- Classic SysAdmin: Linux 101: Updating Your System
- Ubuntu Linux
- Fedora Linux
- Final Thoughts
- Обновление Ubuntu до новой версии
- Обновление Ubuntu до новой версии через Менеджер обновлений
- Шаг 1. Настройки обновления системы
- Шаг 2. Обновление пакетов (по необходимости)
- Шаг 3. Обновление Ubuntu до новой версии
- Обновление Ubuntu до новой версии через командную строку
- Шаг 1. Откройте терминал
- Шаг 2. Обновление Ubuntu до новой версии
Classic SysAdmin: Linux 101: Updating Your System
This is a classic article written by Jack Wallen from the Linux.com archives. For more great SysAdmin tips and techniques check out our free intro to Linux course.
Many years ago, when I first began with Linux, installing applications and keeping a system up to date was not an easy feat. In fact, if you wanted to tackle either task you were bound for the command line. For some new users this left their machines outdated or without applications they needed. Of course, at the time, most everyone trying their hand at Linux knew they were getting into something that would require some work. That was simply the way it was. Fortunately times and Linux have changed. Now Linux is exponentially more user friendly – to the point where so much is automatic and point and click – that today’s Linux hardly resembles yesterday’s Linux.
But even though Linux has evolved into the user-friendly operating system it is, there are still some systems that are fundamentally different than their Windows counterparts. So it is always best to understand those systems in order to be able to properly use those system. Within the confines of this article you will learn how to keep your Linux system up to date. In the process you might also learn how to install an application or two.
There is one thing to understand about updating Linux: Not every distribution handles this process in the same fashion. In fact, some distributions are distinctly different down to the type of file types they use for package management.
- Ubuntu and Debian use .deb
- Fedora, SuSE, and Mandriva use .rpm
- Slackware uses .tgz archives which contain pre-built binaries
- And of course there is also installing from source or pre-compiled .bin or .package files.
As you can see there are number of possible systems (and the above list is not even close to being all-inclusive). So to make the task of covering this topic less epic, I will cover the Ubuntu and Fedora systems. I will touch on both the GUI as well as the command line tools for handling system updates.
Ubuntu Linux
Ubuntu Linux has become one of the most popular of all the Linux distributions. And through the process of updating a system, you should be able to tell exactly why this is the case. Ubuntu is very user friendly. Ubuntu uses two different tools for system update:
The Update Manger is a nearly 100% automatic tool. With this tool you will not have to routinely check to see if there are updates available. Instead you will know updates are available because the Update Manager will open on your desktop (see Figure 1) as soon as the updates depending upon their type:
If you want to manually check for updates, you can do this by clicking the Administration sub-menu of the System menu and then selecting the Update Manager entry. When the Update Manager opens click the Check button to see if there are updates available.
Figure 1 shows a listing of updates for a Ubuntu 9.10 installation. As you can see there are both Important Security Updates as well as Recommended Update. If you want to get information about a particular update you can select the update and then click on the Description of update dropdown.
- Check the updates you want to install. By default all updates are selected.
- Click the Install Updates button.
- Enter your user (sudo) password.
- Click OK.
The updates will proceed and you can continue on with  your work. Now some updates may require either you to log out of your desktop and log back in, or to reboot the machine. There are is a new tool in development (Ksplice) that allow even the update of a kernel to not require a reboot.
Once all of the updates are complete the Update Manage main window will return reporting that Your system is up to date.
Now let’s take a look at the command line tools for updating your system. The Ubuntu package management system is called apt. Apt is a very powerful tool that can completely manage your systems packages via command line. Using the command line tool has one drawback – in order to check to see if you have updates, you have to run it manually. Let’s take a look at how to update your system with the help of Apt. Follow these steps:
- Open up a terminal window.
- Issue the command sudo apt-get upgrade.
- Enter your user’s password.
- Look over the list of available updates (see Figure 2) and decide if you want to go through with the entire upgrade.
- To accept all updates click the ‘y’ key (no quotes) and hit Enter.
- Watch as the update happens.
That’s it. Your system is now up to date. Let’s take a look at how the same process happens on Fedora (Fedora 12 to be exact).
Fedora Linux
Fedora is a direct descendant of Red Hat Linux, so it is the beneficiary of the Red Hat Package Management system (rpm). Like Ubuntu, Fedora can be upgraded by:
Depending upon your desktop, you will either use the GNOME or the KDE front-end for PackageKit. In order to open up this tool you simply go to the Administration sub-menu of the System menu and select the Software Update entry.  When the tool opens (see Figure 3) you will see the list of updates. To get information about a particular update all you need to do is to select a specific package and the information will be displayed in the bottom pane.
To go ahead with the update click the Install Updates button. As the process happens a progress bar will indicate where GNOME (or KDE) PackageKit is in the steps. The steps are:
- Resolving dependencies.
- Downloading packages.
- Testing changes.
- Installing updates.
When the process is complete, GNOME (or KDE) PackageKit will report that your system is update. Click the OK button when prompted.
Now let’s take a look at upgrading Fedora via the command line. As stated earlier, this is done with the help of the yum command. In order to take care of this, follow these steps:
- Open up a terminal window (Do this by going to the System Tools sub-menu of the Applications menu and select Terminal).
- Enter the su command to change to the super user.
- Type your super user password and hit Enter.
- Issue the command yum update and yum will check to see what packages are available for update.
- Look through the listing of updates (see Figure 4).
- If you want to go through with the update enter ‘y’ (no quotes) and hit Enter.
- Sit back and watch the updates happen.
- Exit out of the root user command prompt by typing “exit” (no quotes) and hitting Enter.
- Close the terminal when complete.
Your Fedora system is now up to date.
Final Thoughts
Granted only two distributions were touched on here, but this should illustrate how easily a Linux installation is updated. Although the tools might not be universal, the concepts are. Whether you are using Ubuntu, OpenSuSE, Slackware, Fedora, Mandriva, or anything in-between, the above illustrations should help you through updating just about any Linux distribution. And hopefully this tutorial helps to show you just how user-friendly the Linux operating system has become.
Ready to continue your Linux journey? Check out our free intro to Linux course!
Обновление Ubuntu до новой версии
Помимо периодических обновлений пакетов в Ubuntu Linux, раз в полгода (в апреле и октябре) выходят новые версии дистрибутива. Версии нумеруются числами — 18.04, 18.10, 19.04, . которые означают год и месяц выхода дистрибутива.
Когда выходит новая версия дистрибутива, то у пользователей появляется возможность обновиться до этой версии.
В данной статье мы рассмотрим, как обновить Ubuntu Linux до новой версии. Мы рассмотрим два способа обновления системы:
- Используя графическую утилиту Менеджер обновлений.
- Используя командую строку (терминал).
Обновление Ubuntu до новой версии через Менеджер обновлений
Внимание: Процесс обновления Ubuntu до новой версии очень простой. Не пугайтесь количества скриншотов и текста ниже. Мы приводим возможные сообщения, которые могут появиться в процессе обновления.
Шаг 1. Настройки обновления системы
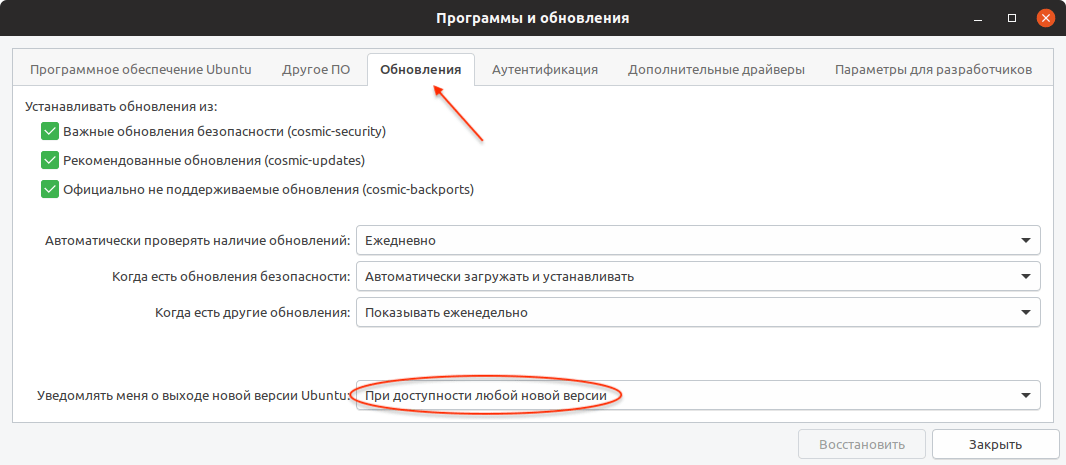
Откройте Лаунчер, нажав сочетание клавиш Super+A , и запустите утилиту Программы и обновления (Software & Updates).
Откроется утилита Программы и обновления. Перейдите на вкладку Обновления и проверьте, что в пункт Уведомлять меня о выходе новой версии Ubuntu ( Notify me of a new Ubuntu version ) установлен в состояние При доступности любой новой версии ( For any new version ) , если нет, то выберите этот пункт. После этого закройте окно.
Шаг 2. Обновление пакетов (по необходимости)
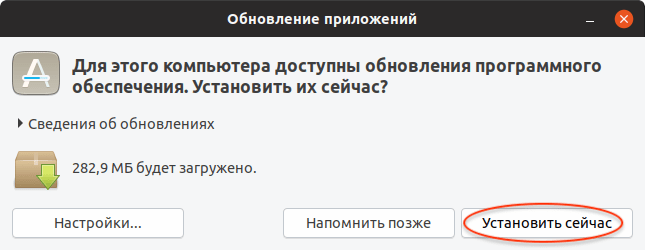
Запустите Менеджер обновлений Ubuntu. Его можно запустить из Лаунчера (нажав Super+A ) и выбрав иконку «Обновление приложений». Перед тем, как обновлять сам дистрибутив до новой версии, может потребоваться обновить пакеты в системе. Поэтому сначала может появиться следующее окно, с предложением обновить пакеты. Нажмите кнопку Установить сейчас , чтобы начать обновление пакетов.
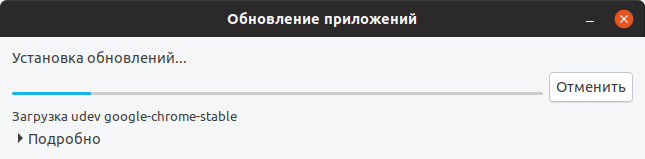
Появится окно для ввода пароля пользователя. Введите пароль. После этого начнется процесс обновления пакетов.
После того, как процесс обновления пакетов завершится, может появиться сообщение о необходимости перезагрузить компьютер. В таком случае перезагрузите компьютер.
Шаг 3. Обновление Ubuntu до новой версии
Снова, как и на предыдущем шаге, запустите Менеджер обновлений Ubuntu (Обновление приложений).
Примечание: Если вдруг снова появилось окно с предложением обновить пакеты, то это означает, что требуется обновить еще некоторые пакеты. Обновите их.
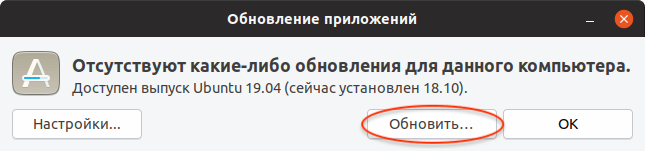
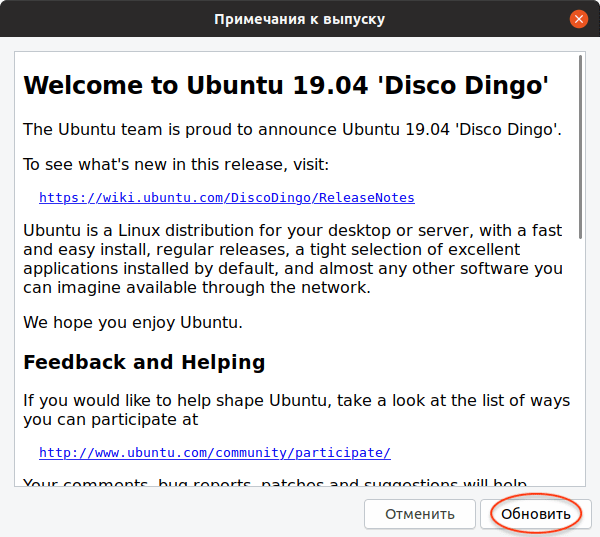
Если вышла новая версия дистрибутива Ubuntu, и ваша система может обновиться до нее, то появится следующее окно. Сообщение вида «Доступен выпуск Ubuntu 19.04 (сейчас установлен 18.10)» информирует вас о том, до какой версии Ubuntu будет обновлена текущая система. Нажмите кнопку Обновить ( Upgrade ) .
Появится запрос на ввод пароля пользователя. Введите пароль и нажмите кнопку Подтвердить .
Появится окно с информацией о версии, до которой будет обновлена текущая система. Нажмите кнопку Обновить .
Начнется подготовка к обновлению системы.
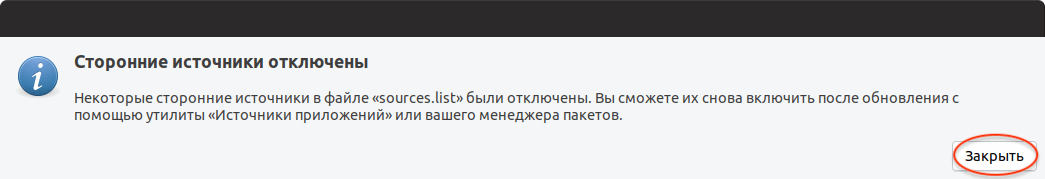
В процессе подготовки может появиться сообщение, информирующее вас о том, что будут отключены некоторые PPA-репозитории (скорее всего вы их добавляли, когда устанавливали какие-нибудь программы). Вы сможете их включить после установки.
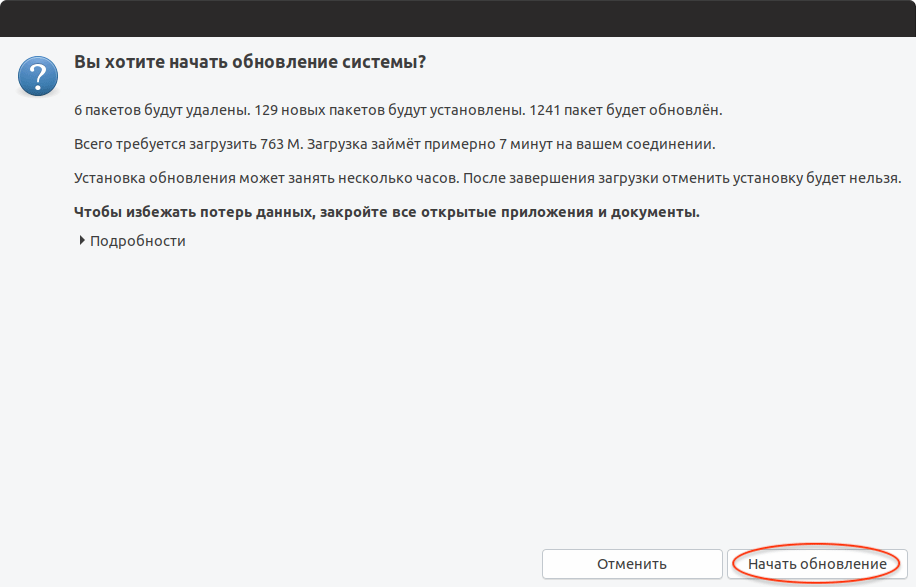
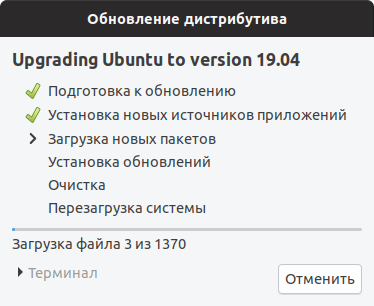
Откроется информационное окно, в котором будет показано сколько пакетов будет обновлено и установлено, и сколько мегабайт данных требуется загрузить в процессе обновления. На данном этапе рекомендуется закрыть все открытые программы. Нажмите кнопку Начать обновление .
Появится еще одно информационное сообщение. Ознакомьтесь с информацией и закройте его.
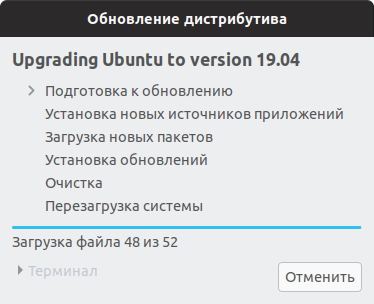
Начнется процесс обновления Ubuntu до новой версии. Процесс может занимать довольно долгое время.
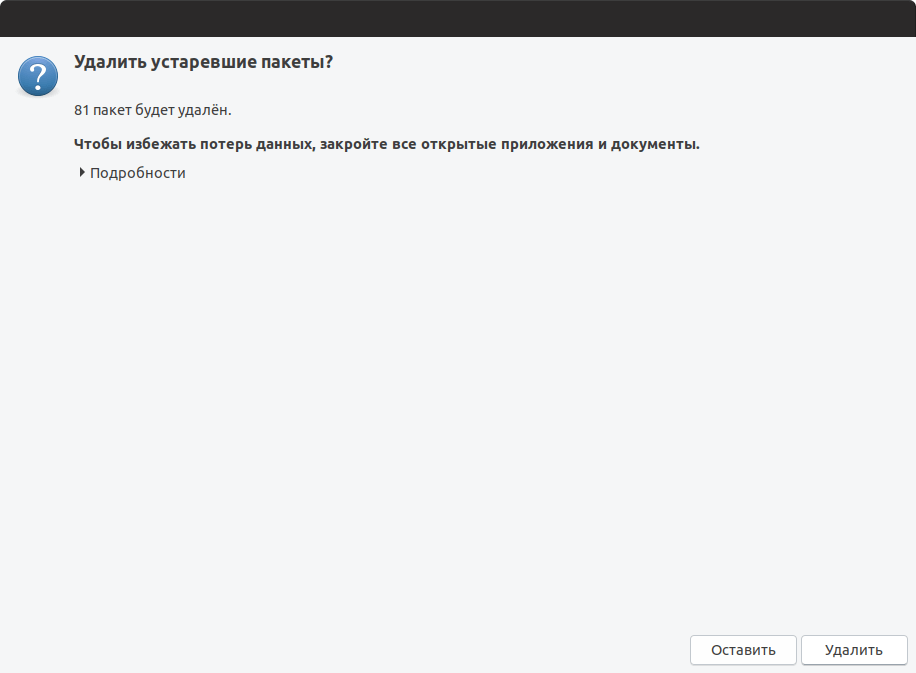
Почти в конце обновления может появиться следующее окно. В нем указано, что будут удалены некоторые пакеты, которые больше не нужны. Нажмите кнопку Удалить .
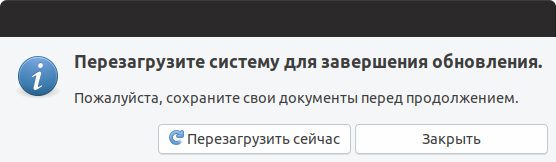
Когда обновление будет выполнено, появится окно с сообщением о необходимости перезагрузить компьютер. Нажмите кнопку Перезагрузить сейчас .
Начнется перезагрузка компьютера. После перезагрузки вы попадете в новую версию Ubuntu.
Обновление Ubuntu до новой версии через командную строку
Шаг 1. Откройте терминал
Откройте терминал. Это можно сделать, нажав сочетание клавиш Ctrl+Alt+T .
Шаг 2. Обновление Ubuntu до новой версии
Обновление Ubuntu до новой версии выполняется в 2 этапа. Сначала нужно обновить все пакеты до новой версии и только потом обновлять саму систему.
Для обновления пакетов, введите в терминале последовательно следующие команды.
sudo apt update sudo apt full-upgradeЕсли будут найдены обновления каких-либо пакетов, то эти пакеты должны быть обновлены.
Теперь выполним непосредственно обновление системы до новой версии. Выполняем команду:
Если будет найдена новая версия Ubuntu, то появится соответствующее сообщение. Нажмите Enter , чтобы начать обновление. Процесс обновления может занять продолжительное время.
В процессе обновления могут выдаваться запросы, на которые вы должны отвечать Да (Yes) или Нет (No). Если у вас русская версия системы, то чтобы ответить Да, нужно ввести д и нажать Enter . Для английской версии систему, нужно ввести y и нажать Enter .
После завершения обновления перезагрузите компьютер.