- How to find (and delete) duplicate files
- 11 Answers 11
- fdupes
- jdupes
- Повторяющиеся файлы в Linux — как избавиться от дубликатов.
- FSlint: инструмент GUI для поиска и удаления дубликатов файлов.
- Панель приборов Fslint
- FDUPES: инструмент CLI для поиска и удаления дубликатов файлов
- Установка на Debian / Ubuntu:
- Установка на Fedora:
- Поиск дубликатов файлов в Linux
- Поиск дубликатов файлов в Linux
How to find (and delete) duplicate files
I have a largish music collection and there are some duplicates in there. Is there any way to find duplicate files. At a minimum by doing a hash and seeing if two files have the same hash. Bonus points for also finding files with the same name apart from the extension — I think I have some songs with both mp3 and ogg format versions. I’m happy using the command line if that is the easiest way.
11 Answers 11
fdupes
I use fdupes for this. It is a commandline program which can be installed from the repositories with sudo apt install fdupes . You can call it like fdupes -r /dir/ect/ory and it will print out a list of dupes. fdupes has also a README on GitHub and a Wikipedia article, which lists some more programs.
It also has a «-d» option that lets you choose which copy you want to keep, and deletes the other ones (or you can keep all of them if you want).
Can you explain in more detail how to delete all duplicates (leaving only a single copy each file) in a recursive directory tree? I want to do this automatically, that is, without having to specify each time which file to keep. It should just select one of the duplicates.
fdupes -r . -d -N should save the first instance and delete the dupes. I just successfully cleared a single folder using fdupes . -d -N non recursively
List of programs/scripts/bash-solutions , that can find duplicates and run under nix :
- dupedit: Compares many files at once without checksumming. Avoids comparing files against themselves when multiple paths point to the same file.
- dupmerge: runs on various platforms (Win32/64 with Cygwin, *nix, Linux etc.)
- dupseek: Perl with algorithm optimized to reduce reads.
- fdf: Perl/c based and runs across most platforms (Win32, *nix and probably others). Uses MD5, SHA1 and other checksum algorithms
- freedups: shell script, that searches through the directories you specify. When it finds two identical files, it hard links them together. Now the two or more files still exist in their respective directories, but only one copy of the data is stored on disk; both directory entries point to the same data blocks.
- fslint: has command line interface and GUI.
- liten: Pure Python deduplication command line tool, and library, using md5 checksums and a novel byte comparison algorithm. (Linux, Mac OS X, *nix, Windows)
- liten2: A rewrite of the original Liten, still a command line tool but with a faster interactive mode using SHA-1 checksums (Linux, Mac OS X, *nix)
- rdfind: One of the few which rank duplicates based on the order of input parameters (directories to scan) in order not to delete in «original/well known» sources (if multiple directories are given). Uses MD5 or SHA1.
- rmlint: Fast finder with command line interface and many options to find other lint too (uses MD5), since 18.04 LTS has a rmlint-gui package with GUI (may be launched by rmlint —gui or from desktop launcher named Shredder Duplicate Finder)
- ua: Unix/Linux command line tool, designed to work with find (and the like).
- findrepe: free Java-based command-line tool designed for an efficient search of duplicate files, it can search within zips and jars.(GNU/Linux, Mac OS X, *nix, Windows)
- fdupe: a small script written in Perl. Doing its job fast and efficiently.1
- ssdeep: identify almost identical files using Context Triggered Piecewise Hashing
for Ubuntu, another way is to open Files, search (control-f) for a given extension (eg .mp3), and then sort on file name; this will allow to delete duplicates by hand, and at the same time show the locations of the duplicates.
FSlint has a GUI and some other features. The explanation of the duplicate checking algorithm from their FAQ:
1. exclude files with unique lengths 2. handle files that are hardlinked to each other 3. exclude files with unique md5(first_4k(file)) 4. exclude files with unique md5(whole file) 5. exclude files with unique sha1(whole file) (in case of md5 collisions). Thanks. Note that the command name is «fslint-gui», and the command line tools are not in $PATH by default — they are in /usr/share/fslint/fslint. I was confused when I didn’t get help on which package it was in by just running fslint (via /usr/lib/command-not-found).
@nealmcb If using sudo apt-get install fslint , the installation currently does put fslint-gui into the path and so I can run it from anywhere by just typing fslint-gui . You can find where fslint-gui lives by typing which fslint-gui (it looks like a Python script).
If your deduplication task is music related, first run the picard application to correctly identify and tag your music (so that you find duplicate .mp3/.ogg files even if their names are incorrect). Note that picard is also available as an Ubuntu package.
That done, based on the musicip_puid tag you can easily find all your duplicate songs.
I just updated the metadata for my library with Picard. I then used fdupes -r -d -N to find and delete duplicates. But it’s still not identifying many duplicates. How exactly did you do this with the musicip_puid ?
It’s been years since then, and I’m afraid I haven’t followed picard; my music library has been safely archived, a few select songs are included in my phone’s media, and all other needs are covered by streaming services. I can only say I remember that the puid did help me locate similar sounding songs. I’m sorry I currently can’t help any more.
Another script that does this job is rmdupe. From the author’s page:
rmdupe uses standard linux commands to search within specified folders for duplicate files, regardless of filename or extension. Before duplicate candidates are removed they are compared byte-for-byte. rmdupe can also check duplicates against one or more reference folders, can trash files instead of removing them, allows for a custom removal command, and can limit its search to files of specified size. rmdupe includes a simulation mode which reports what will be done for a given command without actually removing any files.
I use komparator — sudo apt-get install komparator (Ubuntu 10.04+ ) — as GUI-tool for finding duplicates in manual mode.
For Music related duplicate identification and deletion, Picard (open source) by http://musicbrainz.org/ and Jaikoz (privative) are the best solutions. Jaikoz I believe automatically tags your music based on the data of the song file. You don’t even need the name of the song for it to identify the song and assign all metadata to it. Although the free version can tag only a limited number of songs in one run, but you can run it as many times as you want.
dupeGuru has a dedicated mode for music. It is a cross-platform GUI program and, as of today (February 2021), it is in active development, although it is unclear which releases work on which systems. Check its documentation.
Now that fslint is no longer supported, I’ve switched to fclones. As requested, it matches by hash, and can output a list, or replace files with hard or soft links.
I’ve been using it like this to replace duplicate files with hard links:
fclones group | fclones link jdupes
I found jdupes very easy and extremely fast.
jdupes is a program for identifying and taking actions upon duplicate files such as deleting, hard linking, symlinking, and block-level deduplication (also known as «dedupe» or «reflink»). It is faster than most other duplicate scanners. It prioritizes data safety over performance while also giving expert users access to advanced (and sometimes dangerous) features.
# Search a single directory: jdupes path/to/directory # Search multiple directories: jdupes directory1 directory2 # Search all directories recursively: jdupes --recurse path/to/directory # Search directory recursively and let user choose files to preserve: jdupes --delete --recurse path/to/directory # Search multiple directories and follow subdirectores under directory2, not directory1: jdupes directory1 --recurse: directory2 # Search multiple directories and keep the directory order in result: jdupes -O directory1 directory2 directory3 # EXclude files over 1M, sumarize info, recursive jdupes -X size+=:1000k --summarize --recurse ~ Повторяющиеся файлы в Linux — как избавиться от дубликатов.
Если у вас есть такая привычка скачивать все из Интернета, как у меня, у вас будет много дубликатов файлов. Чаще всего я могу найти те же песни или кучу изображений в разных каталогах или в конечном итоге создать резервные копии некоторых файлов в двух разных местах. Это боль – искать эти повторяющиеся файлы вручную и удалять их для очистки дискового пространства. Если вы хотите избавиться от этой боли, существуют различные приложения Linux, которые помогут вам найти эти дубликаты файлов и удалить их. В этой статье мы расскажем о том, как вы можете сделать это в Ubuntu. Примечание. Вы должны знать, что делаете. Если вы используете новый инструмент, всегда лучше попробовать его в структуре виртуального каталога, чтобы выяснить, что он делает, прежде чем принимать его в корневую или домашнюю папку. Кроме того, всегда лучше создавать резервную копию вашей системы Linux!
FSlint: инструмент GUI для поиска и удаления дубликатов файлов.
FSlint помогает вам искать и удалять повторяющиеся файлы, пустые каталоги или файлы с неправильными именами. Он имеет командную строку, а также графический интерфейс с набором инструментов для выполнения множества задач. Чтобы установить FSlint, введите следующую команду в Terminal:
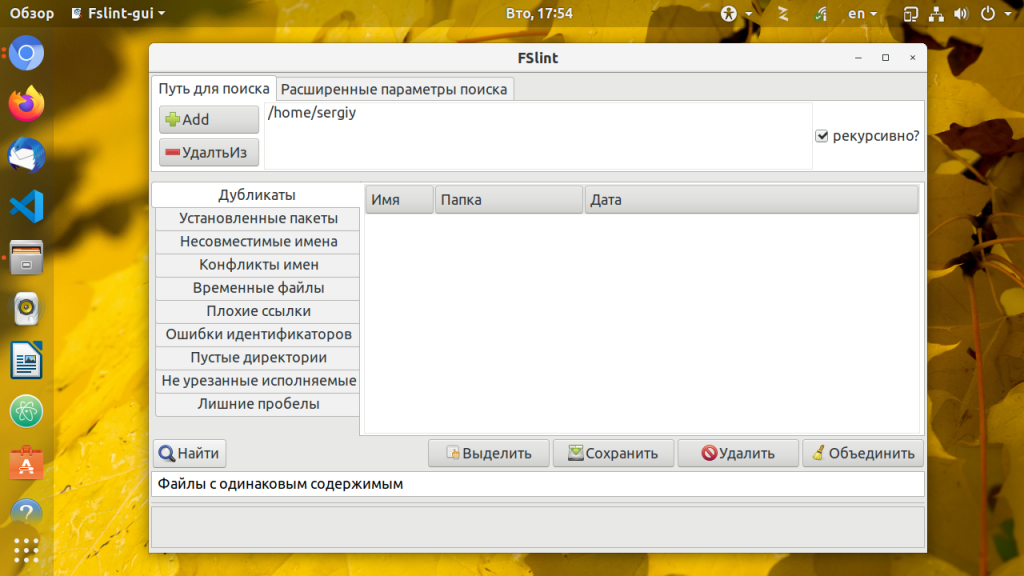
Панель приборов Fslint
FSlint включает в себя ряд опций на выбор. Существуют варианты поиска дубликатов файлов, установленных пакетов, плохих имен, конфликтов имен, временных файлов, пустых каталогов и т. д. Выберите путь поиска и задачу, которую вы хотите выполнить с левой панели, и нажмите «Найти», чтобы найти файлы. После этого вы можете выбрать файлы, которые хотите удалить, и удалить их. Вы можете щелкнуть по любому файловому каталогу из результата поиска, чтобы открыть его, если вы не уверены и хотите дважды проверить его перед удалением. Вы можете выбрать параметры расширенного поиска, где вы можете определить правила для исключения определенных типов файлов или исключить каталоги, которые вы не хотите искать.
FDUPES: инструмент CLI для поиска и удаления дубликатов файлов
FDUPES — это утилита командной строки для поиска и удаления дубликатов файлов в Linux. Она может отображать дубликаты файлов в определенной папке или рекурсивно в папке. Она запрашивает, какой файл сохранить перед удалением, а опция noprompt позволяет удалить все дубликаты файлов, сохраняя первый, не спрашивая вас.
Установка на Debian / Ubuntu:
Установка на Fedora:
Это будет только список дубликатов файлов, они не удалятся автоматически. Вы можете вручную удалить дубликаты файлов или использовать -d:
fdupes -d / path / to / folderЭто ничего не удалит самостоятельно, но отобразит все дубликаты файлов и даст вам возможность удалять файлы по одному или выбрать диапазон файлов для удаления. Если вы хотите удалить все файлы без запроса и сохранения первого, вы можете использовать опцию noprompt -N. fdupes – инструмент командной строки для поиска дубликатов файлов в Ubuntu Linux
Поиск дубликатов файлов в Linux
Дубликаты файлов могут появляться при сохранении резервных копий на диск, одновременном редактировании нескольких версий одного и того же файла или при изменении структуры каталогов. Одни и те же файлы могут быть сохранены несколько раз с различными именами или в разных папках и только засоряют дисковое пространство.
Охота на них каждый раз может стать большой проблемой. Но к счастью существует маленькая утилита которая может сберечь ваше время потраченное на поиск и уничтожение дубликатов файлов на компьютере — FSLint. Она написана на Python. Время навести порядок и удалить старые файлы.
Поиск дубликатов файлов в Linux
Вы можете установить утилиту из официальных репозиториев большинства дистрибутивов Linux. Давайте рассмотрим пример для Ubuntu. Сначала обновите списки пакетов:
После завершения установки вы можете запустить утилиту из главного меню:
В главном окне программы можно выбрать различные варианты поиска неисправностей файловой системы. По умолчанию выбран Поиск дубликатов, ещё вам предстоит настроить папки, в которых будет выполнятся поиск, по умолчанию добавлена только домашняя папка:
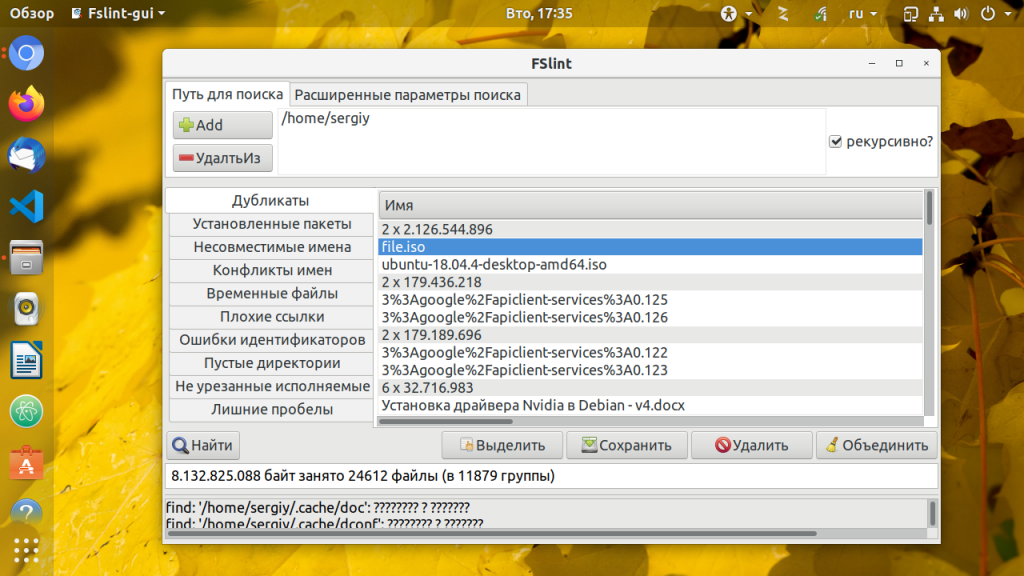
После того как вы выберите каталоги, запустите поиск дубликатов Linux. Для этого надо нажать кнопку Поиск. Утилита сразу же начнёт выводить обнаруженные дубликаты файлов:
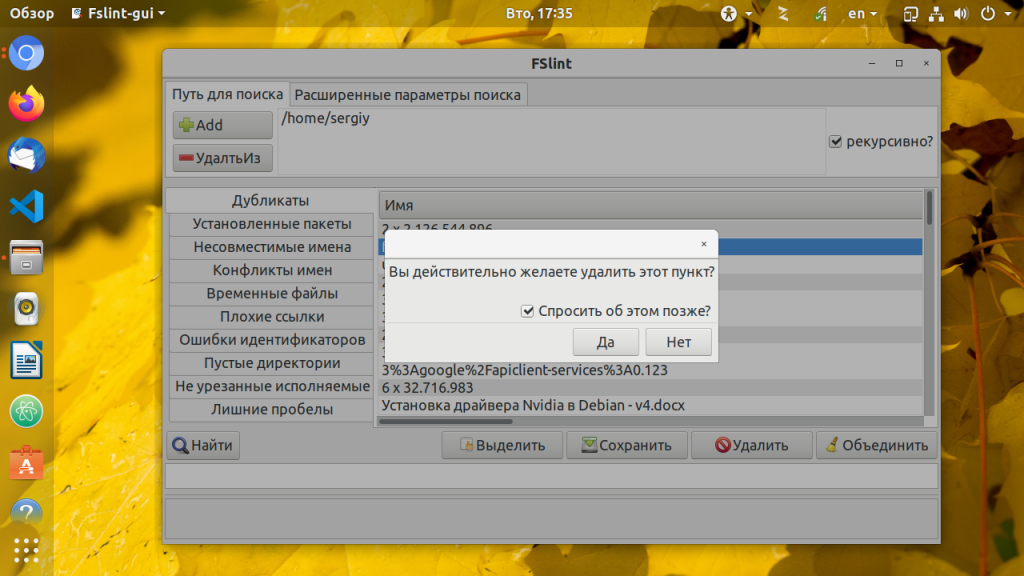
Когда поиск завершится вы сможете удалить файлы, которые вам не нужны, для этого выделите их мышью и нажмите кнопку Удалить. Программа спросит подтверждения действия и удалит файл:
Также вы можете объединить файлы дубликаты с помощью жесткой ссылки. По нажатию кнопки Объединить, утилита объединяет все файлы кроме выделенных. Кроме того, утилита позволяет искать несовместимые имена файлов, временные файлы, плохие ссылки, пустые директории и многое другое. Поэкспериментируйте с ней если будет желание.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.