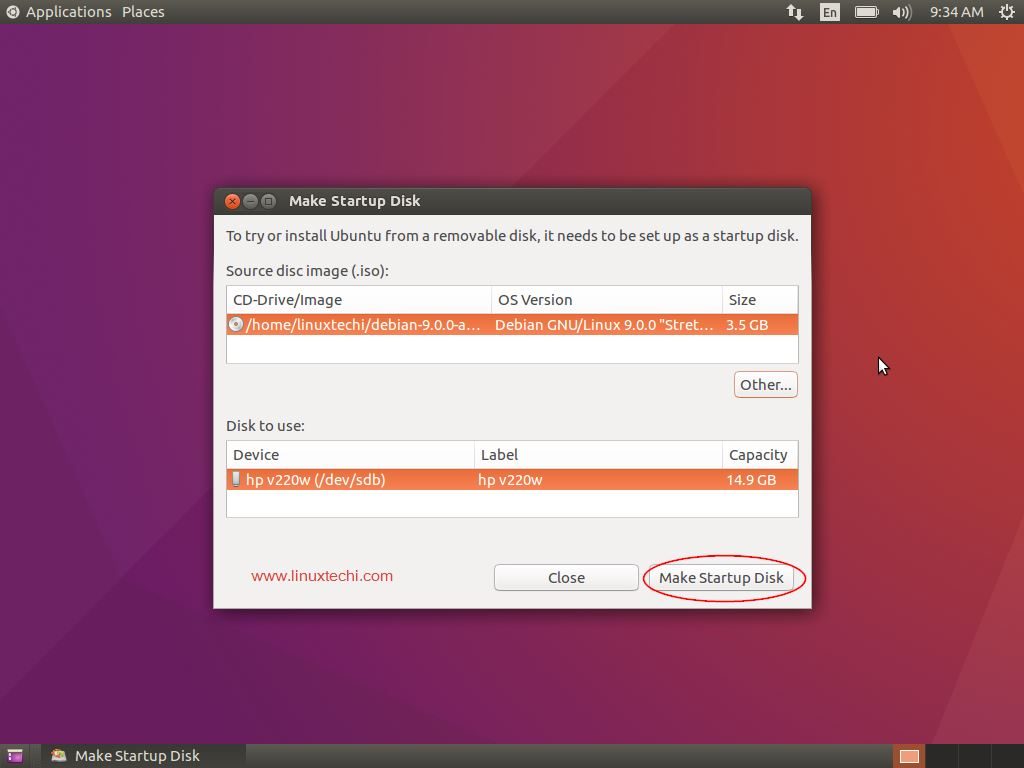
Step:3 ) Once the application is launched, it automatically looks for any ISO file in your Downloads folder and lists that ISO file in the Source image area of the utility,
If you want to choose another ISO file, click “Other” button to open the file and select the ISO you need
The USB flash drive or DVD whichever is connected to your computer is also automatically detected and placed in the “Disk to Use” section.
If not, Click “Other” button to choose the desired disk in which a bootable disk need to be created
Once everything is set, select “Make Startup disk” button to create the bootable disk
UNetbootin
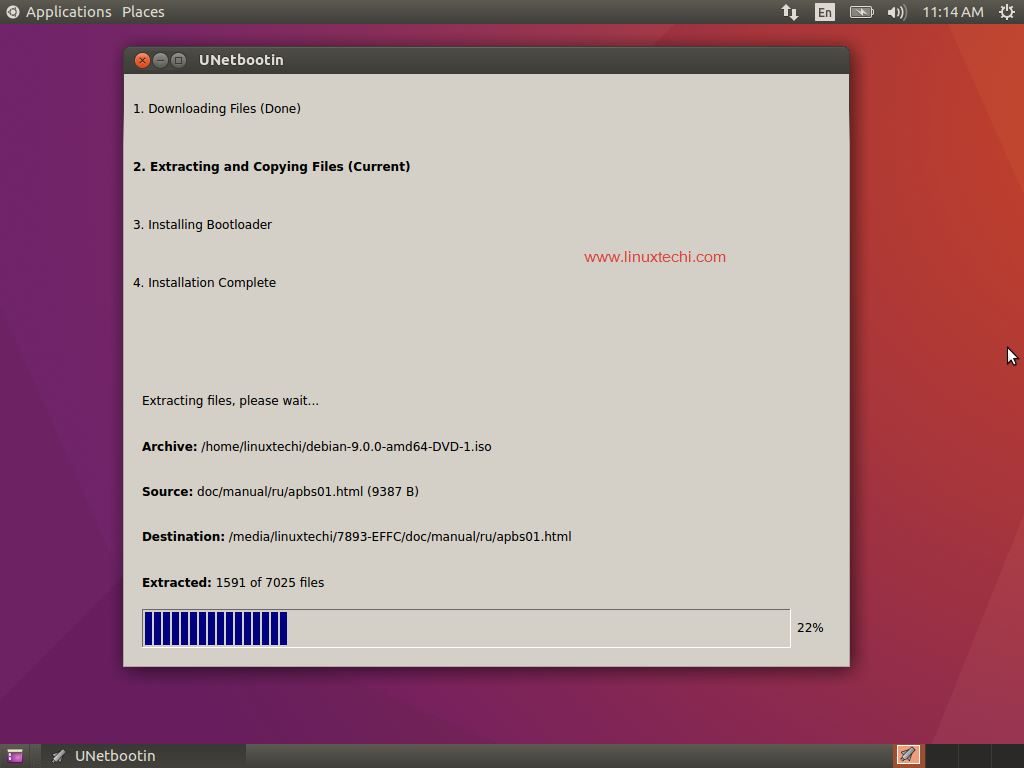
UNetbootin is another tool that allows you to create bootable USB drives as it either downloads the ISO file or you can provide the downloaded ISO file to create a bootable disk easily. With UNetbootin you can create bootable disks for Ubuntu, Fedora and other Linux distributions easily. UNetbootin also helps you to load a lot of system utilities into the USB disk to repair any configuration issues.
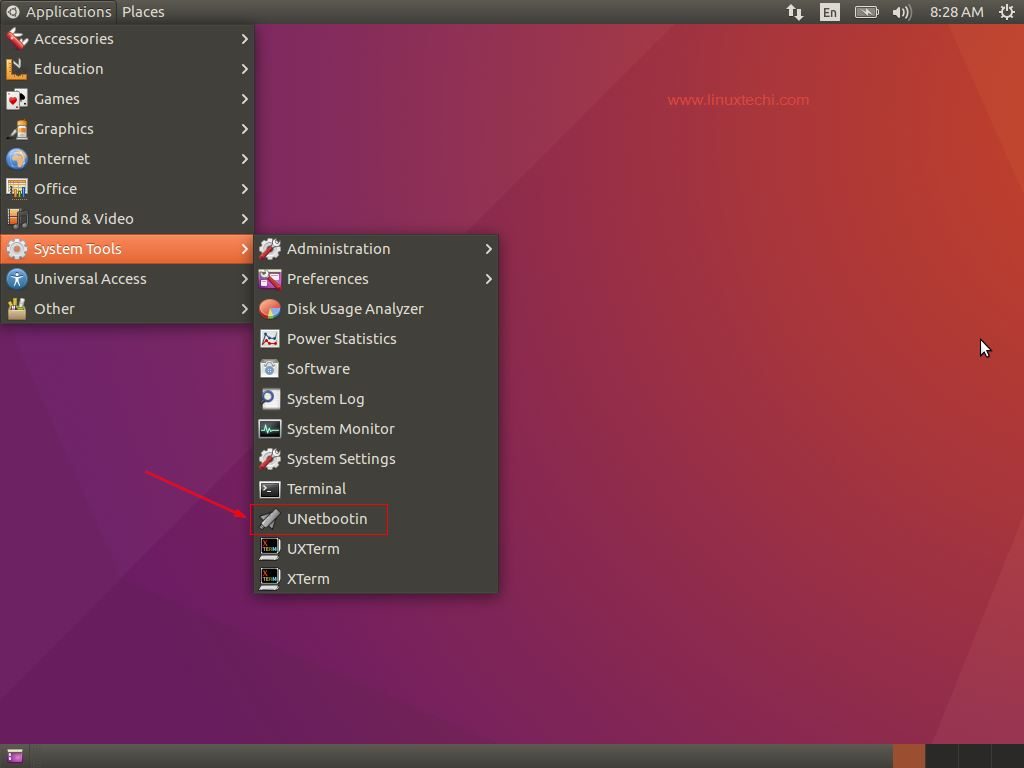
UNetbootin is not installed by default during Ubuntu and Linux Mint installation. Follow below steps to Install UNetbootin on Ubuntu Linux & Linux Mint
[email protected]:~$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gezakovacs/ppa [email protected]:~$ sudo apt-get update [email protected]:~$ sudo apt-get install unetbootin -y
To create a bootable USB disk / DVD using UNetbootin use the beneath steps:
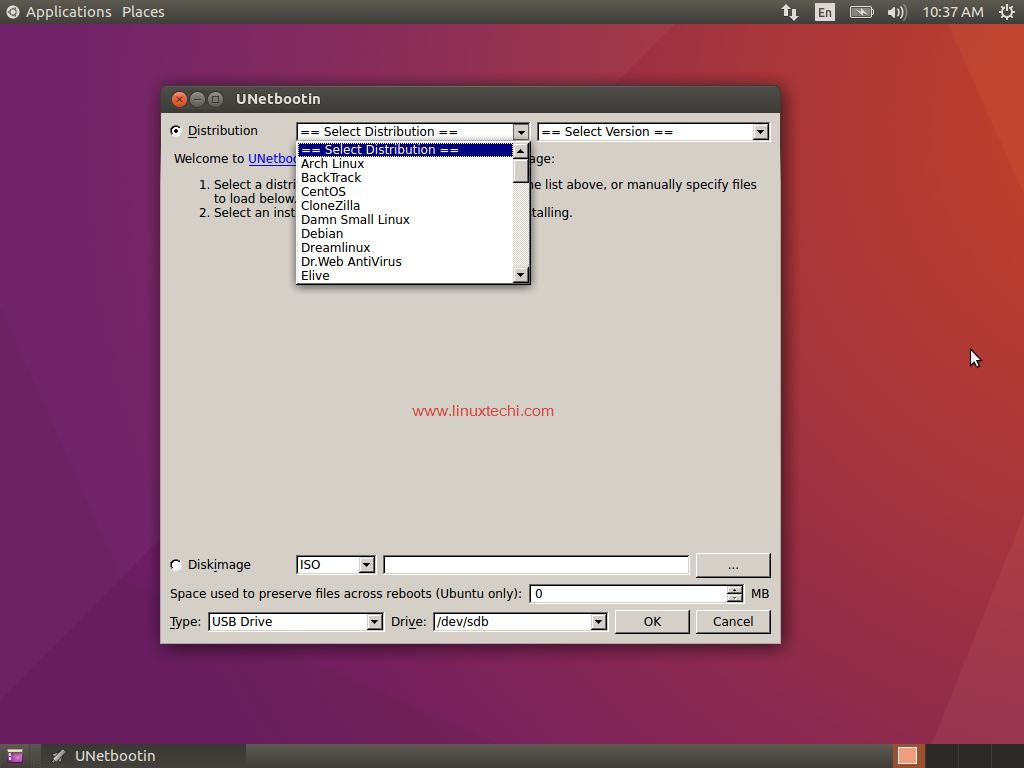
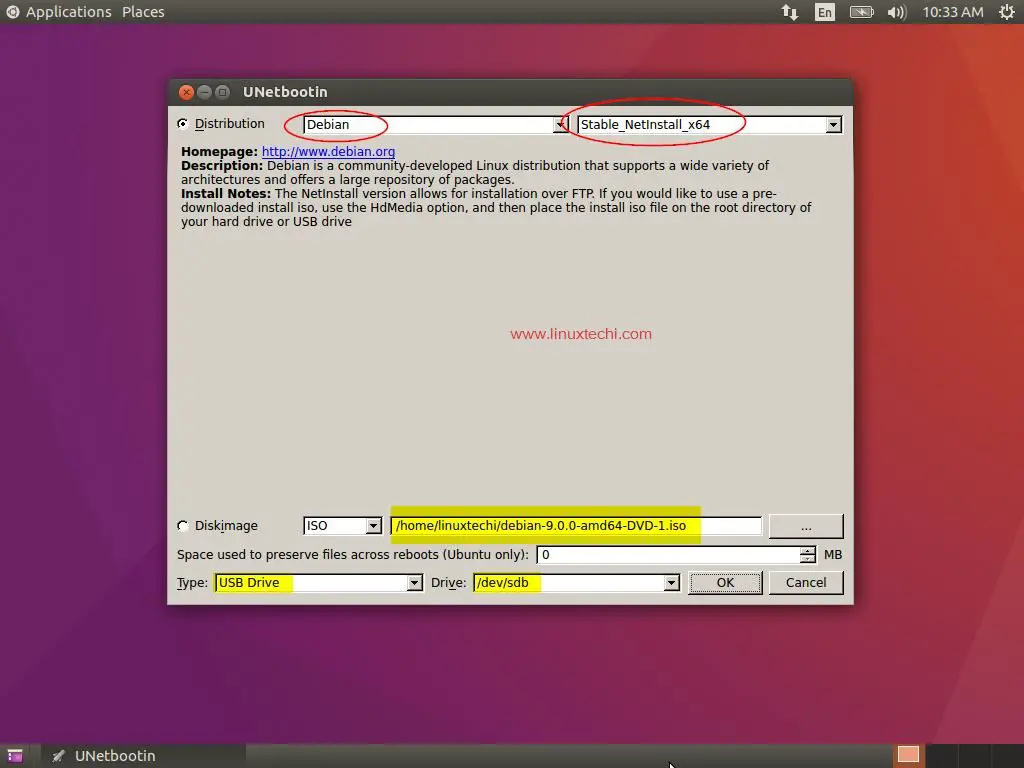
Step:1 ) Open the tool and select the distribution and the version as shown below
Step:2 ) Select the location of the ISO file
Step:3 ) Choose the type of disk USB / DVD in which the bootable disk needs to be created and also specify the drive letter of the USB / DVD disk
Step:4 ) Click “OK” to start the process
dd (Command line Utility)
People looking to burn an ISO from the command line can go for “dd“, an easy and simple command line utility to create your bootable USB flash drive / DVD for Ubuntu/ Linux Mint.
To create a bootable USB disk / DVD using “dd”:
Step:1 ) First step is insert the USB disk in your computer and open the terminal (Press CTRL + ALT + T)
Step:2 ) To find the USB device, you can use the following command:
Take for example our USB disk is in /dev/sdb
Now it is time to unmount the USB disk using the following command
step:3 ) For now let’s assume that the ISO file is in the current folder and then type the following command to burn the ISO into the USB device
lin[email protected]:~$ sudo dd if=ubuntu-17.10-desktop-amd64.iso of=/dev/sdb bs=4M 357+1 records in 357+1 records out 1501102080 bytes (1.5 GB, 1.4 GiB) copied, 164.77 s, 9.1 MB/s [email protected]:~$
‘ubuntu-17.10-desktop-amd64.iso‘ is the ISO file and
‘bs=4M‘ is an optional command to speed up the creation process of the bootable disk
Test Your Bootable Disk
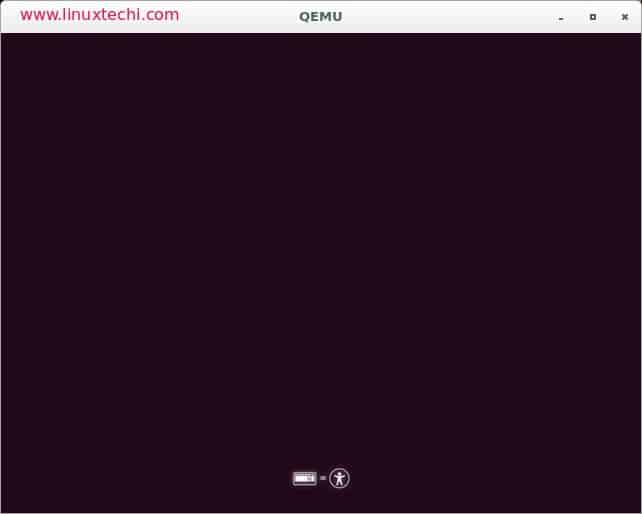
It is better to check if the bootable disk has been created successfully. To check that you need to download a utility called QEMU, a machine emulator and virtualizer.
Open the terminal and install qemu using the following command
Once the qemu has been installed successfully then run the following command
[email protected]:~$ sudo qemu-system-x86_64 -hda /dev/sdb
Your booting process is successful if you see a virtual machine booting from your USB disk / DVD.
That’s conclude the article, I hope you guys got an idea how we can create Bootable USB / DVD Disk using the above described methods, please do share your feedback and comments if you like the article.
7 thoughts on “How to Create Bootable USB Drive on Ubuntu / Linux Mint”
> Whenever we install Ubuntu and Linux Mint then this (Startup Disk Creator) installed automatically as part of default tools. Mint Cinnamon (17.3) doesn’t have this installed by default. Instead it uses something called ‘USB Image Writer’. Maybe it’s the same program but the interface was altered somewhat. I’ve lately burned in a few ISOs using ‘USB Image Writer’ and the debian-based stuff has booted fine. Having problems with non-debian stuff (arch-based and others). Most boot their menus fine but all end up not being able to find the ISO directory (weird, maybe it’s my USB hardware). I’m going to try uNetBootin to see if I have better success. I did try multisystem for multiple ISOs on a disk (it installed so much stuff, including qemu) but it turned out to be a failure. Also tried YUMI (under WINE) and it too failed to create a multi-boot system. Reply
Mint XFCE (18.2) doesn’t have this installed by default either. It also uses something called ‘USB Image Writer, as have the preceding XFCE versions. I have had some success using this programme but also some failures. A further disadvantage with it is that the file system on the created USB device is unreadable. Unetbootin has been slightly more productive for me and avoids the unreadable file system issue. I’ve also used dd and that has worked well. Reply
I did all dd (Command line Utility) process and works fine but USB Memory doesnt boot (Im trying PureOS 8.0 Live iso). I made a comparison with another USB Memory with Ubuntu 16.04 iso image. I verified on GParted: PureOS 8.0 Live: System Files=unknowed, Options=boot, hidden.
UBUNTU 16: System Files=fat32, Options=boot, lba. (this boot normally). What you think about? Reply
lol so true… its like going to the cop telling them you lost your documents, and they ask for your documents to identify yourself …
he should have show it , how to do it from windows or whatever. Reply
These are Linux boot options for use IN a Linux installation. What about making a Linux boot and install disc in Windows? MOST of us wanting to try Linux distros will be coming from a Windows PC and we seriously need such a Linux boot and install tutorial as you have here. We will likely NOT be getting a disc from another Linux user because we don’t know any. So, let’s make it easy -as many say Linux is- to get involved. Since the most recent info says 0.6% of all PC’s have Linux installed, I’m very sure that’s what the Linux community wants as well. [BTW: with apologies, Barry, you are regrettably short sighted] Reply
Hi Pradeep, Informative Post! Thank you so much for sharing this valuable post on How to Create Bootable USB Disk / DVD on Ubuntu / Linux Mint. And i am pretty impressed with the in-depth article you have provided in the post. And it really worked for me. Keep sharing such posts… Cheers,
Abhay Reply
Create the bootable media¶
The easiest way to install Linux Mint is with a USB stick.
If you cannot boot from USB, you can use a blank DVD.
How to make a bootable USB stick¶
In Linux Mint¶
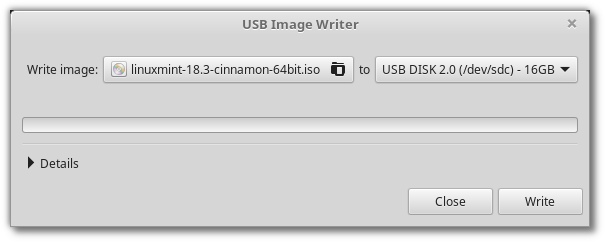
Right-click the ISO file and select Make Bootable USB Stick , or launch Menu ‣ Accessories ‣ USB Image Writer .
Select your USB device and click Write .
In Windows, Mac OS, or other Linux distributions¶
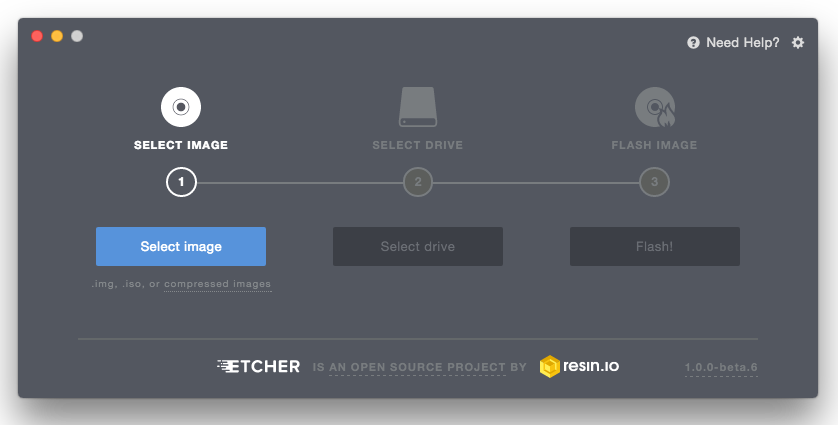
Download Etcher, install it and run it.
Click Select image and select your ISO file.
Click Select drive and select your USB stick.
How to make a bootable DVD¶
Optical discs are slow and burning to disc is prone to errors.
To prevent issues, burn at the lowest possible speed.
Burn the content of the ISO onto the DVD, not the ISO file itself. When finished, your DVD should contain directories such as boot and casper , it shouldn’t be an empty DVD containing an .iso file.
In Linux¶
In Windows¶
Right-click the ISO file and select Burn disk image .
To make sure the ISO was burned without any errors, select Verify disc after burning .
In Mac OS¶
Right-click the ISO file and select Burn Disk Image to Disc .
© Copyright 2017, Linux Mint Revision d8fbd844 .
Versions latest Downloads pdf html epub On Read the Docs Project Home Builds Free document hosting provided by Read the Docs.
How to Create Bootable Linux Mint USB Installer in Linux, Windows, or Mac OS
Want to install Linux Mint using an USB drive? Well, here’s the step by step beginner’s guide shows you how to create the bootable USB installer from other Linux, Windows, or Mac OS.
Linux Mint is a popular community-driven Linux distribution based on Ubuntu. At the moment of writing, the latest release is Linux Mint 20.x based on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS. And it features 3 desktop editions:
- Cinnamon – Gnome 3 fork.
- XFCE – Lightweight desktop edition.
- MATE – Gnome 2 fork.
Supported Systems:
The tutorial also works for creating bootable USB installer for Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, Manjaro, Arch Linux, and almost all Linux distros, though the title says for Linux Mint.
Preparation:
Before getting started, you need:
- An USB stick with more than 4 GB memory.
- Computer running Windows, Linux, or Mac OS.
- And download Linux Mint ISO image.
NOTE there are quite a few USB creating tools in the web! However, some of them may sometimes not work or not perfect (e.g., Ventoy does not install in my case). So I choose USB-creator-GTK and USBImager among all the tools I've tested.
Option 1: Create USB installer from an Ubuntu machine.
If you have a PC or laptop running with Ubuntu, then this option is for you as it has an built-in USB creator app. For all other Linux, Windows, and Mac OS, just go option 2.
1. Firstly search for and open USB Creator GTK from system app launcher.
2. Click on “Other …” button and choose the Linux Mint ISO image. And plug-in your USB stick. Finally click on “Make Startup Disk” to start the process.
3. A confirm dialog will pop-up prompts you that ‘All data in the USB drive be lost’.
Same to USBImager in Option 2: It creates two partitions in the USB stick: one for Linux Mint system files (about 2 GB) and anther for boot-loader (about 4 MB). And leave all other free space unallocated.
4. Click ‘Yes’ and it becomes the installing dialog with process bar.
5. If everything’s done successfully. You’ll see the ‘Installation Complete’ dialog.
After that, you can boot the USB stick and start installing Linux Mint.
Option 2: Create bootable USB from Windows, Mac OS, or other Linux.
USBImager is a free and open-source tool that works on Windows XP +, Mac OS 10.13 +, Arch, Manjaro, other Linux, and even Raspberry Pi OS.
This is a tiny tool with less than 200 KB package size. And it just works!
NOTE: if you has already created an USB installed via USBImager. And want to try another Linux Distro via USB. FORMAT the whole USB stick before getting started to avoid an error, or use another tool instead!
You May Also Read
6 Ways to Create Bootable Debian / Ubuntu USB / SD Installer
1. Firstly download & install the tool from its project page:
2. Insert USB stick into your machine.
3. Open USBImager, choose the ISO image, select the USB drive, and finally click the Write button.
4. And just wait, the bottom bar will prompt the installation process.
Conclusion:
There are quite a few tools for creating bootable USB installer. Due to lack of time, I can’t test them one by one.
In this tutorial, USBImager is recommended because it’s free and open source tool with tiny package size. And it runs on most desktop systems. However, after turns your USB stick into OS installer, you can’t use it for other data transfer. The free space is left unallocated, and you can not even create partition on it due to “too many primary partitions” error.