- Linux Development Quickstart
- 1. Recommended Software and Hardware
- 2. Install Unreal Engine
- 2a. Download an Installed Build
- 2b. Build Unreal Engine from Source
- 3. Setting Up a New Project
- 4. Set Up Your Development Environment (C++)
- 5. Build a Project
- 5a. Build a Project In Unreal Editor
- 5b. Build a Project Through the Command Line
- Linux Quick Start
- Learn how to download, build, and run UE4 on Linux.
- 1 — Required Setup
- Registering for an Epic Games Account
- Setting up Git
- Section Result
- 2 — Downloading UE4 on Linux
- Downloading from GitHub
- Cloning with Git
- Section Result
- 3 — Building UE4 on Linux
- Section Result
- 4 — Running UE4 on Linux
- Launching UE4 on Linux
- Creating your First Project
- Section Result
- 5 — On your own!
Linux Development Quickstart
Unreal Engine (UE) supports development on Linux devices using either builds created from source or pre-compiled, installed builds. This page provides instructions on how to set up Unreal Engine on Linux, including your development environment and build pipeline. When you finish this tutorial, you will be ready to develop applications in Unreal Engine using your Linux machine.
1. Recommended Software and Hardware
Unreal Engine is compatible with a variety of Linux distributions and IDEs, as long as they meet these minimum requirements:
Operating System
Any reasonable new Linux distro from CentOS 7.x and up
Linux Kernel Version
Additional Dependencies
We recommend your system meet the following standard so that Unreal Editor performs smoothly:
Recommended Development Hardware
Quad-core Intel or AMD, 2.5 GHz or faster
NVIDIA GeForce 960 GTX or Higher with latest NVIDIA binary drivers
RHI Version
The Vulkan rendering hardware interface (RHI) used on Linux is not friendly to low amounts of VRAM compared with other backends. We strongly recommend using a dedicated GPU with a high amount of VRAM.
To set up your development environment, we recommend the following software, which we test with most frequently:
Operating System
clang 13.0.1 (5.1), clang 15.0.1 (5.2)
Refer to the documentation for your Linux distribution or IDE for further information on how to set them up. While setting up your OS and hardware is outside the scope of this documentation, setting up your IDE to work with Unreal Engine is covered below.
2. Install Unreal Engine
You can set up Unreal Engine on Linux either by installing a pre-compiled build, or by building the engine from source.
2a. Download an Installed Build
The simplest option for running Unreal Engine is to use an Installed Build. To download and install one, follow these steps:
Unreal Engine on Linux supports precompiled installed builds as well as source code builds. For information about using source builds, refer to Building Unreal Engine from Source .
To use a precompiled build, follow these steps:
- Open the Unreal Engine for Linux page. It will prompt you to to create or sign into an Epic Games account. If you already have one, sign in to access the page. If you don’t have an account, click Sign Up to create one.
You can sign up for an Epic Games account with your email, or with a supported social media or gaming platform account.
Download the .zip file containing the version of Unreal Engine that you need.
2b. Build Unreal Engine from Source
To install Unreal Engine from source, refer to Downloading Unreal Engine Source Code . Once you have compiled the engine, run Engine/Binaries/Linux/UnrealEditor from the Terminal to launch Unreal Editor.
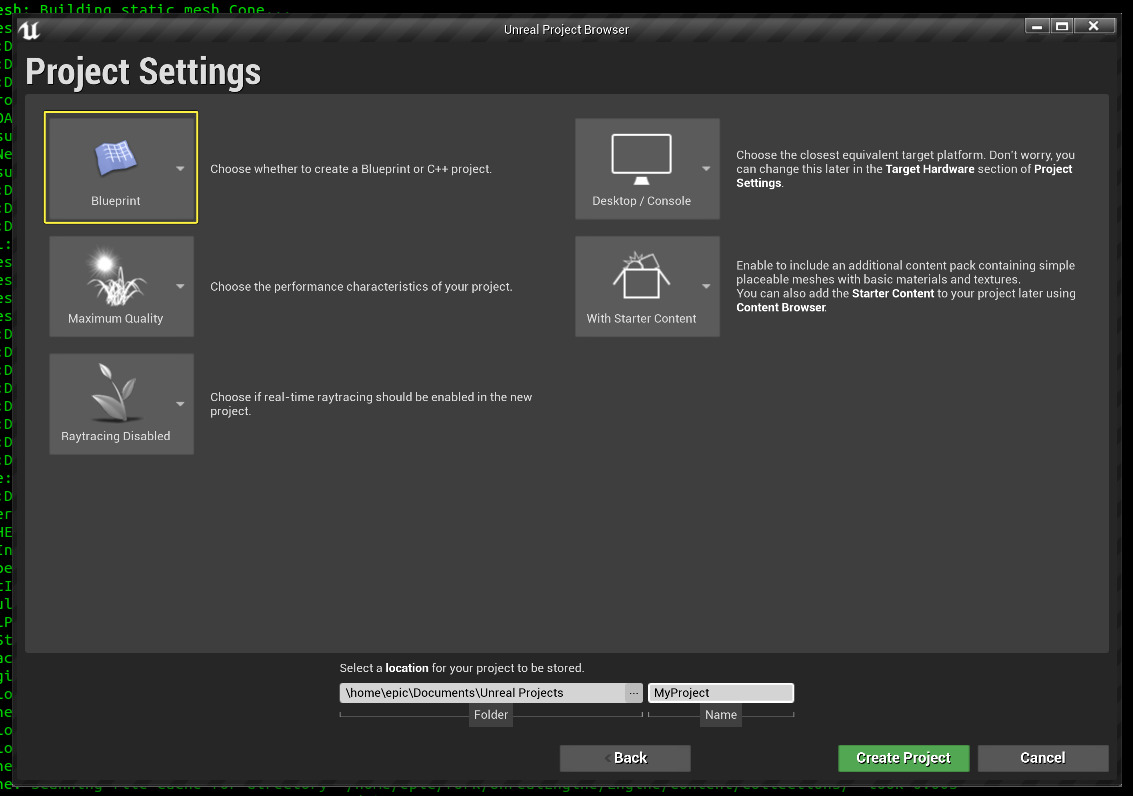
3. Setting Up a New Project
Refer to the instructions in Creating a New Project in Unreal Engine for information on how to set up a new project. You don’t need a specific template or project type for the purposes of this tutorial, but you should make sure it has C++ enabled if you are setting up your environment for C++.
[Screenshot enabling the C++ setting)
4. Set Up Your Development Environment (C++)
If you are planning to develop C++ projects, you need to set up the Clang toolchain and an IDE to work with Unreal Engine. While we don’t require a specific IDE, we recommend using Visual Studio Code or Rider. This section provides instructions that are specific to Visual Studio Code, as it provides a common development environment for other operating systems as well.
- Open a Terminal and run the following command: Sudo apt install clang
- Locate your Unreal Engine install directory and open Build/BatchFiles/Linux , then run SetupToolchain.sh .
- Download and install VS Code as well as the official C / C++ extension pack and C# extension. These are required for reading the source code for both Unreal Engine and its Build Tools.
- Either open Unreal Editor, open your Editor Preferences, and set your Source Code editor to Visual Studio Code, or modify BaseEngine.ini to include the following:
[/Script/SourceCodeAccess.SourceCodeAccessSettings] PreferredAccessor=VisualStudioCodeFor information about configuring VS Code with IntelliSense and other helpful utilities, see Setting Up VS Code for Unreal Engine .
5. Build a Project
Now that your environment is fully set up, you should run a test build of your project to ensure your workflow is fully functioning.
5a. Build a Project In Unreal Editor
Open your project in Unreal Editor, then click the Platforms dropdown and click Linux > Package Project. If your system is configured correctly, Unreal Engine will build, cook, and package your project.
5b. Build a Project Through the Command Line
To build a project through the Command Line, use the RunUAT script’s BuildCookRun command detailed in the Build Operations guide. The following is an example of a working BuildCookRun command:
[UE Root Directory]/RunUAT BuildCookRun -Build -Cook -Stage -Package -Run -Project=[ProjectName]Alternatively, you can use the Turnkey command line to start the same process.
[UE Root Directory]/RunUAT Turnkey -command=ExecuteBuild -platform=Linux -Project=[ProjectName]Normally, you need to use RunUAT from your Unreal Engine source directory. To make this command simpler to run, define a $UE_ROOT environment variable. This makes it possible to use RunUAT with a command such as $UE_ROOT/RunUAT BuildCookRun instead of providing the entire path to the RunUAT script.
Linux Quick Start
Learn how to download, build, and run UE4 on Linux.
Choose your operating system:
At the end of this tutorial, you’ll have Unreal Engine 4 (UE4) running on your Linux machine, having learned how to set up Git (to download UE4 source code), how to fork and clone our source code, build Unreal Engine from source, and how to run Unreal Engine on your Linux machine. Ultimately, the focus of this guide is to show you how to set up the primary workflow needed to get UE4 running on your Linux machine.
1 — Required Setup
Currently, we don’t supply a binary installer of UE4 for Linux users. The good news is that you can compile a binary of Unreal Engine from the same source code that we use to develop the engine. If you want to access our source code, you’ll have to register for an Epic Games account, sign up for a GitHub account, associate your GitHub username with your Epic Games account, and set up Git on your Linux machine.
Registering for an Epic Games Account
If you want to create games with Unreal Engine or contribute to the future of UE4 on Linux, you’ll need to have a valid Epic Games account.
- Navigate to UnrealEngine.com .
- Click Get Unreal.
There are many benefits for having an account with us, including (but not limited to) access to the Unreal Engine community, where you’ll connect with other UE4 Linux developers, and where you’ll be able to keep up with the latest news about Unreal Engine.
Setting up Git
Now that you’ve registered for an Epic Games account, you’re ready to work through the following steps to gain access to the UE4 source code on GitHub.
- Sign up for a GitHub account at GitHub.com .
Click for full image.
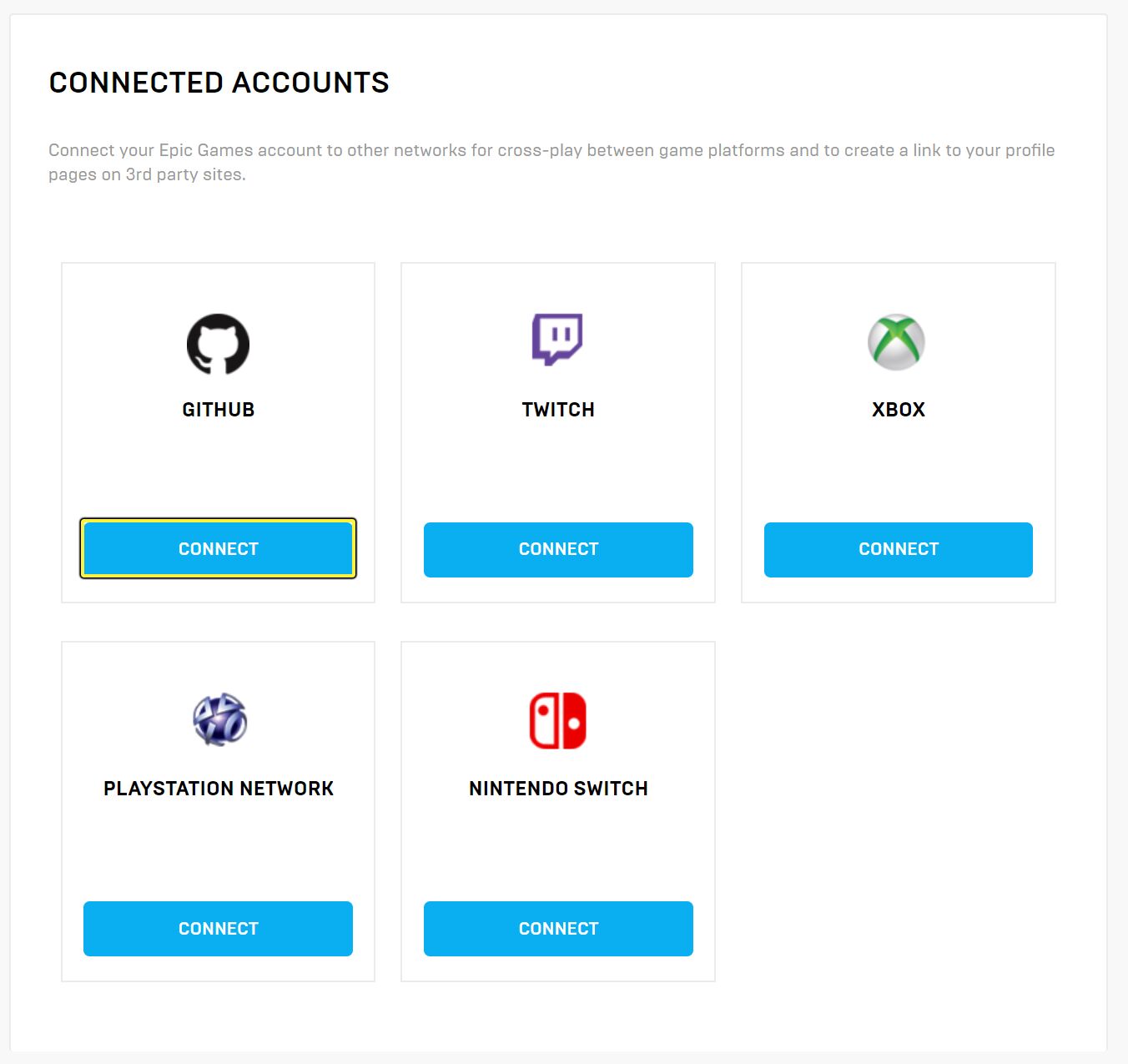
Go to your Epic Games account and click Connected Accounts.
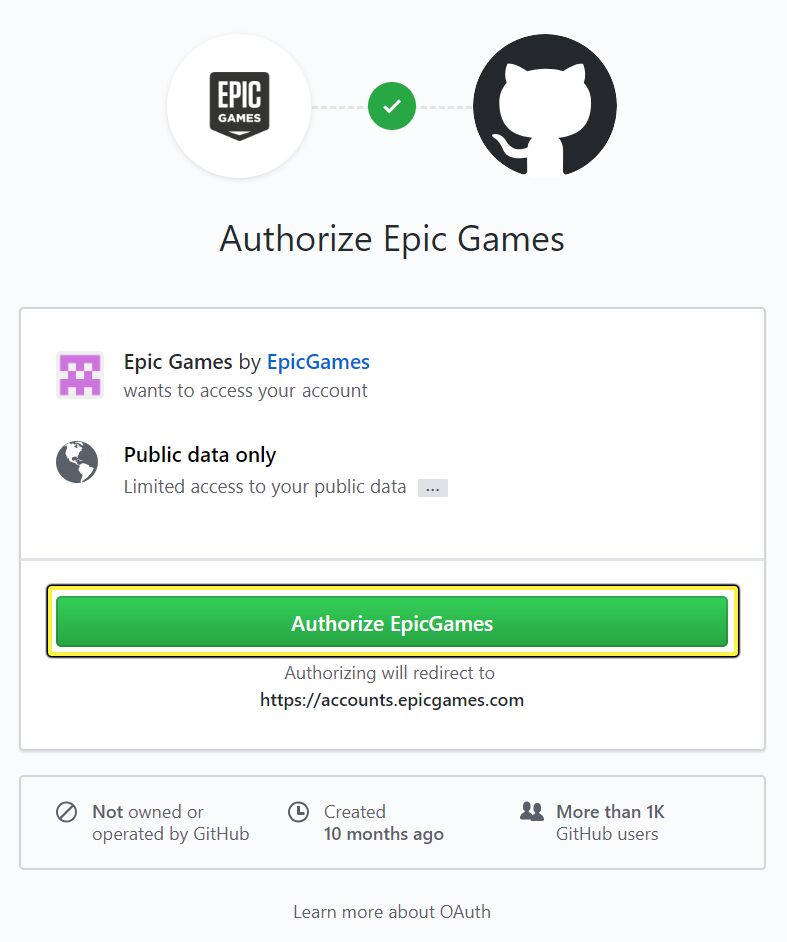
Link your GitHub username by clicking Connect under the GitHub icon.
To authorize the connection click Authorize EpicGames.
Section Result
By now, you’ve registered for an Epic Games account and linked it with your GitHub username. Also, you’ve installed Git and you’re ready for the next step, where you’ll fork and clone the UE4 source code from the Unreal Engine GitHub repository.
2 — Downloading UE4 on Linux
Now that you’ve set up Git on your Linux machine, you’re ready to download the Unreal Engine source code from our GitHub site . There are a couple of ways to download the UE4 source code, one way is to use the download feature on our GitHub page, and the other way is to clone the Unreal Engine repository with your Git client. We’ll cover both ways on this page.
Downloading from GitHub
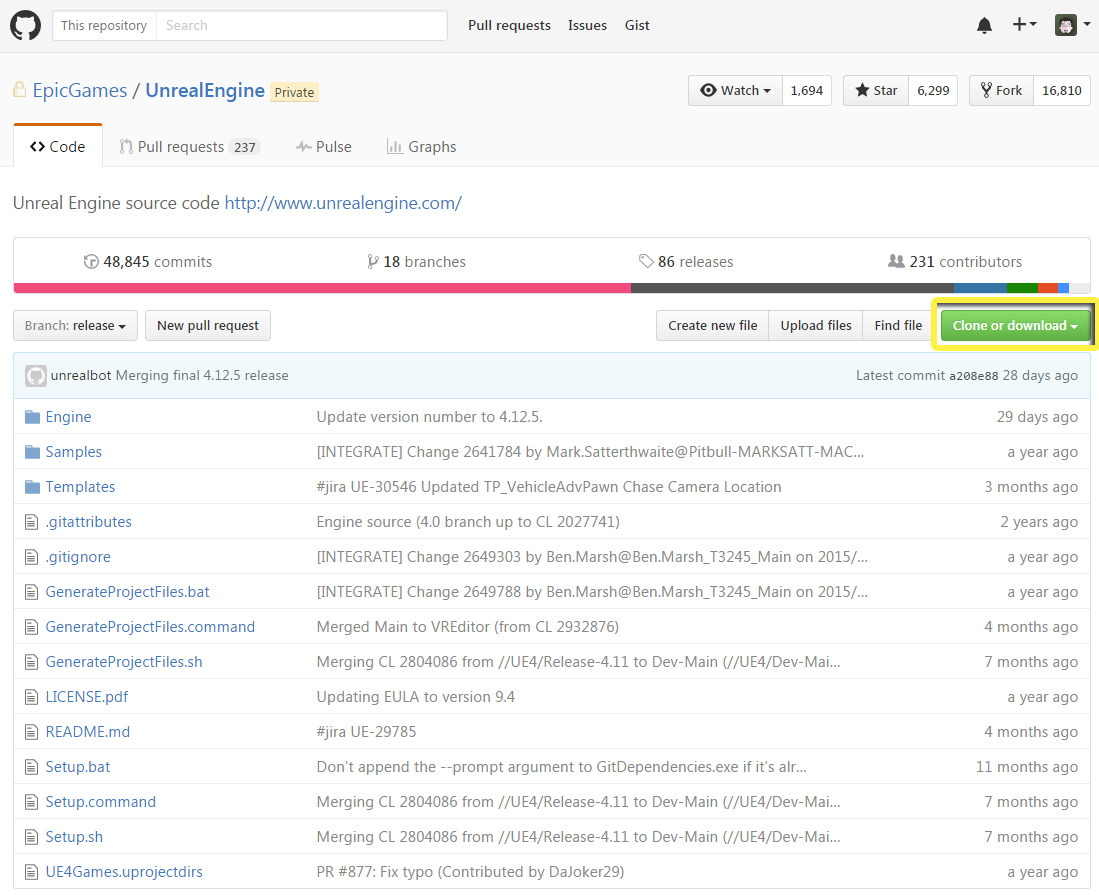
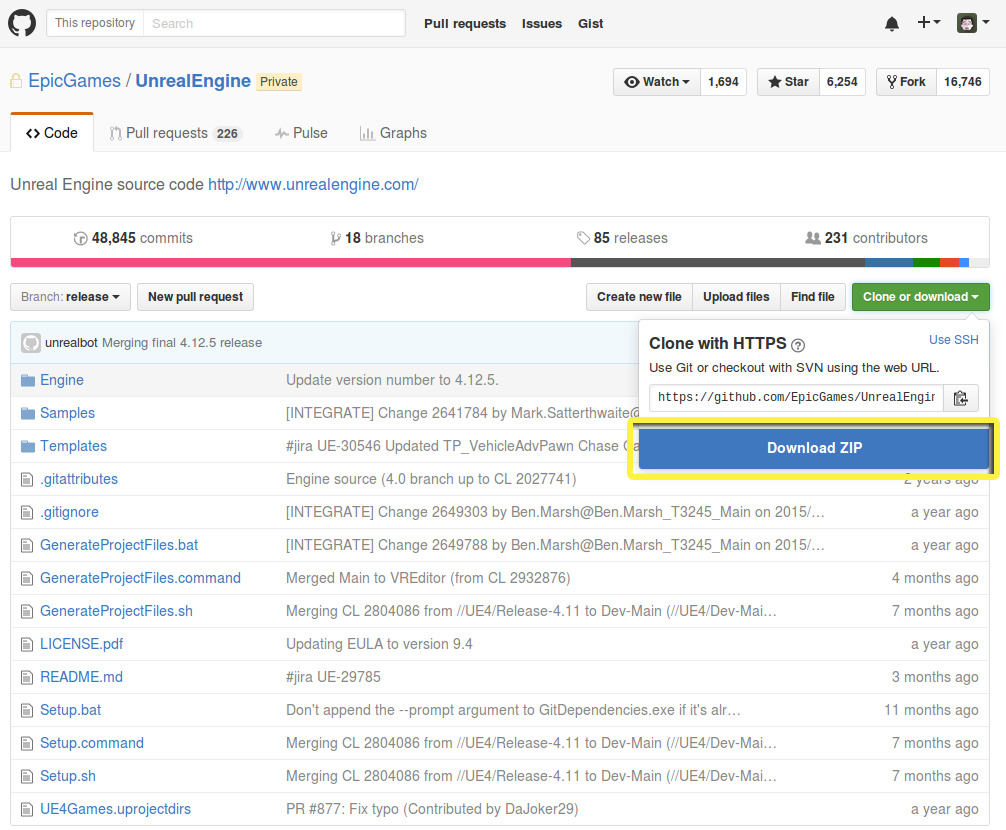
If don’t want to clone the Unreal Engine repository with Git, you can use the Download ZIP button on our GitHub site .
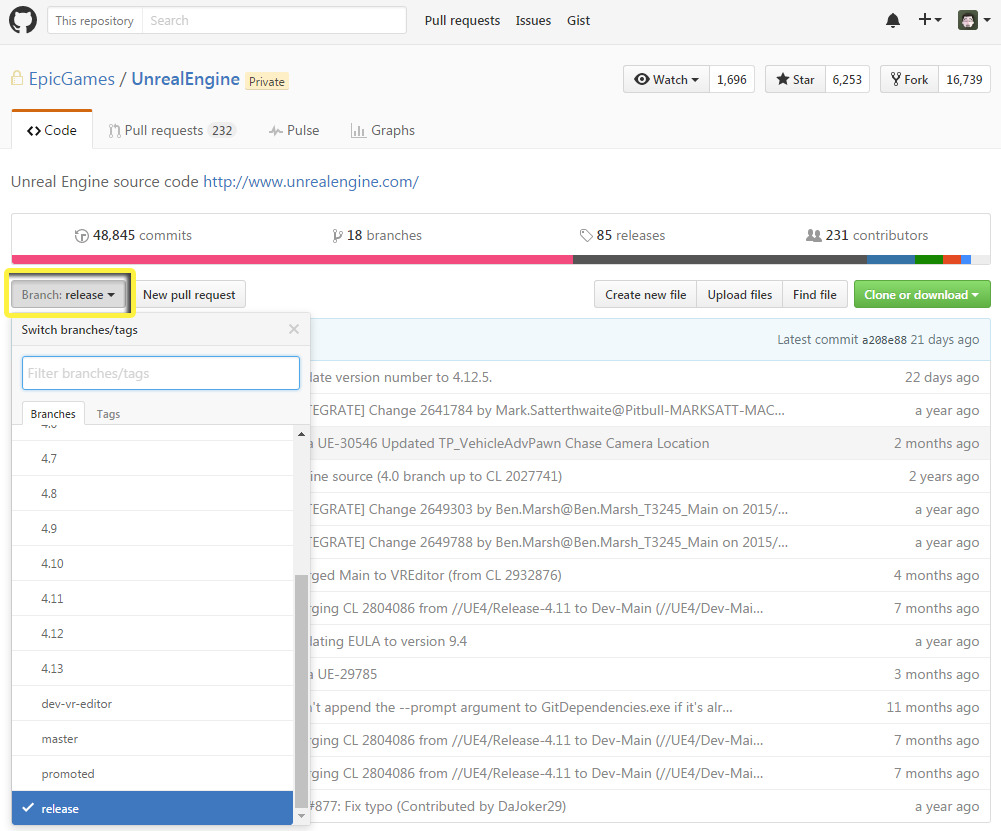
- First, select the branch you want to download by clicking Branch: on the left side of the page. For more info on branches in the Unreal Engine GitHub repository, please see the Source Branches Reference page.
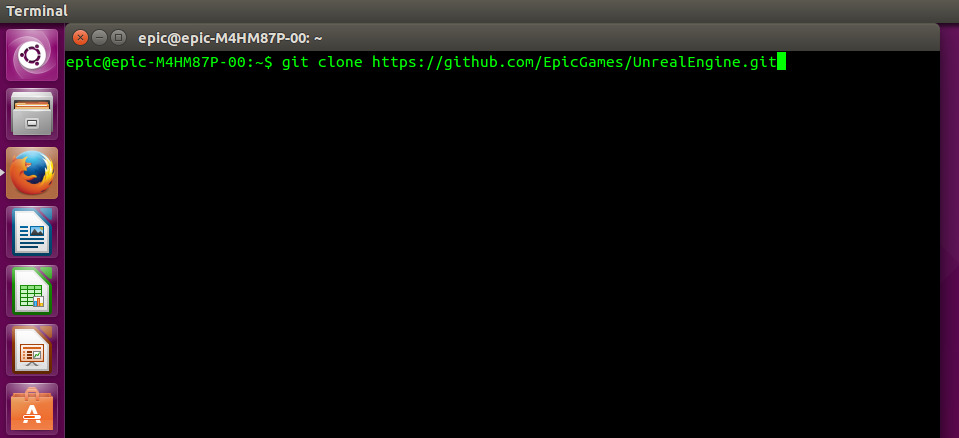
Cloning with Git
If you’re new to cloning with Git, refer to GitHub’s Cloning Guide before executing the following steps.
- Click the Unreal Engine link to access our repository .
Section Result
Whether you downloaded the Unreal Engine source code by using the Download ZIP button on our GitHub site , or by cloning the Unreal Engine repository using Git, you’re ready to build UE4 on Linux with the Unreal Engine source code that is now located on your hard disk.
3 — Building UE4 on Linux
In preparation for this critical step, you downloaded a copy of Unreal Engine’s source code onto your hard disk. During this part of the tutorial, you’ll get to run several utilities from the terminal to build a binary of UE4 on your Linux machine.
Our development and support teams currently use the latest version of Ubuntu; as a result, we may not be able to provide support for other Linux distributions (including other versions of Ubuntu). Additionally, read about Hardware and Software Specifications , and make sure your system has at least one hundred (100) gigabytes of disk space before performing the following steps.
- Inside the root directory, run Setup.sh from the terminal to setup the files needed to generate the project files.
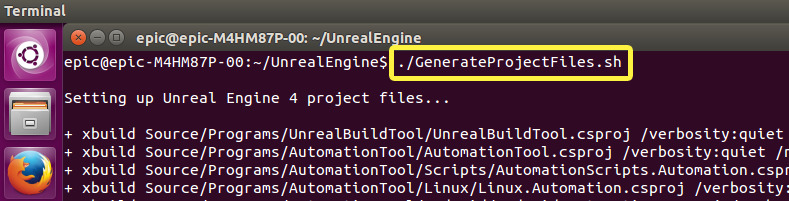
Now, run GenerateProjectFiles.sh from the terminal to generate your project files.
To build the project, run make from the terminal.
Depending on your system’s specifications, it may take anywhere from ten minutes to over an hour to compile the engine. If you want to shorten the time it takes to compile the engine from source, we recommend compiling the source code on a machine that has at least eight (8) gigabytes of RAM, with a multi-core processor having at least eight (8) cores (including hyperthreading).
Section Result
At this point, you should have a fully built binary of UE4 on your hard disk. The time has come to run the engine on your Linux system!
4 — Running UE4 on Linux
As you worked your way to this final step, you linked your Epic Games account with your GitHub username, you downloaded the Unreal Engine source code from our GitHub site, and you compiled a binary of UE4 on your Linux system. The only remaining task is for you to run the UE4 Editor so that you can start making games for the Linux platform.
- Navigate to the editor’s binary path by entering cd Engine/Binaries/Linux/ into the terminal.
- Run UE4Editor to launch the editor.
Launching UE4 on Linux
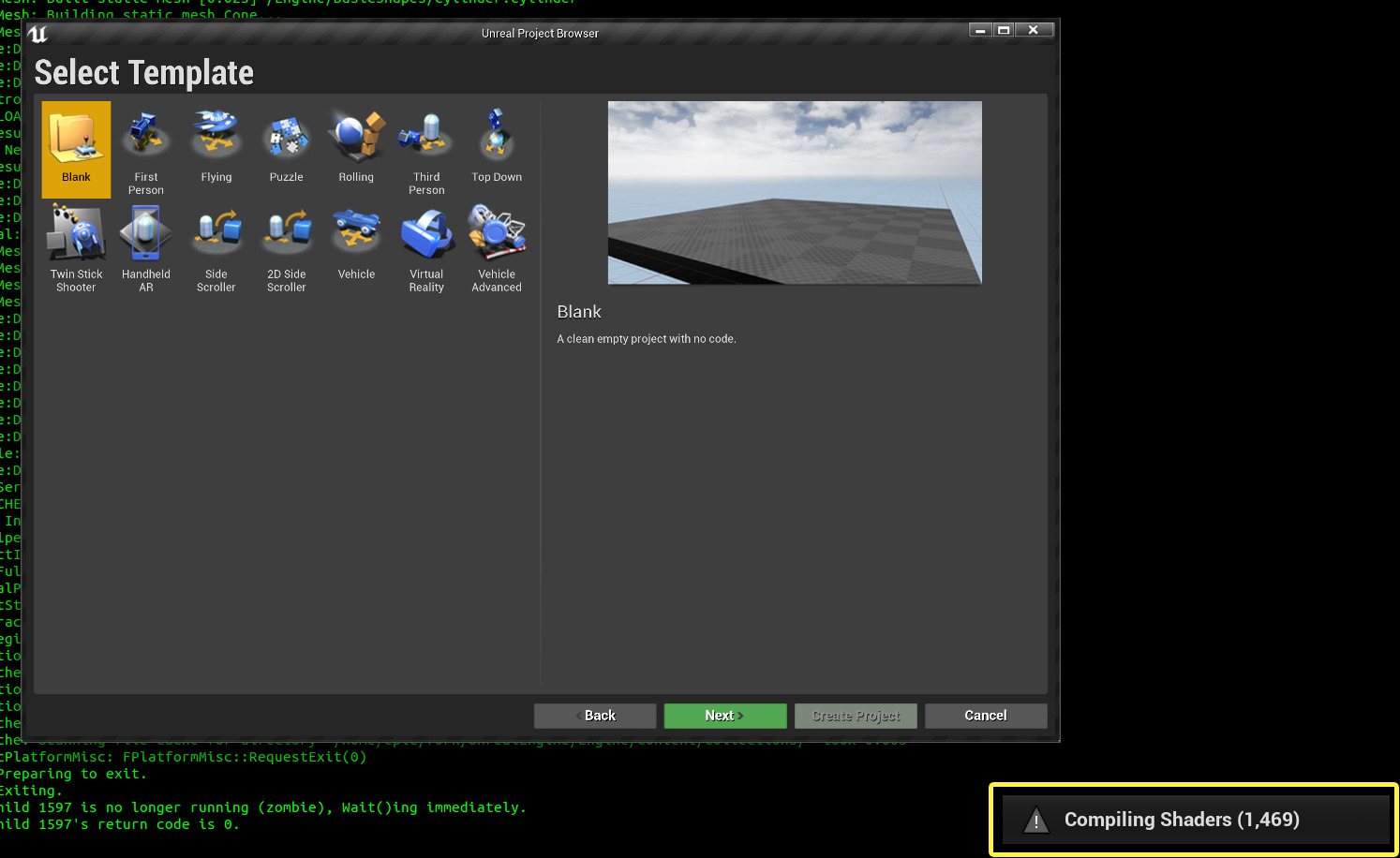
Because you’ve compiled the engine from its source code on Linux, the engine will compile shaders for a few minutes after launching UE4.
Creating your First Project
If you haven’t already set up an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) to work with UE4, we recommend that you start out by creating a Blueprint project.
Section Result
If you’re creating your first game on Linux, you just learned how to establish your primary UE4 workflow on Linux. As you worked your way through this tutorial, you learned:
✓ How to set up Git to download the source code for Unreal Engine.
✓ How to fork and clone Unreal Engine’s source code.
✓ How to build Unreal Engine from source.
✓ How to run Unreal Engine on your Linux machine.
Are you ready to do some exercises on your own?
5 — On your own!
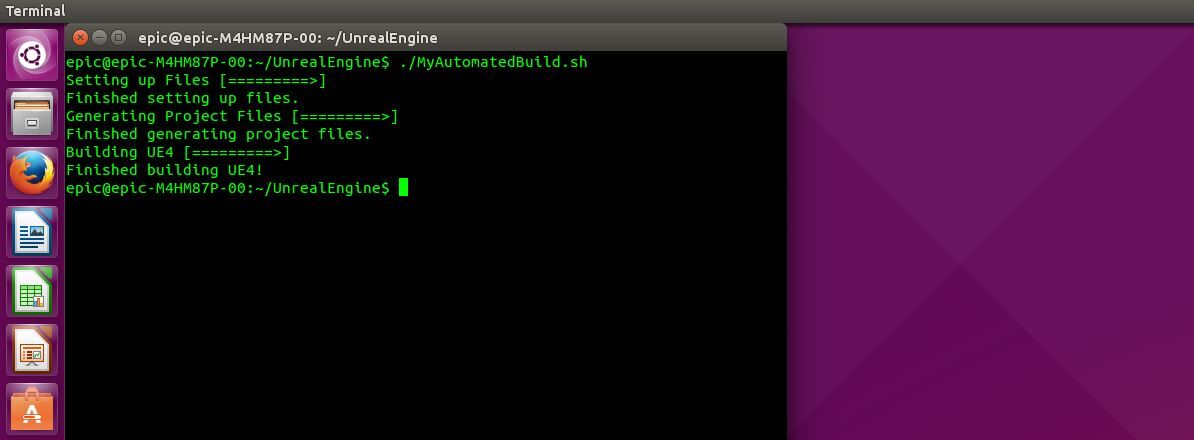
One way of increasing productivity is to write custom shell scripts that you can run from the terminal. If you know how to write shell scripts in Linux, try writing one that automates the process of setting up and building UE4.
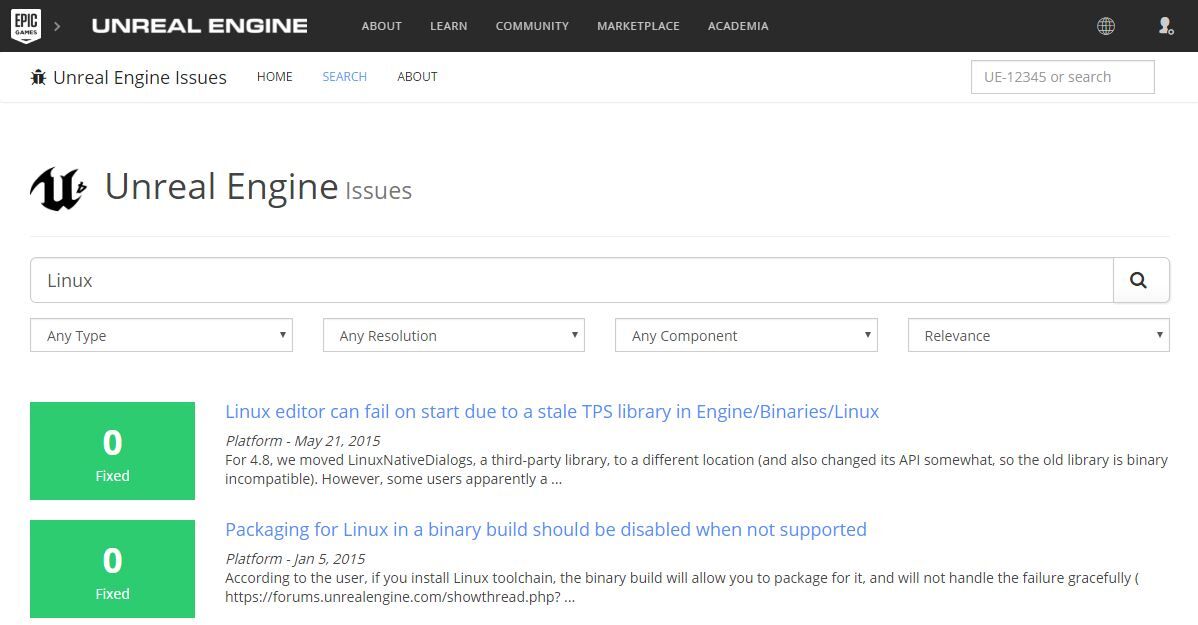
If you want to track the latest developments with UE4 on Linux, read this article and head over to the Unreal Engine Public Issues Tracker to check out the latest public issues impacting UE4 on Linux.
Do you see a public issue that you can fix? If you know how fork and clone our repository to submit pull requests with Git, join our growing community of developers and help shape the future of UE4 on Linux.
If you’re looking to quickly get started making projects with UE4, check-out the following tutorials: