- YuMS / update-git.sh
- How to Easily Update Git in Local Environment using Shell Commands on Mac, Windows, and Linux
- Updating Git on a Mac
- Updating a Local Git Repository
- Updating Git on Windows
- Updating a Local Repository with Changes from a GitHub Repository
- Updating Multiple Git Repositories
- Other helpful code samples for updating Git in local environment using shell commands
- Conclusion
- How to Update Git
- How to Check the Current Git Version?
- How to Update Git
- Update Git on Linux
- Update Git on Windows
- Update Git on Mac
YuMS / update-git.sh
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters. Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| #! /bin/bash |
| sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:git-core/ppa |
| sudo apt-get update |
| sudo apt-get install git -y |
I am quite new to using Linux and I came across these commands while searching for «updating git ubuntu».
Now I want to know exactly what these lines do?
espicially this one -> sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:git-core/ppa
this probably updates everything in the repository (sudo apt-get update) [correct me if I am wrong pretty please]
sudo apt-get install git -y (not sure what the -y flag does here)
Works like a charm. Thanks
After 6 years, still working properly, Thanks.
Thanks! I needed this for ubuntu 18.04
Works like a charm, thanks!
Just what I was looking for. Thanks!
Thanks. Still working smoothly after 7 years.
WSL 2, Ubuntu 18.04, 04.2023
Still working, thanks.
Tried to run on Ubuntu 16.4 but getting below message,
The following packages have unmet dependencies: git : Depends: libpcre2-8-0 but it is not going to be installed Depends: git-man (> 1:2.41.0) but 1:2.7.4-0ubuntu1.9 is to be installed google-chrome-stable : Depends: libu2f-udev but it is not installable Depends: libvulkan1 but it is not going to be installed zoom : Depends: libxcb-xinerama0 but it is not going to be installed E: Unmet dependencies. Try ‘apt-get -f install’ with no packages (or specify a solution).
How to Easily Update Git in Local Environment using Shell Commands on Mac, Windows, and Linux
Learn how to update Git in your local environment using shell commands on Mac, Windows, and Linux. This comprehensive guide covers all the essential steps to keep your Git updated and take advantage of new features and bug fixes.
- Updating Git on a Mac
- Updating a Local Git Repository
- Updating Git on Windows
- Updating a Local Repository with Changes from a GitHub Repository
- Updating Multiple Git Repositories
- Other helpful code samples for updating Git in local environment using shell commands
- Conclusion
- How do I update a local Git repository?
- How do I update my existing Git version?
- How to update Git repository using command line?
- How to update Git version in Linux?
Git is a popular version control system used by developers to manage code changes and collaborate with others. It’s essential to keep Git updated to take advantage of new features and bug fixes. This blog post provides a comprehensive guide on how to update Git in a local environment using shell commands on Mac, Windows, and Linux.
Updating Git on a Mac
To update Git on a Mac, download the official installer from the Git website and run it. If you already have Git installed on your machine, you can check the current version of Git installed using the command “git –version”. After that, download the latest version of Git from the Git website and run the installer to update Git. Finally, verify that Git has been updated using the command “git –version”.
Updating a Local Git Repository
To update a local Git repository from a central repository, use the command “git pull upstream master”. However, it’s recommended to create a safer “git up” alias instead of using “git pull” because it’s more concise and easier to remember. To create the alias, run the following command:
git config --global alias.up 'pull --rebase' There are other useful commands to update Git, such as “git remote update -p” instead of “git pull”. The former will update Git but only remove branches that no longer exist on the remote repository. Additionally, to clone a remote Git repository to a local repository, use the command “git clone”.
If you want to add an upstream remote with the given URL, run the following command:
Finally, to update submodules in a Git repository, use the command “git submodule update”.
Updating Git on Windows
On Windows, you can update Git by uninstalling the current version and downloading the latest version from the Git website to update it. Alternatively, you can use the “git update-git-for-windows” command to update git on windows without uninstalling the previous version. Finally, verify that Git has been updated using the command “git –version”.
Updating a Local Repository with Changes from a GitHub Repository
To update a local repository with changes from a GitHub repository, use “git fetch -t” to fetch tags and “git log HEAD” to check the changes. You can use “git push” to push changes from a local repository to a fork on GitHub. Additionally, use “git checkout” to switch to a branch and update the index and files in the working tree. Finally, use “git pull” to fetch and download content from a remote repository and update the local repository.
Updating Multiple Git Repositories
To update multiple Git repositories at once using a bash script, you can use the following command:
This command will update all Git repositories in the current directory. Additionally, you can use git hooks to automate tasks in a Git repository, Git branching and merging to manage code changes and collaborate with others, Git tags to mark important points in a Git repository’s history, and Git GUI tools to visualize changes and manage Git repositories .
Other helpful code samples for updating Git in local environment using shell commands
In Shell , for instance, git update using git bash code example
# Since Git 2.16.1(2) you can use C:\> git update-git-for-windows#In version between 2.14.2 and 2.16.1, the command was C:\> git updateConclusion
Updating Git on a local environment using shell commands is a critical task for developers. This blog post has provided a comprehensive guide on how to update git on mac , Windows, and Linux. It has covered important points like updating a local Git repository, creating a git alias , updating git on windows , updating a local repository with changes from a GitHub repository, and updating multiple Git repositories using a bash script. By following these steps, developers can keep their Git updated and take advantage of new features and bug fixes, leading to more efficient and effective code management.
How to Update Git
Git is a version control system that allows multiple developers to work on the same project while tracking changes and revisions. Keeping Git up to date brings you the latest features and usability improvements.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to update to the latest version of Git on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
- A system running Linux, Windows, or macOS
- An installed version of Git
- Access to the terminal window (Linux, macOS) or command prompt (Windows)
- An account with administrator-level privileges
How to Check the Current Git Version?
To check the current version of Git, use the following command:
This command works on all operating systems. This example uses Windows:
How to Update Git
Below, we list different ways you can update your version of Git, depending on the operating system you are using. Skip to the section applicable for your machine.
Update Git on Linux
Note: To update Git on a Linux machine, use the appropriate package manager. When working with Git on CentOS, use a package manager such as yum or pacman .
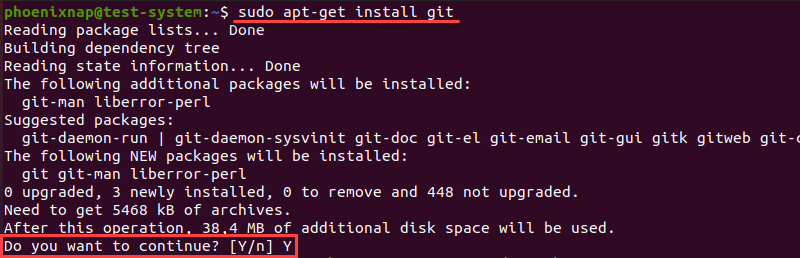
This example shows how to update Git on Ubuntu.
Start by updating the system packages with the following command:
When prompted, type Y and press Enter to confirm the installation.
To verify the installation has completed, check the Git version one more time:
Another way to update Git on Linux is to install it from scratch using the original source code. Check out our guide to installing Git on Ubuntu for details.
Update Git on Windows
The method you use to update Git on Windows depends on the version of Git you are currently running.
For versions prior to 2.14.1, uninstall Git from your system and install a copy of the latest version from scratch. Check out our guide to installing Git on Windows for more details.
For versions from 2.14.2 to 2.16.1, use the following command in your command prompt:
For versions 2.16.1 on, update Git with:
The output above appears when you are running the latest Git version.
Update Git on Mac
The easiest way to update Git on Mac is to use the official installer. Download the installation file from the Git website. Run the installation and follow the install wizard to update Git to the latest version.
Note: Using the install wizard to update Git overwrites the current installation.
Another method is to update Git using Homebrew. If you don’t have Homebrew already, install it by using:
/usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"Update Homebrew to make sure you have the latest installation packages:
Install the latest version of Git with Homebrew:
If you already have Git installed using Homebrew, update to the latest version with:
Check the current Git version to confirm the update:
Note: If checking the Git version after updating results in an output that includes (Apple Git-101) , your system is still running the default Apple version of Git instead of the official one. Change your local path to the Homebrew version of Git to fix this issue:
export PATH=/usr/local/bin:$PATH
After following this tutorial, you should have a fully updated version of Git installed on a Linux, Windows, or macOS machine.
Take a look at our Git Commands Cheat Sheet for a comprehensive primer on working with Git. If you come across a Git merge conflict, make sure to read our article How to Resolve Merge Conflicts in Git.