- Best Way to Run Android Apps and Games on Linux
- Why Running Android Apps Don’t Run Natively on Linux?
- 1. Anbox
- 2. Arc Welder
- 3. Genymotion
- 4. Android-x86
- 5. Android Studio IDE
- About the author
- David Morelo
- Best Ways To Use Android Apps In Ubuntu
- Android Statics
- Genymotion
- Genymotion Features At A Glance
- Download And Install Genymotion In Linux
- Android Studio
- Android Studio Features At A Glance
- Andyroid
- Andyroid Features At A Glance
- Bonus: Remix OS
- Remix OS Features At A Glance
- Conclusion
- Установка и запуск Android-приложений на Linux
Best Way to Run Android Apps and Games on Linux
It’s been some time since Android smartphones came into our lives. The Google Play Store is now home to around 3 million Android apps and games, many of which are so useful or entertaining that many Linux users would like to run them on their favorite operating system.
Thanks to the hard work of some talented developers, there are now multiple ways to run Android apps and games on Linux, and we describe seven of them in this article.
Why Running Android Apps Don’t Run Natively on Linux?
Considering that Android and Linux share the same kernel, one might assume that it would be easy to run Android apps natively on Linux, but it isn’t. That’s because the kernel is just the core of an operating system, and it takes a lot more software than just the kernel to run the applications you interact with on a daily basis.
Furthermore, Android APK files are not straightforward executables (like .exe files on Windows). They are essentially installer packages whose purpose is to extract files to certain specific locations. When executed, the extracted files call certain functions of the Android operating system to access the file system, hardware components, and so on.
Popular Linux distributions make no effort to be compatible with Android apps, so Linux users have to simulate Android devices on their computers using Android emulators or use an operating system that’s compatible with Android apps.
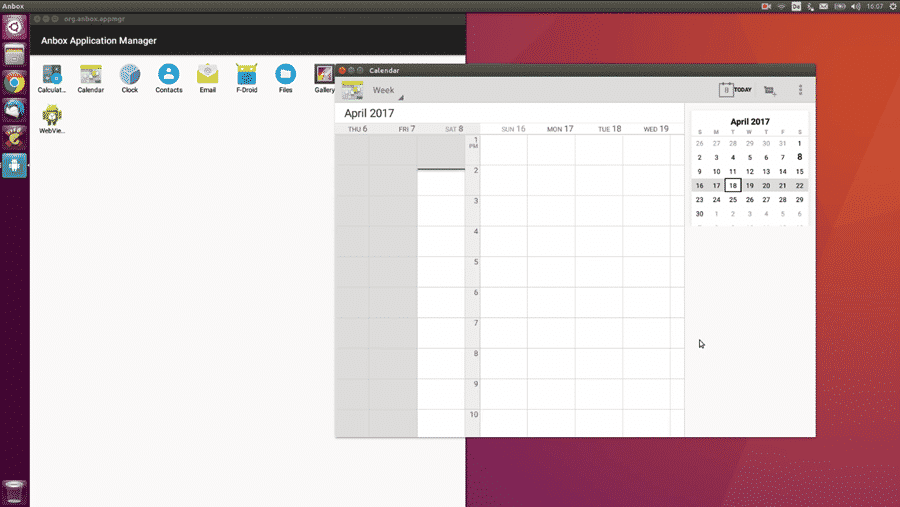
1. Anbox
Anbox is conceptually similar to Wine (a free and open-source compatibility layer that makes it possible to run Windows applications on Linux) because it abstracts hardware access and integrates Android applications with the Linux operating system.
The entire project is open source and licensed under the terms of the Apache and GPLv3 license. The goal of its developers is to make it so that every Android app and game can run on Linux. Because Anbox runs without hardware virtualization, it offers decent performance and tight integration with the host operating system.
Because Anbox is distributed exclusively as a snap (its developers claim that snaps make their lives much easier and allow them to frequently release updates without the need to customize them for multiple distributions), you can install it only on supported distributions unless you install Snap manually, which takes just a few simple commands, all of which are described in detail on Snap’s website.
With Anbox installed, you can add APKs using the Android Debug Bridge (adb). Afterward, you can launch your applications via the host system application launcher and manage them just like all other applications running on your system.
2. Arc Welder
If you’re a Google Chrome user, you can run Android apps on Linux using ARC Welder, also known as App Runtime for Chrome. This Chrome extension is actually intended to let Android developers test and publish their Android Apps to Chrome OS on other platforms, but that doesn’t mean you can’t use it for your personal purposes.
Because Arc Welder is a tool for developers, it doesn’t provide access to apps published in the Google Play Store. In order to run an Android app, you first need to find and download its APK file and then open the file using Arc Welder. Fortunately, there are many websites that let you easily download APK files, including APKMirror, APKPure, or APK Store.
Unfortunately, Arc Welder was last updated in June 2018, so bugs are to be expected. Still, you would be hard-pressed to find and easier way to run Android apps on Linux.
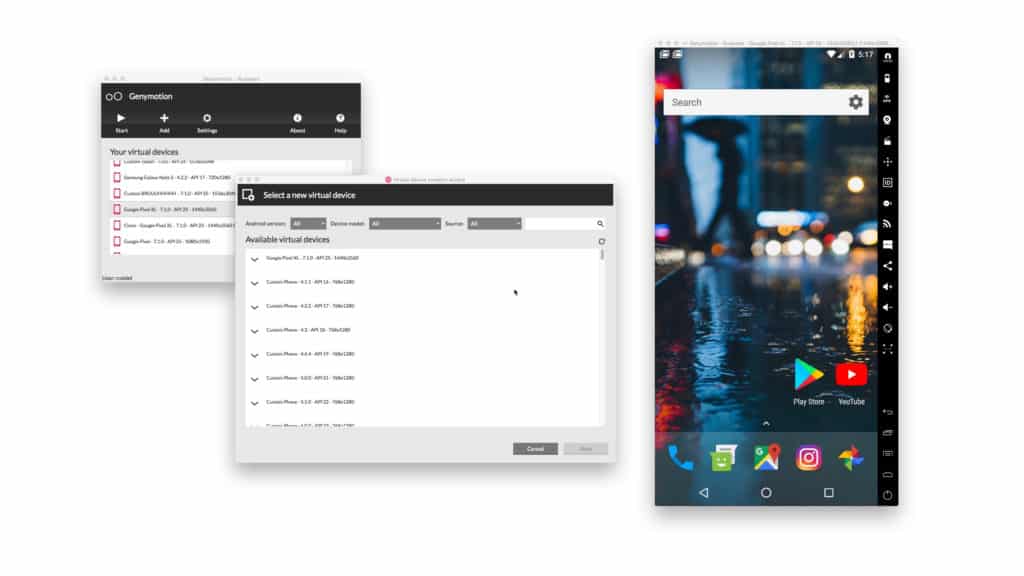
3. Genymotion
Because this is the year 2020, we can’t recommend the once-popular Android emulation solution called Shashlik anymore. The last version of Shashlik was released in 2016, and its developers have been quiet ever since. However, we can recommend something even better: Genymotion.
This cloud-based Android emulator is a boon to all Android developers who would like to streamline app testing and enjoy virtually unlimited scalability thanks to the computing power of Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and Alibaba Cloud.
Genymotion can emulate over 3,000 Android device configurations and simulate every imaginable scenario thanks to its full set of hardware sensors. The only problem is that you get only 60 minutes of use for free, and then it’s 5 cents per minute.
4. Android-x86
Android-x86 is a project whose aim is to port Android to the x86 instruction set. Because Android-x86 is a complete operating system, you need virtualization software like VirtualBox to run it inside your Linux distribution.
When setting up a VirtualBox virtual machine for Android-x86, Set Type to Linux, and Version to Linux 2.6 or newer. Allocate at least 2 GB of RAM and create a new hard disk image with 8 GB of storage space or more. Load the Android-x86 installation image and follow the official installation instructions.
When running Android-x86 inside a virtual machine, you can’t really expect great performance because Android-x86 is meant to run on bare metal.
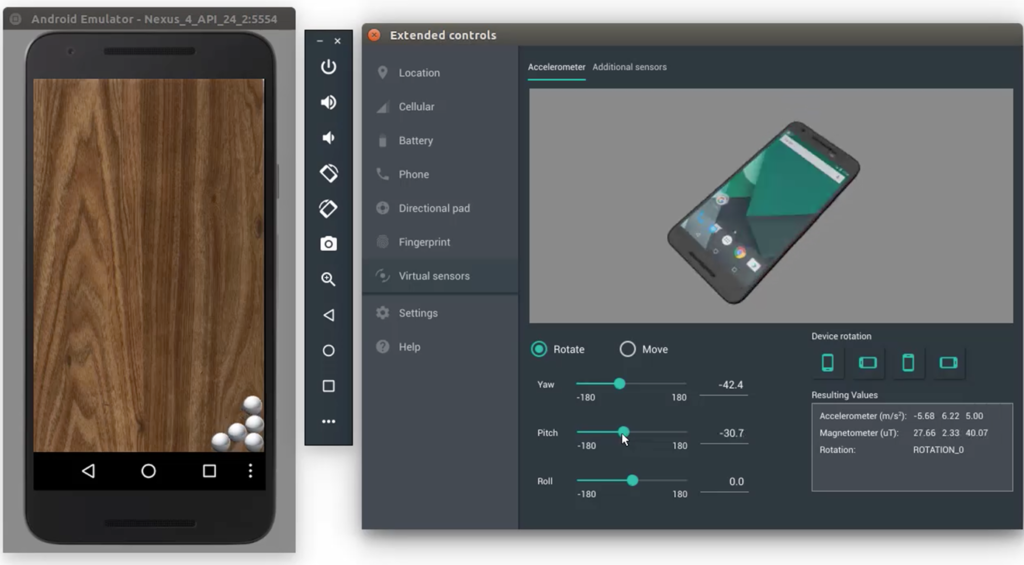
5. Android Studio IDE
Android Studio IDE is Google’s official integrated development environment for Android. It’s built on JetBrains’ IntelliJ IDEA software and runs on Linux, Windows, macOS, and Chrome OS. Included with Android Studio IDE is an Android emulator intended for running and debugging apps in the Android studio.
To install the emulator, choose the Android Emulator component in the SDK Tools tab of the SDK Manager. Open the app you want to run and click the green play-like button in the menu bars at the top. When asked to choose a device, click the Create New Virtual Device button and specify its properties. Once you’re finished, select it from the list of available virtual devices and click OK. The virtual device should start up right away and automatically open your application.
The Android Emulator inside Android Studio IDE doesn’t exactly amaze with its performance or usability, but it gets the job done when you just want to run a single Android app on Linux without installing it on your smartphone.
About the author
David Morelo
David Morelo is a professional content writer in the technology niche, covering everything from consumer products to emerging technologies and their cross-industry application
Best Ways To Use Android Apps In Ubuntu
Android, the most-used mobile operating system worldwide with tons of users, daily updates, releases and much more. So what if we could run some Android applications on your Linux distro? Play your android preferred game on a bigger screen? In this article, we will talk about a few available (but good) Android Emulators that allow us to run android in Linux. But first, let us see some android statistics.
Android Statics
- More than 1.4 billion users
- 87.7% of global share (November 2016)
- An average of 1.5 Million android activated devices every day
Genymotion
Genymotion is a multiplatform Android emulator with 5.5 Million registered users and more than 10,000 enterprise customers.
It can emulate more than 40 Android devices with access to all android versions and unlimited application installation. It is fast, reliable, memory efficient and is used by many Android developers for testing their applications.
Genymotion Features At A Glance
- Use your laptop webcam as the video source for your Android camera.
- Test your app with various charge levels and see how it handles those use cases.
- Genymotion works on Linux, Windows, Mac OS X.
- Use the GPS widget to easily develop and test your geolocation-based apps.
- Test your website in various Android browsers: Webkit for Android, Firefox for Android and much more.
- It allows us to easily Download pre-configured Android Images of various Android Versions.
- Supports drag and drop file transfer from the host to the virtual device.
Download And Install Genymotion In Linux
First, you need to be signed up on the Genymotion website to use the emulator. Genymotion runs as a virtual machine on top of VirtualBox so, for it to run, VirtualBox needs to be installed. Download Genymotion Personal Edition or a paid one.
Now install the app and you’re good to go.
Android Studio
It is an Android IDE provided by Google with the purpose of accelerating development and built of higher-quality applications.
Android Studio provides the fastest tools for building apps for every type of Android device. It allows code editing, debugging, performance tooling, a flexible build system, and an instant build/deploy system that allow you to focus on building unique and high-quality apps.
Android Studio Features At A Glance
Instant run – when clicking run/debug Android Studio’s Instant Run feature pushes code and resource changes to your running app, it runs the apps without having to redeploy the whole app for seeing the changes immediately.
Intelligent code editor – for developers, the code editor helps you write better code, work faster, and be more productive by offering advanced code completion, refactoring, and code analysis;
Optimized for all android devices and versions.
Andyroid
Although it still on closed alpha for Linux they accept the invitation for testers. You can use it as a full operational android for playing games on your desktop, WhatsApp, and other messaging applications. It uses the host network and unlimited storage.
Andyroid Features At A Glance
- Full Android UI
- Google Play Store
- App Sync to Mobile
- Phone as Controller
- Android access to local File System
- Multi-Touch support
- Cloud Save in Android
- X86 native apps
- ARM support
- Sensors Integration
- OpenGL Hardware support
- Camera Integration
- Microphone Integration
- Hardware Console
- Run Apps from Desktop
- Desktop Push Notifications
- Developers Support
Bonus: Remix OS
This one is not an emulator but deserves to be on this list. Remix OS is an Android OS that can run android applications and games on your PC.
Remix OS Features At A Glance
- Multiple window multi-tasking.
- Play multiple games simultaneously while chatting with your friends.
- multi-window support means you can spend less time switching between screens and more time doing what you want and need to do.
- PC taskbar on Android start menu notifications.
- PC keyboard shortcuts and mouse right-click use.
- Use your mouse and keyboard with Remix OS just as you would on a PC.
- PC file manager comes with an amazing collection of functionalities for access, transfer, and save files.
- Android mobile screen capture, allows you to target specific apps and games so you don’t have to waste time cropping it out later.
- Free OTA updates.
Conclusion
Lately, even if you don’t own an Android device you can still have the option of running some applications or games (for example, WhatsApp, Contacts, Gmail, etc). Android is widely used worldwide and keeps growing and getting polished every day.
So What emulator would you use or will opt to the Installable Operating System? Let me know in the comment section below. If you use any other emulator to run android apps in Linux, share it with us in the comment section below.
Установка и запуск Android-приложений на Linux
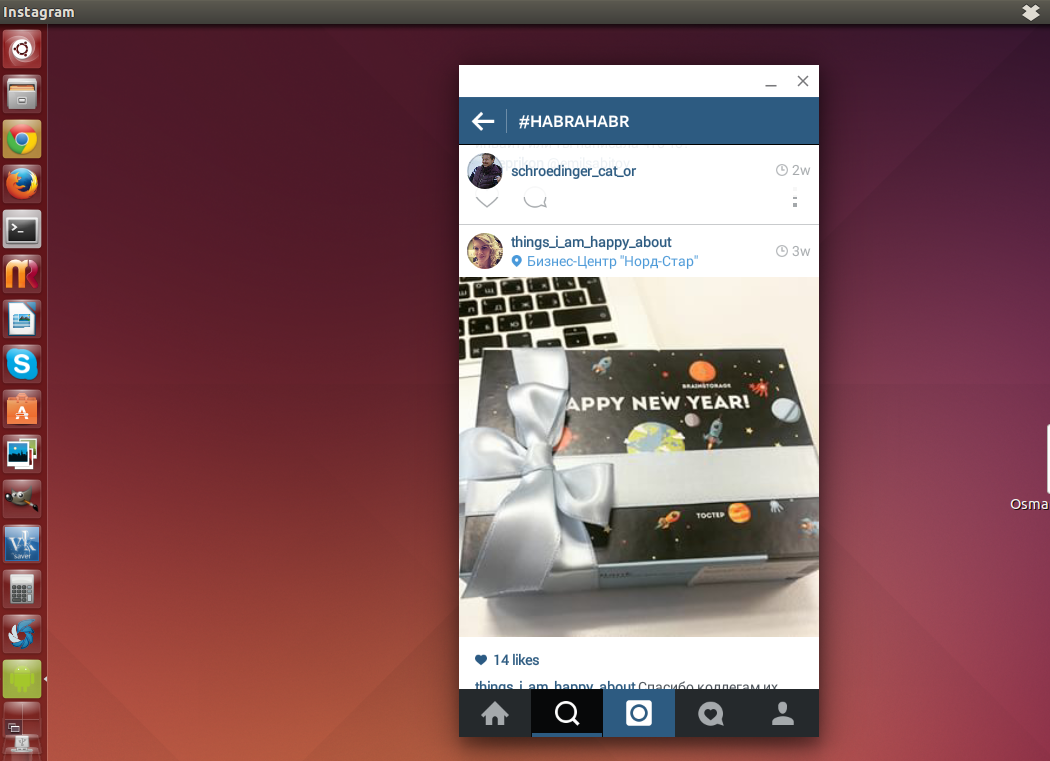
Как известно, многие Android-приложения можно нативно запускать на Chrome OS благодаря библиотеке Chrome App Runtime.
С помощью расширений chromeos-apk и ARChon запуск Android APK стал возможен и на других ОС.
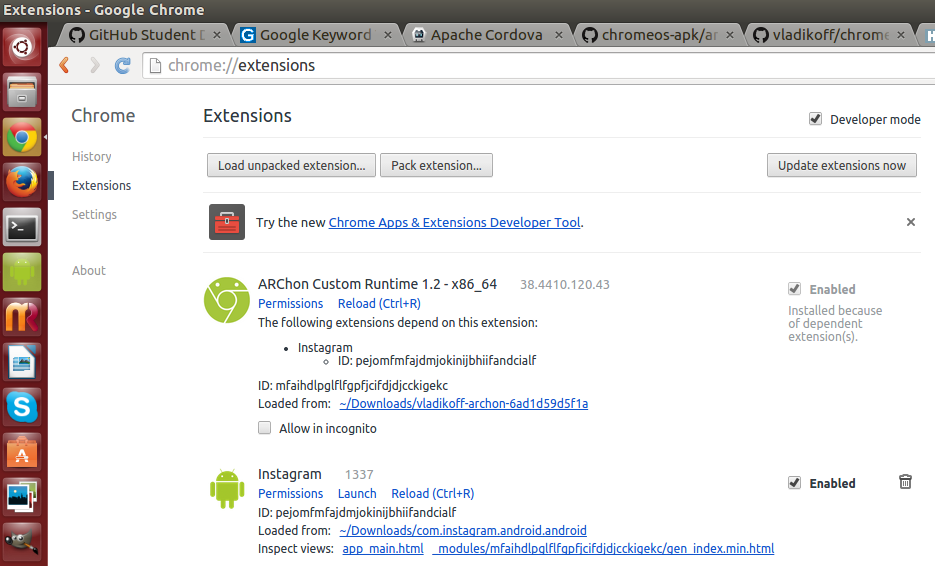
Устанавливаем ARChon Runtime
1) Скачиваем и распаковываем ARChon в произвольную дирректорию;
2) Открываем Chrome и включаем Developer mode в chrome://extensions/;
3) Кликаем «Load unpacked extension» и устанавливаем распакованный ARChon.
Далее необходимо подготовить архив APK для установки.
Устанавливаем chromeos-apk
1) Для Ubuntu прежде всего нужно установить библиотеку lib32stdc++6:
sudo apt-get install lib32stdc++6 2) chromeos-apk можно установить с помощью менеджера пакетов npm (поставляется вместе с node.js).
3) Сейчас можно установить непосредственно chromeos-apk:
npm install chromeos-apk -g Теперь все готово к распаковке APK.
Подготавливаем APK с помощью chromeos-apk
1) Для распаковки APK-архива выполняем:
chromeos-apk path/to/file.apk 2) Теперь у нас есть Chrome-APK расширение, и все что нужно — загрузить (chrome://extensions/) и запустить его.
UPD: полезные ссылки от sequence
ARChon Packager: создает архивы для archon из установленных в телефоне приложений.
twerk: расширение хром, сильно облегчает конвертацию apk.