- Where and How are Passwords Stored on Linux
- Examining the /etc/passwd File
- Searching User in the /etc/passwd File
- View the /etc/passwd File’s Permissions
- Examine the File /etc/shadow
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Karim Buzdar
- How to View and Understand the /etc/passwd file in Linux
- Viewing and understanding the /etc/passwd file
- How to edit the /etc/passwd file
- The /etc/shadow file
- The /etc/group file
- Conclusion
- About the author
- David Adams
Where and How are Passwords Stored on Linux
“A username and password for a single account are the primary requirements for accessing a Linux system. In order to verify a user during a system login attempt, all user accounts passwords are saved in a file or database. Finding this file on a user’s machine is beyond the knowledge and abilities of every user. Linux checks the password given by the user against an entry in one or more files located in the directory named “/etc.” when the user logs in with a username and password.
All the crucial data required for user login is stored in the /etc/passwd files. The user’s account information is kept in the /etc/passwd file, to put it another way. The entire list of users on your Linux system is contained in this plain text file. It contains data about the user name, password, group ID, user id, shell, and home directory. Only superuser or root user accounts should have restricted write access permissions.”
This article will show you where and how to save the passwords for system user accounts on Linux distributions.
Examining the /etc/passwd File
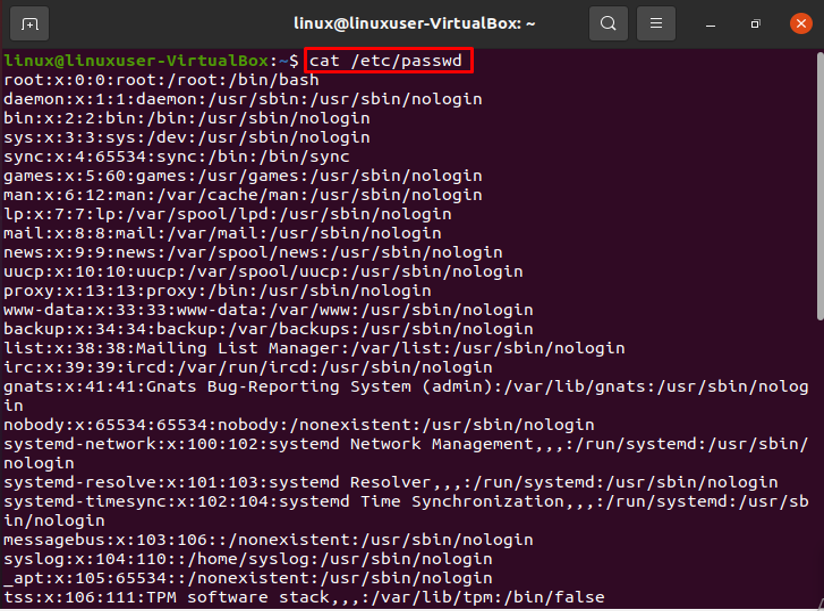
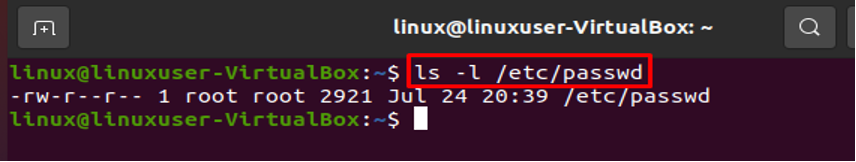
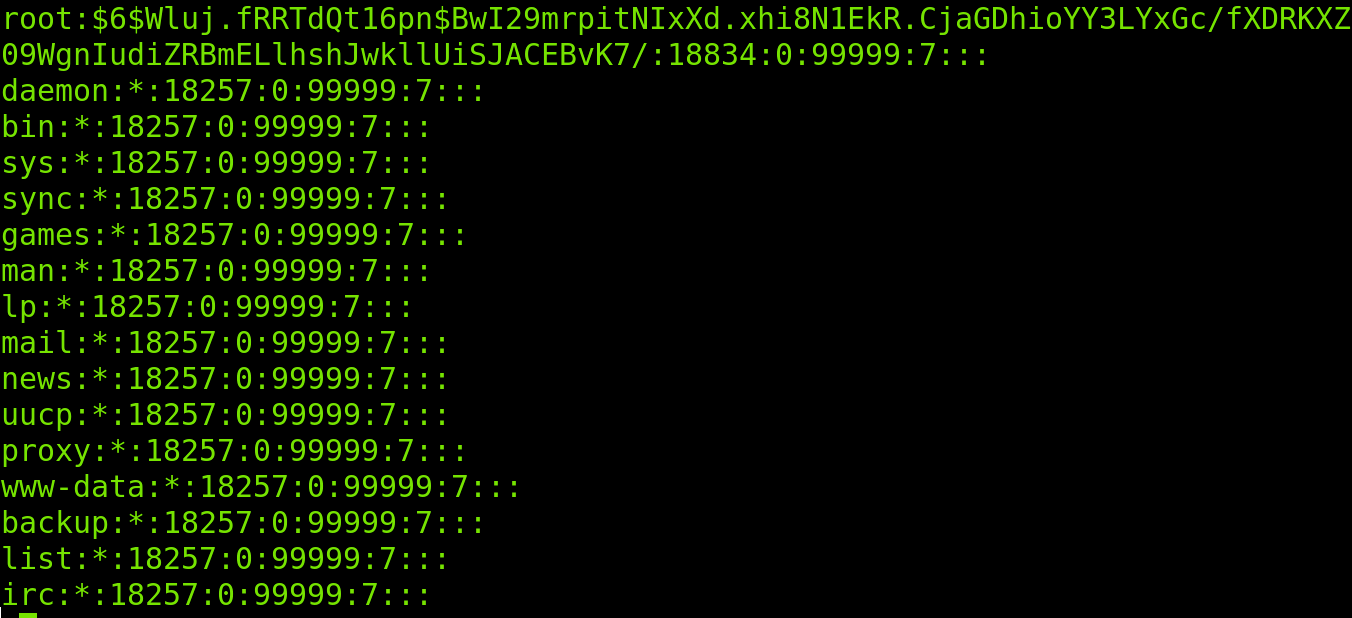
In order to run administrative commands, you must have root access. The details of your system’s user account are in the /etc/passwd file. The colon “:” symbol separates each stored field. The following command will display each entry in the /etc/passwd file:
The command mentioned above will list every user on your Linux system, and hence terminal’s screen will show the following format:
The information about the currently used account is shown in the highlighted portion below.
There are several fields of data divided by colons (:).
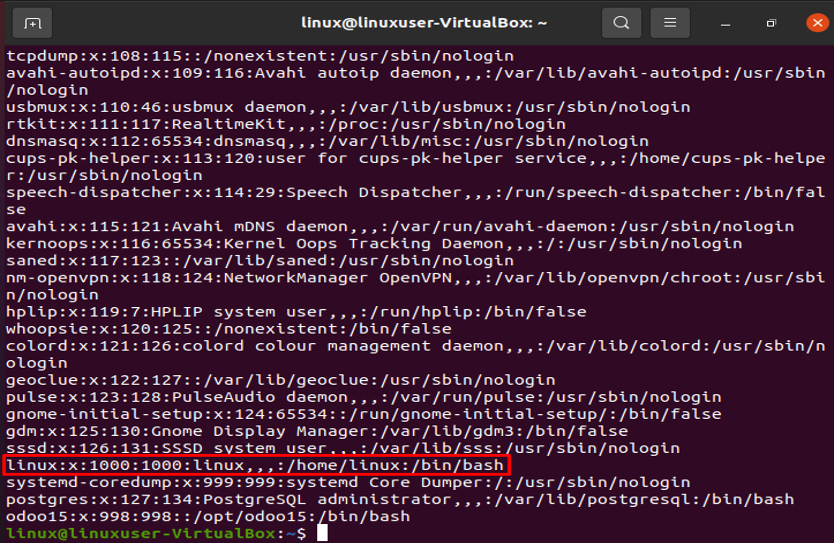
Linux: Username is shown in field one. The username field can only have between 1 and 32 characters. Linux is the username in the sample above.
Password (x): The “x” character denotes the encrypted password, as can be seen in the aforementioned example.
UID (1000): Each user must have their own unique user ID. The user ID in the aforementioned screenshot is 1000.
GID (1000): The group ID is represented by the following field. The GID is kept in the file /etc/group. The example indicates that the user is a member of group 1000.
Details (linux): Comments should go in the field below. You can enter further details about the identified person in this box, such as the individual’s complete name, contact information, etc. The user does not offer a phone number in the case above, though.
Home directory (/home/linux): The location of the user’s current home directory is displayed in this field. It will show “/” if the requested directory does not exist.
/bin/bash shell: /bin/bash is the default absolute path for a shell or command.
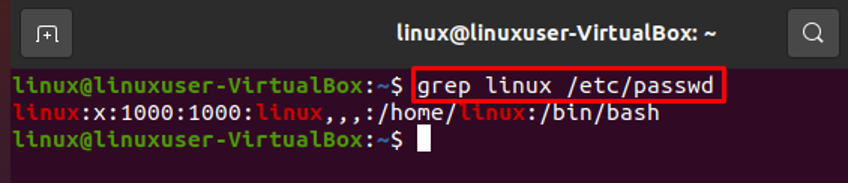
Searching User in the /etc/passwd File
A specific user can be found easily by using the grep command. For instance, if we wish to search for the username “linux” in the /etc/passwd file, we may quickly do it by using the following command, which will save us time:
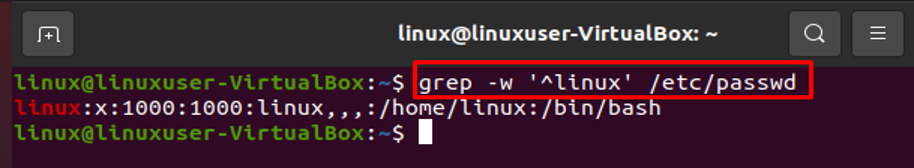
In this regard, we can also use the following command:
View the /etc/passwd File’s Permissions
As we stated above, the /etc/passwd file must have the owner be superuser or root, and all users other than root should have read rights.
To check the read rights on the file, type the following:
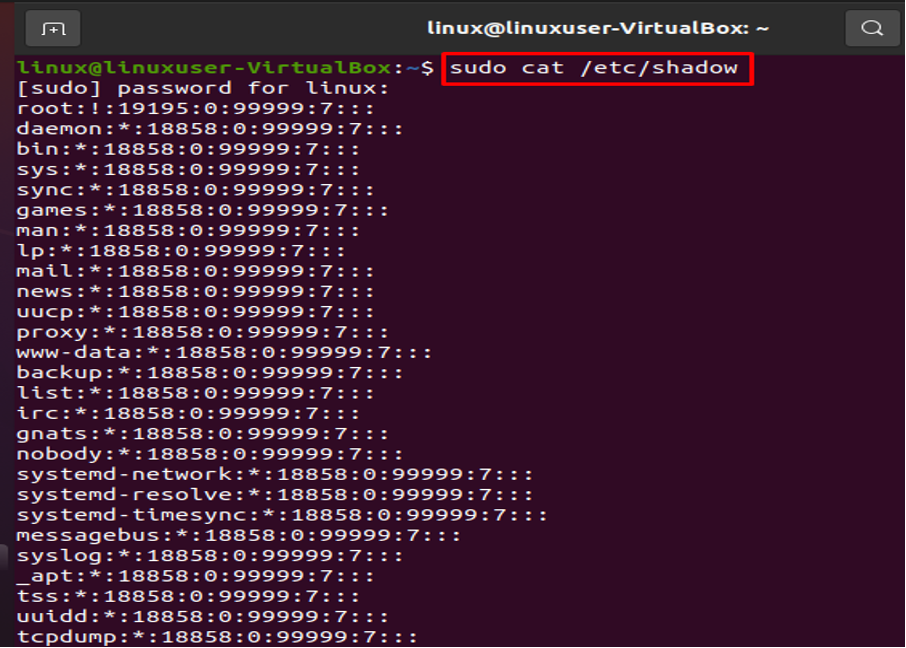
Examine the File /etc/shadow
Your whole encrypted password collection is stored in the root-only /etc/shadow file. Every password is viewable in encrypted form. Let’s execute the next command to show the content:
Conclusion
The aforementioned article demonstrates that the Linux operating system keeps all user account details and passwords in the /etc/passwd file. Additionally, we have seen every encrypted password kept in the /etc/shadow file. To learn more about the user’s group, you can also look through the /etc/group file.
About the author
Karim Buzdar
Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. He blogs at LinuxWays.
How to View and Understand the /etc/passwd file in Linux
This tutorial explains how to view the /etc/passwd file in Linux and how to interact with it.After reading this article you will understand what the /etc/passwd file is, how to understand, and how to read it. The content also includes instructions to edit the file properly. Additionally, you will find an explanation on /etc/shadow and /etc/group files.
Viewing and understanding the /etc/passwd file
The /etc/passwd file stores vital information (described below) about users such as username, home directory, etc.
Since this file contains vital information for all users, it has reading permissions and it is not necessary to have privileges to see it.
You can read the /etc/passwd file by using the less command followed by the path as shown below.
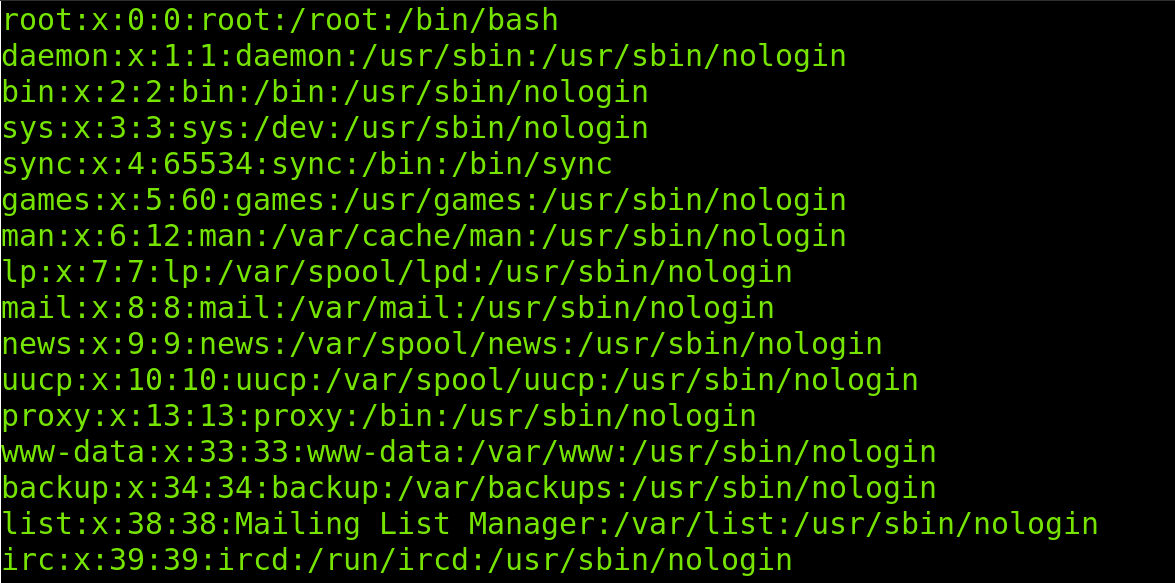
Let’s take the first two lines to explain the structure of the /etc/passwd file in the following table:
| root | x | 0 | 0 | root | /root | /bin/bas |
| daemon | x | 1 | 1 | daemon | /usr/sbin | /usr/sbin/nologin |
| USER | AUTH | UID | GID | GECOS | HOME | SHELL |
The first two rows contain the same data shown in the first two lines of the /etc/passwd in the image above. It is important to note that each item is separated by two dots; you can consider the two dots as columns.
The meaning of each column is:
- USER: The first field shows the username.
- AUTHENTICATION: The second field shows the password status, if an x, the password is stored in the /etc/shadow file, if an
- UID: The third field shows the user ID.
- GID: The fourth field shows the group ID.
- GECOS: This field stores user information such as full name, phone number, and email.
- HOME: This field contains the path to the home directory.
- SHELL: Finally, the last field shows the shell for the user.
The x in the second field indicates the password is encrypted and stored in the /etc/shadow file. This file is protected by permissions and can only be read by privileged users. If instead of an X you see an asterix (*) or exclamation mark (!), it means that the password is blank and the user does not need a password to login.
The user ID 0 is reserved for the root user. IDs bigger than 500 can be assigned to users. Below 500 IDs are reserved for the system.
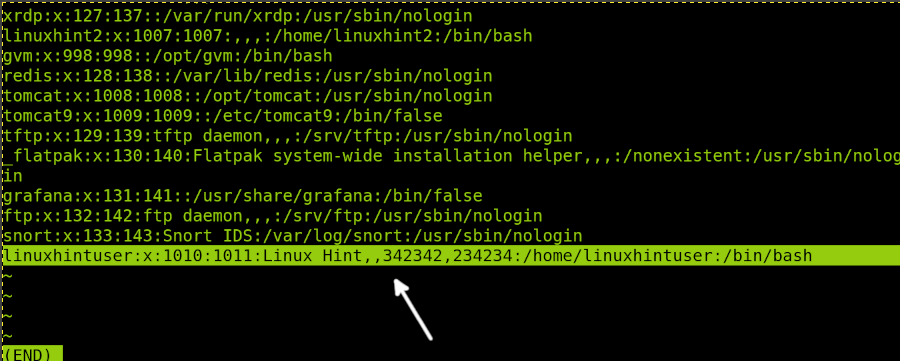
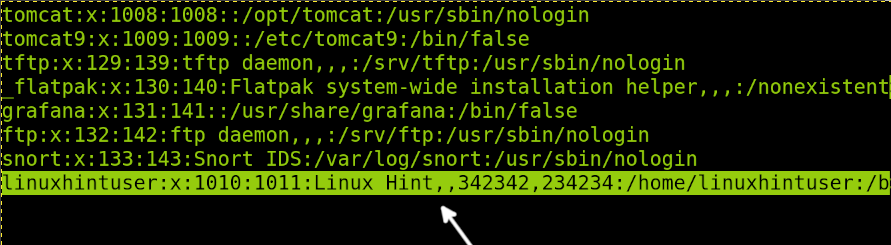
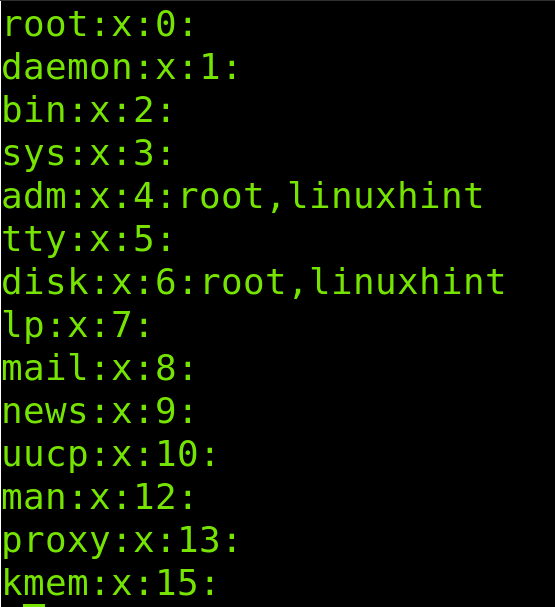
In the following figure you can see the linuxhintuser line including some GECOS information such as full name (Linux Hint) and phone numbers:
Years ago, passwords were stored in the /etc/passwd file. this was changed. Passwords are now stored in the /etc/shadow file which needs privileges.
The /etc/passwd file is accessible to every user because it holds information users need to interact with the system, for example, to login.
How to edit the /etc/passwd file
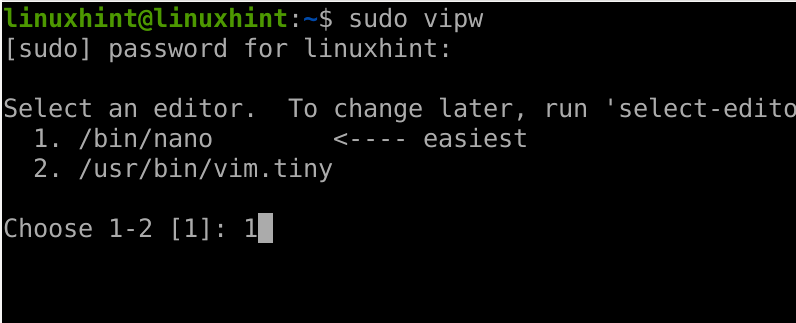
The /etc/passwd can be edited using the vipw command. This command is also useful to edit /etc/shadow (When used with the -s flag) and /etc/group files.
To edit the /etc/passwd file, run the vipw command and when asked, select the text editor of your preference. In my case I’m selecting nano as shown below.
As you can see in the following figure, after running the vipw command, the /etc/passwd file will be opened with a text editor. You can then edit all fields.
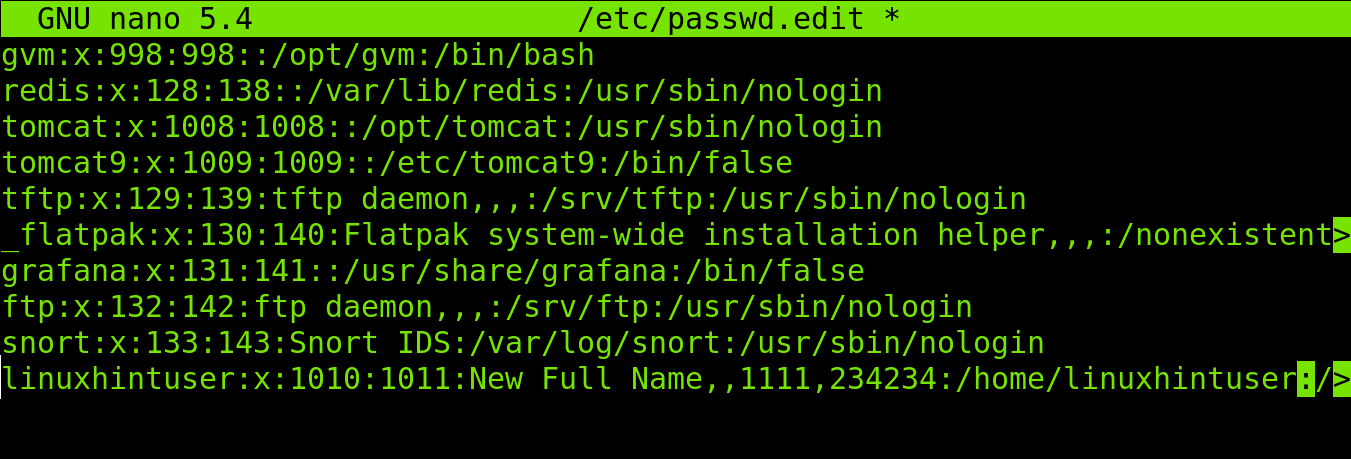
In the example below I will edit the linuxhintuser information (Last line). As you can see, the full name is Linux Hint, phone numbers are 342342 and 234234.
As shown in the example below, I edited the full name, replacing the full name (linuxhintuser) with “New Full Name” and editing phone numbers.
Once you are done editing the file, close and save changes.
After closing and saving the file, you will be warned about possible changes you may need to reproduce in the /etc/shadow file. This is not necessary if you don’t edit the password.
You can check the /etc/passwd file using the less or cat commands and you will see changes were properly applied.
Additional functions for the vipw command can be implemented using flags:
- -g: The -g flag is used to edit the /etc/group file containing information about user groups.
- -s: This flag is used to edit both the /etc/shadow and /etc/gshadow files.
- -p: The -p flag is used to edit the passwd database.
- -h: This flag is used to display the help menu.
As you can see in the content above, the /etc/passwd is linked to other files like /etc/shadow and /etc/group, both of which are described below.
The /etc/shadow file
As said previously, formerly Linux/Unix passwords were stored in the /etc/passwd file, which was dangerous since every user has access to it. A user with access to the encrypted password can easily break it by using one of the online databases or through brute force.
To solve this exposure, the /etc/shadow file was implemented to store user encrypted passwords without reading permissions or without super user privileges.
You can see the /etc/shadow file by using cat or less commands as root or with sudo as shown previously.
As you can see in the screenshot below, there are 9 columns (Defined by two dots each). Each field contains the first information:
- 1: Username.
- 2: Encrypted password.
- 3: Last password change in days, counting from Jan, 1970.
- 4: Minimum days a user can keep a password before changing it.
- 5: Maximum days a user can keep a password before changing it (If 99999, then no limit)
- 6: In this field the root can define when a user will be requested to change the password.
- 7: This field shows when an account will be inactive after password expiration.
- 8: Password expiration date (Counting from 1 Jan, 1970).
- 9: The last field is reserved without containing useful information.
As you can see, the /etc/shadow file only contains password related information.
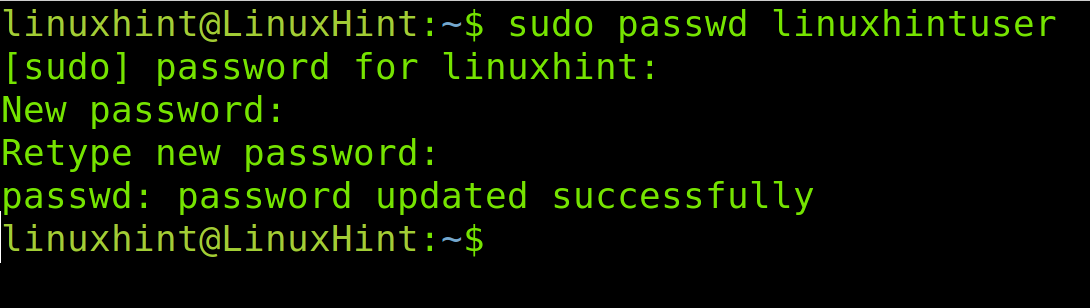
To change a password within this file, you need to execute the passwd command followed by the username whose password you want to replace, as shown in the figure below where the linuxhintuser password is updated.
As you can see above, the password was successfully changed.
The /etc/group file
The /etc/group file stores information on groups. This file, like both /etc/passwd and /etc/shadow, also can be edited with the vipw command.
You can read the /etc/group file using the less command as done before.
The file looks like the following screenshot, containing 4 columns with group related information, where the first field is group name, the second field is password related, the third is the GID (Group ID) and the fourth shows the group users.
I also would recommend studying the usermode command, some examples are available at https://linuxhint.com/sudo_linux/, also related to user administration. This command is also recommended by the passwd command man page.
Conclusion
As you can see, any user can view the passwd file easily. The /etc/passwd file is the first defense against unauthorized accesses. All files are imperative to get information on users and administer them properly. The way to edit those files vipw is explained in this document. All steps are valid for all Linux distributions, since these files are universal for Linux systems, and even for some Unix. Always remember you can read the main page for additional information.
Thank you for reading this tutorial explaining how to view and how to understand the /etc/passwd file. Keep following us for additional Linux tutorials.
About the author
David Adams
David Adams is a System Admin and writer that is focused on open source technologies, security software, and computer systems.