How can I uninstall a nvidia driver completely ?
As expected, Nvidia drivers have reduced my customizations. I can’t login to Unity 3D session. I can’t find any content to help me to uninstall the driver and I don’t know what to do as I have never uninstalled them before.
7 Answers 7
For Ubuntu 12.04-22.04
Commands can be executed to terminal. You can open a terminal with Ctrl + Alt + T keys combo.
If you remove —purge the nvidia driver you will be OK. No need to blacklist something, but sometimes maybe a force-load of the nouveau module needed.
First uninstall completely the driver.
Search what packages from nvidia you have installed.
except the package nvidia-common all other packages should be purged.
If you want to be sure that you will purge everything related to nvidia you can give this command
sudo apt-get remove --purge '^nvidia-.*' the .* in the end means (Purge everything that begins ( ^ ) with the name nvidia- )
above command will also remove the nvidia-common package and the nvidia-common package has as a dependency the ubuntu-desktop package.
So after above command you should also give the installation command for ubuntu-desktop package
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-desktop Also sometimes the nouveau driver get blacklisted from nvidia driver. With purge command it should UN-blacklisted. If you want to be sure that nouveau will be load in boot, you can force-load it by add it to /etc/modules
echo 'nouveau' | sudo tee -a /etc/modules Last , search for the xorg.conf file and remove it as well
sudo apt-get remove --purge '^nvidia-.*' sudo apt-get install ubuntu-desktop sudo rm /etc/X11/xorg.conf echo 'nouveau' | sudo tee -a /etc/modules Although all above commands not needed, this is my way to completely purge the nvidia driver and use the open source nounveau.
Your recipe just solved for me a similar problem that kept me last night fiddling with my computer until 3 am. Not enough thanks.
On my Ubuntu 16.04 LTS there is no nvidia-common package so the extra step of sudo apt-get install ubuntu-desktop can be omitted. Also there is no /etc/X11/xorg.conf file. Running locate xorg.conf reveals many files.
I just used the nvidia-uninstall.
In my case I got the driver directly from the nvidia website.
Thank you so much for saving my system! If this hadn’t worked, I would have probably had to reinstall my entire system.
@InfiniteLoops, that must be caused by you installing the drivers from repository. The driver that’s installed from NVidia website does have the nvidia-uninstall command in 2019.
I realize that this is an old answer, but I have to add an answer here for sake of clarity and system stability.
First off, the * is an expansion operator for the shell which will grab everything and remove a lot of files you don’t need to remove. The safest way to remove the nvidia driver is to do
Search for nvidia-xxx.xx version or nvidia-driver-xxx.xx version and then type
$ sudo apt purge nvidia-xxx.xx $ sudo apt purge nvidia-driver-xxx.xx It will only remove that package but will also flag its dependencies for removal.
To remove the dependencies is easy.
$ sudo apt autoremove $ sudo apt autoclean So for example, if you have the 390.xx package installed, it would be.
$ dpkg -l | grep -i nvidia ii libnvidia-cfg1-390:amd64 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVIDIA binary OpenGL/GLX configuration library ii libnvidia-common-390 390.48-0ubuntu3 all Shared files used by the NVIDIA libraries ii libnvidia-compute-390:amd64 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVIDIA libcompute package ii libnvidia-compute-390:i386 390.48-0ubuntu3 i386 NVIDIA libcompute package ii libnvidia-decode-390:amd64 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVIDIA Video Decoding runtime libraries ii libnvidia-decode-390:i386 390.48-0ubuntu3 i386 NVIDIA Video Decoding runtime libraries ii libnvidia-encode-390:amd64 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVENC Video Encoding runtime library ii libnvidia-encode-390:i386 390.48-0ubuntu3 i386 NVENC Video Encoding runtime library ii libnvidia-fbc1-390:amd64 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVIDIA OpenGL-based Framebuffer Capture runtime library ii libnvidia-fbc1-390:i386 390.48-0ubuntu3 i386 NVIDIA OpenGL-based Framebuffer Capture runtime library ii libnvidia-gl-390:amd64 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVIDIA OpenGL/GLX/EGL/GLES GLVND libraries and Vulkan ICD ii libnvidia-gl-390:i386 390.48-0ubuntu3 i386 NVIDIA OpenGL/GLX/EGL/GLES GLVND libraries and Vulkan ICD ii libnvidia-ifr1-390:amd64 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVIDIA OpenGL-based Inband Frame Readback runtime library ii libnvidia-ifr1-390:i386 390.48-0ubuntu3 i386 NVIDIA OpenGL-based Inband Frame Readback runtime library ii nvidia-compute-utils-390 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVIDIA compute utilities ii nvidia-dkms-390 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVIDIA DKMS package ii nvidia-driver-390 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVIDIA driver metapackage ii nvidia-kernel-common-390 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 Shared files used with the kernel module ii nvidia-kernel-source-390 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVIDIA kernel source package ii nvidia-prime 0.8.8 all Tools to enable NVIDIA's Prime ii nvidia-settings 390.42-0ubuntu1 amd64 Tool for configuring the NVIDIA graphics driver ii nvidia-utils-390 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVIDIA driver support binaries ii xserver-xorg-video-nvidia-390 390.48-0ubuntu3 amd64 NVIDIA binary Xorg driver $ apt-cache search nvidia | grep driver nvidia-settings - Tool for configuring the NVIDIA graphics driver ubuntu-drivers-common - Detect and install additional Ubuntu driver packages vdpau-driver-all - Video Decode and Presentation API for Unix (driver metapackage) xserver-xorg-video-nouveau - X.Org X server -- Nouveau display driver nvidia-340-dev - NVIDIA binary Xorg driver development files nvidia-384 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-390 nvidia-384-dev - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-390 nvidia-driver-390 - NVIDIA driver metapackage nvidia-utils-390 - NVIDIA driver support binaries xserver-xorg-video-nvidia-390 - NVIDIA binary Xorg driver bumblebee-nvidia - NVIDIA Optimus support using the proprietary NVIDIA driver kubuntu-driver-manager - Driver Manager for Kubuntu kubuntu-driver-manager-dbg - Driver Manager for Kubuntu -- debug symbols nvidia-common - transitional package for ubuntu-drivers-common nvidia-304 - NVIDIA legacy binary driver - version 304.137 nvidia-304-dev - NVIDIA binary Xorg driver development files nvidia-340 - NVIDIA binary driver - version 340.107 nvidia-387-dev - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-390 nvidia-387 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-390 nvidia-390-dev - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-390 nvidia-390 - Transitional package for nvidia-driver-390 nvidia-driver-396 - NVIDIA driver metapackage nvidia-utils-396 - NVIDIA driver support binaries xserver-xorg-video-nvidia-396 - NVIDIA binary Xorg driver Once you’ve targeted the package to remove, do
$ sudo apt purge nvidia-390 (nvidia-driver-XXX) -y $ sudo apt autoremove -y $ sudo apt autoclean Make sure to install whatever driver you plan on using right after you do this and if you don’t have livepatch because of whatever reason, just reboot your system and you should be good to go.
This way you don’t ever have to worry about removing system dependencies while clearing out your drivers. You’ll have a sane and stable system afterwards and don’t have to worry about re-installing other packages that your system may depend on. That’s apt s job, not yours.
How to Clean Install NVIDIA Drivers on Debian 11
While installing the official NVIDIA drivers on Debian 11, things may go wrong in many ways. This may result in the official NVIDIA drivers not working on your computer/laptop. Or, in the worst-case scenario break the operating system and show you a black screen.
To solve this problem, you can try to uninstall the official NVIDIA drivers completely from your Debian 11 operating system and try to install the official NVIDIA drivers again.
In this article, I am going to show you how to uninstall the official NVIDIA drivers from Debian 11 completely so that you can clean install the official NVIDIA drivers on Debian 11.
Table of Contents:
Completely Uninstalling Official NVIDIA Drivers from Debian 11
First, open a Terminal app on Debian 11 from the Application menu.
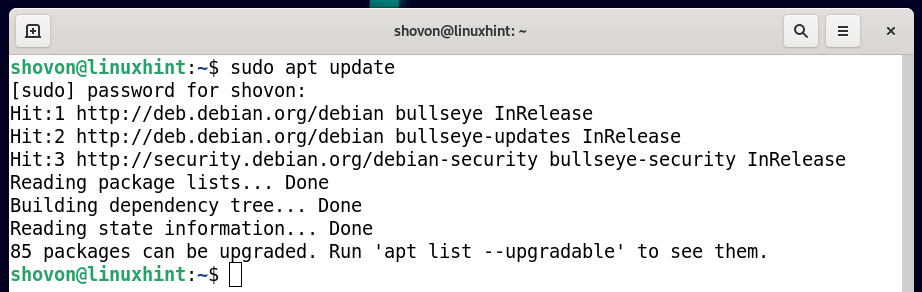
Then, update the APT package repository cache with the following command:
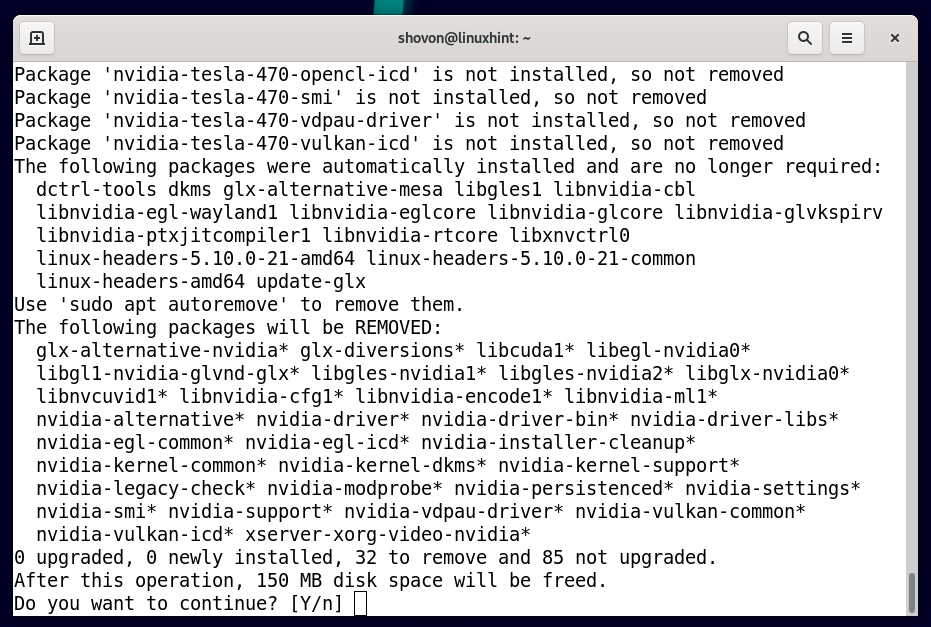
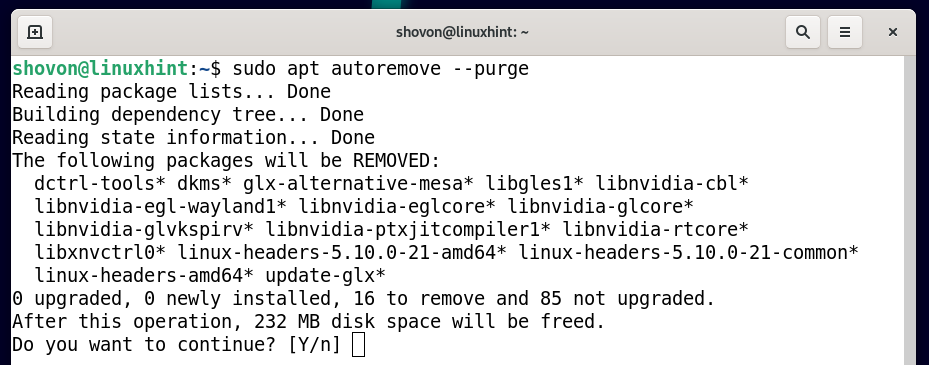
To remove the official NVIDIA drivers from Debian 11 completely, run the following command:
To confirm the uninstallation, press Y and then press .
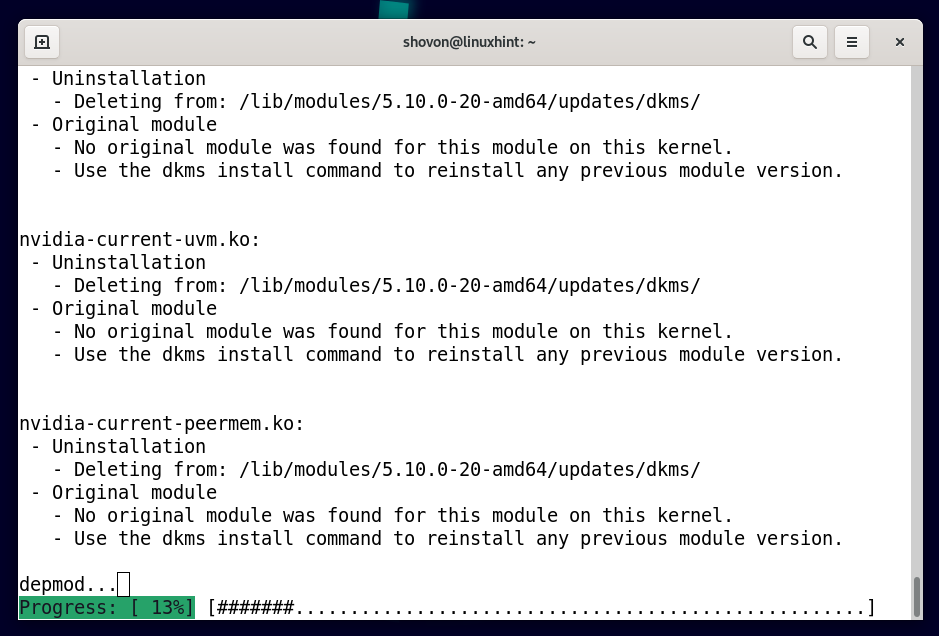
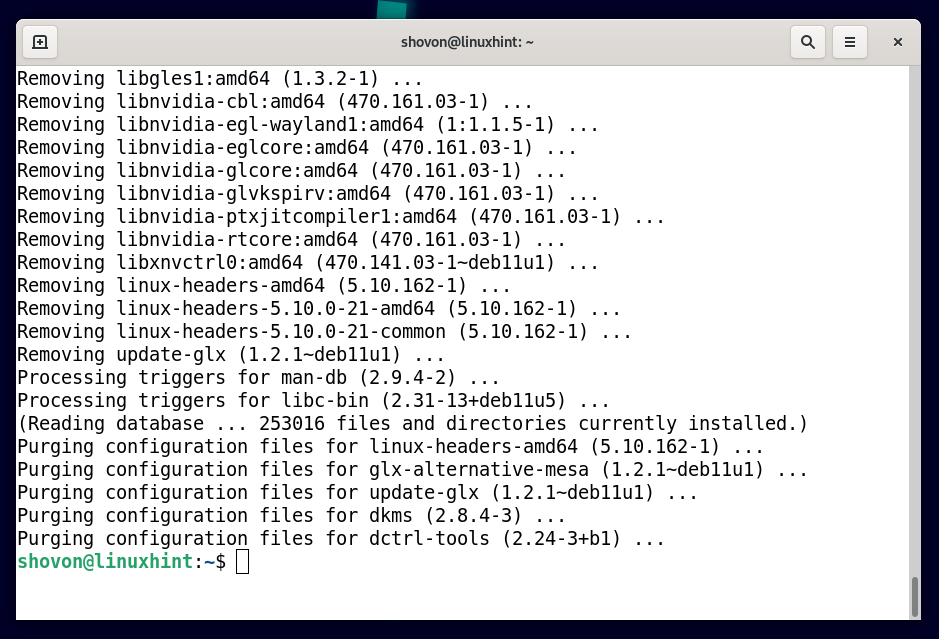
The official NVIDIA drivers are being uninstalled. It will take a while to complete.
At this point, the official NVIDIA drivers should be uninstalled.
To remove the dependency packages of the official NVIDIA drivers as well, run the following command:
To confirm the action, press Y and then press .
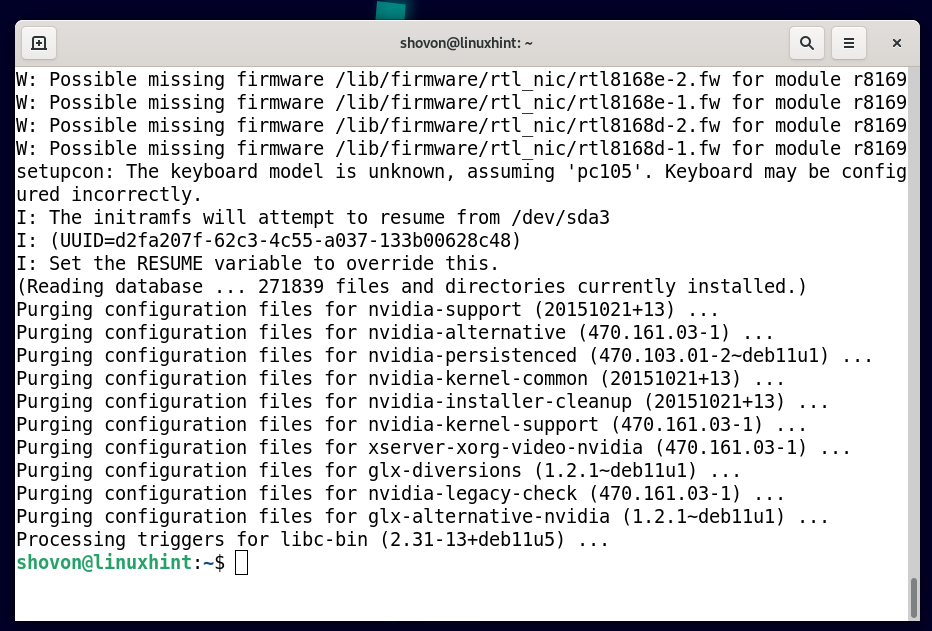
The dependency packages of the official NVIDIA drivers are being removed. It will take a while to complete.
At this point, all the dependency packages of the official NVIDIA drivers should be removed.
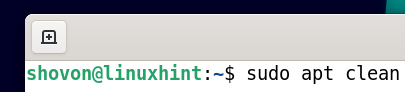
Run the following command to delete all the cached NVIDIA drivers packages along with the dependency packages to save disk space:
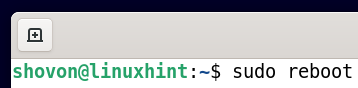
For the changes to take effect, run the following command to restart your computer/laptop:
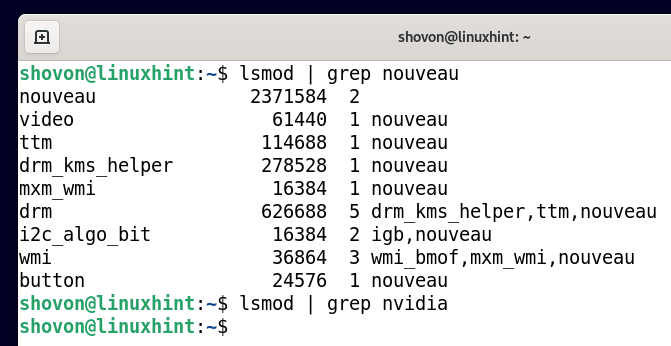
Once your computer/laptop starts, you should see that the nouveau kernel modules are used instead of the official nvidia kernel modules. So, the official NVIDIA drivers are uninstalled completely and Debian 11 successfully switched to the open-source Nouveau drivers.
Re-installing/Clean Installing Official NVIDIA Drivers on Debian 11
At this point, the official NVIDIA drivers should be uninstalled from Debian 11 completely. Now, you can try to install the official NVIDIA drivers on Debian 11 again and see if your problem is resolved. If you need any assistance in installing the official NVIDIA drivers on Debian 11, check the article Install NVIDIA Drivers on Debian 11.
Conclusion
I have shown you how to uninstall the official NVIDIA drivers from Debian 11 completely so that you can clean install the official NVIDIA drivers again on Debian 11 in case you have any problems getting the official NVIDIA drivers to work on Debian 11.
About the author
Shahriar Shovon
Freelancer & Linux System Administrator. Also loves Web API development with Node.js and JavaScript. I was born in Bangladesh. I am currently studying Electronics and Communication Engineering at Khulna University of Engineering & Technology (KUET), one of the demanding public engineering universities of Bangladesh.