- How to Manage Users and Groups on Ubuntu 22.04
- A Quick Overview
- 1. Create a new user
- 2. Understanding the /etc/passwd file
- 3. Change the login name of a user
- 4. Change the user ID of a user
- 5. Change the group of a user
- 6. Add a user to the sudoers group
- 7. Change the password of a user
- 8. Delete a user
- 9. Delete a home directory of a user
- 10. Add a new group
- 11. Understanding /etc/group file
- 12. Create a system group
- 13. Add a new group with specific GID
- 14. Remove a user from the group
- 15. Delete a group
- Conclusion
- Users and groups administrations from the command line in Linux
- Creating groups under Linux:
- Creating users under Linux:
- Command adduser vs useradd
- Creating or changing a user password under Linux:
- Modifying users under Linux:
- Lock/Unlock user account
- Deleting users under Linux:
- Modifying groups under Linux:
- Deleting groups under Linux:
- Graphic user and groups management under Ubuntu Linux (Gnome)
- About the author
- David Adams
How to Manage Users and Groups on Ubuntu 22.04
Linux is a multi-user and multi-tasking operating system. User and group management are the two most important tasks to be performed by Linux administrators.
In Linux, each user has their own login name and a home directory. Every user belongs to a primary group, and users can be added to multiple secondary groups. All users in the group will have the same group permission on files and folders. This makes it easier to provide permission for multiple users.
This tutorial will demonstrate how to manage users and groups in the Linux system.
A Quick Overview
The command-line tools to manage the users and groups in Linux are:
adduser / useradd : To add a user
addgroup / groupadd : To add a group
usermod : To modify a user account
deluser / userdel : To delete a user
delgroup / groupdel : To delete a group
passwd : To change the user’s password
We will cover the practical examples of all commands in this article. To follow the tutorial, you will need to switch to the root user or any user with sudo privileges.
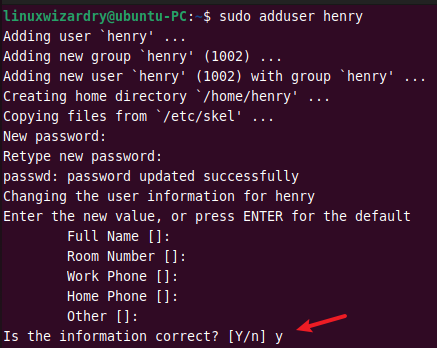
1. Create a new user
You can add a new user to the system using the adduser command. The following command creates a new user henry in the system.
It will prompt you to enter the password for the new user and other user details.
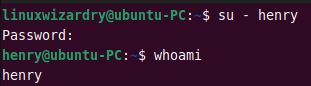
To verify the user, you can try to log in as a new user.
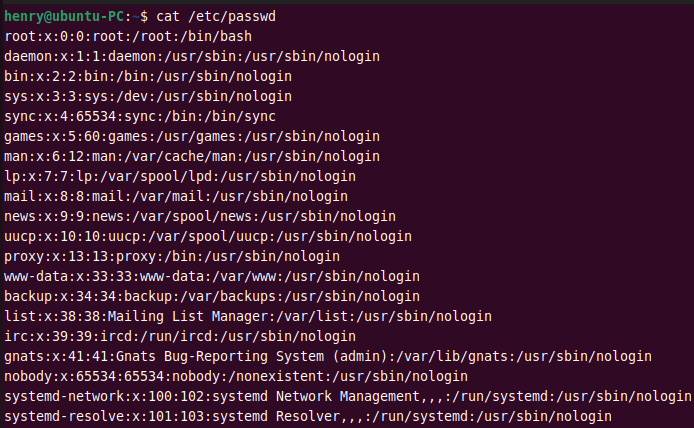
2. Understanding the /etc/passwd file
The /etc/passwd is a plain text file that stores the user account information in Linux. You can use the cat command to view the content of /etc/passwd .
Each user has one entry per line. The fields are separated by a colon : symbol and contains the following information.
username:password:UID:GID:GECOS:home_directory:shell
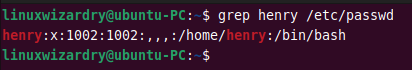
The new entries are saved at the end of a file. To find a user henry , you can see the last entries. Alternatively, you can use the grep command.
3. Change the login name of a user
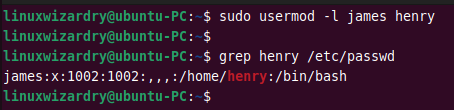
You can use the usermod command to change a user’s login name in Linux. This command renames the user henry to james .
$ sudo usermod -l james henry
As you can see, the username is changed to james .
4. Change the user ID of a user
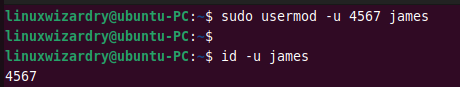
By default, the system automatically sets the next available UID when creating a user. The usermod command with -u flag can be used to change the UID of a user.
The following command changes the user ID of james to 4567 .
$ sudo usermod -u 4567 james
5. Change the group of a user
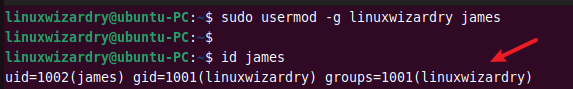
The -g option with usermod command changes the primary group of a user. For example, to change the primary group of a user james to linuxwizardry , you can run this command.
$ sudo usermod -g linuxwizardry james
The specified group must already exist in the system.
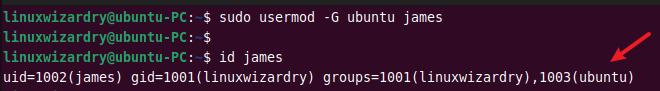
In Linux, a user can have only one primary group. But you can assign a user to multiple secondary groups. The -G flag allows you to specify the secondary group for a user.
The following command adds a user james to the group ubuntu .
$ sudo usermod -G ubuntu james
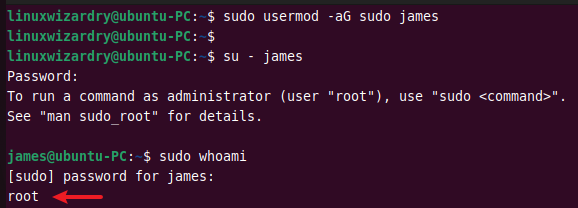
6. Add a user to the sudoers group
You can add a user to the sudoers group and provide sudo privileges to that user. This command adds a user james to the sudo group.
$ sudo usermod -aG sudo james
The -a option adds a user to the group without removing the current group.
Next, log in as a user james and run the sudo command to confirm.
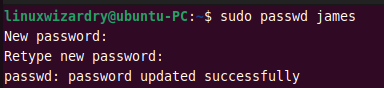
7. Change the password of a user
The passwd command is used to change the user’s password in Linux. The following command changes the password of a user james .
8. Delete a user
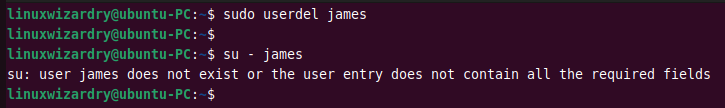
When the user account is not needed, you might want to delete it from the system. The userdel command helps to remove a user in Linux.
The below command deletes a user james from the system.
9. Delete a home directory of a user
The usedel command without any flags only removes a user. It does not delete the home directory of a user in the /home directory.
To delete a user along with its home directory, you can use:
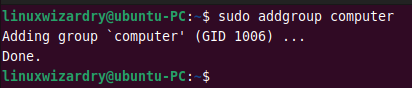
10. Add a new group
You can add a new group to the system using the groupadd or addgroup command. The following example creates a new group computer on the system.
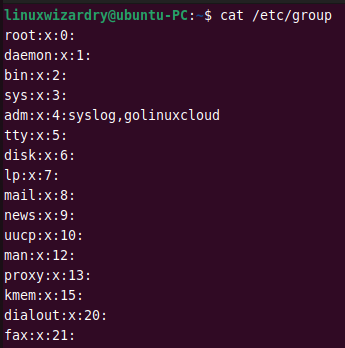
11. Understanding /etc/group file
The /etc/group file stores the group details in a list. Each entry contains the following group information for each group.
group_name:group_pwd:group_id:group_list
You can display the entries in /etc/group file with the cat command.
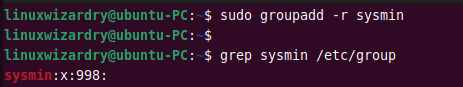
12. Create a system group
If you need to add a new system group, you can use the -r flag with the groupadd command. This command creates a new system group sysmin .
Output:
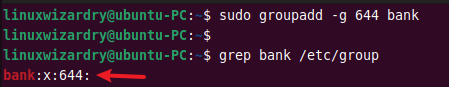
13. Add a new group with specific GID
When creating a new group, the system assigns the next available group ID by default. You can change this behavior and specify a GID for a new group with the -g flag.
The following command creates a new group bank with a custom group ID 644 .
Output:
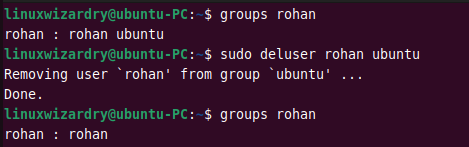
14. Remove a user from the group
Sometimes you might need to remove a user from the secondary groups. You can do it by specifying the username and group to the deluser command.
The below command removes a user rohan from the group ubuntu .
$ sudo deluser rohan ubuntu
Output:
15. Delete a group
You can remove a group from the system using the delgroup or groupdel command.
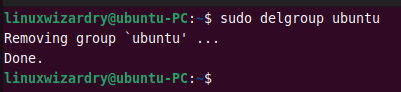
To delete a group ubuntu , run the following command.
Output:
If the specified group is the primary group of any user, it cannot be deleted. You must first change the primary group of a user.
Conclusion
Managing users and groups is one of the essential skills for every Linux administrator. You have learned the different examples of user and group management commands in Linux. Now you know how to perform the tasks like creating new users and groups, adding users to groups, changing the username and password, deleting users and groups, and much more.
We hope you found this article helpful. Please let us know if you have any confusion about any examples in the comment section below.
Users and groups administrations from the command line in Linux
Linux offers us a lot of useful tools to keep our environment’s safety and order, assigning or denying permissions to users and groups is a primary tool on any linux system. For security reasons only root users and users within the sudo group are able to manage users and groups.Through the command line, it is easy to create and modify or remove users, to restrict or release permissions, while allowing us to log users activity.
To manage permissions lets start by becoming the root user. Enter the command “su” to become root and press “Enter”, type the password when requested. If you don’t have root access we must use the sudo command before running a privileged command. For information on sudo you can read Managing sudo privileges.
Note: remember Linux is a case sensitive OS.
After authenticating we can manage users and groups.
Creating groups under Linux:
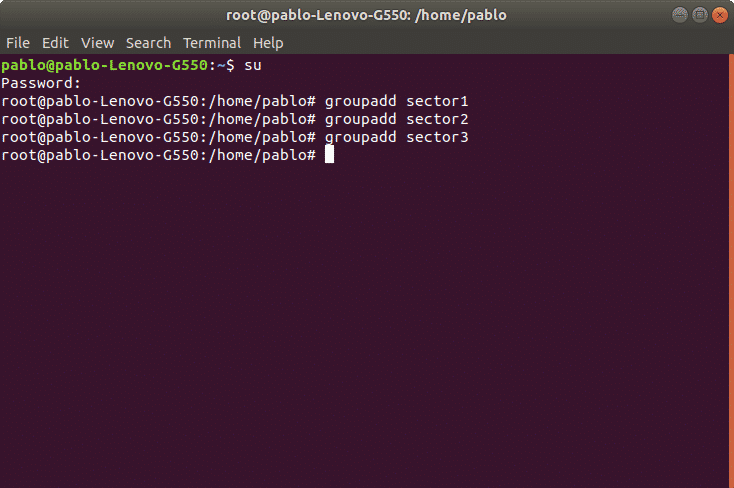
To create groups we’ll use first the command “groupadd” followed by the group’s name. The syntax is: “groupadd ”.
In the following picture is an example where I create three groups: sector1, sector2 and sector3. To do it on the command line type:
Once the groups are created we can create users to be assigned to the groups.
Creating users under Linux:
Using the command “useradd” we can add a user to our system. The proper syntax is “useradd [options] ”
Among the most used options we have:
-g Main user group (gid)
-d User Home directory, by default located at /home/
-m Create Home directory in case it doesn’t exist.
-s Assign a specific shell to the user, by default it is /bin/bash.
As an example we will create the user nicolas and will assign him the group sector1, also we’ll define the user’s home and shell.
Now we’ll do the same with user martin to be added to group sector2, and a third user ivan for sector3. We’ll use the same syntax:
Command adduser vs useradd
While the command useradd runs a system binary file the command adduser is a perl script to interact with useradd. With the adduser command, the advantage is the home is created automatically. If using the command adduser we need to specify the -m option.
Creating or changing a user password under Linux:
After adding a user with the command “useradd” we need to set a password for the user using the command “passwd”. Remember Linux is case sensitive.
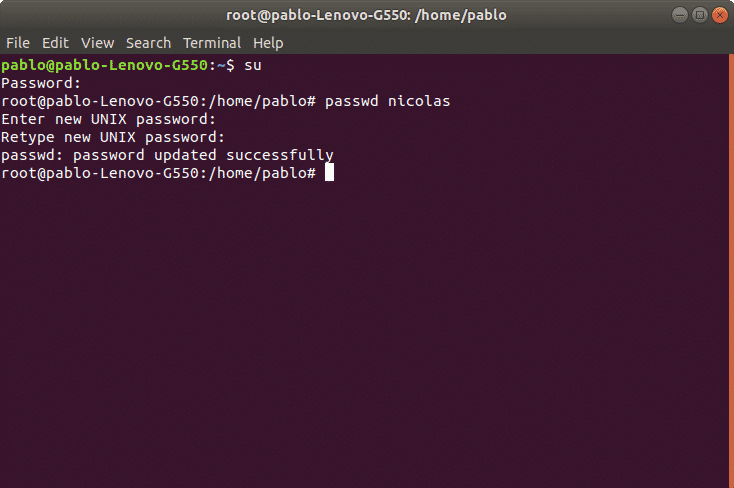
In the following example we’ll create a password for the user nicolas using the following syntax:
Then it will request for password and confirmation, after confirmation the password will be established. We can know the process succeeded when the system returns “password updated successfully” like in the image:
passwd nicolas
Enter new UNIX password: ( ingresar contraseña )
Retype new UNIX password: ( repetir contraseña )
passwd: password updated successfully
Modifying users under Linux:
We can edit the user’s username, his home directory, his shell and groups to which he belongs among more options. For this we’ll use the command “usermod”.
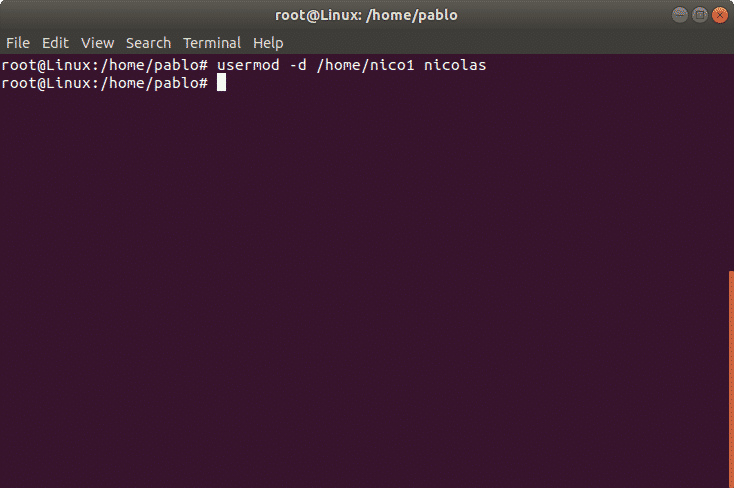
As an example we’ll modify the user nicholas’ home directory which we previously defined as /home/nicolas and we’ll replace it for /home/nico1.
The previous command updated the user’s home.
Lock/Unlock user account
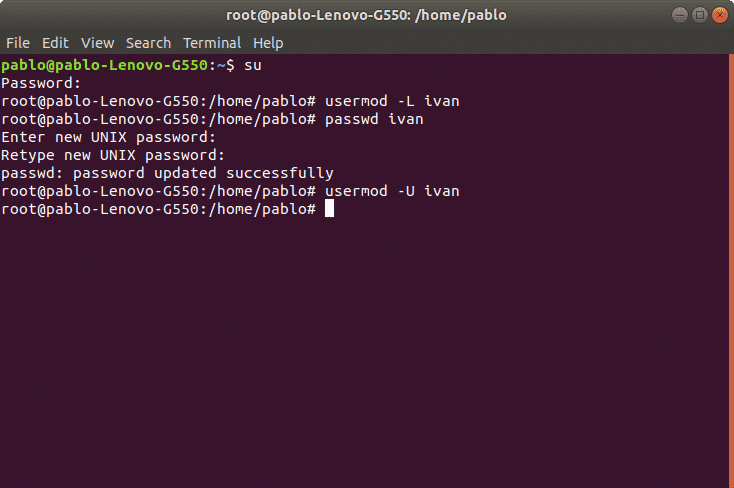
We can also lock a user account. In the following example we’ll lock user ivan account. The parameter -L (lock) will block the user account. The syntax is:
To enable a locked user we can use the -U (Unlock) parameter. In the following example we will unlock the user ivan:
Deleting users under Linux:
We can remove a user with the command userdel followed by the username. We can also combine parameters, among most used options we have:
-f remove user files.
-r remove user home and mail tail.
In the following example we’ll delete the user account “ivan”
Note: The command “userdel” won’t remove the user if is running process.
Modifying groups under Linux:
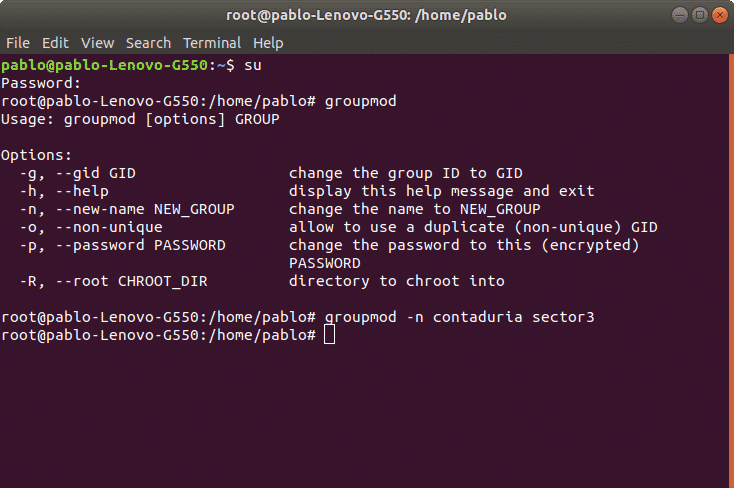
In order to modify groups we’ll use the command “groupmod”. This command allows to modify a group name or user gid. The syntax is:
In the following example we’ll modify the group name for “sector3” to “contaduria”
Deleting groups under Linux:
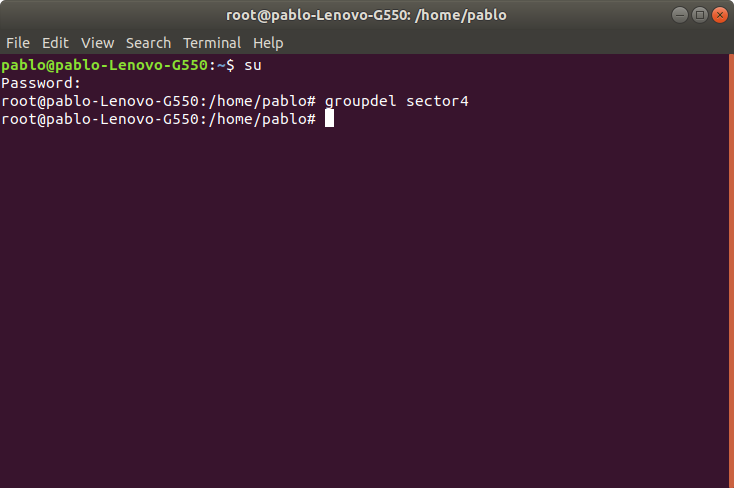
We can remove a group using the command “groupdel” followed by the group name. For example, to remove the group sector4 we’ll use the following syntax:
In this case it would be just:
Note: If another user is a member of the group we try to remove, the command won’t remove the group.
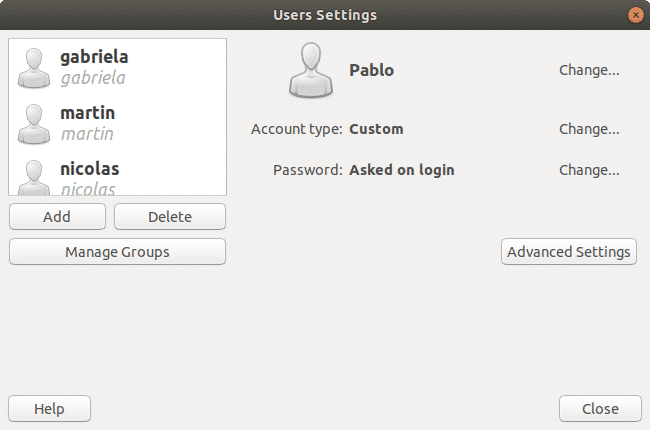
Graphic user and groups management under Ubuntu Linux (Gnome)
Ubuntu offers a graphical management for users and groups. The interface is user friendly, intuitive and easy to use.
If we haven’t installed this interface on the terminal run:
When asked for confirmation press “Y” and “enter”
The following NEW packages will be installed
Once finished we can run the tool from the command line as “users-admin”
Thank you for reading this article. Now you can easily manage users and groups on linux.
About the author
David Adams
David Adams is a System Admin and writer that is focused on open source technologies, security software, and computer systems.