- How do you change the default shell for ALL USERS to bash?
- 3 Answers 3
- 3 способа изменить оболочку пользователя по умолчанию в Linux
- 1. Утилита usermod
- 2. Утилита chsh
- 3. Измените оболочку пользователя в файле /etc/passwd.
- 3 Ways to Change a Users Default Shell in Linux
- 1. usermod Utility
- 2. chsh Utility
- 3. Change User Shell in /etc/passwd File
- How to Change the Default User Shell in Linux OS
- Find the current shell name
- List available shells in Linux
- Changing default sh shell to bash shell
- Using chsh utility
- Using usermod command
- By editing in passwd file
- Change the current user shell
- Conclusion
How do you change the default shell for ALL USERS to bash?
I want every new user from now on to have bash as their shell by default. I know that to change your own shell to bash, you would use the command «chsh -s /bin/bash», but how do I automatically set all future users’ shell to bash by default?
3 Answers 3
The adduser defaults file is /etc/adduser.conf . The default shell defined by the DSHELL variable is /bin/bash by default.
Most likely you don’t need this because useradd is a very low-level utility, and it’s hardly ever used directly.
If you use useradd, edit the /etc/default/useradd skeleton file (don’t forget to make a backup though).
Set the SHELL variable to /bin/bash instead of /bin/sh .
Now every time you use useradd to add a new user bash is automatically their default shell.
Already existing users
If you want to change the shell of already existing users you have to edit the /etc/passwd file (please make sure to back have a backup of it).
Here is a description of the columns
- login name
- optional encrypted password
- numerical user ID
- numerical group ID
- user name or comment field
- user home directory
- optional user command interpreter
In that order separated by colons (:) like this.
For more information about that file consult the man page man 5 passwd .
3 способа изменить оболочку пользователя по умолчанию в Linux
В этой статье мы расскажем, как изменить оболочку пользователя в Linux. Оболочка — это программа, которая принимает и интерпретирует команды; есть несколько оболочек, таких как bash, sh, ksh, zsh, fish и многие другие менее известные оболочки, доступные в Linux.
Bash (/bin/bash) — это популярная оболочка в большинстве, если не во всех системах Linux, и обычно она используется по умолчанию для учетных записей пользователей.
Существует несколько причин для изменения пользовательской оболочки в Linux, включая следующие:
- Чтобы заблокировать или отключить обычный вход пользователей в Linux с помощью оболочки nologin.
- Используйте сценарий или программу-оболочку оболочки для входа в пользовательские команды перед их отправкой в оболочку для выполнения. Здесь вы указываете оболочку оболочки в качестве оболочки входа пользователя.
- Для удовлетворения требований пользователя (желающего использовать определенную оболочку), особенно с правами администратора.
При создании учетных записей пользователей с помощью утилит useradd или adduser можно использовать флаг —shell для указания имени оболочки входа пользователя, отличного от указанного в соответствующих файлах конфигурации.
Доступ к оболочке входа можно получить из текстового интерфейса или через SSH с удаленного компьютера Linux. Однако, если вы входите в систему через графический интерфейс пользователя (GUI), вы можете получить доступ к оболочке из эмуляторов терминала, таких как xterm, konsole и многих других.
Давайте сначала перечислим все доступные оболочки в вашей системе Linux, введите.
# cat /etc/shells /bin/sh /bin/bash /sbin/nologin /bin/tcsh /bin/csh /bin/dash
Прежде чем продолжить, обратите внимание, что:
- Пользователь может изменить свою оболочку на любую вещь, которая, однако, должна быть указана в файле /etc/shells.
- Только root может запускать оболочку, не указанную в файле /etc/shells.
- Если учетная запись имеет ограниченную оболочку входа, только root может изменить оболочку этого пользователя.
Теперь давайте обсудим три разных способа изменить пользовательскую оболочку Linux.
1. Утилита usermod
usermod — это утилита для изменения данных учетной записи пользователя, хранящихся в файле /etc/passwd, а параметр -s или —shell используется для изменения оболочки входа пользователя.
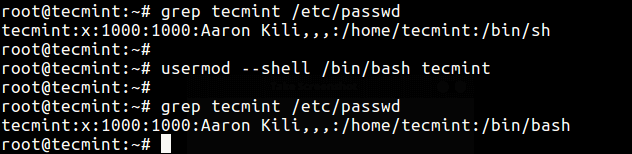
В этом примере мы сначала проверим информацию об учетной записи пользователя tecmint, чтобы просмотреть его оболочку входа по умолчанию, а затем изменим ее оболочку входа с /bin/sh на /bin/bash как следует.
# grep tecmint /etc/passwd # usermod --shell /bin/bash tecmint # grep tecmint /etc/passwd
2. Утилита chsh
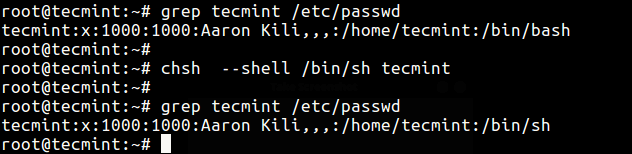
chsh — это утилита командной строки для изменения оболочки входа в систему с помощью параметра -s или -shell, подобного этому.
# grep tecmint /etc/passwd # chsh --shell /bin/sh tecmint # grep tecmint /etc/passwd
Два приведенных выше метода изменяют оболочку, указанную в файле /etc/passwd, который вы можете редактировать вручную, как в третьем методе ниже.
3. Измените оболочку пользователя в файле /etc/passwd.
В этом методе просто откройте файл /etc/passwd с помощью любого из ваших любимых текстовых редакторов командной строки и измените оболочку конкретного пользователя.
Когда закончите редактирование, сохраните и закройте файл.
Не забудьте прочитать эти связанные темы:
- Знакомство с файлами инициализации оболочки и профилями пользователей в Linux
- Понимание Linux Shell и советов по написанию сценариев Basic Shell — часть I
- Как писать и использовать собственные функции и библиотеки оболочки
- Знакомство с различными классификациями команд оболочки и их использованием
В этой статье мы описали различные способы смены оболочки пользователя в Linux. Чтобы поделиться с нами своими мыслями, используйте раздел комментариев ниже.
3 Ways to Change a Users Default Shell in Linux
In this article, we will describe how to change a user’s shell in Linux. The shell is a program that accepts and interprets commands; there are several shells such as bash, sh, ksh, zsh, fish and many other lesser known shells available on Linux.
Bash (/bin/bash) is a popular shell on most if not all Linux systems, and it’s normally the default shell for user accounts.
There are several reasons for changing a user’s shell in Linux including the following:
- To block or disable normal user logins in Linux using a nologin shell.
- Use a shell wrapper script or program to login user commands before they are sent to a shell for execution. Here, you specify the shell wrapper as a user’s login shell.
- To meet a user’s demands (wants to use a specific shell), especially those with administrative rights.
When creating user accounts with the useradd or adduser utilities, the —shell flag can be used to specify the name of a user’s login shell other than that specified in the respective configuration files.
A login shell can be accessed from a text based interface or via a SSH from remote Linux machine. However, if you login via a graphical user interface (GUI), you can access the shell from a terminal emulators like xterm, konsole and many more.
Let’s first list all available shells on your Linux system, type.
# cat /etc/shells /bin/sh /bin/bash /sbin/nologin /bin/tcsh /bin/csh /bin/dash
Before you proceed any further, note that:
- A user can change their own shell to any thing: which, however must be listed in the /etc/shells file.
- Only root can run a shell not listed in /etc/shells file.
- If an account has a restricted login shell, then only root can change that user’s shell.
Now let’s discuss three different ways to change Linux user shell.
1. usermod Utility
usermod is a utility for modifying a user’s account details, stored in the /etc/passwd file and the -s or —shell option is used to change the user’s login shell.
In this example, we’ll first check user tecmint’s account information to view his default login shell and then change its login shell from /bin/sh to /bin/bash as follows.
# grep tecmint /etc/passwd # usermod --shell /bin/bash tecmint # grep tecmint /etc/passwd
2. chsh Utility
chsh is a command line utility for changing a login shell with the -s or –shell option like this.
# grep tecmint /etc/passwd # chsh --shell /bin/sh tecmint # grep tecmint /etc/passwd
The two methods above all modify the shell specified in /etc/passwd file which you can edit manually as in the third method below.
3. Change User Shell in /etc/passwd File
In this method, simply open the /etc/passwd file using any of your favorite command line text editors and change a specific users shell.
When your done editing, save and close the file.
Do not forget to read these related topics:
In this article, we described various ways of changing a user’s shell in Linux. To share any thoughts with us, use the comment section below.
How to Change the Default User Shell in Linux OS
You must have been familiar with the bash shell which we commonly use in the Linux system. In most of the Linux operating systems the default shell is bash but do you know we can change the default bash shell to any other shell like sh, fish, zsh, csh etc. In this article, we will learn how to change the default user shell in Linux OS.
Find the current shell name
To change the default user shell, first of all find the current shell you are using. In the Linux system, the default user shell is bash. There is one file named passwd under the directory /etc that stores essential user account information which is needed during the user log in. We can identify the current user shell using that file.
Run the following command to check current user information stored in the file /etc/passwd.
In the above example, aayush is the username and bash is the current shell.
Also, you can use echo command to check the current user shell.
List available shells in Linux
To change the user default shell, we need to find out the available shell lists in the Linux system.
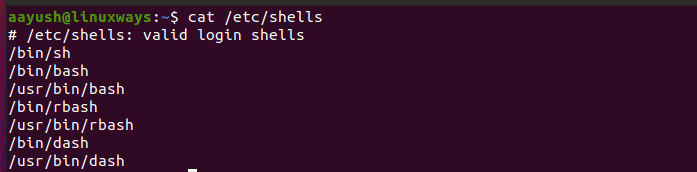
Installed shells can be listed by using the following command.
It can be seen that different types of shell such as bash, rbash and dash are available in the system.
Before changing the shell, remember the following things.
- Root user can be used to change login shell of other users
- If any user account has restricted login shell, then only root user can change the user’s shell
- Users will be able to change the shell listed in /etc/shells only.
Changing default sh shell to bash shell
In the Linux operating system, there are many ways to change the default login shell. In this article, we will explain some commonly used methods.
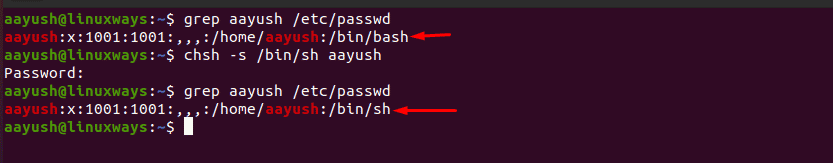
Using chsh utility
If you want to change the default user shell then the chsh utility can be very useful. Run the command chsh with the option -s to change the user shell. It also modifies the /etc/passwd file.
Where , aayush is the username and sh is the shell we are going to change.
In this example, the default user shell has been changed from bash to sh.
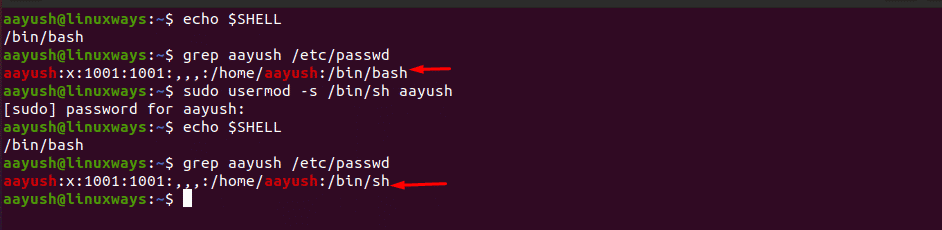
Using usermod command
The usermod utility is another way to modify the user account. You just need to specify the option -s or -shell to change the default shell for a user. Remember that you need to have a root privileged account to make the changes. Using usermod does not change the user’s current shell but sets a default shell to be used in the next login.
$ sudo usermod -s /bin/bash aayush
In the above example, the default shell of the user has been changed from bash to sh.
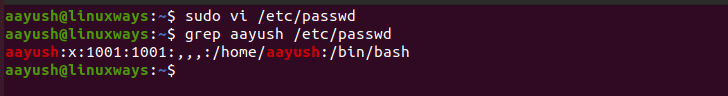
By editing in passwd file
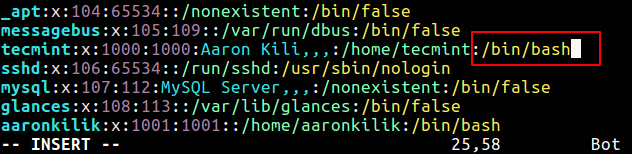
In the linux system, essential user’s information is stored in the file /etc/passwd which is needed to login. Default user shell can also be changed by manually editing this file. For this edit the file /etc/passwd using any text editor and change the shell after the username and home directory of a user and save a file.
Change the current user shell
Changing the current user shell is simple and easy. Just type the shell you want to use in the terminal. But this does not change the default shell for the next login.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned different ways to change default user shell in Linux OS
Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications including CCNA RS, SCP, and ACE. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various websites.