- How to Create Arch Linux Bootable USB on Windows & Mac
- Method 1: Diskpart Command
- Method 2: UUByte LiteBoot
- Method 3: Create Arch Linux Bootable USB on Mac using dd Command
- The Bottom Line
- How to Install Arch Linux from USB
- Prerequisites
- How to install Arch Linux from USB
- How to create a bootable USB for Arch Linux
- How to install Arch Linux for USB
- How to setup Arch Linux
- Step 1: Partitioning the disk
- Step 1.1: Create BIOS boot partition
- Step 1.2: Create Linux Swap
- Step 1.3: Create Linux Filesystem
- Step 2: Make the file system
- Step 3: Mount the storage device
- Step 4: Copy the operating system files
- Step 5: Root account configuration
- Step 6: Install GRUB for Linux Kernel
- Conclusion
How to Create Arch Linux Bootable USB on Windows & Mac
Arch is a famous Linux distribution among system administrators and advanced users who prefer playing Linux from a high level. It only has a basic OS and you are free to build the system based on Arch rules. If you are interested in Arch Linux, then you should first create Arch Linux Bootable USB for installation. Here you will get the 3 utmost methods to help you to complete the task. The methods are simple and easy to apply and all you need to just follow the steps listed below.
Method 1: Diskpart Command
diskpart is a text-based free utility shipped with Windows. It means you can use this tool on all Windows machines, including the latest Windows 10. The core function of diskpart is for disk management, such as creating partitions, deleting partitions, merging partitions, etc. In this part, we are going to use this powerful tool to create a bootable Linux USB from Arch ISO image.
Step 1: First and foremost, download Arch Linux ISO file from its official website. If the download speed was slow, kindly pick up a mirror near to you.
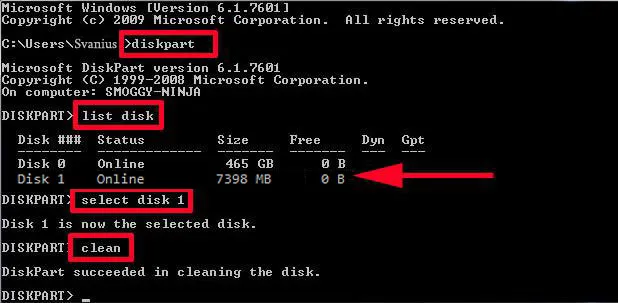
Step 2: Now, insert an USB flash drive and then run Command Prompt as administrator. To do this task, click on the Start menu, type CMD in the search bar and then select ‘Run as administrator’. In the command box, type diskpart and then press the Enter key.
Step 3: Soon, you will get a list of drives attached to current machine, Disk 1 shows the USB and you need to select the same and for that, type this command: select disk 1
Step 4: After selecting Disk 1, you need to clean it and for that, type clean. Now, you need to create a new primary partition for the USB by typing create partition primary.
Step 5: After completing the above step, type select partition 1 and hit the ‘Enter’ key. Now, type active in the box and press the ‘Enter’ key.
Step 6: To format the USB, you need to type: format fs=ntfs quick
Step 7: Now, close the Diskpart section by typing exit in the command box.
Step 8: After completing the above step, move to the download folder, extract files from Arch ISO and paste all the files to the USB drive.
That’s it; An Arch Linux Bootable USB is ready to use. This method looks simple, but there are lots of commands and if you enter any incorrect command, then you will fail to accomplish the task.
Method 2: UUByte LiteBoot
Command Prompt is definitely not a good option for most people as you have to deal with command prompt, which should be 100% correct for each comamnd. It is tough and hard to understand if you were not familiar with tech terms. So in this section, we will introduce a GUI-based software that do the same job as Command Prompt but a lot of easier.
UUByte LiteBoot is an ultimate boot toolkit for creating bootable USB not only for Linux but also for Windows and macOS. The user interface is built with a modern design and no complex settings to be made during the creation process. All you need to do is several mouse clicks. The settings are completed automatically at the background.
Step 1: Download and install LiteBoot on your PC. Now, launch the software and soon, you will get the Registration window and if you have purchased the license key, then click on the ‘Register’ button. However, if you don’t have the license key, then purchase LiteBoot to access its full features.
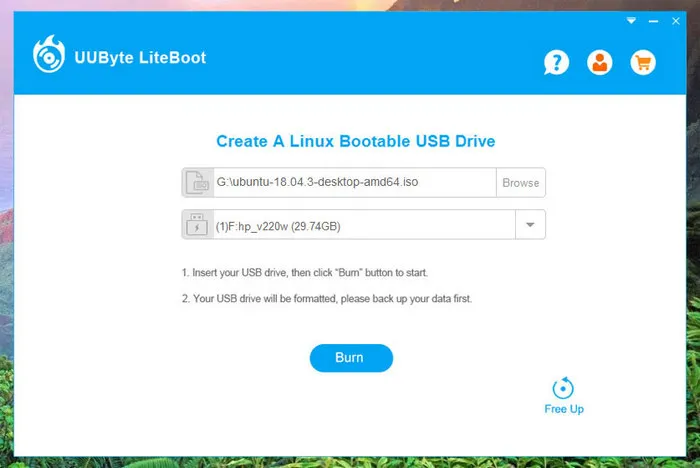
Step 2: After completing the registration process, click ‘Linux Boot’ on the main window and tap the ‘Browse’ button to load the Arch Linux ISO file into the program.
Step 3: Now, select the inserted USB drive name from the drop-down list and click on the ‘Burn’ button to burn Arch Linux ISO to USB drive. The rest of the tasks will be done by LiteBoot in less than 5 minutes. No addition actions to be made!
Step 4: After the bootbale USB is created successfully with LiteBoot, you should insert the drive into the target machine. Then let the computer boot from USB and start installing Arch Linux.
This method is very simple to follow and even the beginner can create an Arch Linux Bootable USB with the help of this amazing software.
Method 3: Create Arch Linux Bootable USB on Mac using dd Command
If you are using Mac OS, then the ‘dd’ command will help you to create Arch Linux bootable USB and the prime role of such command is to copy and transform the respective file. To perform this task, you will need a USB drive and the downloaded file of Arch Linux in order to create a bootable USB on macOS.
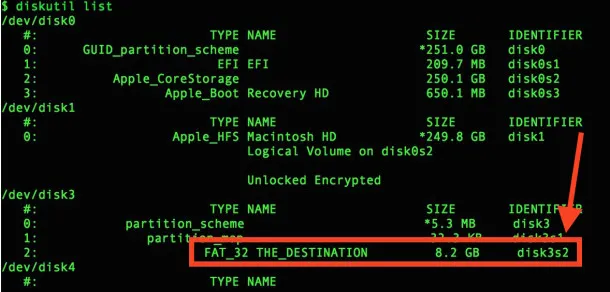
Step 1: Locate the inserted USB drive and for that launch the terminal and type the command: diskutil list
Step 2: Thereafter, you will get the list of drives, note down the name of the USB drive. Now, you need to format the USB and for that type the command (assuming the USB name is disk4 in above screenshot): umount /dev/disk4
Step 3: After providing the path of the USB, type the command provided below in the terminal box to wipe out all the existing data in the USB drive: mkfs.vfat /dev/disk4
Step 4: Now, you need to give the path of the USB followed by the path of Arch Linux ISO file and the command for the same is:
sudo dd bs=4M if=arch.iso of=disk4.
Note: In place of input, you will have to give the path of the Arch Linux ISO file and in place of target USB drive, you need to provide the location of the USB and it will be the same one as you found in Step 1.
That’s it’ your Bootable USB is ready to use. The method is a bit technical one and to perform this task, you will have to pay more attention amid providing the USB path and the Arch Linux ISO file. If you make any mistake in these steps, then you will fail to create an Arch Linux Bootable USB.
The Bottom Line
The ‘add’ and ‘diskpart’ methods, based on text commands, need a lot of time and attention because you need to play with the commands and if you will do any foul, then you won’t get the result. However, in the UUByte method, you don’t have to work more because the software is capable enough to complete the task and all you need to follow the guidance provided by LiteBoot.
How to Install Arch Linux from USB
Arch Linux is one of the simplest and easiest-to-learn Linux distros for intermediate Linux users. By default, it ships with command line accessibility which may not attract a new user. As Arch is command-line based, it is perceived that its installation is also tricky. However, the reality is the opposite of the saying. Keeping in view, we have provided this guide to install Arch Linux from USB with the following learning outcomes:
Prerequisites
To install Arch Linux from USB, you must have the following set of prerequisites before doing so.
- ISO of Arch Linux:Download the ISO file of Arch Linux
- USB booting tool: A booting tool (Etcher recommended) is required to make the USB bootable. Download BalenaEtcher
How to install Arch Linux from USB
For better understanding, we have divided this into various sub-sections. Like, the bootable USB will be created in the upcoming section and the installation of Arch Linux from USB would be carried out in the later section.
How to create a bootable USB for Arch Linux
Here, various steps are demonstrated to create a bootable USB for Arch Linux.
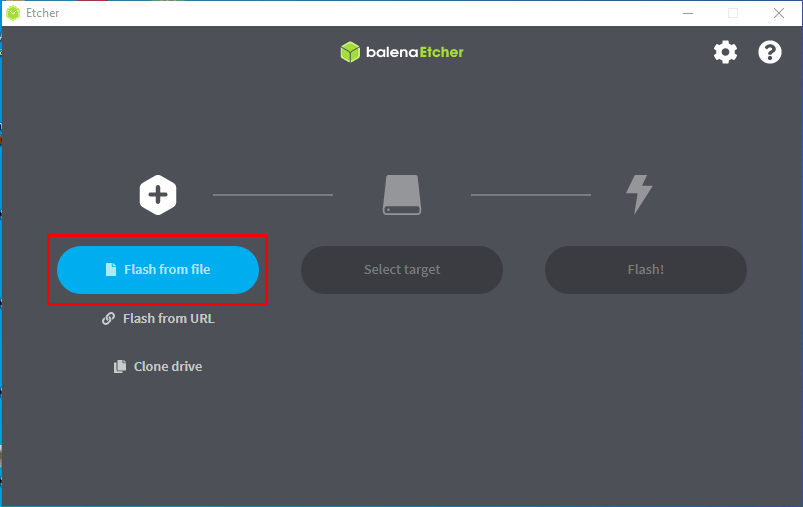
Step 1: Open the Etcher,
As you have downloaded the ISO file so, click on “Flash from file” and choose the ISO file where you have saved it.
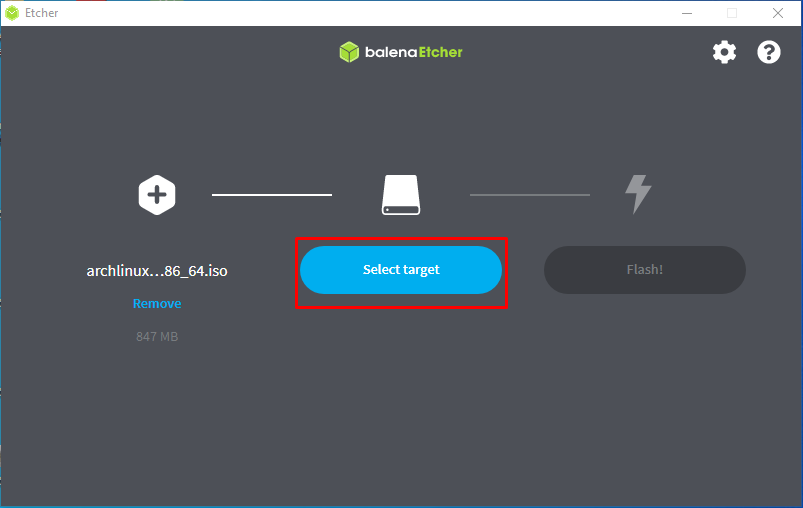
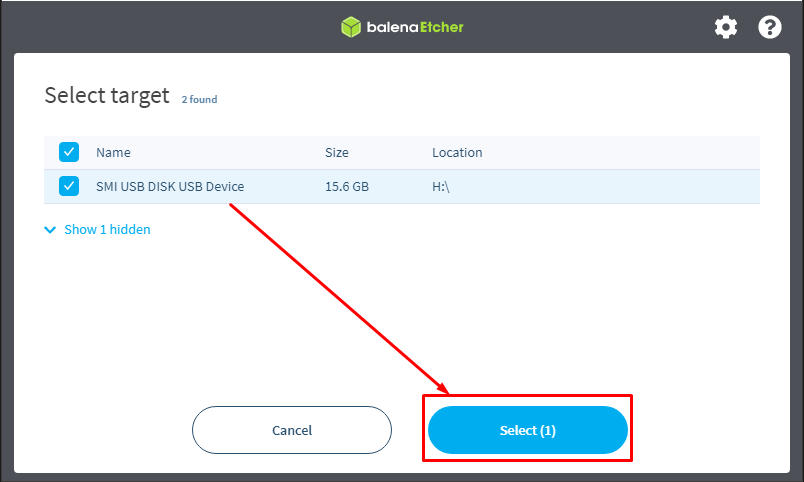
Step 2: After loading the file, choose “Select target“:
Choose the USB drive which will be used to map the ISO file of Arch Linux and click on “Select” to continue.
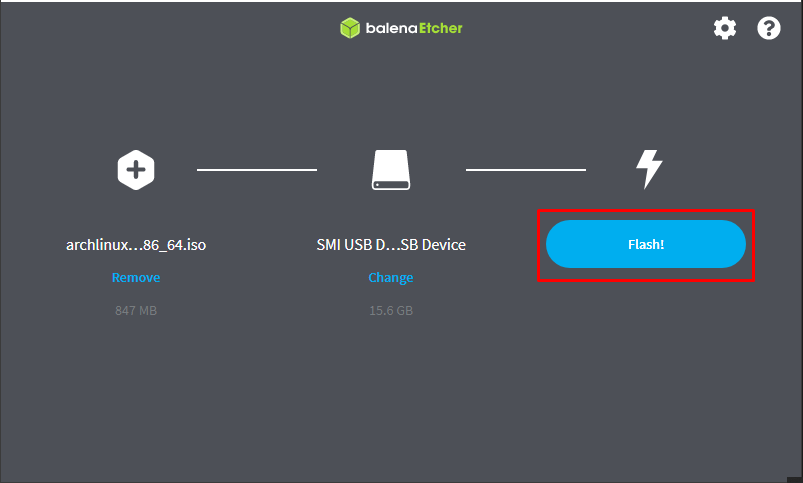
Step 3: You are now good to go for flash process. To do so, click on “Flash“:
It would take several moments, and you will get the following interface at the end.
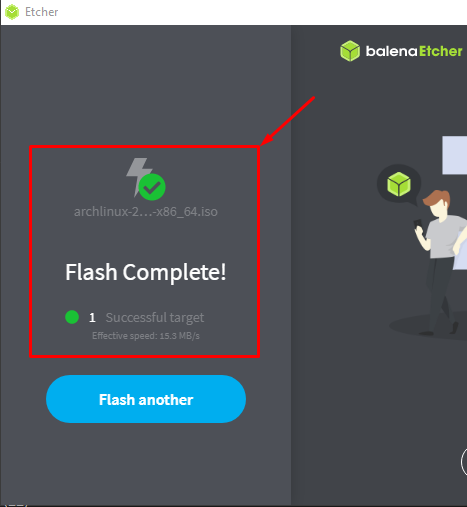
Congratulations! Flash Complete!
How to install Arch Linux for USB
To proceed with the steps in this process, you must have a USB that is ready to Boot.
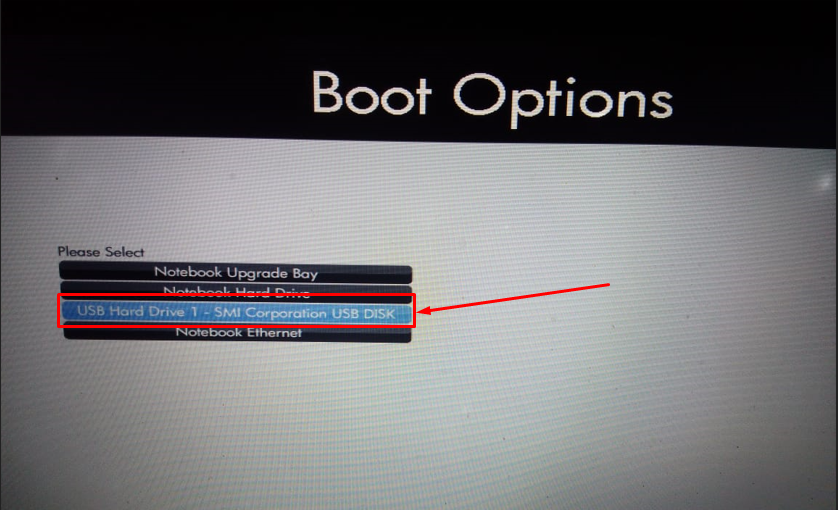
Step 1: Insert the USB and reboot your system, by entering the BIOS of your machine.
Step 2: Choose the relevant USB device that is set to Bootable
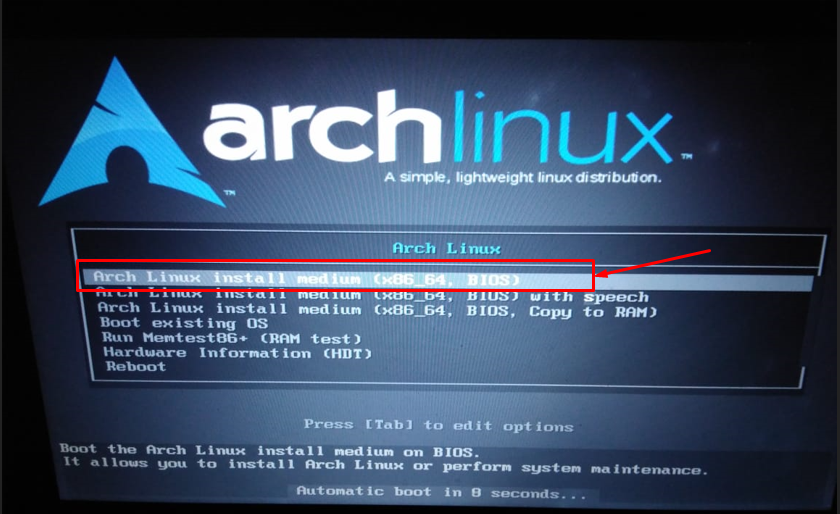
Once the boot is successful, you will get the following interface, choose the first one as shown below, or it will automatically be selected after a few moments.
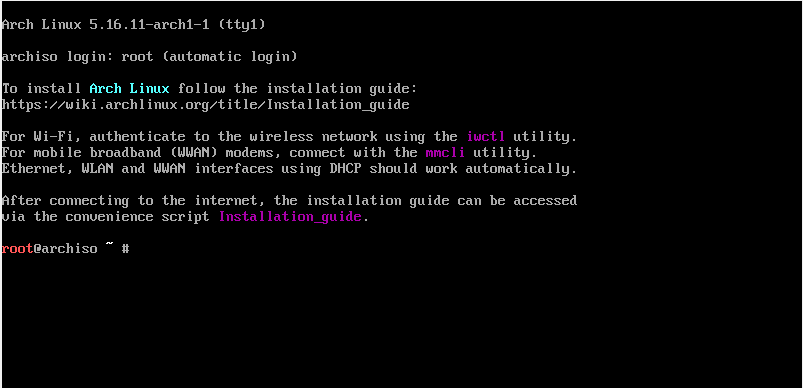
It will automatically load the prerequisites and after few times you will land inside the Arch terminal as can be seen below.
Wait, it is just a terminal and you have not made any partition to save the execution of your commands. At this moment, your data will not be stored as the operating system will process the execution on RAM.
How to setup Arch Linux
Here are the steps that must be performed to get the smooth performance of Arch Linux.
Step 1: Partitioning the disk
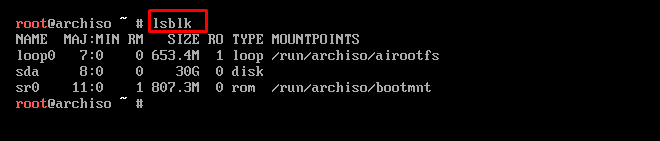
Currently, the drive is not mounted anywhere as can be observed in the output of the following command.
Step 1.1: Create BIOS boot partition
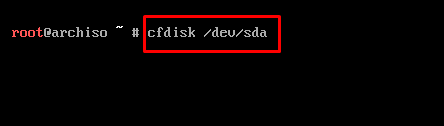
As our main memory is named “sda“, so let’s execute “cfdisk” command on “sda” partition to make the partition.
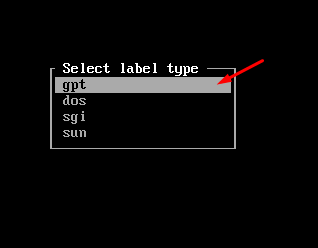
Choose the label type as “gpt“:
Now, you will land on the following interface,
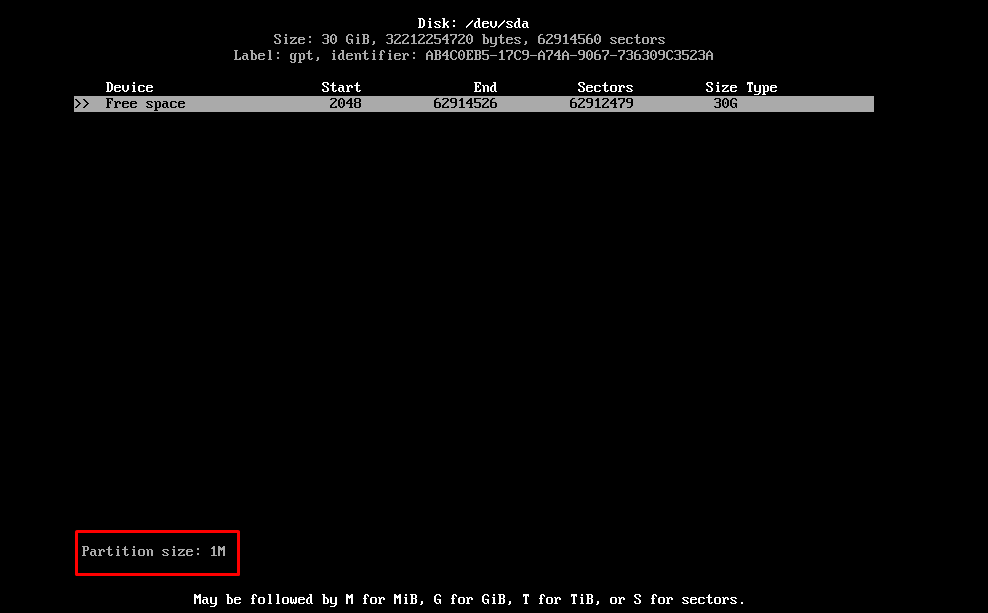
Create a portion of “size=1M“. By default, its type will be “Linux filesystem“. However, we have created this for BIOS boot, so, to change it, click on the “Type” option on the bottom of the window.
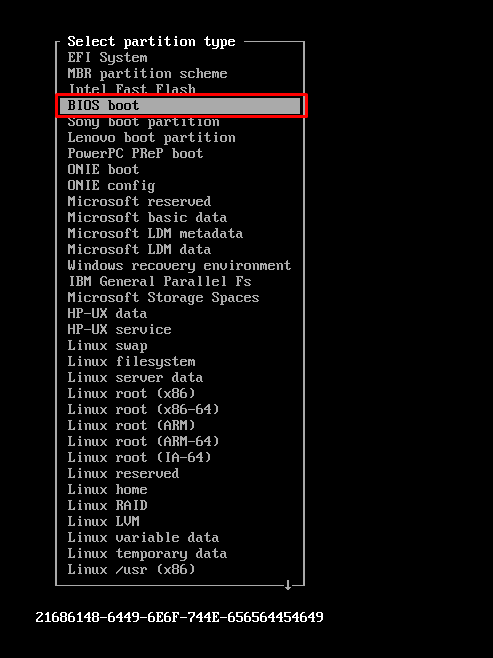
After clicking on “Type“, you would get a list of available disk types. Choose “BIOS boot” from here.
Step 1.2: Create Linux Swap
It is highly recommended to have a swap partition on your Linux system as it is quite helpful when your physical RAM is occupied. Whenever your RAM is full, the inactive programs are transferred to the swap partition to vacate some space on the RAM.
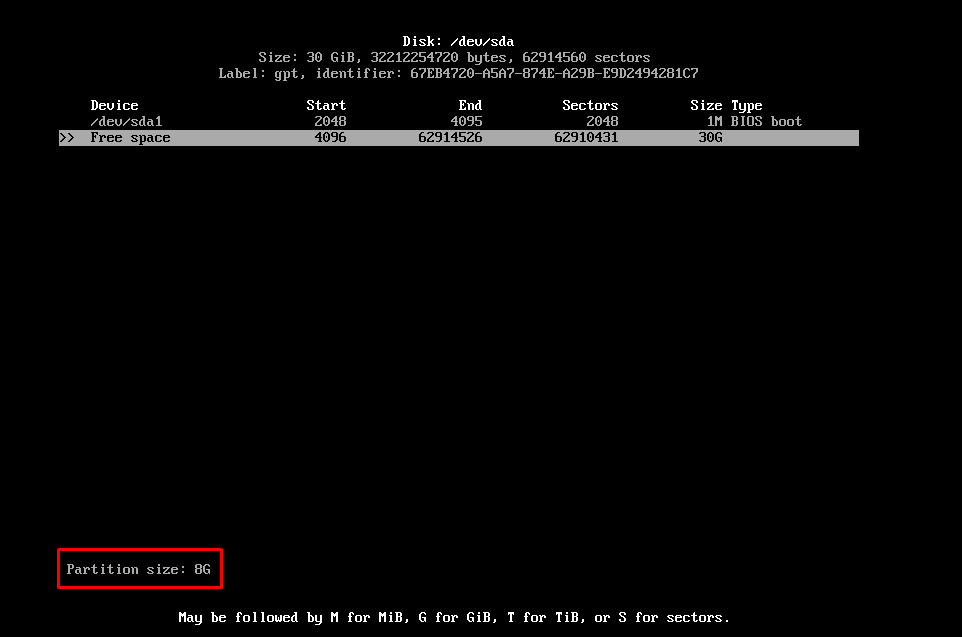
Click on “Free space” and create a partition of “8G” (Swap partition is recommended to be double of your RAM, so, in our case, it would be 8GB.):
Now click on the “Type” option placed on the bottom of the window:
And choose “Linux swap” partition as we did here.
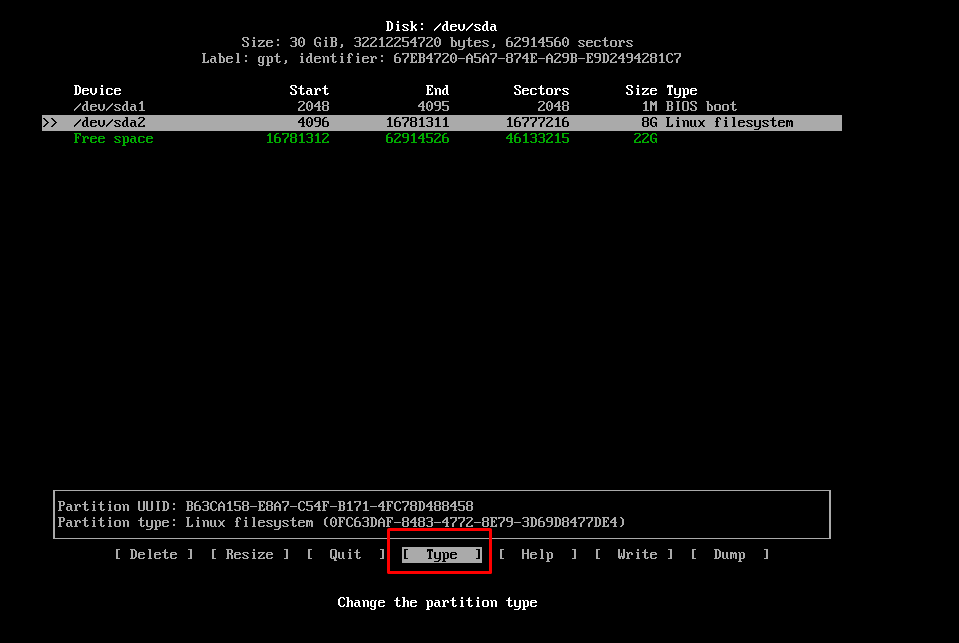
Step 1.3: Create Linux Filesystem
Set the “Type” of the rest of the free space to “Linux filesystem”
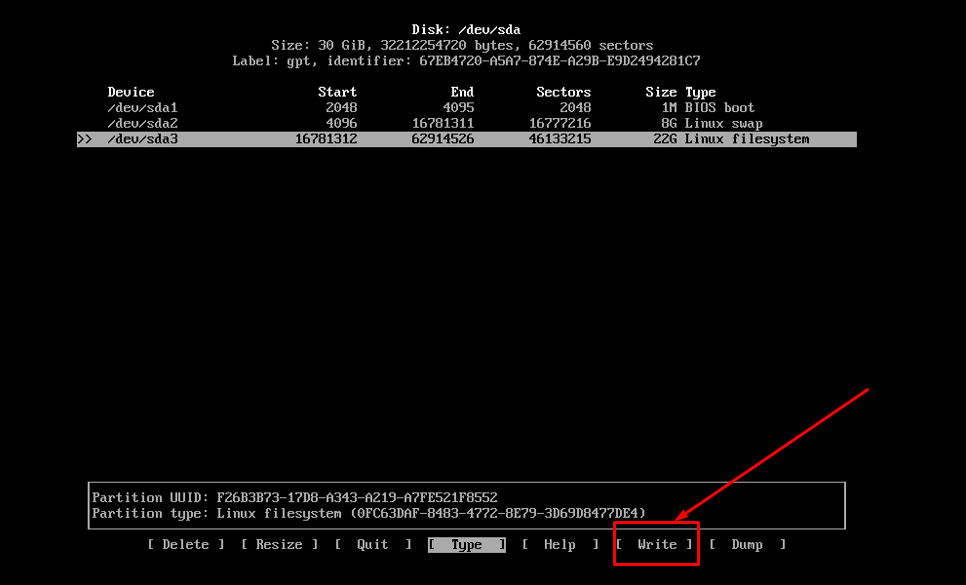
Once done, click on the “Write” option:
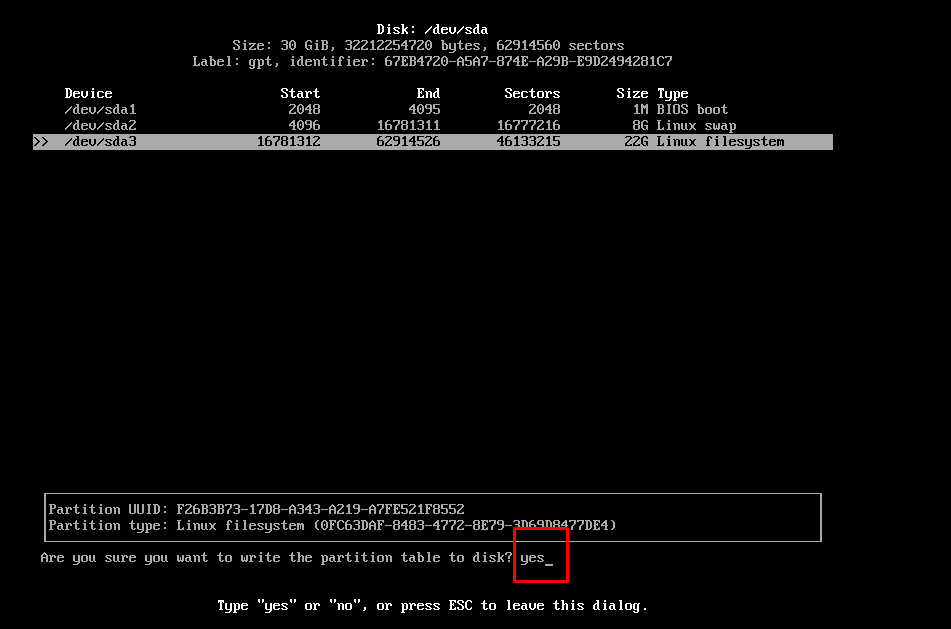
And type “yes” to make the changes permanent.
After doing so, you can observe the changes by issuing the following command.
The output shows that the “sda” is divided into “sda1”, “sda2”, and “sda3” that we made in step 1.
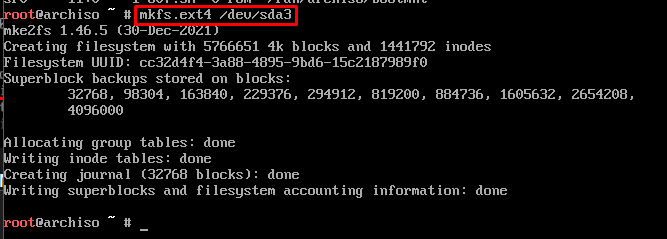
Step 2: Make the file system
After creating a partition, make the file system as per the partitions.
The “/dev/sda3” is our main partition, so we will set its file system to “ext4” by issuing the following command.
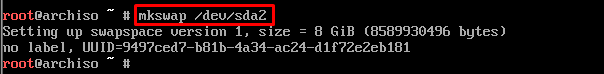
And for swap partition, the command would be as follows:
Lastly, enable the devices and filesystem for swap partition via the following command.
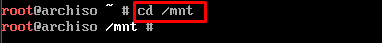
Step 3: Mount the storage device
In Linux, mounting is required to enable the user to use/open the files on the device storage. To do so, first change the directory to “mnt” as we did here:
Now use the mount command to mount the “/dev/sda3” to the “/mnt” directory by issuing the following command.
Step 4: Copy the operating system files
Once mounting is performed, you can use the “pacstrap” utility to perform the system installation of Arch on “/dev/sda3” (as we have mounted this storage device inside “/mnt” directory). In our case the command is as follows:
After copying OS files, now generate the fstab table to detect the mount points inside the directory “/mnt“.
Copy the “genfstab” output’s to “/mnt/etc/fstab” directory with the help of command provided here:
Step 5: Root account configuration
After mounting the device, change the root and point it towards the mount directory via the following command.
And set the password for the root account
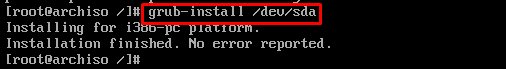
Step 6: Install GRUB for Linux Kernel
After creating the root user, use the following command to install GRUB on main device storage (“/dev/sda“) to load the Linux kernel at the startup.
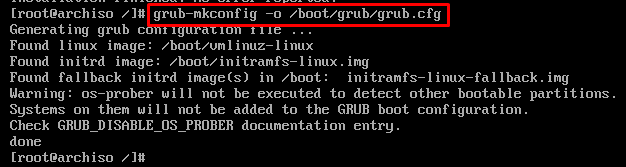
Meanwhile, generate the grub configuration file by issuing the following command.
Lastly, enable the dhpcpd service as it does not start by default. To do so, use the following command.
Congratulations! Here you go with Arch Linux.
Now you can install and configure your favorite programs/applications through Arch Linux.
Conclusion
Arch Linux is lightweight but equipped with the master features of Linux. An outline of the steps to install Arch Linux from USB is provided in this guide. First, you would have to make the USB bootable and then use that USB for installation. Additionally, we have presented various setup steps that are recommended to perform. By default, Arch ships with command line support which better suits an intermediate Linux user. However, it still needs various setup steps that we have illustrated here as well.